Deploy Data API builder to Azure Container Apps
Diagram of the sequence of the deployment guide including these locations, in order: Overview, Plan, Prepare, Publish, Monitor, and Optimization. The 'Publish' location is currently highlighted.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Data API builder CLI. Install the CLI.
Azure CLI. Install the Azure CLI.
Existing supported database addressable from Azure.
Build the configuration file
To start, build a Data API builder (DAB) configuration file to connect to your existing database. This file is used later with the final container.
Create an empty directory on your local machine to store the configuration file.
Initialize a new base configuration file using
dab init. Use the following settings at a minimum on initialization.Setting Value Database type Select a supported database type. Connection string Use the @env()function to reference theDATABASE_CONNECTION_STRINGenvironment variable.dab init --database-type "<database-type>" --connection-string "@env('DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRING')"Important
Some database types will require additional configuration settings on initialization.
Add at least one database entity to the configuration. Use the
dab addcommand to configure an entity. Configure each entity to allow all permissions for anonymous users. Repeatdab addas many times as you like for your entities.dab add "<entity-name>" --source "<schema>.<table>" --permissions "anonymous:*"Open and review the contents of the dab-config.json file. You use this file later in this guide.
Host configuration in Azure Files
Next, upload the configuration file to a file share created within Azure Files. This file share is eventually mounted to the final container as a volume.
Sign into the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.com).
Create a new resource group. You will use this resource group to for all new resources in this guide.
Tip
We recommend naming the resource group msdocs-dab-aca. All screenshots in this guide use this name.
Create an Azure Storage account. Use these settings to configure the account.
Setting Value Resource group Select the resource group you created earlier Storage account name Enter a globally unique name Region Select an Azure region Performance Select Standard Redundancy Select Locally-redundant storage (LRS) Enable storage account key access Select Enabled 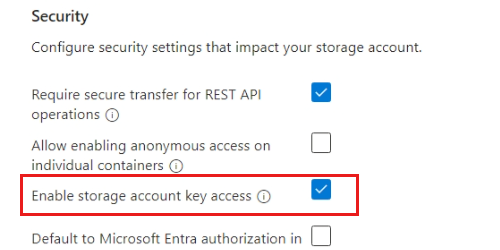
Navigate to the new storage account in the Azure portal.
Select File shares in the Data storage section of the resource menu. Then, select File share from the command bar to create a new share in the storage account. Use the following settings to configure the new file share.
Setting Value Name Enter configAccess tier Select Hot Enable backup Do not select 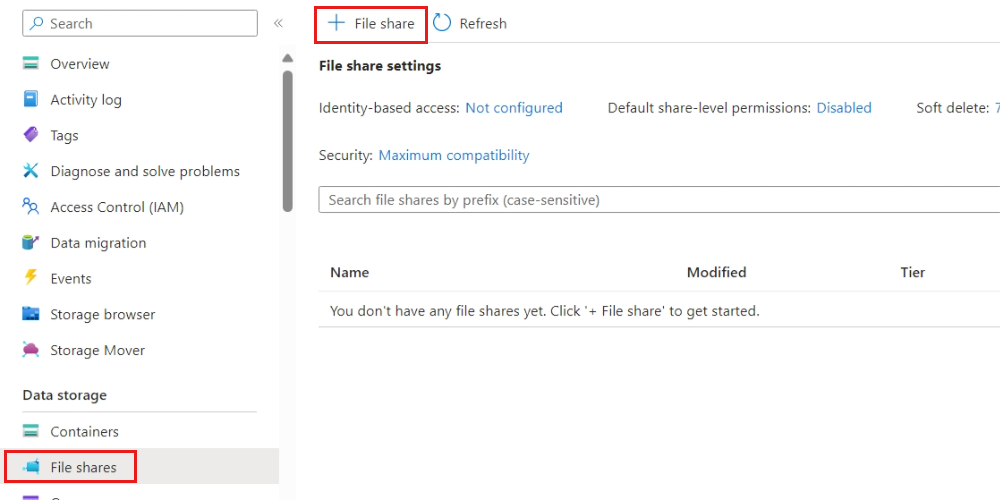
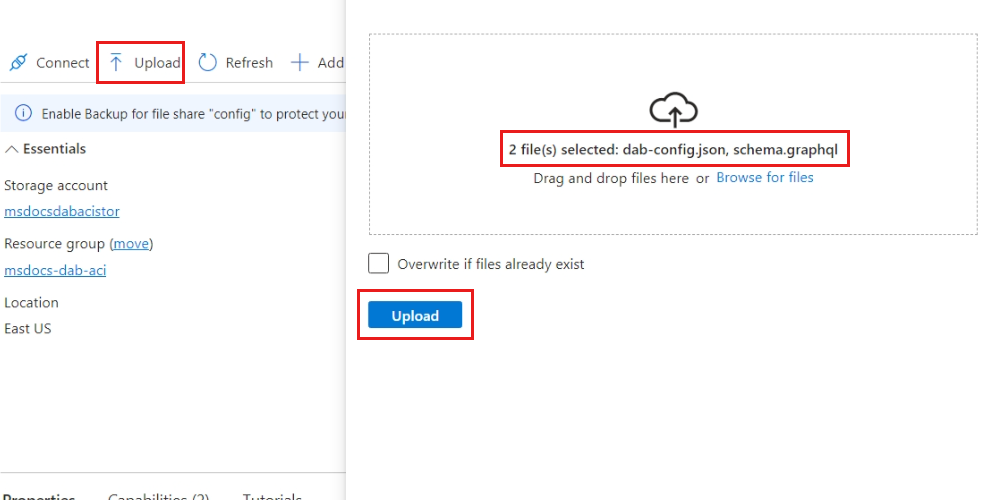
Upload the dab-config.json and any other required files to the share. Use the Upload option in the command bar to open the Upload files dialog. Select both files and then select Upload.
