Introduction to Kubernetes compute target in Azure Machine Learning
APPLIES TO:
 Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
Azure CLI ml extension v2 (current)
 Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
Python SDK azure-ai-ml v2 (current)
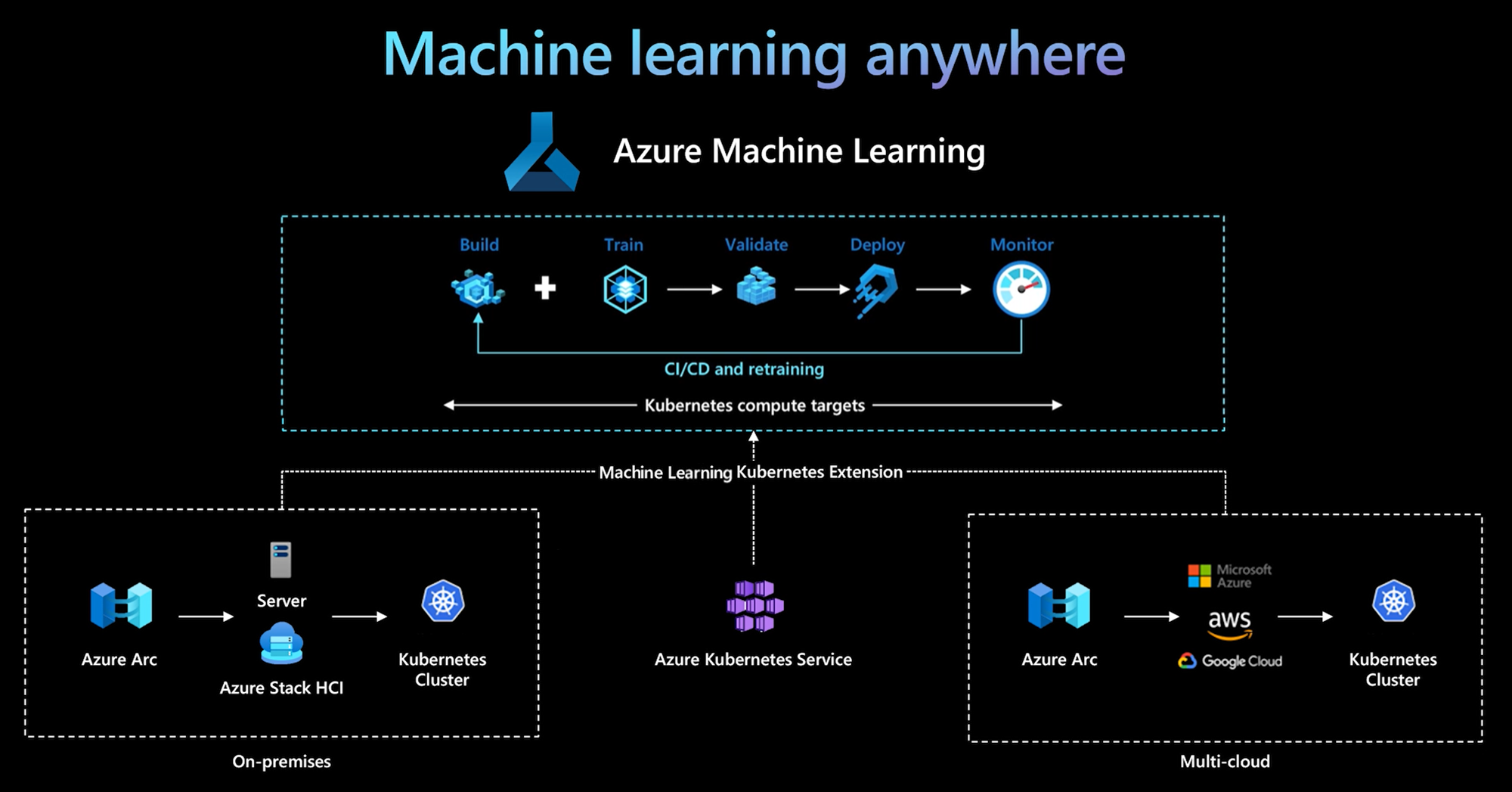
The Azure Machine Learning CLI and Python SDK v2 provide support for a Kubernetes compute target. You can enable an existing Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster or Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes (Arc Kubernetes) cluster as a Kubernetes compute target. Use the compute in Machine Learning to train or deploy models.
