Self-hosted integration runtime autoupdate and expire notification
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article describes how to let self-hosted integration runtime autoupdate to the latest version and how Azure Data Factory (ADF) manages the versions of self-hosted integration runtime.
How to check your self-hosted integration runtime version
You can check the version either in your self-hosted integration runtime client or in the ADF portal:
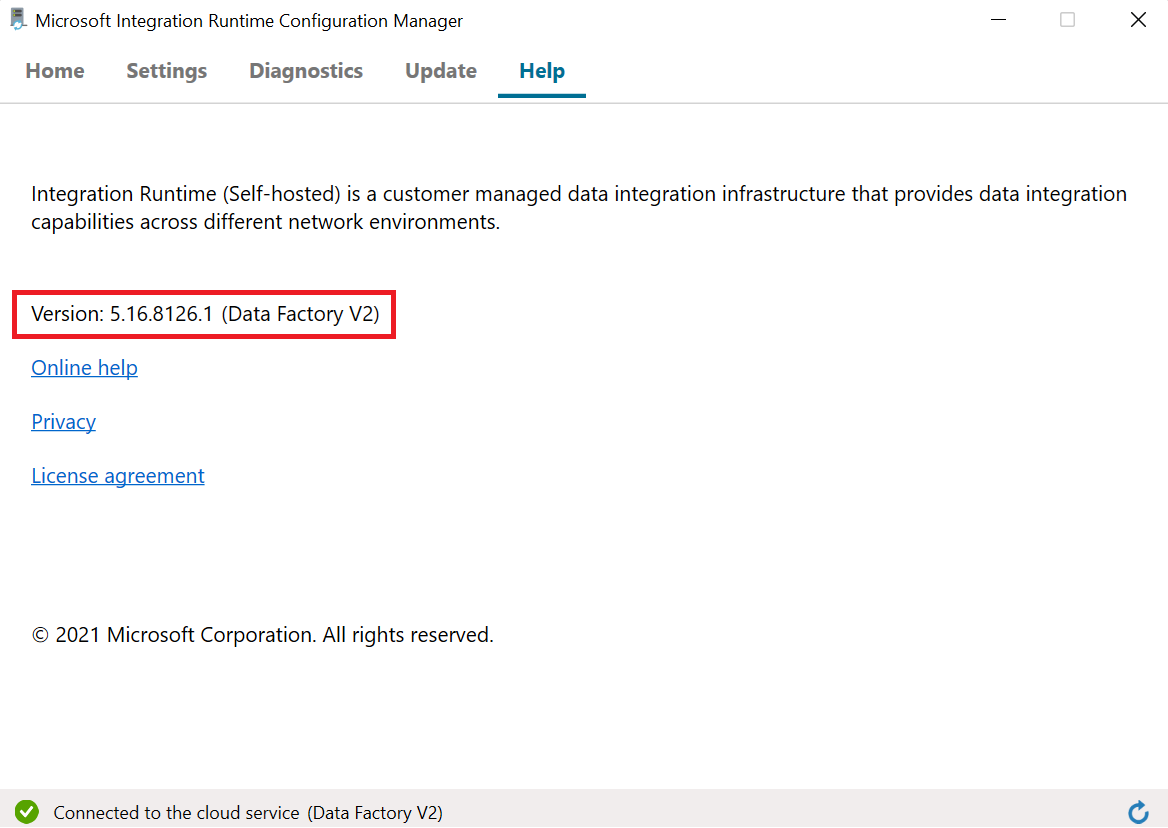
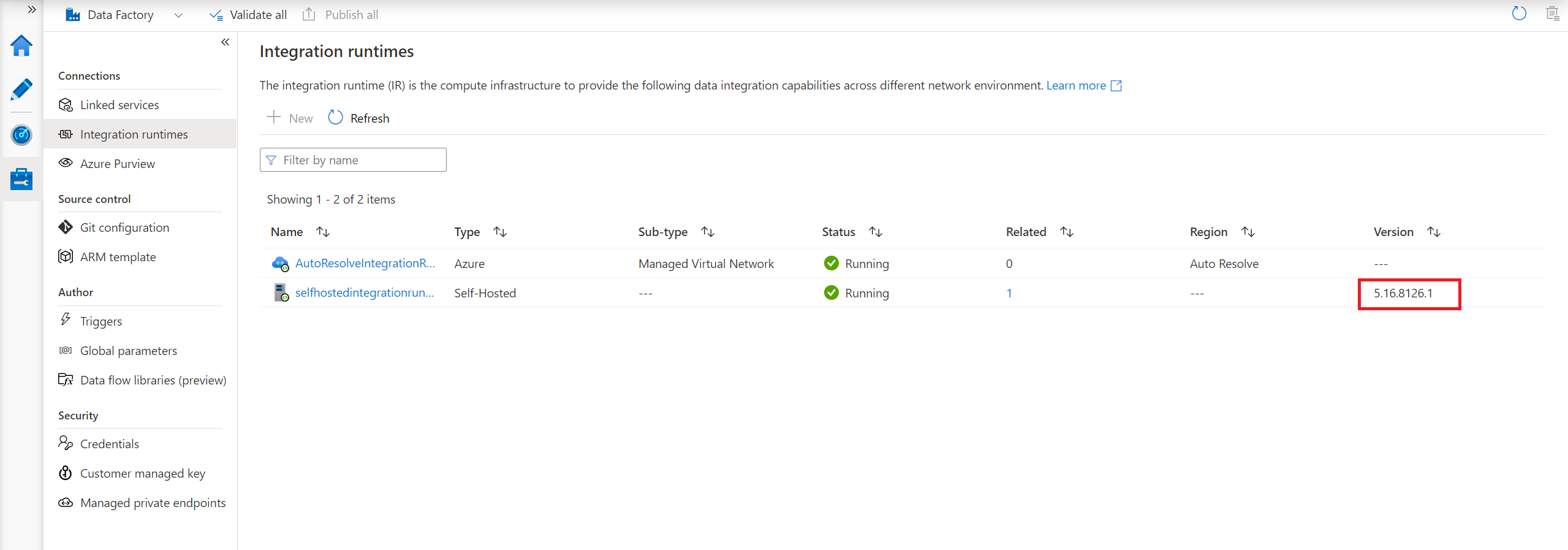
Self-hosted Integration Runtime Autoupdate
Generally, when you install a self-hosted integration runtime in your local machine or an Azure Virtual Machine, you have two options to manage the version of self-hosted integration runtime: autoupdate or maintain manually. Typically, ADF releases one new version of self-hosted integration runtime every month, which includes new features released, bugs fixed, and enhancements. So we recommend users to update to the latest version.
The most convenient way is to enable autoupdate when you create or edit self-hosted integration runtime. The self-hosted integration runtime is automatically update to newer version. You can also schedule the update at the most suitable time slot as you wish.
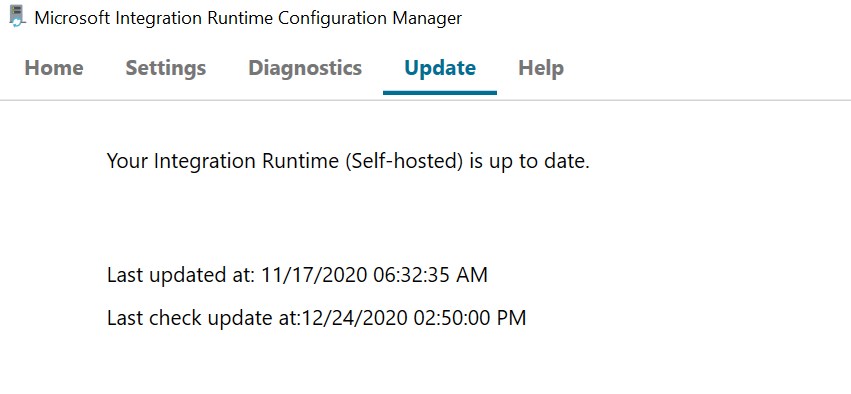
You can check the last update datetime in your self-hosted integration runtime client.
You can use this PowerShell command to get the autoupdate version.
Note
If you have multiple self-hosted integration runtime nodes, there is no downtime during auto-update. The auto-update happens in one node first while others are working on tasks. When the first node finishes the update, it will take over the remained tasks when other nodes are updating. If you only have one self-hosted integration runtime, then it has some downtime during the auto-update.
Autoupdate version vs latest version
To ensure the stability of self-hosted integration runtime, we release a new version each month and push an auto-update every three months, using a stable version from the preceding three months. So you may find that the autoupdated version is the previous version of the actual latest version. If you want to get the latest version, you can go to download center and do so manually. Additionally, auto-update to a new version is managed internally. You can't change it.
The self-hosted integration runtime Auto-update page in the ADF portal shows the newer version if current version is old. When your self-hosted integration runtime is online, this version is autoupdate version and automatically update your self-hosted integration runtime in the scheduled time. But if your self-hosted integration runtime is offline, the page only shows the latest version.
