Quickstart: Use GitHub Actions to push to Azure Artifacts
Azure DevOps Services
Get started using GitHub Actions and Azure Artifacts together. GitHub Actions help you automate your software development workflows from within GitHub. You can use GitHub Actions to deploy to an Azure Artifacts feed.
Prerequisites
- A GitHub account with a repository. Join GitHub and create a repository.
- An Azure Artifact feed that you'll push your NuGet package to from a GitHub workflow. Get Started with NuGet Packages.
- Set up a user-assigned managed identity with an associated federated credential.
- Create a user-assigned managed identity.
- Copy the values for Client ID, Subscription ID, and Directory (tenant) ID to use later in your GitHub Actions workflow.
- Assign an appropriate role to your user-assigned managed identity.
- Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity to trust tokens issued by GitHub Actions to your GitHub repository.
- Have permission to assign a managed identity to the Contributor group in Azure DevOps. Project Administrators and Collection Administrators both have this permission.
Note
An alternative approach is to use an Microsoft Entra application with a service principal and federated authentication credential to connect Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions. To learn more about this approach, see Configure an app to trust an external identity provider.
Assign permissions to your managed identity in Azure DevOps
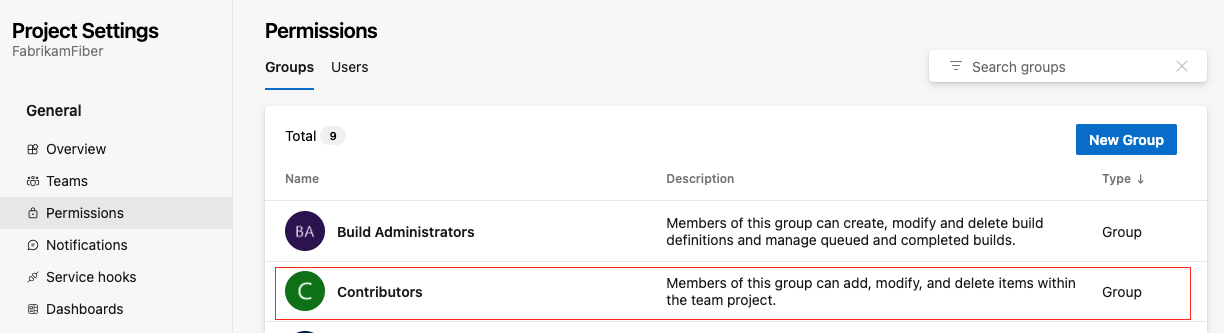
To assign your managed identity to the Contributor team, follow these steps:
Sign in to your project (
https://dev.azure.com/{Your_Organization/Your_Project}).Go to Project settings.
Select General > Permissions.
Choose the Contributors group.
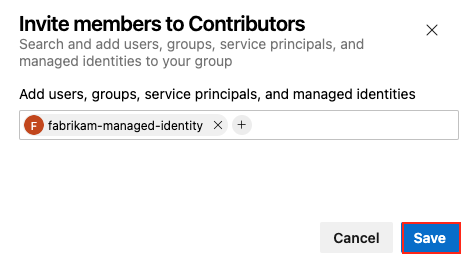
Select the Members tab and then select Add.
Search and find the managed identity.
Select Save to add the identity to the Contributors group.
Create GitHub secrets
You need to provide your managed identity's Client ID, Tenant ID, and Subscription ID to the login action. These values are stored in GitHub secrets and referenced in your workflow.
In GitHub, go to your repository.
Go to Settings in the navigation menu.
Select Security > Secrets and variables > Actions.

Select New repository secret.
Create secrets for
AZURE_CLIENT_ID,AZURE_TENANT_ID, andAZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID. Use these values from your managed identity for your GitHub secrets:GitHub secret Microsoft Entra application AZURE_CLIENT_ID Application (client) ID AZURE_TENANT_ID Directory (tenant) ID AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID Subscription ID Save each secret by selecting Add secret.
Create a GitHub workflow that builds an artifact
GitHub workflows are a series of actions (like tasks in Azure Pipelines). This workflow automates the process of building, testing, packaging, and publishing a .NET project to Azure Artifacts using a managed identity and federated authentication. The workflow:
- Uses the azure/login action to log in to Azure using a managed identity.
- Installs the credential provider for Azure Artifacts.
- Extracts an access token using Azure CLI and configures the authentication provider to use the Azure DevOps token.
- Sets up a .NET Core CLI environment with the setup-dotnet action.
- Restores dependencies, builds the project and its dependencies into a set of binaries, and runs all unit tests associated with the project.
- Packs the code into a NuGet package with the GitHub Run ID environmental variable included in the version number.
- Publishes the NuGet package to Azure Artifacts.
Create a new YAML file
In your repository on GitHub, create a new YAML file in the
.github/workflowsdirectory.Copy the following contents into your YAML file. Customize the
AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL,BUILD_CONFIGURATION, andDOTNET_VERSIONvalues.- Set
AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URLto the registry url for your Azure Artifacts Feed. - Set the
BUILD_CONFIGURATION. - Set
DOTNET_VERSIONto the version of your project.