This article describes how you can use the Kubernetes compute target in Machine Learning, including usage scenarios, recommended best practices, and a comparison of the KubernetesCompute and legacy AksCompute targets.
How the Kubernetes compute target works
Azure Machine Learning Kubernetes compute supports two kinds of Kubernetes cluster.
| Compute | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AKS cluster | Within Azure | With your self-managed AKS cluster in Azure, you can gain security and controls to meet compliance requirement and flexibility to manage your team's machine learning workload. |
| Arc Kubernetes cluster | Outside Azure | With Arc Kubernetes cluster, you can train or deploy models in any on-premises or multicloud infrastructure, or the edge. |
With a simple cluster extension deployment on AKS or Arc Kubernetes cluster, Kubernetes cluster is seamlessly supported in Machine Learning to run training or inference workload. It's easy to enable and use an existing Kubernetes cluster for Machine Learning workload with the following process:
Step 1: Prepare an Azure Kubernetes Service cluster or Arc Kubernetes cluster.
Step 2: Deploy the Azure Machine Learning cluster extension.
Step 3: Attach the Kubernetes cluster to your Azure Machine Learning workspace.
Step 4: Use the Kubernetes compute target from the CLI v2, SDK v2, or the Azure Machine Learning studio UI.
Here are the primary responsibilities in this process:
The IT-operation team is responsible for Steps 1, 2, and 3. This team prepares an AKS or Arc Kubernetes cluster, deploys the Machine Learning cluster extension, and attaches the Kubernetes cluster to the Machine Learning workspace. In addition to these essential compute setup steps, the IT-operation team also uses familiar tools, such as the Azure CLI or kubectl, to complete the following tasks for the Data-science team:
Configure network and security options, such as outbound proxy server connection or Azure firewall, inference router (azureml-fe) setup, SSL/TLS termination, and virtual network setup.
Create and manage instance types for different machine learning workload scenarios and gain efficient compute resource utilization.
Troubleshoot workload issues related to Kubernetes cluster.
The Data-science team begins their tasks after the IT-operations team finishes compute setup and creation of the compute targets. This team discovers a list of available compute targets and instance types in the Machine Learning workspace. The compute resources can be used for training or inference workload. The Data-science team specifies the compute target name and instance type name by using their preferred tools or APIs. They can use the Azure Machine Learning CLI v2, Python SDK v2, or the Machine Learning studio UI.
Kubernetes usage scenarios
With Arc Kubernetes cluster, you can build, train, and deploy models in any on-premises and multicloud infrastructure by using Kubernetes. This strategy opens some new use patterns previously not possible in a cloud setting environment. The following table provides a summary of the new use patterns enabled when you work with Azure Machine Learning Kubernetes compute:
| Usage pattern | Location of data | Goals and requirements | Scenario configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Train model in cloud, deploy model on-premises | Cloud | Use cloud compute to support elastic compute needs or special hardware such as a GPU. Model deployment must be on-premises for security, compliance, or latency requirements. |
- Azure-managed compute in cloud - Customer-managed Kubernetes on-premises - Fully automated machine learning operations in hybrid mode, including training and model deployment steps that transition seamlessly between cloud and on-premises - Repeatable, all assets properly tracked, model retrained as needed, deployment updated automatically after retraining |
| Train model on-premises and cloud, deploy to both cloud and on-premises | Cloud | Combine on-premises investments with cloud scalability. Bring cloud and on-premises compute under single pane of glass. Access single source of truth for data in cloud and replicate on-premises (lazily on usage or proactively). Enable cloud compute primary usage when on-premises resources aren't available (in use or in maintenance) or don't meet specific hardware requirements (GPU). |
- Azure-managed compute in cloud. Customer-managed Kubernetes on-premises - Fully automated machine learning operations in hybrid mode, including training and model deployment steps that transition seamlessly between cloud and on-premises - Repeatable, all assets properly tracked, model retrained as needed, deployment updated automatically after retraining |
| Train model on-premises, deploy model in cloud | On-premises | Store data on-premises to meet data-residency requirements. Deploy model in the cloud for global-service access or to enable compute elasticity for scale and throughput. |
- Azure-managed compute in cloud - Customer-managed Kubernetes on-premises - Fully automated machine learning operations in hybrid mode, including training and model deployment steps that transition seamlessly between cloud and on-premises - Repeatable, all assets properly tracked, model retrained as needed, deployment updated automatically after retraining |
| Bring your own AKS in Azure | Cloud | Gain more security and controls. Establish all private IP machine learning to prevent data exfiltration. |
- AKS cluster behind an Azure virtual network - Private endpoints in the same virtual network for Azure Machine Learning workspace and associated resources Fully automated machine learning operations |
| Full machine learning lifecycle on-premises | On-premises | Secure sensitive data or proprietary IP, such as machine learning models, code, and scripts. | - Outbound proxy server connection on-premises - Azure ExpressRoute and Azure Arc private link to Azure resources - Customer-managed Kubernetes on-premises - Fully automated machine learning operations |
Limitations for Kubernetes compute target
A KubernetesCompute target in Azure Machine Learning workloads (training and model inference) has the following limitations:
- The availability of Preview features in Azure Machine Learning isn't guaranteed.