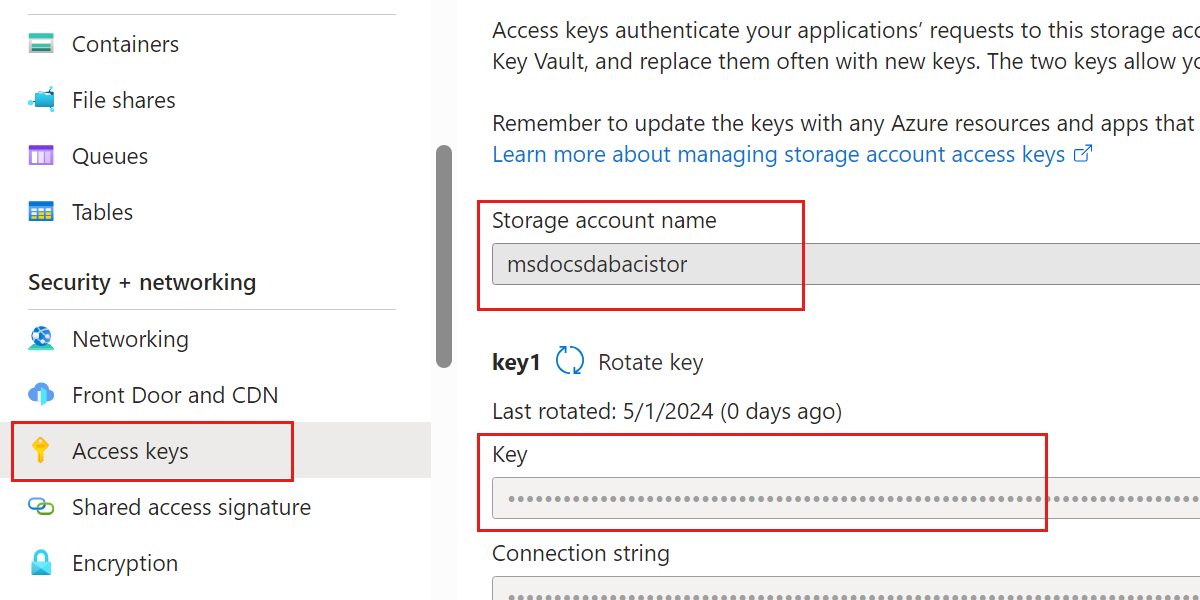
Select Access keys in the Security + networking section of the resource menu. Then, record the Storage account name and Key values from this page. You will use these values later in this guide.
Create the base container app
Now, create the container in Azure using Azure Container Apps. This container hosts the Data API builder image without a configuration.
