Overview of the Terraform AzAPI provider
The AzAPI provider is a thin layer on top of the Azure ARM REST APIs. It enables you to manage any Azure resource type using any API version, enabling you to utilize the latest functionality within Azure. AzAPI is a first-class provider designed to be used on its own or in tandem with the AzureRM provider.
Benefits of using the AzAPI provider
The AzAPI provider features the following benefits:
- Supports all Azure control plane services:
- Preview services and features
- All API versions
- Full Terraform state file fidelity
- Properties and values are saved to state
- No dependency on Swagger
- Common and consistent Azure authentication
- Built-in preflight validation
- Granular control over infrastructure development
- Robust VS Code Extension
Resources
To allow you to manage all Azure resources and features without requiring updates, the AzAPI provider includes the following generic resources:
| Resource Name | Description |
|---|---|
azapi_resource |
Used to fully manage any Azure (control plane) resource (API) with full CRUD. Example Use Cases: New preview service New feature added to existing service Existing feature / service not currently covered |
azapi_update_resource |
Used to manage resources or parts of resources that don't have full CRUD Example Use Cases: Update new properties on an existing service Update pre-created child resource - such as DNS SOA record. |
azapi_resource_action |
Used to perform a single operation on a resource without managing the lifecycle of it Example Use Cases: Shut down a Virtual Machine Add a secret to a Key Vault |
azapi_data_plane_resource |
Used to manage a specific subset of Azure data plane resources Example Use Cases: KeyVault Certificate Contacts Synapse Workspace Libraries |
Usage hierarchy
Overall, usage should follow these steps:
- It's always recommended to start with performing as many operations as possible within
azapi_resource. - If the resource type doesn't exist within
azapi_resourcebut does fall under one of the types supported byazapi_data_plane_resource, use that instead. - If the resource already exists in AzureRM or has a property that can't be accessed within
azapi_resource, useazapi_update_resourceto access these specific properties. Resources thatazapi_resourceorazapi_data_plane_resourcedon't support can't be updated through this resource. - If you're trying to perform an action that isn't based on an Azure CRUD-friendly resource,
azapi_resource_actionis less straightforward thanazapi_update_resourcebut more flexible.
Resource configuration examples
The following code snippet configures a resource that doesn't currently exist in the AzureRM provider:
resource "azapi_resource" "publicip" {
type = "Microsoft.Network/Customipprefixes@2021-03-01"
name = "exfullrange"
parent_id = azurerm_resource_group.example.id
location = "westus2"
body = {
properties = {
cidr = "10.0.0.0/24"
signedMessage = "Sample Message for WAN"
}
}
}
The following code snippet configures a preview property for an existing resource from AzureRM:
resource "azapi_update_resource" "test" {
type = "Microsoft.ContainerRegistry/registries@2020-11-01-preview"
resource_id = azurerm_container_registry.acr.id
body = {
properties = {
anonymousPullEnabled = var.bool_anonymous_pull
}
}
}
The following code snippet configures a resource action on an existing AzureRM resource:
resource "azapi_resource_action" "vm_shutdown" {
type = "Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines@2023-07-01"
resource_id = azurerm_linux_virtual_machine.example.id
action = "powerOff”
}
The following code snippet configures a resource that doesn't currently exist in the AzureRM provider due to being provisioned on the data plane:
resource "azapi_data_plane_resource" "dataset" {
type = "Microsoft.Synapse/workspaces/datasets@2020-12-01"
parent_id = trimprefix(data.azurerm_synapse_workspace.example.connectivity_endpoints.dev, "https://")
name = "example-dataset"
body = {
properties = {
type = "AzureBlob",
typeProperties = {
folderPath = {
value = "@dataset().MyFolderPath"
type = "Expression"
}
fileName = {
value = "@dataset().MyFileName"
type = "Expression"
}
format = {
type = "TextFormat"
}
}
parameters = {
MyFolderPath = {
type = "String"
}
MyFileName = {
type = "String"
}
}
}
}
}
Preflight usage example
The following code snippet errors during terraform plan due to AzAPI's built-in preflight validation:
provider "azapi" {
enable_preflight = true
}
resource "azapi_resource" "vnet" {
type = "Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks@2024-01-01"
parent_id = azapi_resource.resourceGroup.id
name = "example-vnet"
location = "westus"
body = {
properties = {
addressSpace = {
addressPrefixes = [
"10.0.0.0/160", # preflight will throw an error here
]
}
}
}
}
Preflight is hidden behind a provider flag but will help throw errors in plan stage.
