Configure MQTT broker authorization
Important
This page includes instructions for managing Azure IoT Operations components using Kubernetes deployment manifests, which is in preview. This feature is provided with several limitations, and shouldn't be used for production workloads.
See the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews for legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
Authorization policies determine what actions the clients can perform on the broker, such as connecting, publishing, or subscribing to topics. Configure the MQTT broker to use one or multiple authorization policies with the BrokerAuthorization resource. Each BrokerAuthorization resource contains a list of rules that specify the principals and resources for the authorization policies.
Link BrokerAuthorization to BrokerListener
To link a BrokerListener resource to a BrokerAuthorization resource, specify the authorizationRef field in the ports setting of the BrokerListener resource. Similar to BrokerAuthentication, the BrokerAuthorization resource can be linked to multiple BrokerListener ports. The authorization policies apply to all linked listener ports. There's one key difference compared with BrokerAuthentication:
Important
To have the BrokerAuthorization configuration apply to a listener port, at least one BrokerAuthentication resource must also be linked to that listener port.
To learn more about BrokerListener, see BrokerListener resource.
Authorization rules
To configure authorization, create a BrokerAuthorization resource in your Kubernetes cluster. The following sections provide examples of how to configure authorization for clients that use usernames, attributes, X.509 certificates, and Kubernetes service account tokens (SATs). For a list of the available settings, see the Broker Authorization API reference.
The following example shows how to create a BrokerAuthorization resource by using both usernames and attributes.
In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
Select the Authorization tab.
Choose an existing authentication policy or create a new one by selecting Create authorization policy.
This broker authorization allows clients with the client IDs temperature-sensor or humidity-sensor, or clients with the attributes organization, with the values contoso and city, and with the value seattle, to:
- Connect to the broker.
- Publish messages to telemetry topics scoped with their client IDs and organization. For example:
temperature-sensorcan publish to/telemetry/temperature-sensorand/telemetry/contoso.humidity-sensorcan publish to/telemetry/humidity-sensorand/telemetry/contoso.some-other-usernamecan publish to/telemetry/contoso.
- Subscribe to
/commands/topics scoped with their organization. For example:temperature-sensorcan subscribe to/commands/contoso.some-other-usernamecan subscribe to/commands/contoso.
Use a username for authorization
To use the MQTT username for authorization, specify them as an array under principals.usernames. Depending on the authentication method, the username might not be verified:
- Kubernetes SAT: Username shouldn't be used for authorization because it's not verified for MQTTv5 with enhanced authentication.
- X.509: Username matches the common name (CN) from a certificate and can be used for authorization rules.
- Custom: Username should only be used for authorization rules if custom authentication validates the username.
To prevent security issues, use the MQTT username for broker authorization only when it can be verified.
Further limit access based on client ID
Because the principals field is a logical OR, you can further restrict access based on client IDs by adding the clientIds field to the brokerResources field. For example, to allow clients with client IDs that start with their building number to connect and publish telemetry to topics scoped with their building, use the following configuration:
In the broker authorization rules for your authorization policy, use the following configuration:
[
{
"brokerResources": [
{
"clientIds": [
"{principal.attributes.building}*"
],
"method": "Connect",
"topics": []
},
{
"clientIds": [],
"method": "Publish",
"topics": [
"sensors/{principal.attributes.building}/{principal.clientId}/telemetry"
]
}
],
"principals": {
"attributes": [
{
"building": "building22"
},
{
"building": "building23"
}
]
}
}
]
Here, if the clientIds weren't set under the Connect method, a client with any client ID could connect as long as it had the building attribute set to building22 or building23. When you add the clientIds field, only clients with client IDs that start with building22 or building23 can connect. This designation ensures that the client has the correct attribute and that the client ID matches the expected pattern.
Authorize clients that use X.509 authentication
You can authorize clients that use X.509 certificates for authentication to access resources based on X.509 properties present on their certificate or their issuing certificates up the chain.
Use attributes
To create rules based on properties from a client's certificate, its root CA, or intermediate CA, define the X.509 attributes in the BrokerAuthorization resource. For more information, see Certificate attributes.
With client certificate subject common name as username
To create authorization policies based on the client certificate subject CN only, create rules based on the CN.
For example, if a client has a certificate with the subject CN = smart-lock, its username is smart-lock. From there, create authorization policies as normal.
