Connect to Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server with encrypted connections
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server supports connecting your client applications to the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) with Transport layer security(TLS) encryption. TLS is an industry standard protocol that ensures encrypted network connections between your database server and client applications, allowing you to adhere to compliance requirements.
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server supports encrypted connections using Transport Layer Security (TLS 1.2) by default and all incoming connections with TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 are denied by default. The encrypted connection enforcement or TLS version configuration on your Flexible Server can be changed as discussed in this article.
Following are the different configurations of SSL and TLS settings you can have for your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance:
Important
According to Removal of Support for the TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 Protocols, we previously planned to fully deprecate TLS 1.0 and 1.1 by September 2024. However, due to dependencies identified by some customers, we have decided to extend the timeline.
- Starting on August 31, 2025, we will begin the forced upgrade for all servers still using TLS 1.0 or 1.1. After this date, any connections relying on TLS 1.0 or 1.1 may stop working at any time. To avoid potential service disruptions, we strongly recommend that customers complete their migration to TLS 1.2 before August 31, 2025.
- Beginning in September 2024, new servers will no longer be permitted to use TLS 1.0 or 1.1, and existing servers will not be allowed to downgrade to these versions.
We strongly recommend that customers update their applications to support TLS 1.2 as soon as possible to avoid service disruptions.
| Scenario | Server parameter settings | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Disable SSL enforcement | require_secure_transport = OFF | If your legacy application doesn't support encrypted connections to Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server, you can disable enforcement of encrypted connections to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance by setting require_secure_transport=OFF. |
| Enforce SSL with TLS version < 1.2 (Will be deprecated in September 2024) | require_secure_transport = ON and tls_version = TLS 1.0 or TLS 1.1 | If your legacy application supports encrypted connections but requires TLS version < 1.2, you can enable encrypted connections, but configure your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance to allow connections with the TLS version (1.0 or 1.1) supported by your application. Supported only with Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server version v5.7 |
| Enforce SSL with TLS version = 1.2(Default configuration) | require_secure_transport = ON and tls_version = TLS 1.2 | This is the recommended and default configuration for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server. |
| Enforce SSL with TLS version = 1.3 | require_secure_transport = ON and tls_version = TLS 1.3 | This is useful and recommended for new applications development. Supported only with Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server version v8.0 |
