Quickstart: Configure an Azure virtual network gateway with Terraform
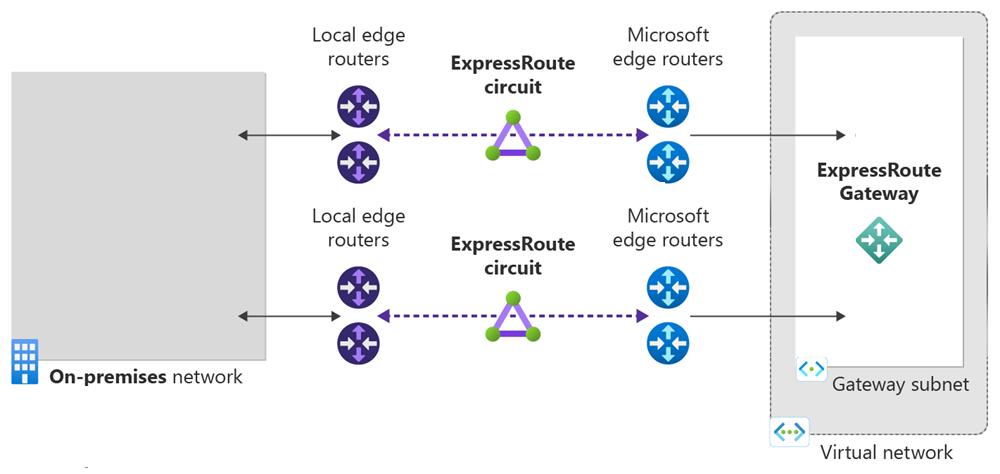
In this quickstart, you use Terraform to create an Azure ExpressRoute circuit with Equinix as the service provider. The circuit uses a Standard SKU with a bandwidth of 50 Mbps and the peering location of Washington, D.C. Private peering is enabled with a primary and secondary subnet of 192.168.10.16/30 and 192.168.10.20/30, respectively. The script also creates a virtual network and a HighPerformance ExpressRoute gateway.
Terraform enables the definition, preview, and deployment of cloud infrastructure. Using Terraform, you create configuration files using HCL syntax. The HCL syntax allows you to specify the cloud provider - such as Azure - and the elements that make up your cloud infrastructure. After you create your configuration files, you create an execution plan that allows you to preview your infrastructure changes before they're deployed. Once you verify the changes, you apply the execution plan to deploy the infrastructure.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Create an Azure resource group with a unique name.
- Create a virtual network with a subnet for the gateway.
- Create a public IP for the gateway.
- Create an ExpressRoute circuit and configure private peering.
- Output the resource group name, ExpressRoute circuit ID, gateway name, gateway IP, and the service key.
Prerequisites
Create an Azure account with an active subscription. You can create an account for free.
Implement the Terraform code
Note
The sample code for this article is located in the Azure Terraform GitHub repo. You can view the log file containing the test results from current and previous versions of Terraform.
See more articles and sample code showing how to use Terraform to manage Azure resources.
Create a directory in which to test and run the sample Terraform code, and make it the current directory.