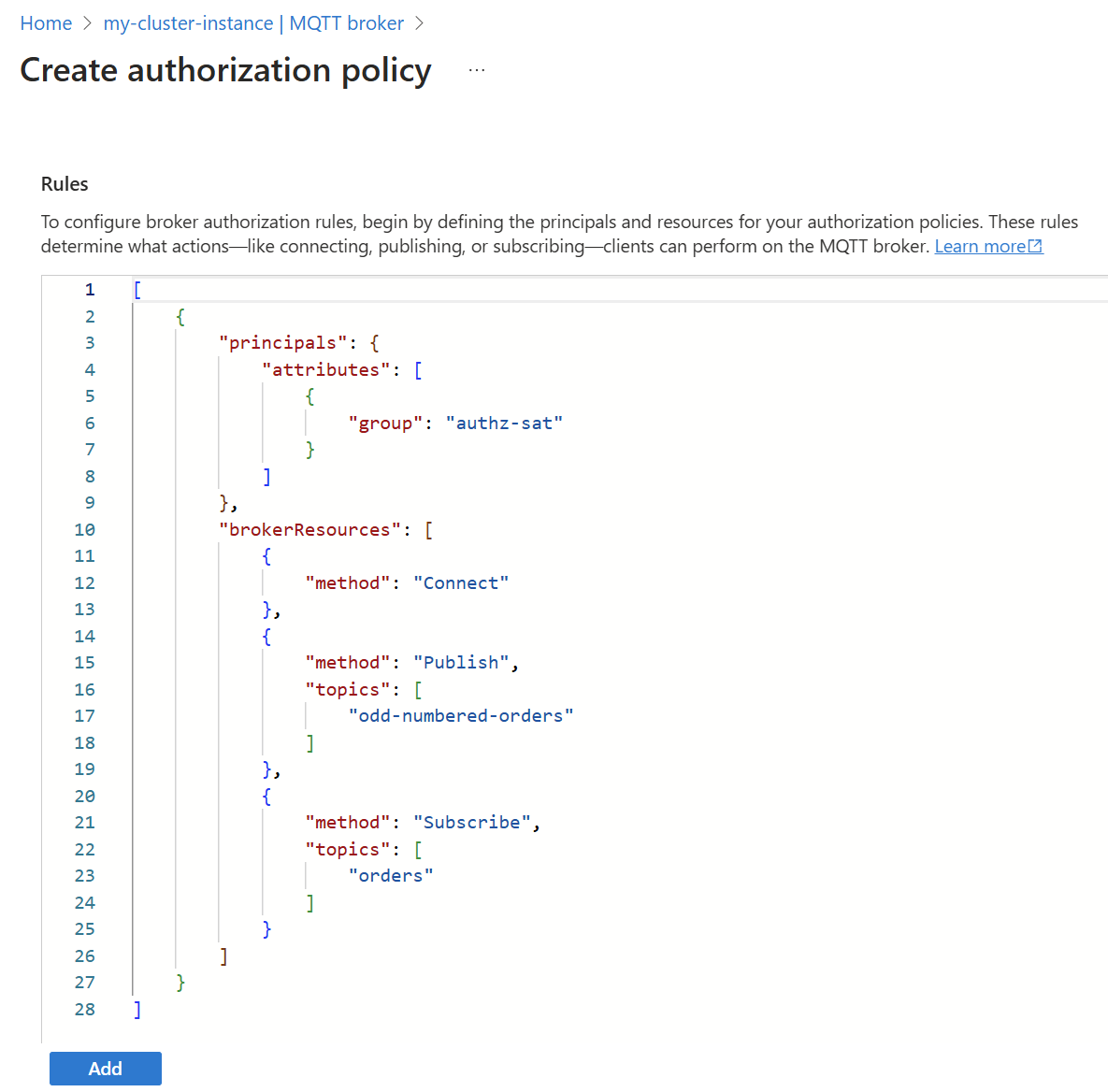
Authorize clients that use Kubernetes service account tokens
Authorization attributes for SATs are set as part of the service account annotations. For example, to add an authorization attribute named group with the value authz-sat, run the command:
kubectl annotate serviceaccount mqtt-client aio-broker-auth/group=authz-sat
Attribute annotations must begin with aio-broker-auth/ to distinguish them from other annotations.