Note
Changes to SSL Cipher on Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server is not supported. FIPS cipher suites is enforced by default when tls_version is set to TLS version 1.2 . For TLS versions other than version 1.2, SSL Cipher is set to default settings which comes with MySQL community installation.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Configure your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance
- With SSL disabled
- With SSL enforced with TLS version
- Connect to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance using mysql command-line
- With encrypted connections disabled
- With encrypted connections enabled
- Verify encryption status for your connection
- Connect to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance with encrypted connections using various application frameworks
Disable SSL enforcement on your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance
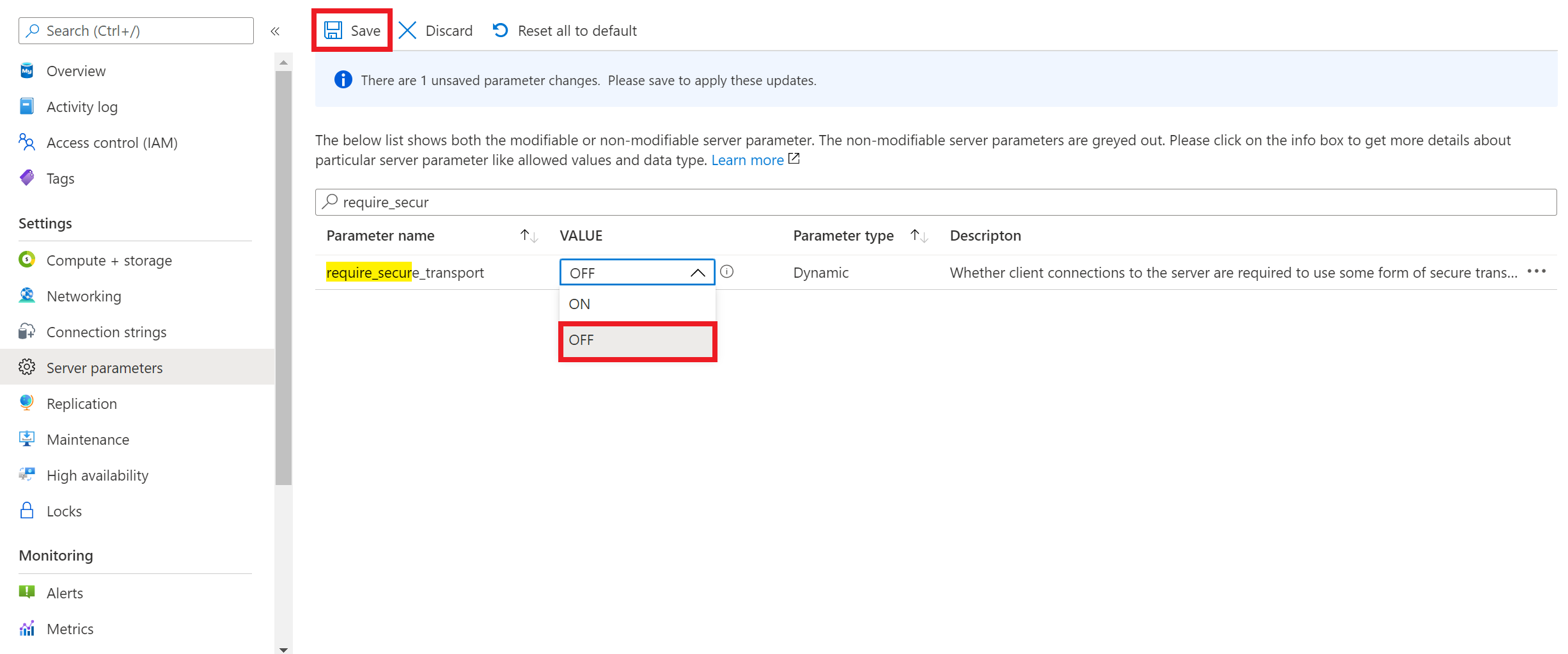
If your client application doesn't support encrypted connections, you need to disable encrypted connections enforcement on your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance. To disable encrypted connections enforcement, you need to set require_secure_transport server parameter to OFF as shown in the screenshot, and save the server parameter configuration for it to take effect. require_secure_transport is a dynamic server parameter which takes effect immediately and doesn't require server restart to take effect.
Connect using mysql command-line client with SSL disabled
The following example shows how to connect to your server using the mysql command-line interface. Use the --ssl-mode=DISABLED connection string setting to disable TLS/SSL connection from mysql client. Replace values with your actual server name and password.
mysql.exe -h mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com -u myadmin -p --ssl-mode=DISABLED
Important
Setting the require_secure_transport to OFF doesn't mean encrypted connections aren't supported on the server side. If you set require_secure_transport to OFF on the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance, but if the client connects with the encrypted connection, it still is accepted. The following connection using mysql client to an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance configured with require_secure_transport=OFF also works as shown below.
mysql.exe -h mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com -u myadmin -p --ssl-mode=REQUIRED
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 17
Server version: 5.7.29-log MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show global variables like '%require_secure_transport%';
+--------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
| +--------------------------+-------+ |
| require_secure_transport | OFF |
| +--------------------------+-------+ |
| 1 row in set (0.02 sec) |
In summary, require_secure_transport=OFF setting relaxes the enforcement of encrypted connections on Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server and allows unencrypted connections to the server from client in addition to the encrypted connections.
