Use a For each task to run another task in a loop
This article discusses using the For each task with your Azure Databricks jobs, including details on adding and configuring the task in the Jobs UI. Use the For each task to run a nested task in a loop, passing a different set of parameters to each iteration of the task.
Adding the For each task to a job requires defining two tasks: The For each task and a nested task. The nested task is the task to run for each iteration of the For each task and is one of the standard Azure Databricks Jobs task types. You cannot add another For each task as the nested task.
For example, you could use the For each task to perform a common set of transformations on multiple tables, passing a table name from a list of table names to each iteration of the task.
Nested tasks that do not have dependencies on each other can be run concurrently.
Add the For each task to a job
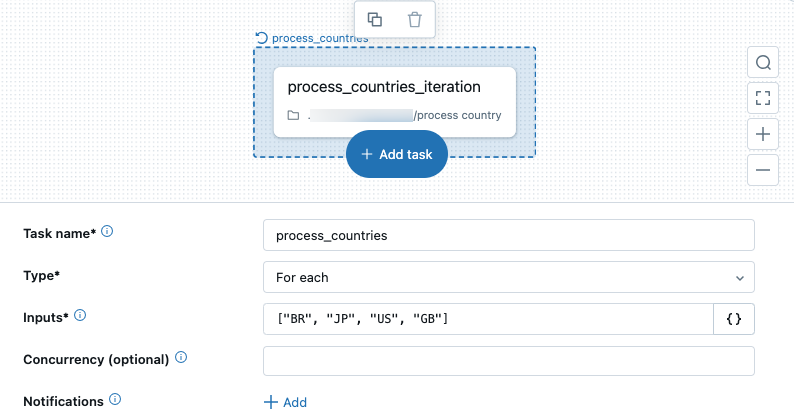
You can add a For each task when you create a job or edit a task in an existing job. To configure a For each task:
In the Type drop-down menu, select For each.
Enter a name for the task in the Task name field.
In the Inputs text box, define the values for the
For eachtask to iterate on as a JSON formatted array of values. To learn more about passing parameters to the nested task, see What parameter types can I use with theFor eachtask?.To optionally set the number of iterations that can run in parallel, enter a Concurrency value for the task. The default value is 1.
To optionally receive notifications for task start, success, or failure, click + Add. See Add notifications on a job.
To complete the configuration of the
For eachtask and add a nested task to run for each iteration, click Add a task to loop over.Select a task type and configuration options for the nested task. Nested tasks are standard task types and have the same configuration options. See Configure and edit Databricks tasks.
To reference parameters passed from the
For eachtask, click Parameters. Use the{{input}}reference to set the value to the array value of each iteration or{{input.<key>}}to reference individual object fields when you iterate over a list of objects.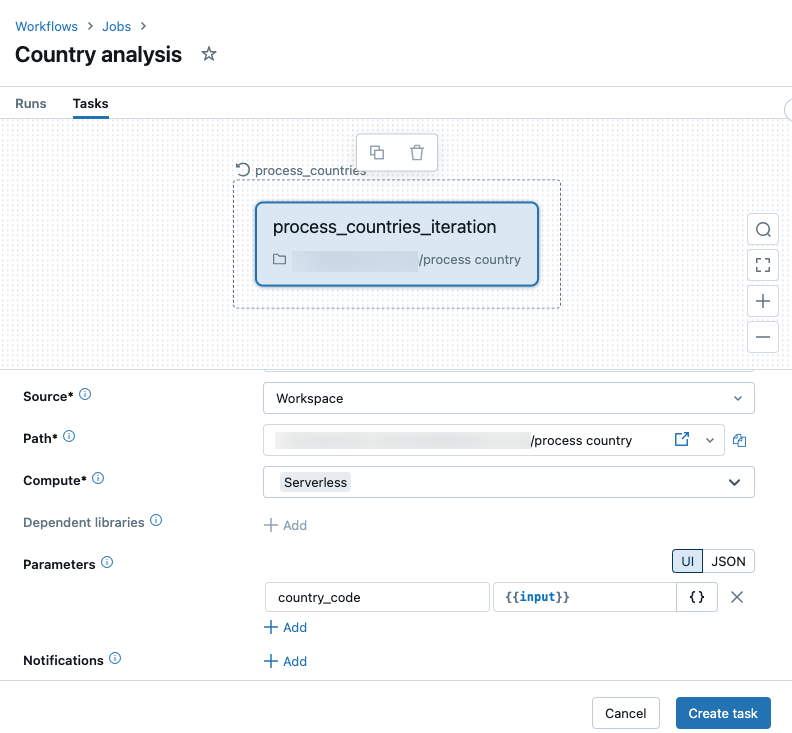
Click Create task.