name: Push a NuGet package to Azure Artifacts with managed identity and federated authentication on: push: branches: - main permissions: id-token: write # Require write permission to Fetch an federated identity token. contents: read # Require read permission to access the repository contents. env: AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL: https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/myorg/nuget-artifact/_packaging/Fabrikam_Feed/nuget/v3/index.json BUILD_CONFIGURATION: 'Release' # set this to the appropriate build configuration DOTNET_VERSION: '6.0' NuGetDirectory: ${{ github.workspace}}/nuget VSS_NUGET_URI_PREFIXES: https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/myorg/ jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: # Checkout the repo - uses: actions/checkout@v4 with: token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} - name: Azure CLI Login uses: azure/login@v2 with: client-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }} tenant-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }} subscription-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }} # Setup .NET Core SDK - name: Setup .NET Core uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v3 with: dotnet-version: ${{ env.DOTNET_VERSION }} # Run dotnet build and package - name: dotnet build and test run: | dotnet restore dotnet build --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' dotnet test --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' # Create the NuGet package in the folder from the environment variable NuGetDirectory - run: dotnet pack --configuration Release --output ${{ env.NuGetDirectory }} # Publish the NuGet package as an artifact, so they can be used in the following jobs - uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3 with: name: nuget if-no-files-found: error retention-days: 7 path: ${{ env.NuGetDirectory }}/*.nupkg az-artifacts-build-and-deploy: needs: build runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v4 with: token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} - name: Azure CLI Login uses: azure/login@v2 with: client-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }} tenant-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }} subscription-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }} - uses: actions/download-artifact@v3 with: name: nuget path: ${{ env.NuGetDirectory }} - name: Setup .NET Core uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v3 with: dotnet-version: ${{ env.DOTNET_VERSION }} source-url: ${{ env.AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL }} env: NUGET_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN}} - name: Install credential provider for Azure Artifacts run: sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://aka.ms/install-artifacts-credprovider.sh)" - name: Extract access token run: | accessToken=$(az account get-access-token --query accessToken --resource 499b84ac-1321-427f-aa17-267ca6975798 -o tsv) echo "::add-mask::$accessToken" echo "ACCESS_TOKEN=$accessToken" >> $GITHUB_ENV - name: Configure authentication provider to use Azure DevOps token run: | echo "VSS_NUGET_ACCESSTOKEN=$ACCESS_TOKEN" >> $GITHUB_ENV - name: dotnet build and publish run: | dotnet restore dotnet build --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' dotnet pack --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' --output ./nupkg --version-suffix ${{ github.run_id }} - name: 'Publish the package to Azure Artifacts' run: dotnet nuget push ${{ env.NuGetDirectory }}/*.nupkg --api-key AzureDevOps --source ${{ env.AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL }}- Set
Prerequisites
- A GitHub account with a repository. Join GitHub and create a repository.
- An Azure Artifact feed that you'll push your NuGet package to from a GitHub workflow. Get Started with NuGet Packages.
- An Azure DevOps personal access token (PAT) to use with your GitHub action. Create a PAT.
- Your PAT needs to have read, write, and manage Packaging permissions.
Authenticate with Azure Pipelines
Use a personal access token (PAT) to connect your GitHub account to Azure DevOps. You can generate a PAT from within Azure DevOps and then store it as a GitHub secret. Within your GitHub workflow, reference the secret so that your GitHub action can authenticate with your Azure DevOps project.
Open your GitHub repository and go to Settings.
Select Security > Secrets and variables > Actions.

Paste in your PAT and give it the name
AZURE_DEVOPS_TOKEN.Select Add secret.
Create a GitHub workflow that builds an artifact
GitHub workflows are a series of actions (like tasks in Azure Pipelines). This workflow:
- Sets up a .NET Core CLI environment with the setup-dotnet action.
- Restores dependencies, builds the project and its dependencies into a set of binaries, and runs all unit tests associated with the project.
- Packs the code into a NuGet package with the GitHub Run ID environmental variable included in the version number.
- Publishes the NuGet package to Azure Artifacts.
Create a new YAML file
In your repository on GitHub, create a new YAML file in the
.github/workflowsdirectory.Copy the following contents into your YAML file. Customize the
AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL,BUILD_CONFIGURATION, andDOTNET_VERSIONvalues.- Set
AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URLto the registry url for your Azure Artifacts Feed. - Set the
BUILD_CONFIGURATION. - Set
DOTNET_VERSIONto the version of your project.
name: Push a NuGet package to Azure Artifacts on: push: branches: - main env: AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL: https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/myorg/nuget-artifact/_packaging/Fabrikam_Feed/nuget/v3/index.json BUILD_CONFIGURATION: 'Release' # set this to the appropriate build configuration DOTNET_VERSION: '6.x' jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: # Checkout the repo - uses: actions/checkout@v2 # Setup .NET Core SDK - name: Setup .NET Core uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v1 with: dotnet-version: ${{ env.DOTNET_VERSION }} # Run dotnet build and package - name: dotnet build and test run: | dotnet restore dotnet build --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' dotnet test --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' az-artifacts-build-and-deploy: needs: build runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: # Checkout the repo - uses: actions/checkout@v2 # Setup .NET Core SDK - name: Setup .NET Core uses: actions/setup-dotnet@v1 with: dotnet-version: ${{ env.DOTNET_VERSION }} source-url: ${{ env.AZURE_ARTIFACTS_FEED_URL }} env: NUGET_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.AZURE_DEVOPS_TOKEN }} # Run dotnet build and package - name: dotnet build and publish run: | dotnet restore dotnet build --configuration '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' dotnet pack -c '${{ env.BUILD_CONFIGURATION }}' --version-suffix $GITHUB_RUN_ID # Publish the package to Azure Artifacts - name: 'dotnet publish' run: dotnet nuget push --api-key AzureArtifacts bin/Release/*.nupkg- Set
Go to your Azure Artifacts feed to verify that you see the package you pushed.
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use your GitHub workflow, disable the workflow.