Enforce SSL with TLS version
To set TLS versions on your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance, you need to set *tls_version- server parameter. The default setting for TLS protocol is TLS 1.2. If your application supports connections to MySQL server with SSL, but require any protocol other than TLS 1.2, you require to set the TLS versions in server parameter. *tls_version- is a static server parameter which requires a server restart for the parameter to take effect. Following are the Supported protocols for the available versions of Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
| Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server version | Supported Values of tls_version | Default Setting |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL 5.7 | TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1(Will be deprecated in September 2024) TLS 1.2 | TLS 1.2 |
| MySQL 8.0 | TLS 1.2, TLS 1.3 | TLS 1.2 |
Connect using mysql command-line client with TLS/SSL
Download the public SSL certificate
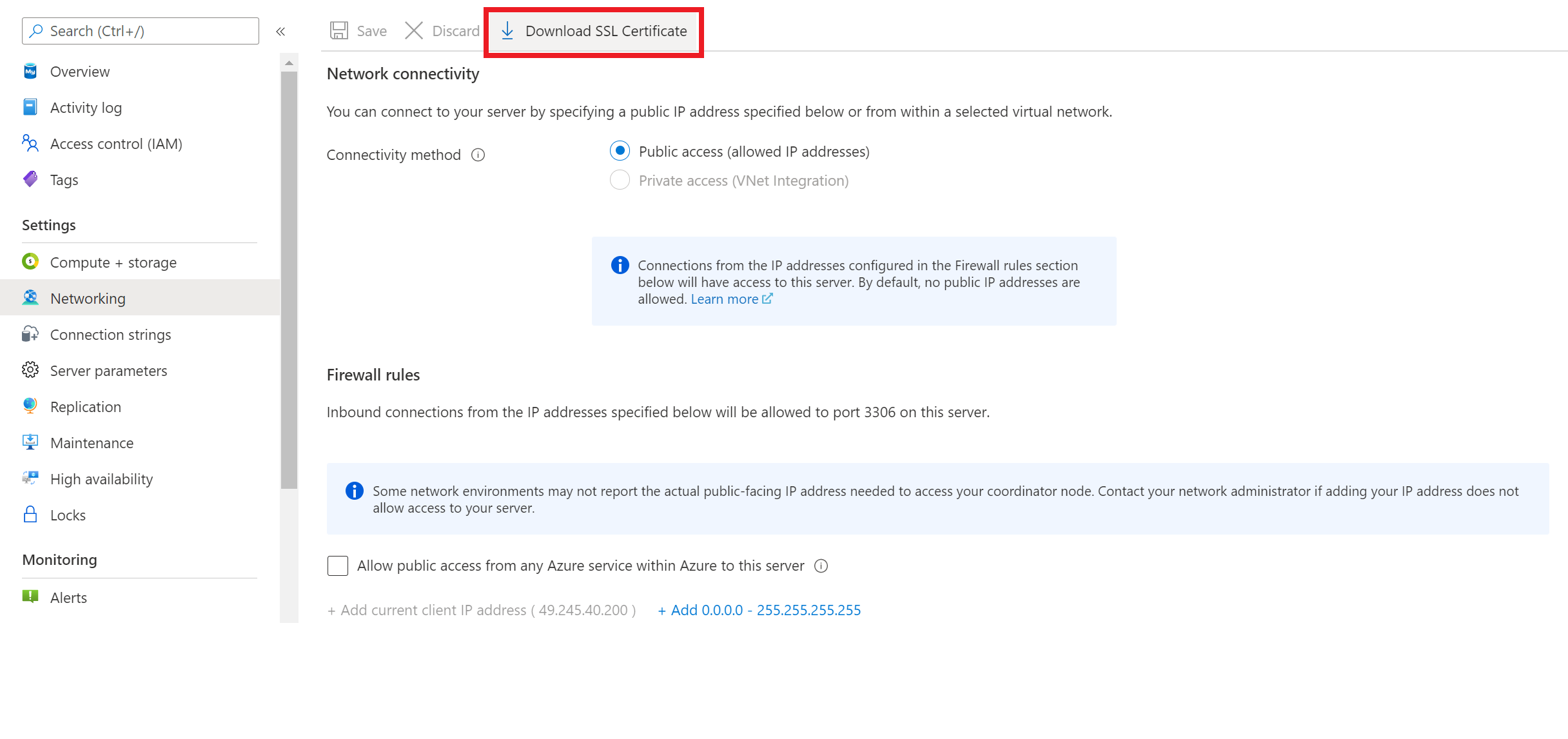
To use encrypted connections with your client applications,you need to download the public SSL certificate, which is also available in Azure portal Networking pane as shown in the screenshot below.
Note
You must download this SSL certificate for your servers in Azure Government cloud.