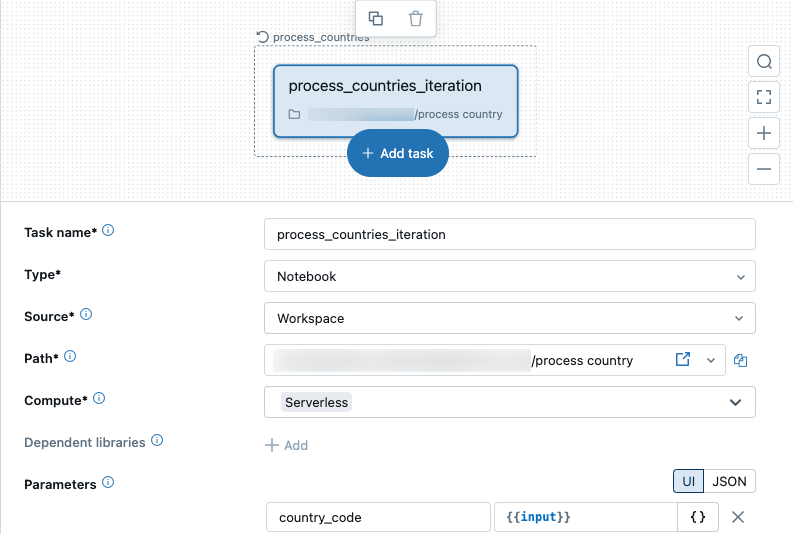
Switch between the For each task and the nested task
The For each task appears in the Jobs UI as a node with the nested task node inside the For each node. To switch between the For each task and the nested task, click the respective nodes.
What parameter types can I use with the For each task?
The For each task passes parameters to each iteration of the nested task. The input is an array of objects, and each object is passed to an iteration of the nested task. There are multiple ways to create the inputs that the task uses: JSON formatted arrays, task values, or job parameters.
Note
Parameters are limited to 10,000 characters, or 48 KB if you use task value references. If your parameters require more than 48 KB, you can pass a lookup to a larger config file. See Use a lookup table for large parameter arrays.
A JSON formatted array of values
When you create or edit a task, you can directly define an array of values for the nested task, using the Inputs text box. This can be an array of the following data types:
- Key-value pairs
- Strings, numbers, or Boolean types
- Arbitrarily complex JSON objects
The Inputs text box is limited to 10,000 characters.
Task value references
You can pass task values from a preceding task. To reference passed task values, use the {{tasks.<task_name>.values.<task_value_name>}} syntax to set the value in the Inputs text box. For example, if a task named generate_countries_list that precedes the For each task sets the following task value:
dbutils.jobs.taskValues.set(key = "countries", value = countries_array)
Then the For each task references the task value in the Inputs text box using the following syntax:
{{tasks.generate_countries_list.values.countries}}.
Task values are limited to 48 KB. To learn more about task values, see Use task values to pass information between tasks.
Job parameters
You can also use job parameters as input. To reference a job parameter, use the following syntax in the Inputs text box: {{job.parameters.<name>}}. For example, {{job.parameters.countries}}.
Job parameters are limited to 10,000 characters. To learn more about job parameters, see Configure job parameters.
Reference a For each task in downstream tasks
The For each task is the top-level task, and downstream tasks can specify it as a dependency. Downstream tasks cannot depend on or reference the nested task.
Run and monitor a job with a For each task
Running a job with a For each task is identical to running any other job.
Viewing and managing job runs is also identical to any other job, except the task run history for a For each task, which is presented as a table of task iterations. See View task run history for a For each task.