Network Fabric Controller overview
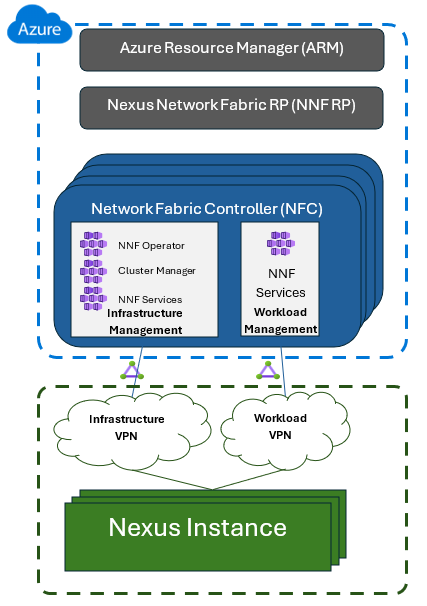
The Network Fabric Controller (NFC) is an Azure resource that allows customers to establish on-premises network infrastructure and workloads using Azure within an Azure region. The NFC acts as a conduit, connecting the Azure control plane to your on-site network hardware, such as routers, switches, and storage appliances. It enables network functions like virtualization, firewall, and gateway, while also facilitating seamless management and configuration of your network infrastructure. Its main role is to manage multiple Network Fabric (NF) instances connected to Nexus on-premises instances. This setup allows for structured grouping of NF instances within a designated Azure region. Additionally, NFC can be used to establish and modify configurations for Network Fabrics, Isolation Domains, Network Racks, and Network Devices within each Azure Operator Nexus instance.
The NFC is responsible for bootstrapping and managing network fabric instances. These NF instances are connected to the NFC through redundant ExpressRoute circuits. These circuits are linked to the management VPN, which is exclusively provided by the operator for management purposes. You can manage the lifecycle of a Network Fabric Controller through Azure using supported interfaces like Azure CLI and REST API. For example, you can create an NFC using Azure Command Line Interface (AzureCLI) and also check its status or delete it.
An NFC is a crucial component of the Azure Operator Nexus solution, a service that enables the connection between Azure and on-premises environments. With an NFC, you can:
- Establish a secure and private connection between your on-premises network and Azure using ExpressRoute, bypassing the public internet.
- Manage the network fabric, which comprises physical network devices like CE routers, Top of the Rack switches, Management Switches, Network Packet Broker devices, Terminal Servers, and storage appliances.
- Enable essential network functions, including virtualization, firewall, and gateway, which provide services and security at the logical layer of the network.
Key capabilities of Network Fabric Controller
The Network Fabric Controller (NFC) plays a critical role in managing network fabric instances in the following ways:
- Centralized Management: The NFC provides a centralized platform for managing multiple network fabric (NF) instances. This allows for efficient control and monitoring of these instances.
- Bootstrapping: All bootstrapping operations for network fabric instances are performed through the NFC. This ensures a standardized and streamlined process for initiating these instances.
- Connectivity: The NFC ensures reliable and continuous connectivity by establishing connections to NF instances using redundant ExpressRoute circuits.
- VPN Management: The ExpressRoute circuits connected to the NF instances are linked to an operator-provided management VPN, exclusively used for management purposes, enhancing control over the NF instances.
- Operations and Management Network: The NFC connects each NF instance's Operations and Management network (O&M) to the management VPN, enabling efficient operations and management of the network fabric instances.
In summary, the NFC plays a pivotal role in overseeing on-site network devices and their settings, as well as establishing segregated infrastructure and workload networks.
