Migrate Azure Firewall Standard to Premium using Terraform
Terraform enables the definition, preview, and deployment of cloud infrastructure. Using Terraform, you create configuration files using HCL syntax. The HCL syntax allows you to specify the cloud provider - such as Azure - and the elements that make up your cloud infrastructure. After you create your configuration files, you create an execution plan that allows you to preview your infrastructure changes before they're deployed. Once you verify the changes, you apply the execution plan to deploy the infrastructure.
If you use Terraform to deploy standard Azure Firewall with classic rules, you can modify your Terraform configuration file to migrate your firewall to Azure Firewall Premium using a Premium firewall policy.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Deploy a standard Azure Firewall with classic rules using Terraform
- Import the firewall rules into a premium firewall policy
- Edit the Terraform configuration file to migrate the firewall
1. Configure your environment
- Azure subscription: If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Configure Terraform: If you haven't already done so, configure Terraform using one of the following options:
2. Implement the Terraform code
Create a directory in which to test the sample Terraform code and make it the current directory.
Create a file named
main.tfand insert the following code:resource "random_pet" "prefix" { prefix = var.prefix length = 1 } resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-rg" location = var.resource_group_location } resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "vnet" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-vnet" address_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"] location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } resource "azurerm_subnet" "subnet" { name = "AzureFirewallSubnet" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.vnet.name address_prefixes = ["10.0.1.0/24"] } resource "azurerm_public_ip" "pip" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-pip" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name allocation_method = "Static" sku = "Standard" } resource "azurerm_firewall" "main" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-fw" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name sku_name = "AZFW_VNet" sku_tier = "Standard" ip_configuration { name = "configuration" subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet.id public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.pip.id } } resource "azurerm_firewall_application_rule_collection" "app-rc" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-app-rc" azure_firewall_name = azurerm_firewall.main.name resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name priority = 100 action = "Allow" rule { name = "testrule" source_addresses = [ "10.0.0.0/16", ] target_fqdns = [ "*.google.com", ] protocol { port = "443" type = "Https" } } } resource "azurerm_firewall_network_rule_collection" "net-rc" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-net-rc" azure_firewall_name = azurerm_firewall.main.name resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name priority = 100 action = "Allow" rule { name = "dnsrule" source_addresses = [ "10.0.0.0/16", ] destination_ports = [ "53", ] destination_addresses = [ "8.8.8.8", "8.8.4.4", ] protocols = [ "TCP", "UDP", ] } }Create a file named
variables.tfand insert the following code:variable "resource_group_location" { type = string default = "eastus" description = "Location of the resource group." } variable "prefix" { type = string default = "firewall-standard" description = "Prefix of the resource name" }
3. Initialize Terraform
Run terraform init to initialize the Terraform deployment. This command downloads the Azure provider required to manage your Azure resources.
terraform init -upgrade
Key points:
- The
-upgradeparameter upgrades the necessary provider plugins to the newest version that complies with the configuration's version constraints.
4. Create a Terraform execution plan
Run terraform plan to create an execution plan.
terraform plan -out main.tfplan
Key points:
- The
terraform plancommand creates an execution plan, but doesn't execute it. Instead, it determines what actions are necessary to create the configuration specified in your configuration files. This pattern allows you to verify whether the execution plan matches your expectations before making any changes to actual resources. - The optional
-outparameter allows you to specify an output file for the plan. Using the-outparameter ensures that the plan you reviewed is exactly what is applied.
5. Apply a Terraform execution plan
Run terraform apply to apply the execution plan to your cloud infrastructure.
terraform apply main.tfplan
Key points:
- The example
terraform applycommand assumes you previously ranterraform plan -out main.tfplan. - If you specified a different filename for the
-outparameter, use that same filename in the call toterraform apply. - If you didn't use the
-outparameter, callterraform applywithout any parameters.
6. Import the firewall rules into a premium policy
Now you have a standard firewall with classic rules. Next, create a premium Firewall Policy and import the rules from the firewall.
- On the Azure portal, select Create a resource.
- Search for firewall policy and select it.
- Select Create.
- For Resource group select test-resources .
- For Name, type prem-pol.
- For Region, select East US.
- For Policy tier, select Premium.
- Select Next: DNS Settings, and continue until you reach the Rules page.
- On the Rules page, select Import rules from an Azure Firewall.
- Select testfirewall, and then select Import.
- Select Review + create.
- Select Create.