Save the certificate file to your preferred location. For example, this tutorial uses c:\ssl or \var\www\html\bin on your local environment or the client environment where your application is hosted. This allows applications to connect securely to the database over SSL.
If you created your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance with Private access (VNet Integration), you need to connect to your server from a resource within the same VNet as your server. You can create a virtual machine and add it to the VNet created with your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance.
If you created your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance with Public access (allowed IP addresses), you can add your local IP address to the list of firewall rules on your server.
You can choose either mysql.exe or Use MySQL Workbench with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server--> to connect to the server from your local environment.
The following example shows how to connect to your server using the mysql command-line interface. Use the --ssl-mode=REQUIRED connection string setting to enforce TLS/SSL certificate verification. Pass the local certificate file path to the --ssl-ca parameter. Replace values with your actual server name and password.
sudo apt-get install mysql-client
wget --no-check-certificate https://dl.cacerts.digicert.com/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem
mysql -h mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com -u mydemouser -p --ssl-mode=REQUIRED --ssl-ca=DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem
Note
Confirm that the value passed to --ssl-ca matches the file path for the certificate you saved.
If you are connecting to the Azure Database for MySQL- Flexible with SSL and are using an option to perform full verification (sslmode=VERTIFY_IDENTITY) with certificate subject name, use <servername>.mysql.database.azure.com in your connection string.
If you try to connect to your server with unencrypted connections, you'll see error stating connections using insecure transport are prohibited similar to one below:
ERROR 3159 (HY000): Connections using insecure transport are prohibited while --require_secure_transport=ON.
Verify the TLS/SSL connection
Execute the mysql status command to verify that you've connected to your MySQL server using TLS/SSL:
mysql> status
Confirm the connection is encrypted by reviewing the output, which should show: SSL: Cipher in use is. This cipher suite shows an example and based on the client, you can see a different cipher suite.
How to identify the TLS protocols configured on your server ?
You can run the command SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'tls_version'; and check the value to understand what all protocols are configured.
mysql> SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'tls_version';
How to find which TLS protocol are being used by my clients to connect to the server?
You can run the below command and look at tls_version for the session to identify which TLS version is used to connect.
SELECT sbt.variable_value AS tls_version, t2.variable_value AS cipher,
processlist_user AS user, processlist_host AS host
FROM performance_schema.status_by_thread AS sbt
JOIN performance_schema.threads AS t ON t.thread_id = sbt.thread_id
JOIN performance_schema.status_by_thread AS t2 ON t2.thread_id = t.thread_id
WHERE sbt.variable_name = 'Ssl_version' and t2.variable_name = 'Ssl_cipher' ORDER BY tls_version;
Connect to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance with encrypted connections using various application frameworks
Connection strings that are pre-defined in the "Connection Strings" page available for your server in the Azure portal include the required parameters for common languages to connect to your database server using TLS/SSL. The TLS/SSL parameter varies based on the connector. For example, "useSSL=true", "sslmode=required", or "ssl_verify_cert=true" and other variations.
To establish an encrypted connection to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance over TLS/SSL from your application, refer to the following code samples:
WordPress
Download SSL public certificate and add the following lines in wp-config.php after the line // **MySQL settings - You can get this info from your web host** //.
//** Connect with SSL ** //
define('MYSQL_CLIENT_FLAGS', MYSQLI_CLIENT_SSL);
//** SSL CERT **//
define('MYSQL_SSL_CERT','/FULLPATH/on-client/to/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem');
PHP
$conn = mysqli_init();
mysqli_ssl_set($conn,NULL,NULL, "/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem", NULL, NULL);
mysqli_real_connect($conn, 'mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com', 'myadmin', 'yourpassword', 'quickstartdb', 3306, MYSQLI_CLIENT_SSL);
if (mysqli_connect_errno()) {
die('Failed to connect to MySQL: '.mysqli_connect_error());
}
PHP (Using PDO)
$options = array(
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_SSL_CA => '/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem'
);
$db = new PDO('mysql:host=mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com;port=3306;dbname=databasename', 'myadmin', 'yourpassword', $options);
Python (MySQLConnector Python)
try:
conn = mysql.connector.connect(user='myadmin',
password='<password>',
database='quickstartdb',
host='mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com',
ssl_ca='/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem')
except mysql.connector.Error as err:
print(err)
Python (PyMySQL)
conn = pymysql.connect(user='myadmin',
password='<password>',
database='quickstartdb',
host='mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com',
ssl={'ca': '/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem'})
Django (PyMySQL)
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'quickstartdb',
'USER': 'myadmin',
'PASSWORD': 'yourpassword',
'HOST': 'mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com',
'PORT': '3306',
'OPTIONS': {
'ssl': {'ca': '/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem'}
}
}
}
Ruby
client = Mysql2::Client.new(
:host => 'mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com',
:username => 'myadmin',
:password => 'yourpassword',
:database => 'quickstartdb',
:sslca => '/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem'
)
Golang
rootCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
pem, _ := ioutil.ReadFile("/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem")
if ok := rootCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(pem); !ok {
log.Fatal("Failed to append PEM.")