Create a file named
main.tf, and insert the following code:# Create Resource Group resource "random_pet" "rg_name" { prefix = var.resource_group_name_prefix } resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" { location = var.resource_group_location name = random_pet.rg_name.id } # Random String for unique naming resource "random_string" "name" { length = 8 special = false upper = false lower = true numeric = false } # Create Virtual Network resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" { name = "vnet-${random_string.name.result}" address_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"] location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } # Create Subnet for Gateway resource "azurerm_subnet" "gateway_subnet" { name = "GatewaySubnet" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.name address_prefixes = ["10.0.0.0/24"] } # Create Public IP for Gateway resource "azurerm_public_ip" "gateway_ip" { name = "pip-${random_string.name.result}" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name allocation_method = "Static" sku = "Standard" } # Create ExpressRoute Gateway resource "azurerm_virtual_network_gateway" "gateway" { name = "gateway-${random_string.name.result}" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name type = "ExpressRoute" vpn_type = "RouteBased" active_active = false enable_bgp = false sku = "HighPerformance" ip_configuration { name = "vnetGatewayConfig" public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.gateway_ip.id subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.gateway_subnet.id } } # Create ExpressRoute Circuit resource "azurerm_express_route_circuit" "circuit" { name = "erc-${random_string.name.result}" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location service_provider_name = "Equinix" peering_location = "Washington DC" bandwidth_in_mbps = 50 sku { tier = "Standard" family = "MeteredData" } } # Create ExpressRoute Circuit Peering resource "azurerm_express_route_circuit_peering" "private" { peering_type = "AzurePrivatePeering" express_route_circuit_name = azurerm_express_route_circuit.circuit.name resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name primary_peer_address_prefix = "192.168.10.16/30" secondary_peer_address_prefix = "192.168.10.20/30" vlan_id = 200 peer_asn = 65001 # Provide a valid private ASN here }Create a file named
outputs.tf, and insert the following code:output "resource_group_name" { value = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } output "express_route_circuit_id" { value = azurerm_express_route_circuit.circuit.id } output "gateway_name" { value = azurerm_virtual_network_gateway.gateway.name } output "gateway_ip" { value = azurerm_public_ip.gateway_ip.ip_address } output "service_key" { value = azurerm_express_route_circuit.circuit.service_key sensitive = true }Create a file named
providers.tf, and insert the following code:terraform { required_providers { azurerm = { source = "hashicorp/azurerm" version = "~>3.0" } random = { source = "hashicorp/random" version = "~>3.0" } } } provider "azurerm" { features {} }Create a file named
variables.tf, and insert the following code:variable "resource_group_location" { type = string default = "eastus" description = "Location of the resource group." } variable "resource_group_name_prefix" { type = string default = "rg" description = "Prefix of the resource group name that's combined with a random ID so name is unique in your Azure subscription." }
Initialize Terraform
Run terraform init to initialize the Terraform deployment. This command downloads the Azure provider required to manage your Azure resources.
terraform init -upgrade
Key points:
- The
-upgradeparameter upgrades the necessary provider plugins to the newest version that complies with the configuration's version constraints.
Create a Terraform execution plan
Run terraform plan to create an execution plan.
terraform plan -out main.tfplan
Key points:
- The
terraform plancommand creates an execution plan, but doesn't execute it. Instead, it determines what actions are necessary to create the configuration specified in your configuration files. This pattern allows you to verify whether the execution plan matches your expectations before making any changes to actual resources. - The optional
-outparameter allows you to specify an output file for the plan. Using the-outparameter ensures that the plan you reviewed is exactly what is applied.
Apply a Terraform execution plan
Run terraform apply to apply the execution plan to your cloud infrastructure.
terraform apply main.tfplan
Key points:
- The example
terraform applycommand assumes you previously ranterraform plan -out main.tfplan. - If you specified a different filename for the
-outparameter, use that same filename in the call toterraform apply. - If you didn't use the
-outparameter, callterraform applywithout any parameters.
Verify the results
Get the Azure resource group name.
resource_group_name=$(terraform output -raw resource_group_name)Get the gateway name.
gateway_name=$(terraform output -raw gateway_name)Run
az network vnet-gateway showto view the Azure virtual network gateway.az network vnet-gateway show --name $gateway_name --resource-group $resource_group_name
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resources created via Terraform, do the following steps:
Run terraform plan and specify the
destroyflag.terraform plan -destroy -out main.destroy.tfplanKey points:
- The
terraform plancommand creates an execution plan, but doesn't execute it. Instead, it determines what actions are necessary to create the configuration specified in your configuration files. This pattern allows you to verify whether the execution plan matches your expectations before making any changes to actual resources. - The optional
-outparameter allows you to specify an output file for the plan. Using the-outparameter ensures that the plan you reviewed is exactly what is applied.
- The
Run terraform apply to apply the execution plan.
terraform apply main.destroy.tfplan
Troubleshoot Terraform on Azure
Troubleshoot common problems when using Terraform on Azure.
Next steps
See more articles about Azure virtual network gateway.
To learn how to link a virtual network to a circuit, continue to the ExpressRoute tutorials.