Slurm
Slurm is a highly configurable open source workload manager. See the Slurm project site for an overview.
Note
As of CycleCloud 8.4.0, the Slurm integration has been rewritten to support new features and functionality. See the Slurm 3.0 documentation for more information.
Slurm can easily be enabled on a CycleCloud cluster by modifying the "run_list" in the configuration section of your cluster definition. The two basic components of a Slurm cluster are the 'master' (or 'scheduler') node which provides a shared filesystem on which the Slurm software runs, and the 'execute' nodes which are the hosts that mount the shared filesystem and execute the jobs submitted. For example, a simple cluster template snippet may look like:
[cluster custom-slurm]
[[node master]]
ImageName = cycle.image.centos7
MachineType = Standard_A4 # 8 cores
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:default]]]
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:master]]]
[[[configuration]]]
run_list = role[slurm_master_role]
[[nodearray execute]]
ImageName = cycle.image.centos7
MachineType = Standard_A1 # 1 core
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:default]]]
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:execute]]]
[[[configuration]]]
run_list = role[slurm_master_role]
slurm.autoscale = true
# Set to true if nodes are used for tightly-coupled multi-node jobs
slurm.hpc = true
slurm.default_partition = true
Slurm can easily be enabled on a CycleCloud cluster by modifying the "run_list" in the configuration section of your cluster definition. The two basic components of a Slurm cluster are the 'scheduler' node which provides a shared filesystem on which the Slurm software runs, and the 'execute' nodes which are the hosts that mount the shared filesystem and execute the jobs submitted. For example, a simple cluster template snippet may look like:
[cluster custom-slurm]
[[node scheduler]]
ImageName = cycle.image.centos7
MachineType = Standard_A4 # 8 cores
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:default]]]
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:scheduler]]]
[[[configuration]]]
run_list = role[slurm_scheduler_role]
[[nodearray execute]]
ImageName = cycle.image.centos7
MachineType = Standard_A1 # 1 core
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:default]]]
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:execute]]]
[[[configuration]]]
run_list = role[slurm_scheduler_role]
slurm.autoscale = true
# Set to true if nodes are used for tightly-coupled multi-node jobs
slurm.hpc = true
slurm.default_partition = true
Editing Existing Slurm Clusters
Slurm clusters running in CycleCloud versions 7.8 and later implement an updated version of the autoscaling APIs that allows the clusters to utilize multiple nodearrays and partitions. To facilitate this functionality in Slurm, CycleCloud pre-populates the execute nodes in the cluster. Because of this, you need to run a command on the Slurm scheduler node after making any changes to the cluster, such as autoscale limits or VM types.
Making Cluster Changes
The Slurm cluster deployed in CycleCloud contains a script that facilitates this. After making any changes to the cluster, run the following as root (e.g., by running sudo -i) on the Slurm scheduler node to rebuild the slurm.conf and update the nodes in the cluster:
/opt/cycle/slurm/cyclecloud_slurm.sh remove_nodes
/opt/cycle/slurm/cyclecloud_slurm.sh scale
Note
For CycleCloud versions < 7.9.10, the cyclecloud_slurm.sh script is located in /opt/cycle/jetpack/system/bootstrap/slurm.
Important
If you make any changes that affect the VMs for nodes in an MPI partition (such as VM size, image, or cloud-init), the nodes must all be terminated first.
The remove_nodes command prints a warning in this case, but it does not exit with an error.
If there are running nodes, you will get an error of This node does not match existing scaleset attribute when new nodes are started.
/opt/cycle/slurm/cyclecloud_slurm.sh apply_changes
Note
For CycleCloud versions < 8.2, the cyclecloud_slurm.sh script is located in /opt/cycle/jetpack/system/bootstrap/slurm.
If you make changes that affect the VMs for nodes in an MPI partition (such as VM size, image, or cloud-init), and the nodes are running, you will get an error of This node does not match existing scaleset attribute when new nodes are started. For this reason, the apply_changes command makes sure the nodes are terminated, and fails with the following error message if not: The following nodes must be fully terminated before applying changes.
If you are making a change that does NOT affect the VM properties for MPI nodes, you do not need to terminate running nodes first. In this case, you can make the changes by using the following two commands:
/opt/cycle/slurm/cyclecloud_slurm.sh remove_nodes
/opt/cycle/slurm/cyclecloud_slurm.sh scale
Note
The apply_changes command only exists in CycleCloud 8.3+, so the only
way to make a change in earlier versions is with the above remove_nodes + scale commands.
Make sure that the remove_nodes command does not print a warning about nodes that need to be terminated.
Creating additional partitions
The default template that ships with Azure CycleCloud has two partitions (hpc and htc), and you can define custom nodearrays that map directly to Slurm partitions. For example, to create a GPU partition, add the following section to your cluster template:
[[nodearray gpu]]
MachineType = $GPUMachineType
ImageName = $GPUImageName
MaxCoreCount = $MaxGPUExecuteCoreCount
Interruptible = $GPUUseLowPrio
AdditionalClusterInitSpecs = $ExecuteClusterInitSpecs
[[[configuration]]]
slurm.autoscale = true
# Set to true if nodes are used for tightly-coupled multi-node jobs
slurm.hpc = false
[[[cluster-init cyclecloud/slurm:execute:2.0.1]]]
[[[network-interface eth0]]]
AssociatePublicIpAddress = $ExecuteNodesPublic
Memory settings
CycleCloud automatically sets the amount of available memory for Slurm to use for scheduling purposes. Because the amount of available memory can change slightly due to different Linux kernel options, and the OS and VM can use up a small amount of memory that would otherwise be available for jobs, CycleCloud automatically reduces the amount of memory in the Slurm configuration. By default, CycleCloud holds back 5% of the reported available memory in a VM, but this value can be overridden in the cluster template by setting slurm.dampen_memory to the percentage of memory to hold back. For example, to hold back 20% of a VM's memory:
slurm.dampen_memory=20
Disabling autoscale for specific nodes or partitions
While the built-in CycleCloud "KeepAlive" feature does not currently work for Slurm clusters, it is possible to disable autoscale for a running Slurm cluster by editing the slurm.conf file directly. You can exclude either individual nodes or entire partitions from being autoscaled.