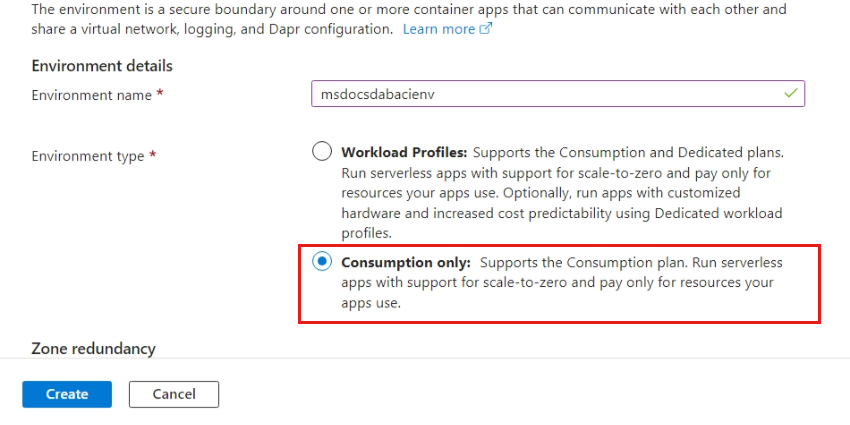
Create an Azure Container Apps resource. As part of the process of creating the app resource, you will be required to create an environment. Use these settings to configure both resources.
Resource Setting Value Environment Environment name Enter a globally unique name Environment Environment type Select Consumption only Environment Logs destination Select Don't save logs App Resource group Select the resource group you created earlier App Storage account name Enter a globally unique name App Region Select the same region as the storage account App Use quickstart image Do not select App Image source Select Docker Hub or other registries App Image type Select Public App Registry login server Enter mcr.microsoft.comApp Image and tag Enter azure-databases/data-api-builder:latestApp Environment variables - Name Enter DATABASE_CONNECTION_STRINGApp Environment variables - Value Enter the connection string for your database. App Ingress Ensure Enabled is selected App Ingress traffic Select Accepting traffic from anywhere App Client certificate mode Select Ignore App Ingress type Select HTTP App Target port Enter 5000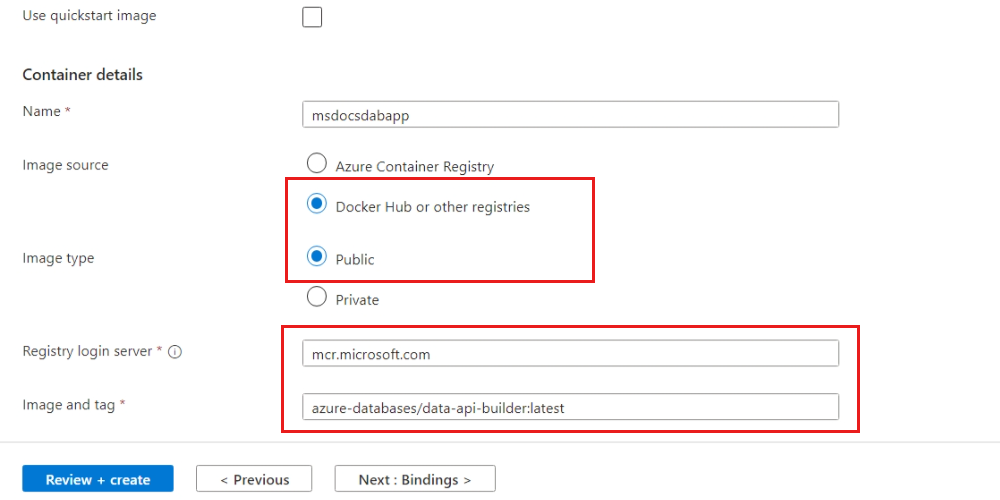
Tip
We recommend using a connection string that does not include authorization keys. Instead, use managed identities and role-based access control to manage access between your database and host. For more information, see Azure services that use managed identities.
Navigate to the new container app in the Azure portal.
Use the Application URL field in the Essentials section to browse to the container app's website. Observe the response indicating that the DAB container is running and the status is healthy.
{ "status": "healthy", "version": "1.1.7", "app-name": "dab_oss_1.1.7" }Note
The version number and name will vary based on your current version of Data API builder. At this point, you cannot navigate to any API endpoints. These endpoints will be available once you mount a DAB configuration file.
Mount the configuration files
Finally, mount the configuration files from the Azure Files share to the container app. This step allows the Data API builder to use the configuration file to connect to your database.
Navigate to the container environment created previously in this guide using the Azure portal.
Select Azure files in the Settings section of the resource menu. Then, select Add from the command bar to add an existing file share to the container environment. Use the following settings to configure the new file share. Then save the new file share configuration.