Resources
To create an NFC, you must provide the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Resource Group | The Resource Group attribute specifies the name of the group that encompasses the NFC. As a critical and mandatory parameter, this attribute requires definition at the point of creation and is immutable thereafter. It necessitates the existence of a corresponding resource group in the Command Line Interface (CLI) equipped with the requisite parameters. |
| Location | The Location attribute determines the geographical positioning of the NFC. It is a compulsory parameter that must be set during the initial creation process. Post-creation modifications to this attribute are not permissible. This attribute must correspond to a predefined location available in the CLI, complete with all necessary parameters. |
| Resource Name | The Resource Name attribute uniquely identifies the NFC. This mandatory attribute, which cannot be altered post-creation, must adhere to specific formatting rules: it should be alphanumeric, devoid of special characters, and conform to length restrictions as per Azure Resource Manager (ARM) standards. |
| Ipv4AddressSpace | The Ipv4AddressSpace attribute, though optional, is a crucial parameter for defining the IPv4 address space allocated to the NFC. It is immutable and cannot be reset once set. The default configuration for this attribute is a 10.0.0.0/19 address space, with an allowable range extending from /19 to /16. The assigned address must be a valid IPv4 address and cannot be null. |
| Ipv6AddressSpace | The Ipv6AddressSpace attribute, also optional, specifies the IPv6 address space for the NFC. This mandatory and immutable parameter defaults to FC00::/59, with the permissible range being /59. It requires a valid IPv6 address, which can be of types such as site local, unique local, or global unicast, and cannot be null. |
| InfrastructureExpressRouteConnections | This attribute outlines the express route connections essential for infrastructure services. It is a mutable attribute that allows for modifications and reconfigurations. For NFC creation and provisioning, this attribute is necessary. It encompasses two mandatory sub-attributes: expressRouteCircuitId (the Azure resource ID for the express route circuit, required to be of type Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/circuitName) and expressRouteAuthorizationKey (the authorization key for the circuit, mandated to be of type Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/authorizations). |
| WorkloadExpressRouteConnections | Pertaining to workload services, this attribute details the express route connections. It is a flexible attribute, allowing for updates and reapplications. It includes two critical sub-attributes: expressRouteCircuitId (the Azure resource ID of the express route circuit, which must align with the type Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/circuitName) and expressRouteAuthorizationKey (the authorization key for the circuit, required to be of type Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/authorizations). Both sub-attributes are mandatory for the attribute's functionality. |
Call flow
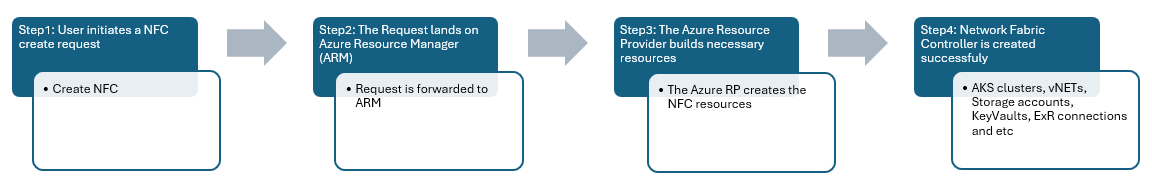
When a user initiates a request to create a Network Fabric Controller (NFC), the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) receives the request. Subsequently, the request is forwarded to the Nexus Network Fabric Resource Provider.
The Network Fabric Controller resource is created based on the request. It consists of several internal resources at a high level, including:
- NFC cluster
- Infrastructure cluster
- Tenant cluster
- ExpressRoute connections for both infrastructure and tenant networks
- Azure ARC resources
- Virtual Networks
Payload examples
Create a Network Fabric Controller:
az networkfabric controller create \
--resource-group "NFCResourceGroupName" \
--location "eastus" \
--resource-name "nfcname" \
--ipv4-address-space "10.0.0.0/19" \
--infra-er-connections '[{"expressRouteCircuitId": "/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-01", "expressRouteAuthorizationKey": "<auth-key>"}]' \
--workload-er-connections '[{"expressRouteCircuitId": "/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-02"", "expressRouteAuthorizationKey": "<auth-key>"}]'
Update Network Fabric Controller with two new ExR:
az networkfabric controller update \
--resource-group "NFCResourceGroupName" \
--location "eastus" \
--resource-name "nfcname" \
--ipv4-address-space "10.0.0.0/19" \
--infra-er-connections "[{expressRouteCircuitId:'/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-01',expressRouteAuthorizationKey:'<auth-key>'},{expressRouteCircuitId:'/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-02',expressRouteAuthorizationKey:'<auth-key>'}]"
--workload-er-connections "[{expressRouteCircuitId:'/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-03',expressRouteAuthorizationKey:'<auth-key>'},{expressRouteCircuitId:'/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-04',expressRouteAuthorizationKey:'<auth-key>'}]"
Note
There is no support for Patch yet.