}
mysql.RegisterTLSConfig("custom", &tls.Config{RootCAs: rootCertPool})
var connectionString string
connectionString = fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s:3306)/%s?allowNativePasswords=true&tls=custom",'myadmin' , 'yourpassword', 'mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com', 'quickstartdb')
db, _ := sql.Open("mysql", connectionString)
Java (MySQL Connector for Java)
# generate truststore and keystore in code
String importCert = " -import "+
" -alias mysqlServerCACert "+
" -file " + ssl_ca +
" -keystore truststore "+
" -trustcacerts " +
" -storepass password -noprompt ";
String genKey = " -genkey -keyalg rsa " +
" -alias mysqlClientCertificate -keystore keystore " +
" -storepass password123 -keypass password " +
" -dname CN=MS ";
sun.security.tools.keytool.Main.main(importCert.trim().split("\\s+"));
sun.security.tools.keytool.Main.main(genKey.trim().split("\\s+"));
# use the generated keystore and truststore
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStore","path_to_keystore_file");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword","password");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStore","path_to_truststore_file");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword","password");
url = String.format("jdbc:mysql://%s/%s?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true", 'mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com', 'quickstartdb');
properties.setProperty("user", 'myadmin');
properties.setProperty("password", 'yourpassword');
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
Java (MariaDB Connector for Java)
# generate truststore and keystore in code
String importCert = " -import "+
" -alias mysqlServerCACert "+
" -file " + ssl_ca +
" -keystore truststore "+
" -trustcacerts " +
" -storepass password -noprompt ";
String genKey = " -genkey -keyalg rsa " +
" -alias mysqlClientCertificate -keystore keystore " +
" -storepass password123 -keypass password " +
" -dname CN=MS ";
sun.security.tools.keytool.Main.main(importCert.trim().split("\\s+"));
sun.security.tools.keytool.Main.main(genKey.trim().split("\\s+"));
# use the generated keystore and truststore
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStore","path_to_keystore_file");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword","password");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStore","path_to_truststore_file");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword","password");
url = String.format("jdbc:mariadb://%s/%s?useSSL=true&trustServerCertificate=true", 'mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com', 'quickstartdb');
properties.setProperty("user", 'myadmin');
properties.setProperty("password", 'yourpassword');
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
.NET (MySqlConnector)
var builder = new MySqlConnectionStringBuilder
{
Server = "mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com",
UserID = "myadmin",
Password = "yourpassword",
Database = "quickstartdb",
SslMode = MySqlSslMode.VerifyCA,
SslCa = "DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem",
};
using (var connection = new MySqlConnection(builder.ConnectionString))
{
connection.Open();
}
Node.js
var fs = require('fs');
var mysql = require('mysql');
const serverCa = [fs.readFileSync("/var/www/html/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem", "utf8")];
var conn=mysql.createConnection({
host:"mydemoserver.mysql.database.azure.com",
user:"myadmin",
password:"yourpassword",
database:"quickstartdb",
port:3306,
ssl: {
rejectUnauthorized: true,
ca: serverCa
}
});
conn.connect(function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
});
Related content
- Use MySQL Workbench with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Use PHP with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Create and manage virtual networks for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server using the Azure CLI
- networking in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server firewall rules