Setting Value Name Enter config-shareStorage account name Name of the storage account recorded earlier in this guide. Storage account key Key of the storage account recorded earlier in this guide. File share Enter configAccess mode Select Read only 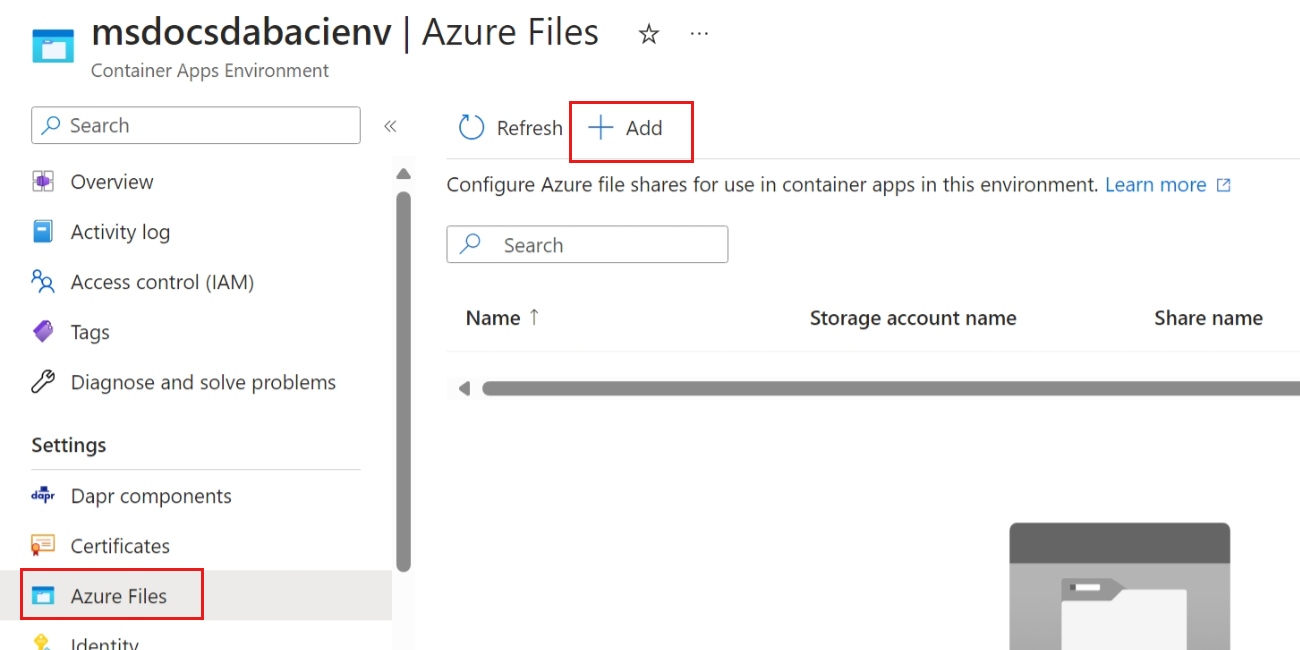
Navigate to the container app again in the Azure portal.
Select Revisions and replicas in the Application section of the resource menu. Then, select Create new revision from the command bar to start the process of configuring a new revision for your container app.
Navigate to the Volumes section and select the Add option. Use the following settings to configure the new volume. After configuring the volume, Add the volume to the container revision.
Setting Value Volume type Select Azure file volume Name Enter config-volumeFile share Enter config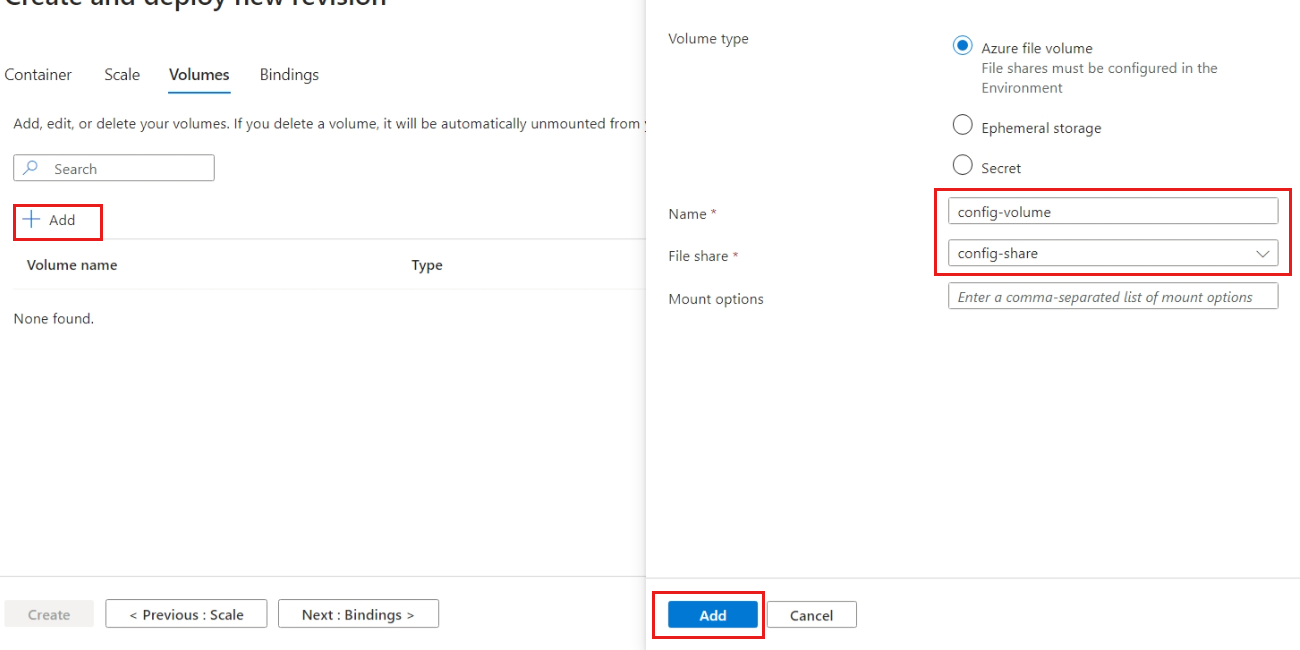
Navigate to the Container section, select the single current container, and then select the Edit option. Use the following settings to configure two mounts for the container. Save your changes.