7. Edit the Terraform configuration file to migrate the firewall
Open the main.tf file, and make the following changes:
Add the following 'data' section:
data "azurerm_firewall_policy" "prem-pol" { name = "prem-pol" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name }Modify the firewall resource:
resource "azurerm_firewall" "fw" { name = "testfirewall" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name firewall_policy_id = data.azurerm_firewall_policy.prem-pol.id sku_tier = "Premium" ip_configuration { name = "configuration" subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.subnet.id public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.pip.id } }Delete the classic rule collections:
resource "azurerm_firewall_application_rule_collection" "app-rc" { name = "apptestcollection" azure_firewall_name = azurerm_firewall.fw.name resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name priority = 100 action = "Allow" rule { name = "testrule" source_addresses = [ "10.0.0.0/16", ] target_fqdns = [ "*.google.com", ] protocol { port = "443" type = "Https" } } } resource "azurerm_firewall_network_rule_collection" "net-rc" { name = "nettestcollection" azure_firewall_name = azurerm_firewall.fw.name resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name priority = 100 action = "Allow" rule { name = "dnsrule" source_addresses = [ "10.0.0.0/16", ] destination_ports = [ "53", ] destination_addresses = [ "8.8.8.8", "8.8.4.4", ] protocols = [ "TCP", "UDP", ] } }
8. Apply the modified Terraform execution plan
terraform plan -out main.tfplanterraform apply main.tfplan
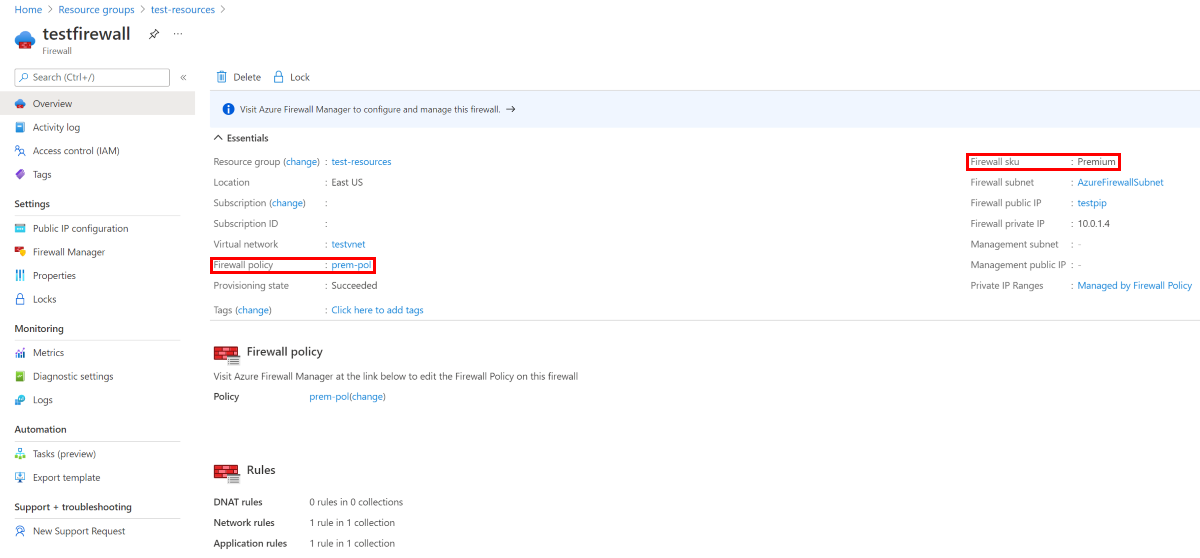
9. Verify the results
- Select the test-resources resource group.
- Select the testfirewall resource.
- Verify the Firewall sku is Premium.
- Verify the firewall is using the prem-pol firewall policy.
10. Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resources created via Terraform, do the following steps:
Run terraform plan and specify the
destroyflag.terraform plan -destroy -out main.destroy.tfplanKey points:
- The
terraform plancommand creates an execution plan, but doesn't execute it. Instead, it determines what actions are necessary to create the configuration specified in your configuration files. This pattern allows you to verify whether the execution plan matches your expectations before making any changes to actual resources. - The optional
-outparameter allows you to specify an output file for the plan. Using the-outparameter ensures that the plan you reviewed is exactly what is applied.
- The
Run terraform apply to apply the execution plan.
terraform apply main.destroy.tfplan
Troubleshoot Terraform on Azure
Troubleshoot common problems when using Terraform on Azure