Delete a Network Fabric Controller:
az networkfabric controller delete --resource-group "NFCResourceGroupName" --resource-name "nfcname"
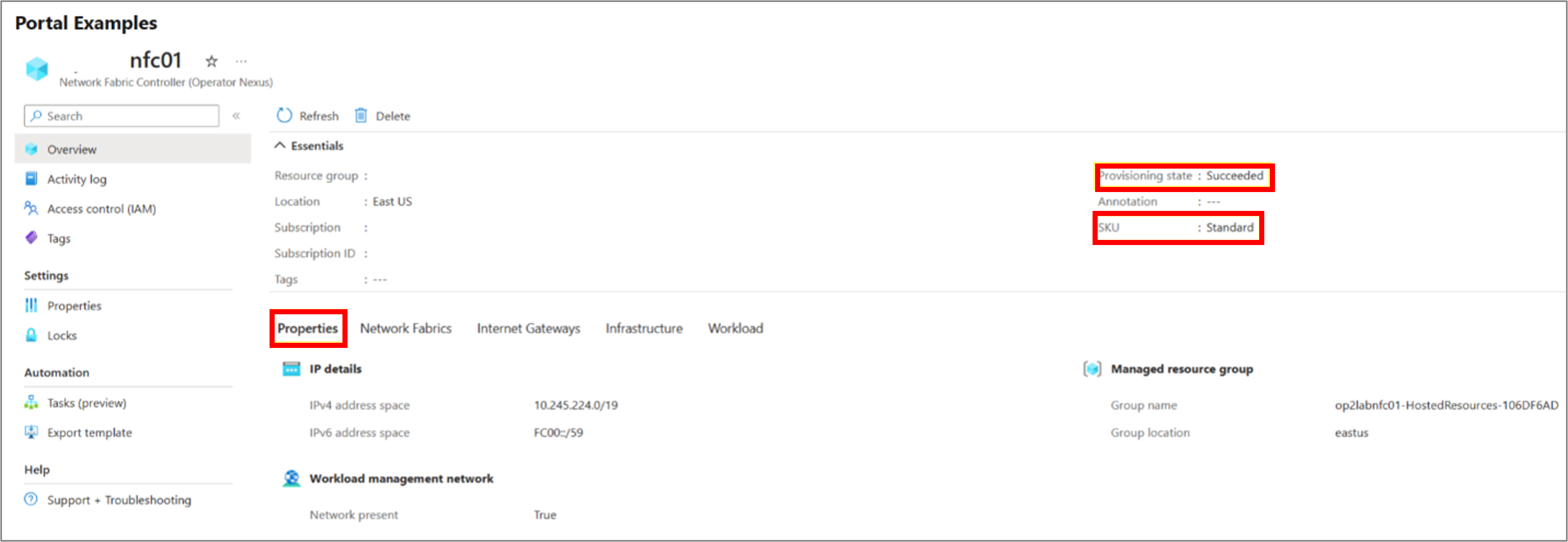
Portal examples
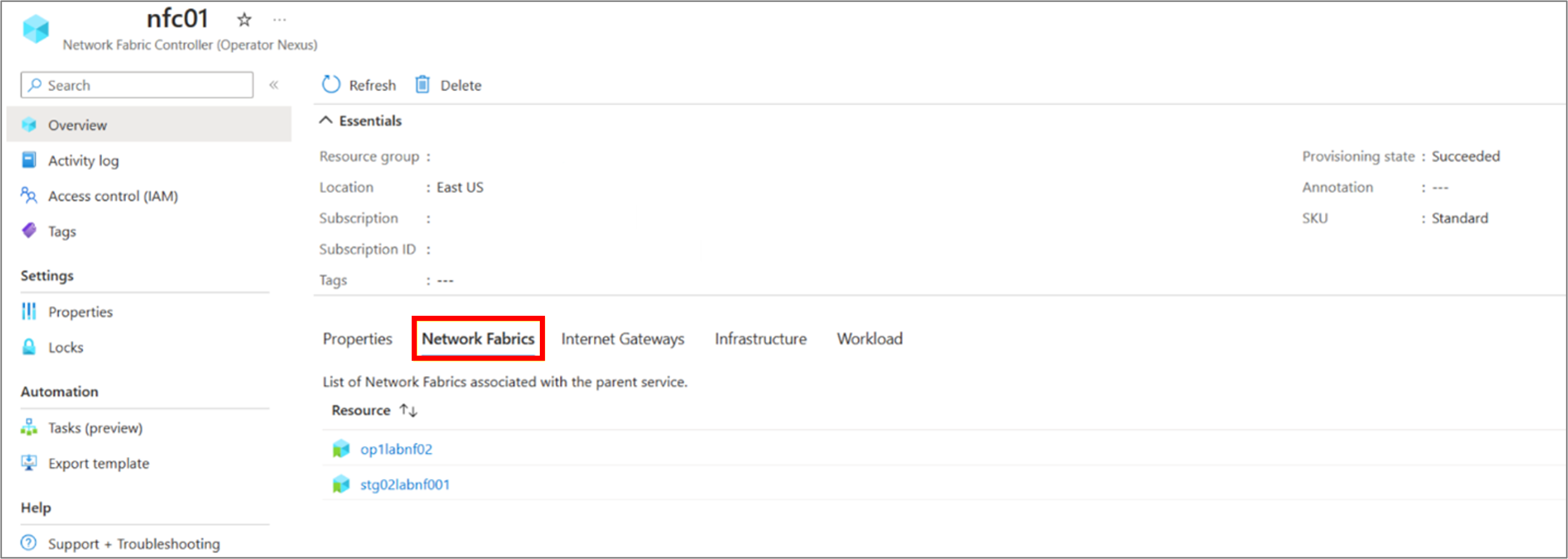
Network Fabrics that are associated with Network Fabric Controller:
Managed Resource Group:
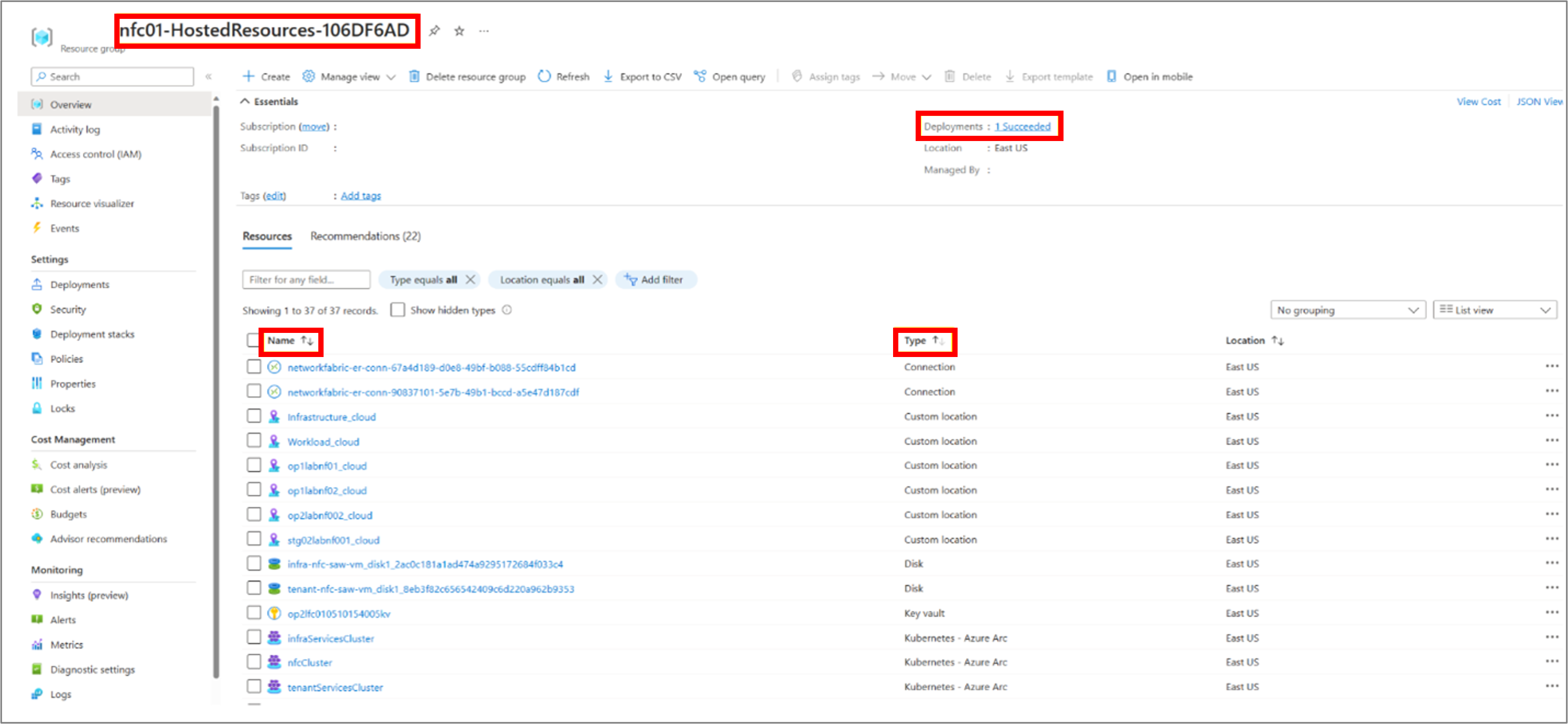
Provisioned NFC's JSON
{
"id": "/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/NFCResourceGroupName/providers/Microsoft.ManagedNetworkFabric/networkFabricControllers/nfcname",
"name": "NFCName",
"type": "microsoft.managednetworkfabric/networkfabriccontrollers",
"location": "eastus",
"systemData": {
"createdBy": "email@address.com",
"createdByType": "User",
"createdAt": "2023-XX-XXT09:38:34.8310058Z",
"lastModifiedBy": "d1bd24c7-b27f-477e-86dd-939e107873d7",
"lastModifiedByType": "Application",
"lastModifiedAt": "2023-XX-XXT09T11:48:34.3748593Z"
},
"properties": {
"infrastructureExpressRouteConnections": [
{
"expressRouteCircuitId": "/subscriptions/xxxxxx-xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-02"
