Compute
Azure Databricks compute refers to the selection of computing resources available in the Azure Databricks workspace. Users need access to compute to run data engineering, data science, and data analytics workloads, such as production ETL pipelines, streaming analytics, ad-hoc analytics, and machine learning.
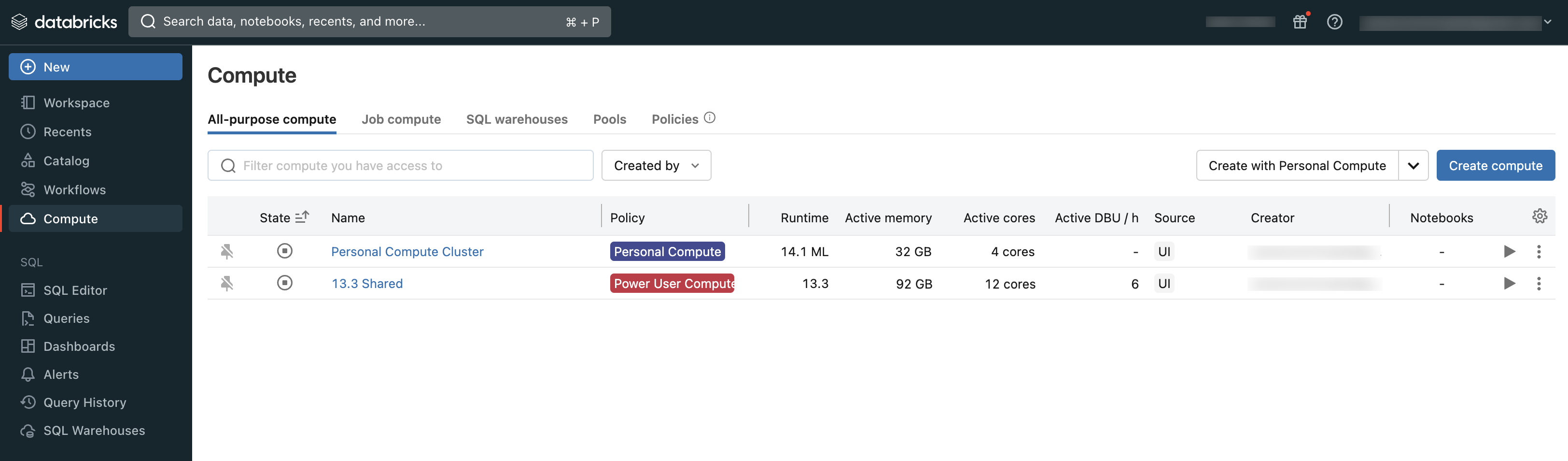
Users can either connect to existing compute or create new compute if they have the proper permissions.
You can view the compute you have access to using the Compute section of the workspace:
Types of compute
These are the types of compute available in Azure Databricks:
Serverless compute for notebooks: On-demand, scalable compute used to execute SQL and Python code in notebooks.
Serverless compute for jobs: On-demand, scalable compute used to run your Databricks jobs without configuring and deploying infrastructure.
All-purpose compute: Provisioned compute used to analyze data in notebooks. You can create, terminate, and restart this compute using the UI, CLI, or REST API.
Jobs compute: Provisioned compute used to run automated jobs. The Azure Databricks job scheduler automatically creates a job compute whenever a job is configured to run on new compute. The compute terminates when the job is complete. You cannot restart a job compute. See Configure compute for jobs.
Instance pools: Compute with idle, ready-to-use instances, used to reduce start and autoscaling times. You can create this compute using the UI, CLI, or REST API.
Serverless SQL warehouses: On-demand elastic compute used to run SQL commands on data objects in the SQL editor or interactive notebooks. You can create SQL warehouses using the UI, CLI, or REST API.
Classic SQL warehouses: Used to run SQL commands on data objects in the SQL editor or interactive notebooks. You can create SQL warehouses using the UI, CLI, or REST API.
The articles in this section describe how to work with compute resources using the Azure Databricks UI. For other methods, see What is the Databricks CLI? and the Databricks REST API reference.
Databricks Runtime
Databricks Runtime is the set of core components that run on your compute. The Databricks Runtime is a configurable setting in all-purpose of jobs compute but autoselected in SQL warehouses.
Each Databricks Runtime version includes updates that improve the usability, performance, and security of big data analytics. The Databricks Runtime on your compute adds many features, including:
- Delta Lake, a next-generation storage layer built on top of Apache Spark that provides ACID transactions, optimized layouts and indexes, and execution engine improvements for building data pipelines. See What is Delta Lake?.
- Installed Java, Scala, Python, and R libraries.
- Ubuntu and its accompanying system libraries.
- GPU libraries for GPU-enabled clusters.
- Azure Databricks services that integrate with other components of the platform, such as notebooks, jobs, and cluster management.
For information about the contents of each runtime version, see the release notes.
Runtime versioning
Databricks Runtime versions are released on a regular basis:
- Long Term Support versions are represented by an LTS qualifier (for example, 3.5 LTS). For each major release, we declare a “canonical” feature version, for which we provide three full years of support. See Databricks support lifecycles for more information.
- Major versions are represented by an increment to the version number that precedes the decimal point (the jump from 3.5 to 4.0, for example). They are released when there are major changes, some of which may not be backwards-compatible.
- Feature versions are represented by an increment to the version number that follows the decimal point (the jump from 3.4 to 3.5, for example). Each major release includes multiple feature releases. Feature releases are always backward compatible with previous releases within their major release.