- Models (including the foundational model) from the Model Catalog and Registry aren't supported on Kubernetes online endpoints.
- The process of creating a model inference deployment inside the cluster has a timeout limit of 20 minutes. This includes downloading the image, downloading the model, and initializing the user scripts.
- Azure Machine Learning extension supports Kubernetes Baseline Pod Security Standard.
- Training on Kubernetes compute doesn't support auto scale nodes.
Recommended best practices
This section summarizes recommended best practices for working with a Kubernetes compute.
Separation of responsibilities between the IT-operations team and Data-science team. As described earlier, managing your own compute and infrastructure for machine learning workload is a complex task. The best approach is to have the IT-operations team handle the task, so the Data-science team can focus on machine learning models for organizational efficiency.
Create and manage instance types for different machine learning workload scenarios. Each machine learning workload uses different amounts of compute resources, such as CPU/GPU and memory. Azure Machine Learning implements the instance type as a Kubernetes custom resource definition (CRD) with properties of nodeSelector and resource request/limit. With a carefully curated list of instance types, IT-operations can target machine learning workload on specific nodes and manage compute resource utilization efficiently.
Multiple Azure Machine Learning workspaces share the same Kubernetes cluster. You can attach a Kubernetes cluster multiple times to the same Machine Learning workspace or different workspaces. This process creates multiple compute targets in a single workspace or multiple workspaces. Because many customers organize data science projects around Machine Learning workspace, multiple data science projects can now share the same Kubernetes cluster. This approach significantly reduces machine learning infrastructure management overheads and enhances IT cost saving.
Team/project workload isolation using Kubernetes namespace. When you attach a Kubernetes cluster to a Machine Learning workspace, you can specify a Kubernetes namespace for the compute target. All workloads run by the compute target are placed under the specified namespace.
Comparison of KubernetesCompute and legacy AksCompute targets
With the Azure Machine Learning CLI/Python SDK v1, you can deploy models on AKS by using the legacy AksCompute target. Both the KubernetesCompute and AksCompute targets support AKS integration, but the support approach is different. The following table summarizes the key differences:
| Capability | AksCompute (legacy) | KubernetesCompute |
|---|---|---|
| Use the CLI/SDK v1 | Yes | No |
| Use the CLI/SDK v2 | No | Yes |
| Set up training | No | Yes |
| Apply real-time inference | Yes | Yes |
| Apply batch inference | No | Yes |
| Access new features for real-time inference | No new features development | Active roadmap available |
In consideration of these differences, and the overall Machine Learning evolution to use the CLI/SDK v2, the recommended approach is to use Kubernetes compute target (KubernetesCompute) for AKS model deployment.
For more information, explore the following articles:
- Review supported Kubernetes versions and regions
- Connect Machine Learning jobs with custom data storage
Machine learning examples
Machine learning examples are available in the Azure Machine Learning (azureml-examples) repository on GitHub. In any example, replace the compute target name with your Kubernetes compute target, and run the sample.
Here are several options:
- Training job samples with the CLI v2
- Training job samples with the SDK v2
- Model deployment with online endpoint samples and the CLI v2
- Model deployment with online endpoint samples and the SDK v2
- Batch endpoint samples with the CLI v2