}
],
"workloadExpressRouteConnections": [
{
"expressRouteCircuitId": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/ER-Dedicated-WUS2-AFO-Circuits/providers/Microsoft.Network/expressRouteCircuits/MSFT-ER-Dedicated-PvtPeering-WestUS2-AFO-Ckt-03"
}
],
"ipv4AddressSpace": "10.245.224.0/19",
"managedResourceGroupConfiguration": {
"location": "eastus",
"name": "nfc01-HostedResources-106DF6AD"
},
"provisioningState": "Succeeded",
"workloadManagementNetwork": true,
"infrastructureServices": {
"ipv4AddressSpaces": [
"10.245.224.0/21"
],
"ipv6AddressSpaces": []
},
"workloadServices": {
"ipv4AddressSpaces": [
"10.245.252.0/22"
],
"ipv6AddressSpaces": []
},
"ipv6AddressSpace": "FC00::/59",
"isWorkloadManagementNetworkEnabled": "True",
"nfcSku": "Standard"
}
}
Activity log:
FAQs on Network Fabric Controller (NFC) Setup and Management
How many Express Routes are required by default to initialize a Network Fabric Controller?
To successfully set up a Network Fabric Controller, at least two Express Routes are necessary: one for the Infrastructure Network and another for the Tenant Network.
What are the recommended Express Route Circuits for the Infrastructure Network and Tenant Network?
For optimal performance and redundancy, it is recommended to utilize two Express Route Circuits for both the Infrastructure and Tenant Networks.
What types of NFC SKUs are available?
NFC supports the Standard SKU and uses virtual machines from the DSv3 family.
Is it possible to update the NFC with a new Express Route Circuit?
Yes, once the NFC is successfully provisioned, it can be updated with a new Express Route Circuit.
What is the typical time frame for NFC creation?
The creation process of an NFC typically ranges from 45 to 60 minutes.
How long does it take to delete an NFC? Similar to the creation process, deleting an NFC usually takes between 45 and 60 minutes.
What steps should be taken if the NFC fails to initialize on the first attempt?
If the NFC does not provision successfully on the first try, the recommended course of action is to clean up and recreate the NFC. This is due to the lack of support for updating the NFC during intermediate failures.