Data Sources
The AzAPI provider supports a variety of useful data sources:
| Data Source Name | Description |
|---|---|
azapi_resource |
Used to read information from any Azure (control plane) resource (API). Example Use Cases: New preview service New feature added to existing service Existing feature / service not currently covered |
azapi_client_config |
Access client information such as subscription ID and tenant ID. |
azapi_resource_action |
Used to perform a single read operation on a resource without managing the lifecycle of it Example Use Cases: List Keys Read status of VM |
azapi_data_plane_resource |
Used to access a specific subset of Azure data plane resources Example Use Cases: KeyVault Certificate Contacts Synapse Workspace Libraries |
azapi_resource_id |
Access a resource's resource ID, with the ability to output information such as subscription ID, parent ID, resource group name, and resource name. |
azapi_resource_list |
List all resources under a given parent resource ID. Example Use Cases: Resources under a subscription / resource group Subnets under a virtual network |
Authentication using the AzAPI provider
The AzAPI provider enables the same authentication methods as the AzureRM provider. For more information on authentication options, see Authenticate Terraform to Azure.
Experience and lifecycle of the AzAPI provider
This section describes some tools to help you use the AzAPI provider.
VS Code extension and Language Server
The AzAPI VS Code extension provides a rich authoring experience with the following benefits:
- List all available resource types and API versions.

- Auto-completion of the allowed properties and values for any resource.
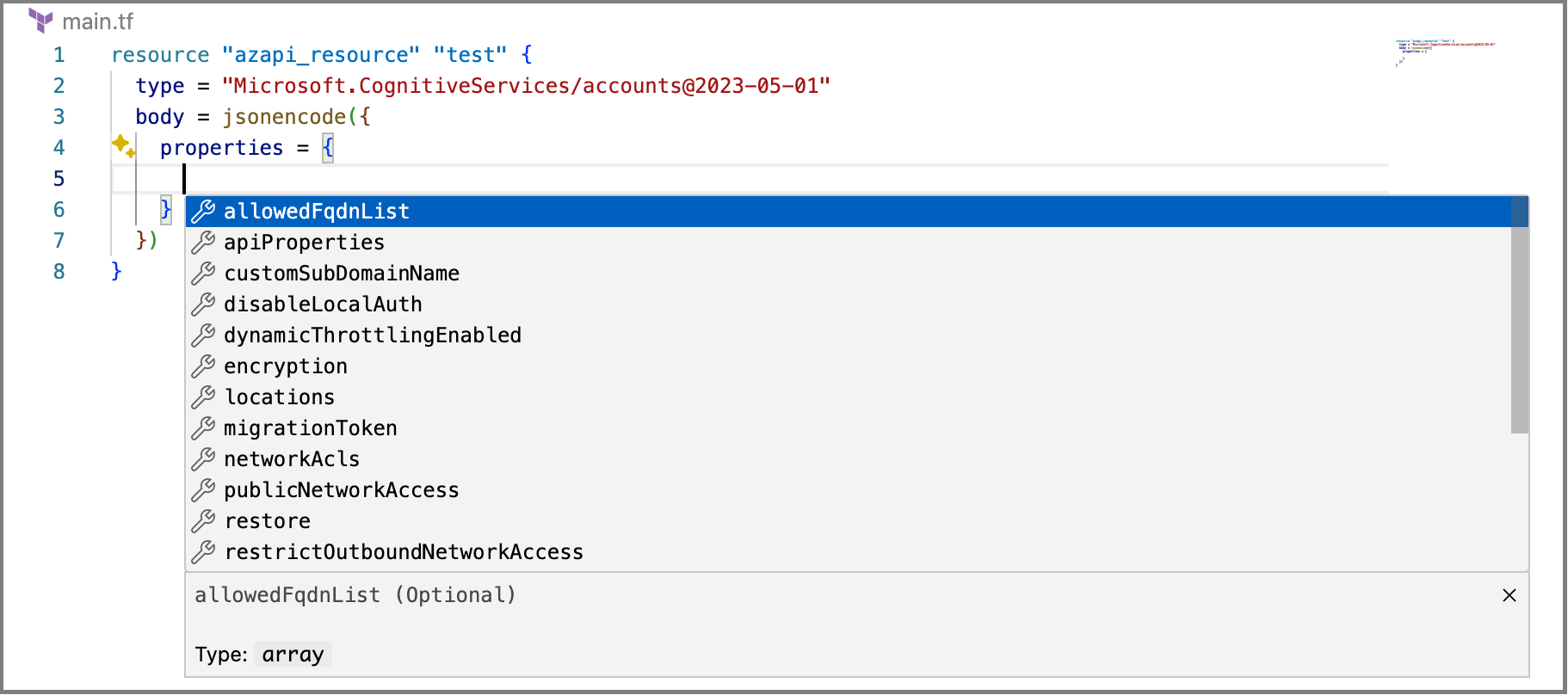
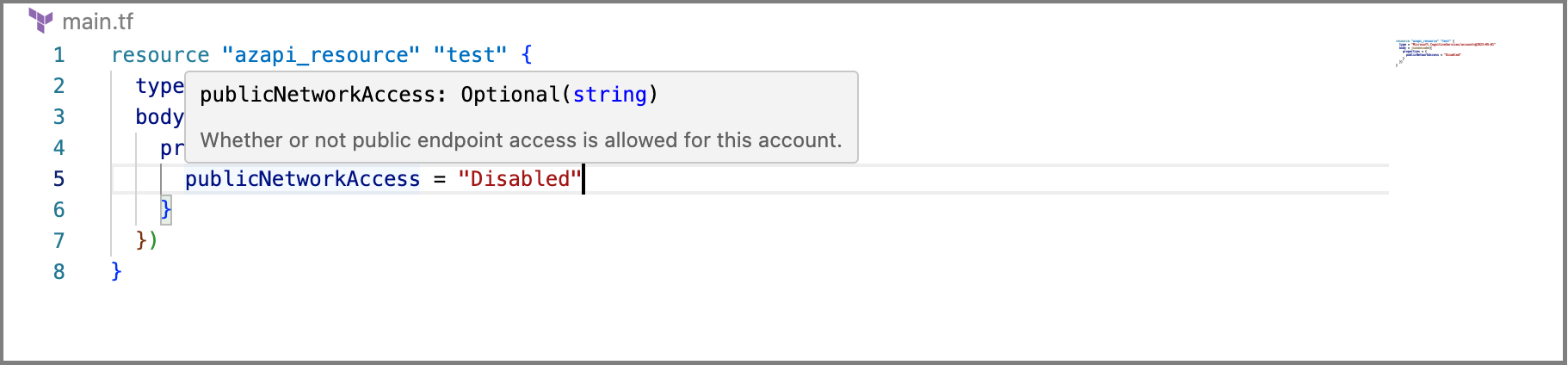
- Show hints when hovering over a property.