The portal does not offer date selection. This means you can only select the time, while the date is determined by the backend system. Typically, the date will be set for a few days after the self-hosted integration runtime receives the auto-update notification, giving customers sufficient time to make their selection.
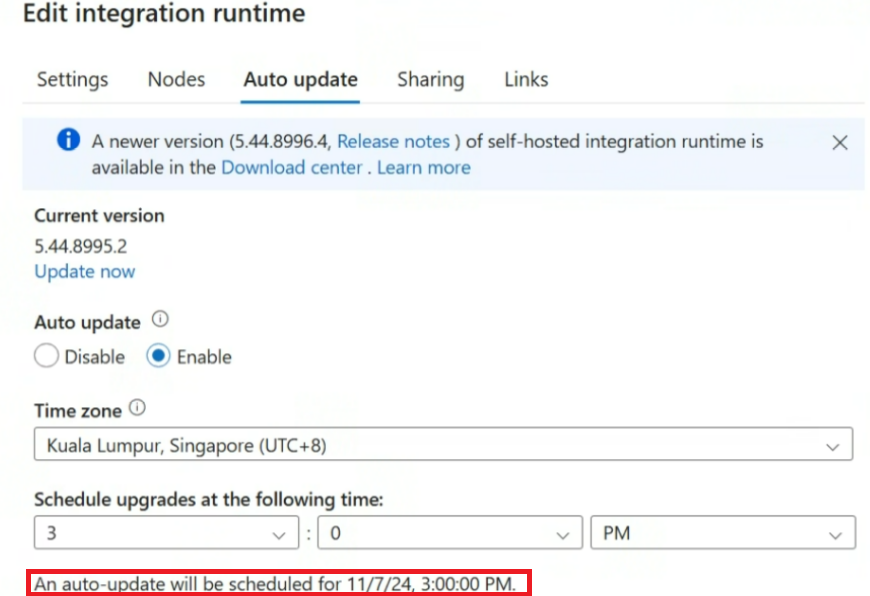
If you have multiple nodes, and for some reasons that some of them aren't autoupdated successfully. Then these nodes roll back to the version, which was the same across all nodes before the autoupdate.
Self-hosted Integration Runtime Expire Notification
If you want to manually control which version of self-hosted integration runtime, you can disable the setting of autoupdate and install it manually. Each version of self-hosted integration runtime expires in one year. The expiring message is shown in ADF portal and self-hosted integration runtime client 90 days before expired.
Warning
If the self-hosted integration runtime becomes expired, it will display an offline status and no longer work properly.
When you receive the expired notification, you can use following PowerShell command to find all expired and expiring self-hosted integration runtime in your environment. Then you can upgrade them accordingly.
$upperVersion = "<expiring version>" # the format is [major].[minor]. For example: 5.25
$subscription = "<subscription id>"
az login
az account set --subscription "$subscription"
$factories = az datafactory list | ConvertFrom-Json
$results = @();
for ($i = 0; $i -lt $factories.Count; $i++) {
$factory = $factories[$i]
Write-Progress -Activity "Checking data factory '$($factory.name)'" -PercentComplete $($i * 100.0 / $factories.Count)
$shirs = az datafactory integration-runtime list --factory-name $factory.name --resource-group $factory.resourceGroup | ConvertFrom-Json | Where-Object {$_.properties.type -eq "SelfHosted"}
for ($j = 0; $j -lt $shirs.Count; $j++) {
$shir = $shirs[$j]
Write-Progress -Activity "Checking data factory '$($factory.name)', checking integration runtime '$($shir.name)'" -PercentComplete $($i * 100.0 / $factories.Count + (100.0 * $j / ($factories.Count * $shirs.Count)))
$status = az datafactory integration-runtime get-status --factory-name $factory.name --resource-group $factory.resourceGroup --integration-runtime-name $shir.name | ConvertFrom-Json
$shirVersion = $status.properties.version
$result = @{
subscription = $subscription
resourceGroup = $factory.resourceGroup
factory = $factory.name
integrationRuntime = $shir.name
integrationRuntimeVersion = $shirVersion
expiring_or_expired = (-not [string]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($shirVersion) -and ((([Version]$shirVersion) -lt ([Version]"$($upperVersion).0.0")) -or $shirVersion.StartsWith("$($upperVersion).")))
}
$result | Format-Table -AutoSize
$results += [PSCustomObject]$result
}
}
Write-Host "Expiring or expired Self-Hosted Integration Runtime includes: "
$results | Where-Object {$_.expiring_or_expired -eq $true} | Select-Object -Property subscription,resourceGroup,factory,integrationRuntime,integrationRuntimeVersion | Format-Table -AutoSize