Excluding a node
To exclude a node or multiple nodes from autoscale, add SuspendExcNodes=<listofnodes> to the Slurm configuration file. For example, to exclude nodes 1 and 2 from the hpc partition, add the following to /sched/slurm.conf:
SuspendExcNodes=hpc-pg0-[1-2]
Then restart the slurmctld service for the new configuration to take effect.
Excluding a partition
Excluding entire partitions from autoscale is similar to excluding nodes. To exclude the entire hpc partition, add the following to /sched/slurm.conf
SuspendExcParts=hpc
Then restart the slurmctld service.
Troubleshooting
UID conflicts for Slurm and Munge users
By default, this project uses a UID and GID of 11100 for the Slurm user and 11101 for the Munge user. If this causes a conflict with another user or group, these defaults may be overridden.
To override the UID and GID, click the edit button for both the scheduler node:


And the execute nodearray:
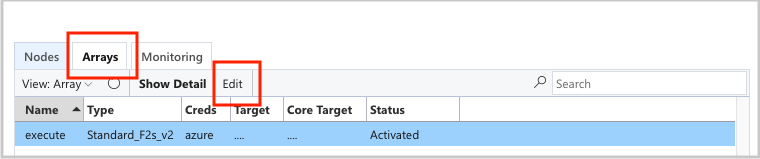
and add the following attributes to the Configuration section:
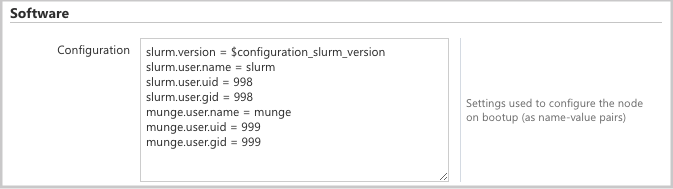
slurm.user.name = slurm
slurm.user.uid = 11100
slurm.user.gid = 11100
munge.user.name = munge
munge.user.uid = 11101
munge.user.gid = 11101
Autoscale
CycleCloud uses Slurm's Elastic Computing feature. To debug autoscale issues, there are a few logs on the scheduler node you can check. The first is making sure that the power save resume calls are being made by checking /var/log/slurmctld/slurmctld.log. You should see lines like:
[2019-12-09T21:19:03.400] power_save: pid 8629 waking nodes htc-1
The other log to check is /var/log/slurmctld/resume.log. If the resume step is failing, there will also be a /var/log/slurmctld/resume_fail.log. If there are messages about unknown or invalid node names, make sure you haven't added nodes to the cluster without following the steps in the "Making Cluster Changes" section above.
Slurm Configuration Reference
The following are the Slurm specific configuration options you can toggle to customize functionality:
| Slurm Specific Configuration Options | Description |
|---|---|
| slurm.version | Default: '18.08.7-1'. This is the Slurm version to install and run. This is currently the default and only option. In the future additional versions of the Slurm software may be supported. |
| slurm.autoscale | Default: 'false'. This is a per-nodearray setting that controls whether Slurm should automatically stop and start nodes in this nodearray. |
| slurm.hpc | Default: 'true'. This is a per-nodearray setting that controls whether nodes in the nodearray will be placed in the same placement group. Primarily used for nodearrays using VM families with InfiniBand. It only applies when slurm.autoscale is set to 'true'. |
| slurm.default_partition | Default: 'false'. This is a per-nodearray setting that controls whether the nodearray should be the default partition for jobs that don't request a partition explicitly. |
| slurm.dampen_memory | Default: '5'. The percentage of memory to hold back for OS/VM overhead. |
| slurm.suspend_timeout | Default: '600'. The amount of time (in seconds) between a suspend call and when that node can be used again. |
| slurm.resume_timeout | Default: '1800'. The amount of time (in seconds) to wait for a node to successfully boot. |
| slurm.install | Default: 'true'. Determines if Slurm is installed at node boot ('true'). If Slurm is installed in a custom image this should be set to 'false'. (proj version 2.5.0+) |
| slurm.use_pcpu | Default: 'true'. This is a per-nodearray setting to control scheduling with hyperthreaded vcpus. Set to 'false' to set CPUs=vcpus in cyclecloud.conf. |
| slurm.user.name | Default: 'slurm'. This is the username for the Slurm service to use. |
| slurm.user.uid | Default: '11100'. The User ID to use for the Slurm user. |
| slurm.user.gid | Default: '11100'. The Group ID to use for the Slurm user. |
| munge.user.name | Default: 'munge'. This is the username for the MUNGE authentication service to use. |
| munge.user.uid | Default: '11101'. The User ID to use for the MUNGE user. |
| munge.user.gid | Default: '11101'. The Group ID to use for the MUNGE user. |
CycleCloud supports a standard set of autostop attributes across schedulers:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| cyclecloud.cluster.autoscale.stop_enabled | Is autostop enabled on this node? [true/false] |
| cyclecloud.cluster.autoscale.idle_time_after_jobs | The amount of time (in seconds) for a node to sit idle after completing jobs before it is scaled down. |
| cyclecloud.cluster.autoscale.idle_time_before_jobs | The amount of time (in seconds) for a node to sit idle before completing jobs before it is scaled down. |