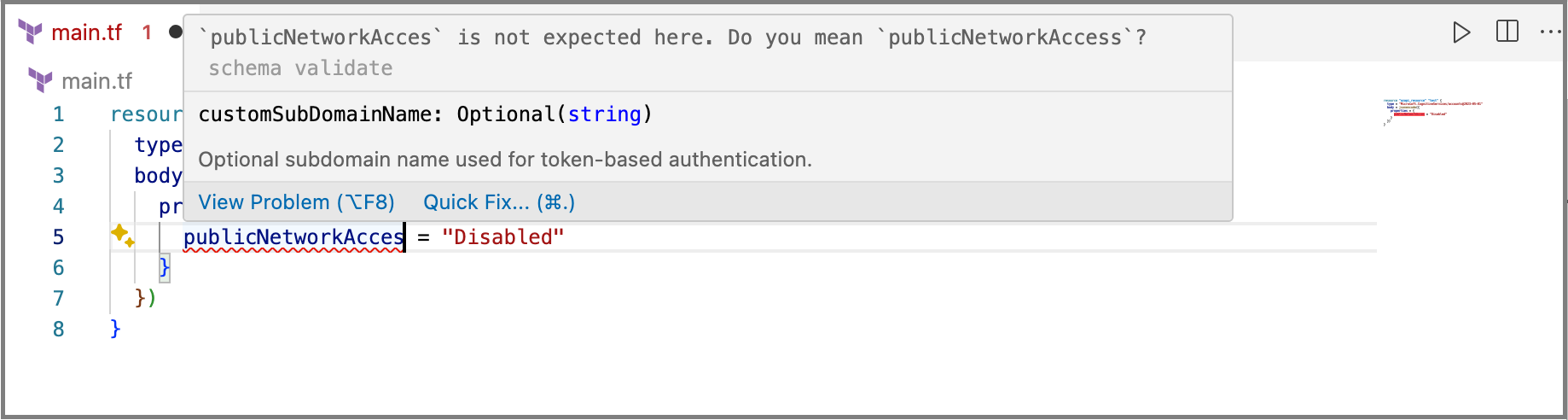
- Syntax validation
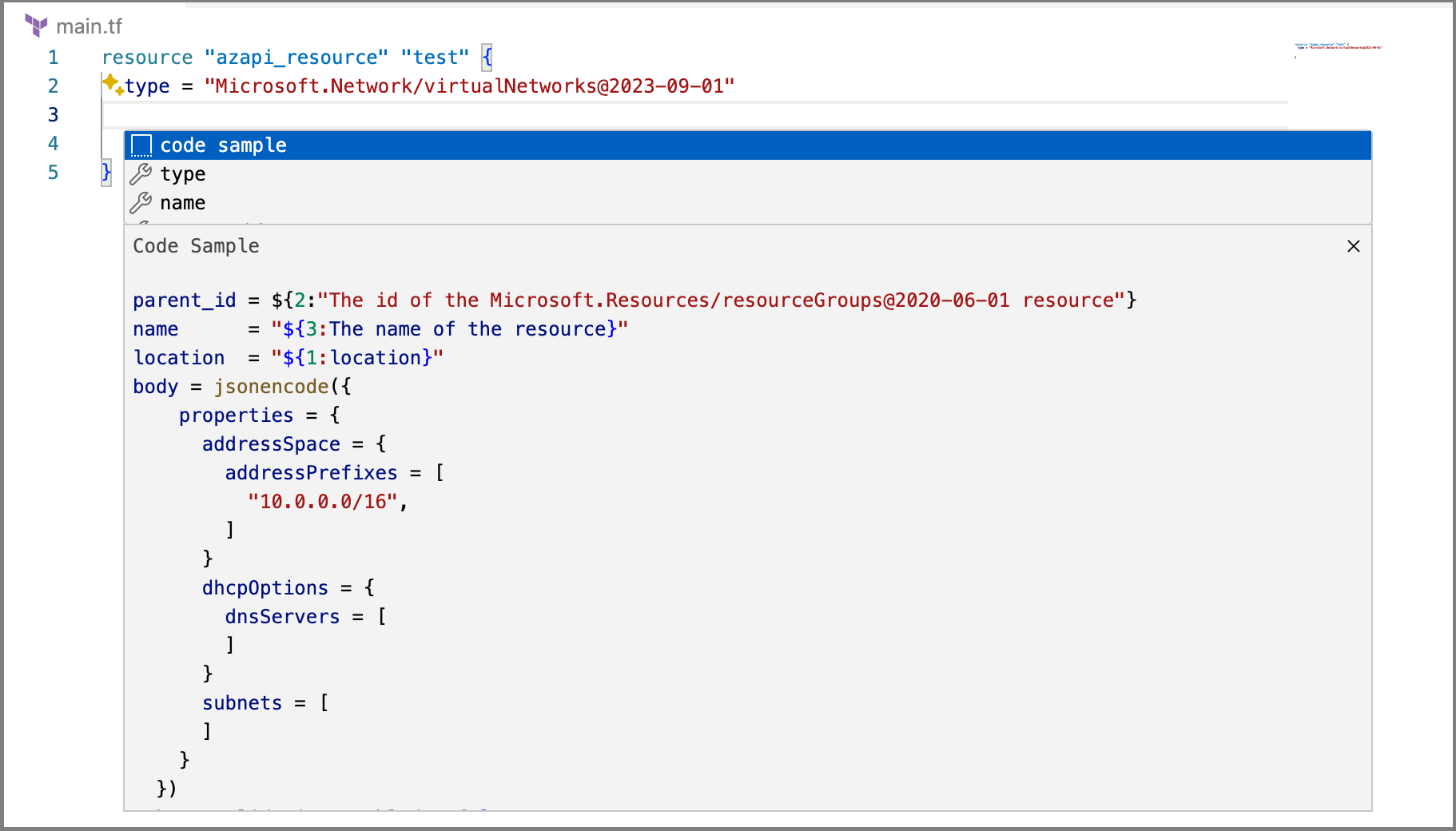
- Auto-completion with code samples.
