Data encryption with customer managed keys for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
With data encryption with customer-managed keys for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server, you can bring your own key (BYOK) for data protection at rest and implement separation of duties for managing keys and data. With customer managed keys (CMKs), the customer is responsible for and ultimately controls the key lifecycle management (key creation, upload, rotation, deletion), key usage permissions, and auditing operations on keys.
Note
Azure Key Vault Managed HSM (Hardware Security Module) is currently supported for customer-managed keys for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
Benefits
Data encryption with customer-managed keys for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server provides the following benefits:
- You fully control data access by the ability to remove the key and make the database inaccessible
- Full control over the key lifecycle, including rotation of the key to aligning with corporate policies
- Central management and organization of keys in Azure Key Vault or Managed HSM
- Ability to implement separation of duties between security officers, DBA, and system administrators
How does data encryption with a customer-managed key work?
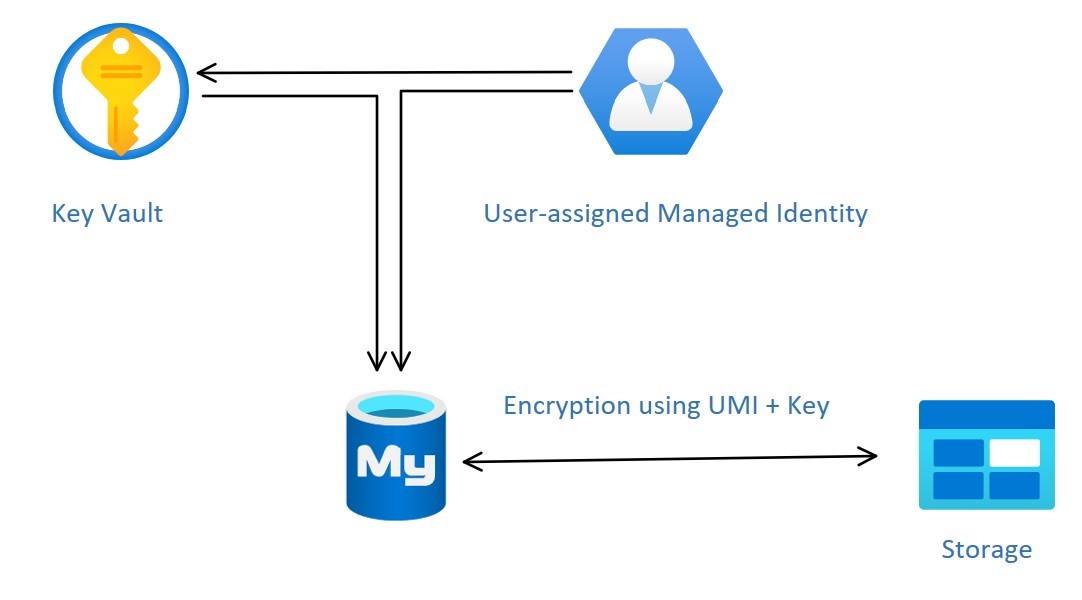
Managed identities in Microsoft Entra ID provide Azure services an alternative to storing credentials in the code by provisioning an automatically assigned identity that can be used to authenticate to any service supporting Microsoft Entra authentication, such as Azure Key Vault (AKV). Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server currently supports only User-assigned Managed Identity (UMI). For more information, see Managed identity types in Azure.
To configure the CMK for an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server, you need to link the UMI to the server and specify the Azure Key vault and key to use.
The UMI must have the following access to the key vault:
- Get: For retrieving the public part and properties of the key in the key vault.
- List: List the versions of the key stored in a Key Vault.
- Wrap Key: To be able to encrypt the DEK. The encrypted DEK is stored in the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance.
- Unwrap Key: To be able to decrypt the DEK. Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server needs the decrypted DEK to encrypt/decrypt the data.
If RBAC is enabled, the UMI must also be assigned the following role:
- Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User or the role with the permissions:
- Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/wrap/action
- Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/unwrap/action
- Microsoft.KeyVault/vaults/keys/read like "Key Vault Crypto Service Encryption User"
- For Managed HSM, assign the Managed HSM Crypto Service Encryption User role
Terminology and description
Data encryption key (DEK): A symmetric AES256 key used to encrypt a partition or block of data. Encrypting each block of data with a different key makes crypto analysis attacks more difficult. Access to DEKs is needed by the resource provider or application instance that encrypts and decrypts a specific block. When you replace a DEK with a new key, only the data in its associated block must be re-encrypted with the new key.
Key encryption key (KEK): An encryption key used to encrypt the DEKs. A KEK that never leaves Key Vault allows the DEKs themselves to be encrypted and controlled. The entity that has access to the KEK might be different than the entity that requires the DEK. Since the KEK is required to decrypt the DEKs, the KEK is effectively a single point by which DEKs can be effectively deleted by deleting the KEK. The DEKs, encrypted with the KEKs, are stored separately. Only an entity with access to the KEK can decrypt these DEKs. For more information, see Security in encryption rest.
How it works
Data encryption with CMKs is set at the server level. For a given server, a CMK, called the key encryption key (KEK), is used to encrypt the service's data encryption key (DEK). The KEK is an asymmetric key stored in a customer-owned and customer-managed Azure Key Vault instance. Key Vault is highly available and scalable secure storage for RSA cryptographic keys, optionally backed by FIPS 140 validated hardware security modules (HSMs). Key Vault doesn't allow direct access to a stored key, but instead provides encryption/decryption services using the key to the authorized entities. The key vault, imported can generate the key, or transferred to the key vault from an on-premises HSM device.
When you configure a flexible server to use a CMK stored in the key vault, the server sends the DEK to the key vault for encryption. Key Vault returns the encrypted DEK stored in the user database. Similarly, the flexible server will send the protected DEK to the key vault for decryption when needed.