As the application has an authorization attribute called authz-sat, there's no need to provide a clientId or username value. The corresponding BrokerAuthorization resource uses this attribute as a principal, for example:
In the broker authorization rules for your authorization policy, use the following configuration:
[
{
"brokerResources": [
{
"clientIds": [],
"method": "Connect",
"topics": []
},
{
"clientIds": [],
"method": "Publish",
"topics": [
"odd-numbered-orders"
]
},
{
"clientIds": [],
"method": "Subscribe",
"topics": [
"orders"
]
}
],
"principals": {
"attributes": [
{
"group": "authz-sat"
}
]
}
}
]
To learn more with an example, see Set up Authorization Policy with Dapr Client.
State store
The MQTT broker provides a state store that clients can use to store state. You can also configure the state store to be highly available.
To set up authorization for clients that use the state store, provide the following permissions:
- Permission to publish to the system key value store
$services/statestore/_any_/command/invoke/requesttopic - Permission to subscribe to the response-topic (set during initial publish as a parameter)
<response_topic>/#
State store keys
The state store is accessed over the MQTT broker on the topic statestore/v1/FA9AE35F-2F64-47CD-9BFF-08E2B32A0FE8/command/invoke.
Because clients have access to the topic, you can specify keys and access levels under the stateStoreResources section of the MQTT broker brokerResources configuration.
The stateStoreResources section format consists of access level, a pattern indicator, and the pattern.
Include the stateStoreResources section in the rules for your authorization policy.
"stateStoreResources": [
{
"method": "", // Values: read, write, readwrite
"keyType": "", //Values: string, pattern, binary. Default is pattern
"keys": [
// List of patterns to match
]
},
]
The method field specifies the access level:
- Read access is specified with
read. Write access is specified withwrite. Read and write access is specified withreadwrite. - Access level is required.
- Read access level implies the actions of
getandkeynotify. - Write access level implies the actions of
set,del, andvdel.
The keyType field specifies the type of key matching:
pattern: Used for glob-style pattern matching.string: Used to do exact match, for example, when a key contains characters that might be otherwise matched as a pattern (*,?,[0-9]).binary: Used to match a binary key.
The keys field specifies the keys to match. You can specify the keys as glob-style patterns, token substitutions, or exact strings.
Glob style examples:
colors/*: All keys under the "colors/" prefixnumber[0-9]: Any key from "number0" to "number9"char?: Any key with the prefix "char" and a single digit suffix, like "charA"*: Full access to all keys
State store keys also support token substitution when key type is
patternand curly braces are reserved for this purpose. Token substitution examples:clients/{principal.clientId}/*usernames/{principal.username}/*rooms/{principal.attributes.room}/*
Here's an example of how you might author your state store resources.
In the broker authorization rules for your authorization policy, add a similar configuration:
[
{
"brokerResources": [
{
"clientIds": [
"{principal.attributes.building}*"
],
"method": "Connect"
},
{
"method": "Publish",
"topics": [
"sensors/{principal.attributes.building}/{principal.clientId}/telemetry/*"
]
},
{
"method": "Subscribe",
"topics": [
"commands/{principal.attributes.organization}"
]
}
],
"principals": {
"attributes": [
{
"building": "17",
"organization": "contoso"
}
],
"usernames": [
"temperature-sensor",
"humidity-sensor"
]
},
"stateStoreResources": [
{
"method": "Read",
"keyType": "Pattern",
"keys": [
"myreadkey",
"myotherkey?",
"mynumerickeysuffix[0-9]",
"clients/{principal.clientId}/*"
]
},
{
"method": "ReadWrite",
"keyType": "Binary",
"keys": [
"xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
]
}
]
}
]
Update authorization
You can update broker authorization resources at runtime without restart. All clients connected at the time of the update of policy are disconnected. Changing the policy type is also supported.
kubectl edit brokerauthorization my-authz-policies
Disable authorization
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT Operations instance.
- Under Components, select MQTT Broker.
- Select the broker listener you want to edit from the list.
- On the port where you want to disable authorization, select None in the authorization dropdown.
Unauthorized publish in MQTT 3.1.1
With MQTT 3.1.1, when publish is denied, the client receives PUBACK with no error because the protocol version doesn't support returning error code. MQTTv5 returns PUBACK with reason code 135 (Not authorized) when publish is denied.