aztfmigrate migration tool
The aztfmigrate tool is designed to help migrate existing resources between the AzAPI and AzureRM providers.
aztfmigrate has two modes: plan and migrate:
- Plan displays the AzAPI resources that can be migrated.
- Migrate migrates the AzAPI resources to AzureRM resources in both the HCL files and the state.
aztfmigrate ensures after migration that your Terraform configuration and state are aligned with your actual state. You can validate the update to state by running terraform plan after completing the migration to see that nothing has changed.
Granular controls over infrastructure
One major benefit of AzAPI is through its ability to fine-tune your configuration to match the right design patterns. There are several ways in which you can do this:
Provider functions
AzAPI (v2.0 and newer) has a slew of provider functions:
| Function Name | Description |
|---|---|
build_resource_id |
Constructs an Azure resource ID given the parent ID, resource type, and resource name. Useful for creating resource IDs for top-level and nested resources within a specific scope. |
extension_resource_id |
Constructs an Azure extension resource ID given the base resource ID, resource type, and additional resource names. |
management_group_resource_id |
Constructs an Azure management group scope resource ID given the management group name, resource type, and resource names. |
parse_resource_id |
This function takes an Azure resource ID and a resource type and parses the ID into its individual components such as subscription ID, resource group name, provider namespace, and other parts. |
resource_group_resource_id |
Constructs an Azure resource group scope resource ID given the subscription ID, resource group name, resource type, and resource names. |
subscription_resource_id |
Constructs an Azure subscription scope resource ID given the subscription ID, resource type, and resource names. |
tenant_resource_id |
Constructs an Azure tenant scope resource ID given the resource type and resource names. |
User-defined retriable errors with the retry block
The AzAPI provider can digest errors when expected through the retry block. For example, if a resource may run into a create timeout issue, the following block of code may help:
resource "azapi_resource" "example" {
# usual properties
retry {
interval_seconds = 5
randomization_factor = 0.5 # adds randomization to retry pattern
multiplier = 2 # if try fails, multiplies time between next try by this much
error_message_regex = ["ResourceNotFound"]
}
timeouts {
create = "10m"
}
Triggers for resource replacement
The AzAPI provider allows you to configure parameters for resource replacement:
replace_triggers_external_values
Replaces the resource if a value changes. For example, if the SKU or zones variables were to be modified, this resource would be re-created:
resource "azapi_resource" "example" {
name = var.name
type = "Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses@2023-11-01"
parent_id = "/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/example"
body = properties = {
sku = var.sku
zones = var.zones
}
replace_triggers_external_values = [
var.sku,
var.zones,
]
}
This can work across a broad set of resources, i.e. a policy assignment when properties of the definition changes.
replace_triggers_refs
Replaces the resource if the referenced value changes. For example, if the SKU name or tier was modified, this resource would be re-created:
resource "azapi_resource" "example" {
type = "Microsoft.Relay/namespaces@2021-11-01"
parent_id = azurerm_resource_group.example.id
name = "xxx"
location = "westus"
body = {
properties = {
}
sku = {
name = "Standard"
tier = "Standard"
}
}
replace_triggers_refs = ["sku"]
}
This would not trigger a replace if a different resource's SKU were to change.