Setting Value Volume name Enter config-volumeMount path Enter /App/dab-config.jsonSub path Enter dab-config.jsonSetting Value Volume name Enter config-volumeMount path Enter /App/schema.graphqlSub path Enter schema.graphql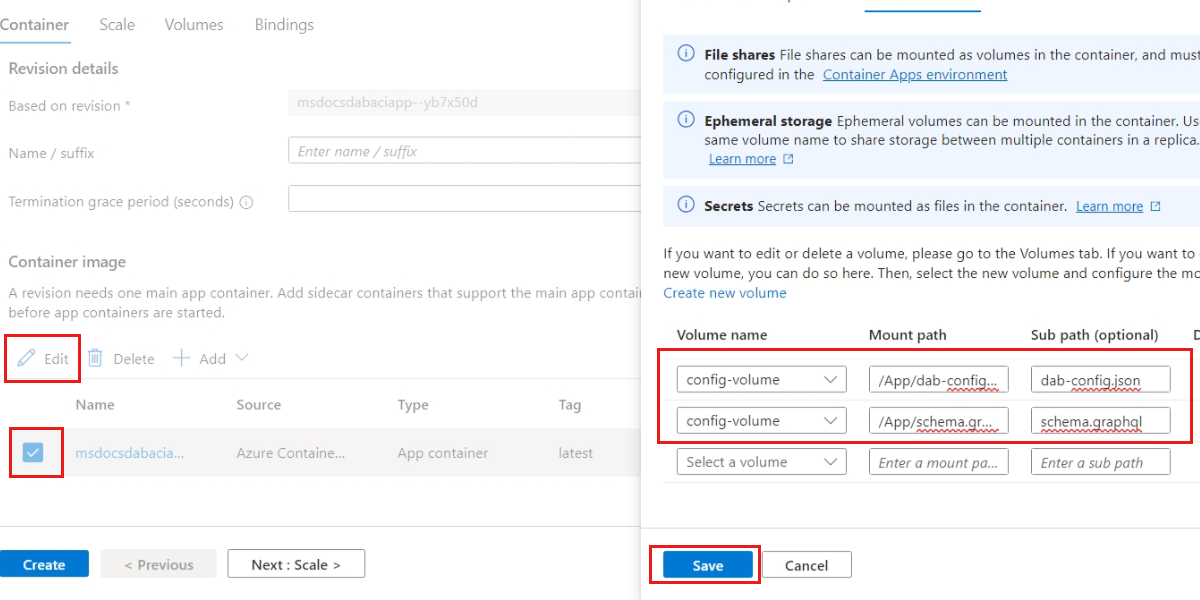
Select Create to create a new revision with the volume mounts you specified. With for the revision to finish deploying.
Use the Application URL field in the Essentials section to browse to the container app's website again. Observe that the response still indicates that the DAB container is healthy.
Navigate to the
/api/swaggerpath for the current running application. Use the Swagger UI to issue an HTTP GET request for one of your entities.
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the sample application or resources, remove the corresponding deployment and all resources.
Navigate to the resource group using the Azure portal.
In the command bar, select Delete.