After logging is enabled, auditors can use Azure Monitor to review Key Vault audit event logs. To enable logging of Key Vault auditing events, see Monitoring your key vault service with Key Vault insights.
Note
Permission changes can take up to 10 minutes to impact the key vault. This includes revoking access permissions to the TDE protector in AKV, and users within this time frame might still have access permissions.
Requirements for configuring data encryption for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server
Before you attempt to configure Key Vault or Managed HSM, be sure to address the following requirements.
- The Key Vault and Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance must belong to the same Microsoft Entra tenant. Cross-tenant Key Vault and flexible server interactions need to be supported. You'll need to reconfigure data encryption if you move Key Vault resources after performing the configuration.
- The Key Vault and Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance must reside in the same region.
- Enable the soft-delete feature on the key vault with a retention period set to 90 days to protect from data loss should an accidental key (or Key Vault) deletion occur. The recover and purge actions have their own permissions in a Key Vault access policy. The soft-delete feature is off by default, but you can enable it through the Azure portal or by using PowerShell or the Azure CLI.
- Enable the Purge Protection feature on the key vault and set the retention period to 90 days. When purge protection is on, a vault or an object in the deleted state can't be purged until the retention period has passed. You can enable this feature using PowerShell or the Azure CLI, and only after you've enabled soft-delete.
Before you attempt to configure the CMK, be sure to address the following requirements.
- The customer-managed key to encrypt the DEK can be only asymmetric, RSA\RSA-HSM(Vaults with Premium SKU) 2048,3072 or 4096.
- The key activation date (if set) must be a date and time in the past. The expiration date not set.
- The key must be in the Enabled state.
- The key must have soft delete with retention period set to 90 days. This implicitly sets the required key attribute recoveryLevel: "Recoverable."
- The key must have purge protection enabled.
- If you're importing an existing key into the key vault, make sure to provide it in the supported file formats (.pfx, .byok, .backup).
Note
For detailed, step-by-step instructions about how to configure date encryption for Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server via the Azure portal, see Data encryption for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server by using the Azure portal.
Recommendations for configuring data encryption
As you configure Key Vault or Managed HSM to use data encryption using a customer-managed key, keep in mind the following recommendations.
- Set a resource lock on Key Vault to control who can delete this critical resource and prevent accidental or unauthorized deletion.
- Enable auditing and reporting on all encryption keys. Key Vault provides logs that are easy to inject into other security information and event management tools. Azure Monitor Log Analytics is one example of a service that's already integrated.
- Keep a copy of the customer-managed key in a secure place or escrow it to the escrow service.
- If Key Vault generates the key, create a key backup before using the key for the first time. You can only restore the backup to Key Vault. For more information about the backup command, see Backup-AzKeyVaultKey.
Note
- It is advised to use a key vault from the same region, but if necessary, you can use a key vault from another region by specifying the "enter key identifier" information. The key vault managed HSM must be in the same region as the MySQL flexible server.
Inaccessible customer-managed key condition
When you configure data encryption with a CMK in Key Vault, continuous access to this key is required for the server to stay online. If the flexible server loses access to the customer-managed key in Key Vault, the server begins denying all connections within 10 minutes. The flexible server issues a corresponding error message and changes the server state to Inaccessible. The server can reach this state for various reasons.
- If you delete the key vault, the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance will be unable to access the key and will move to Inaccessible state. Recover the key vault and revalidate the data encryption to make the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance Available.
- If you delete the key from the key vault, the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance will be unable to access the key and will move to Inaccessible state. Recover the key and revalidate the data encryption to make the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance Available.
- If the key stored in Azure Key Vault expires, the key will become invalid, and the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance will transition into Inaccessible state. Extend the key expiry date using CLI and then revalidate the data encryption to make the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance Available.
Accidental key access revocation from Key Vault
It might happen that someone with sufficient access rights to Key Vault accidentally disables flexible server access to the key by:
- Revoking the key vault's get, list, wrap key and unwrap key permissions from the server
- Deleting the key
- Deleting the key vault
- Changing the key vault's firewall rules
- Deleting the user managed identity used for encryption on the flexible server with a customer managed key in Microsoft Entra ID
Monitor the customer-managed key in Key Vault
To monitor the database state, and to enable alerting for the loss of transparent data encryption protector access, configure the following Azure features:
- Activity log: When access to the Customer Key in the customer-managed Key Vault fails, entries are added to the activity log. You can reinstate access as soon as possible if you create alerts for these events.
- Action groups: Define these groups to send notifications and alerts based on your preferences.
Replica with a customer managed key in Key Vault
Once an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance is encrypted with a customer's managed key stored in Key Vault, any newly created copy of the server is also encrypted. When trying to encrypt an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance with a customer managed key that already has a replica(s), we recommend configuring the replica(s) by adding the managed identity and key. Suppose the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance is configured with geo-redundancy backup. In that case, the replica must be configured with the managed identity and key to which the identity has access and which resides in the server's geo-paired region.
Restore with a customer managed key in Key Vault
When attempting to restore an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance, you can select the user-managed identity and key to encrypt the restore server. Suppose the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance is configured with geo-redundancy backup. In that case, you must configure the restore server with the managed identity and key to which the identity has access and which resides in the server's geo-paired region.
To avoid issues while setting up customer-managed data encryption during restore or read replica creation, it's essential to follow these steps on the source and restored/replica servers:
- Initiate the restore or read replica creation process from the source Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance.
- On the restored/replica server, revalidate the customer-managed key in the data encryption settings to ensure that the User managed identity is given Get, List, Wrap key and Unwrap key permissions to the key stored in Key Vault.
Note
Using the same identity and key as on the source server is not mandatory when performing a restore.