Configure Azure Private Link for Azure Cosmos DB analytical store
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
MongoDB
Gremlin
In this article, you will learn how to set up managed private endpoints for Azure Cosmos DB analytical store. If you are using the transactional store, see Private endpoints for the transactional store article. Using managed private endpoints, you can restrict network access of your Azure Cosmos DB analytical store, to a Managed Virtual Network associated with your Azure Synapse workspace. Managed private endpoints establish a private link to your analytical store.
Note
If you are using Private DNS Zones for Azure Cosmos DB and wish to create a Synapse managed private endpoint to the analytical store sub-resource, you must first create a DNS zone for the analytical store (privatelink.analytics.cosmos.azure.com) linked to your Azure Cosmos DB's virtual network.
Enable a private endpoint for the analytical store
Set up Azure Synapse Analytics workspace with a managed virtual network and data-exfiltration
Create a workspace in Azure Synapse Analytics with data-exfiltration enabled. With data-exfiltration protection, you can ensure that malicious users cannot copy or transfer data from your Azure resources to locations outside your organization’s scope.
The following access restrictions are applicable when data-exfiltration protection is turned on for an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace:
If you are using Azure Spark for Azure Synapse Analytics, access is only allowed to the approved managed private endpoints for Azure Cosmos DB analytical store.
If you are using Synapse serverless SQL pools, you can query any Azure Cosmos DB account using Azure Synapse Link. However, write requests that create external tables as select (CETAS) are only allowed to the approved manage private endpoints in the workspace virtual network.
Note
You cannot change managed virtual network and data-exfiltration configuration after the workspace is created.
Add a managed private endpoint for Azure Cosmos DB analytical store
Note
To perform some of the steps below, you will need to temporarily change the Azure Cosmos DB account networking configuration. Go to the Networking tab in the portal, and click on the Accept connections from within public Azure datacenters and Add Azure Portal Middleware IPs options. After the configuration of your private endpoint, you can revert this action and disable the access.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
From the Azure portal, navigate to your Synapse Analytics workspace and open the Overview pane.
Launch Synapse Studio by navigating to Getting Started pane and select Open under Open Synapse Studio.
In the Synapse Studio, open the Manage tab.
Navigate to Managed private endpoints and select New
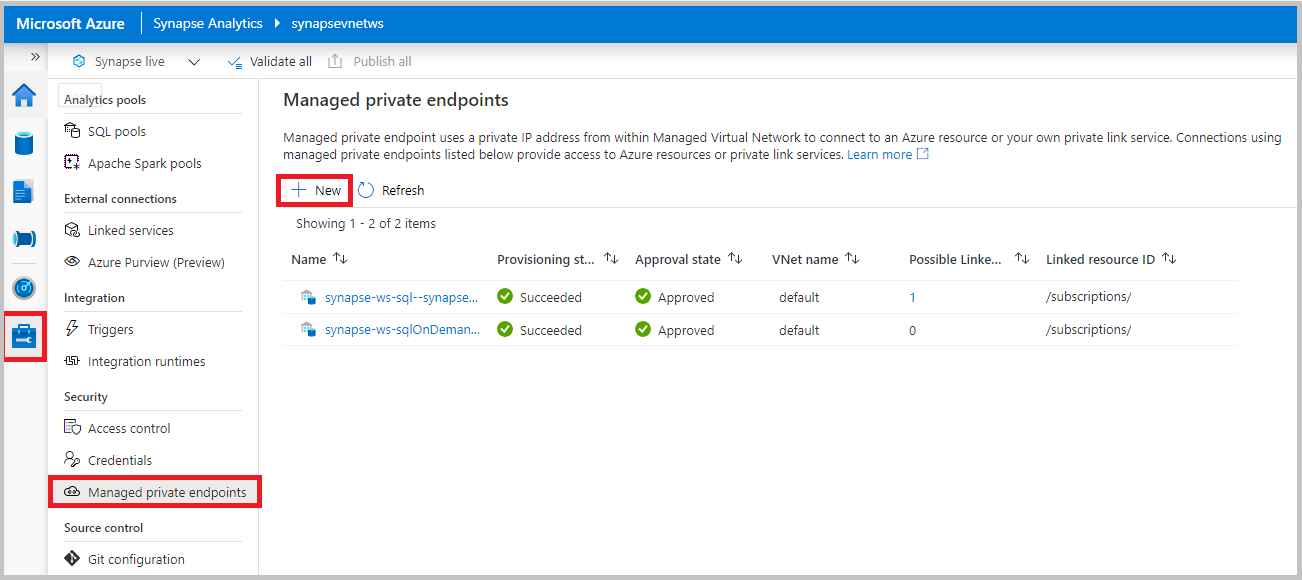
Select Azure Cosmos DB (API for NoSQL) account type > Continue.
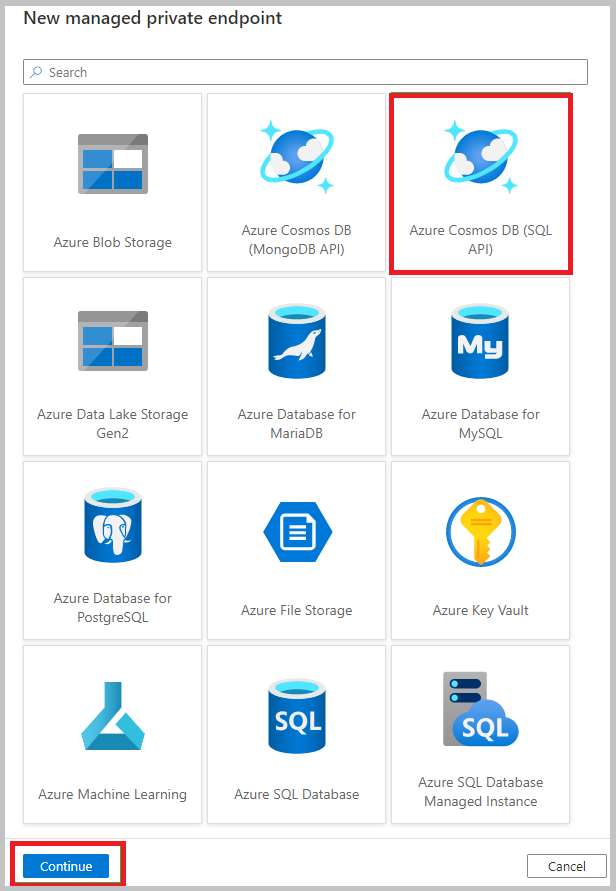
Fill out the New managed private endpoint form with the following details:
- Name - Name for your managed private endpoint. This name cannot be updated after it's created.
- Description - Provide a friendly description to identify your private endpoint.
- Azure subscription - Select an Azure Cosmos DB account from the list of available accounts in your Azure subscriptions.
- Azure Cosmos DB account name - Select an existing Azure Cosmos DB account of type SQL or MongoDB.
- Target sub-resource - Select one of the following options: Analytical: If you want to add the private endpoint for Azure Cosmos DB analytical store. NoSQL (or MongoDB): If you want to add OLTP or transactional account endpoint.
Note
You can add both transactional store and analytical store private endpoints to the same Azure Cosmos DB account in an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace. If you only want to run analytical queries, you may only want to map the analytical private endpoint.
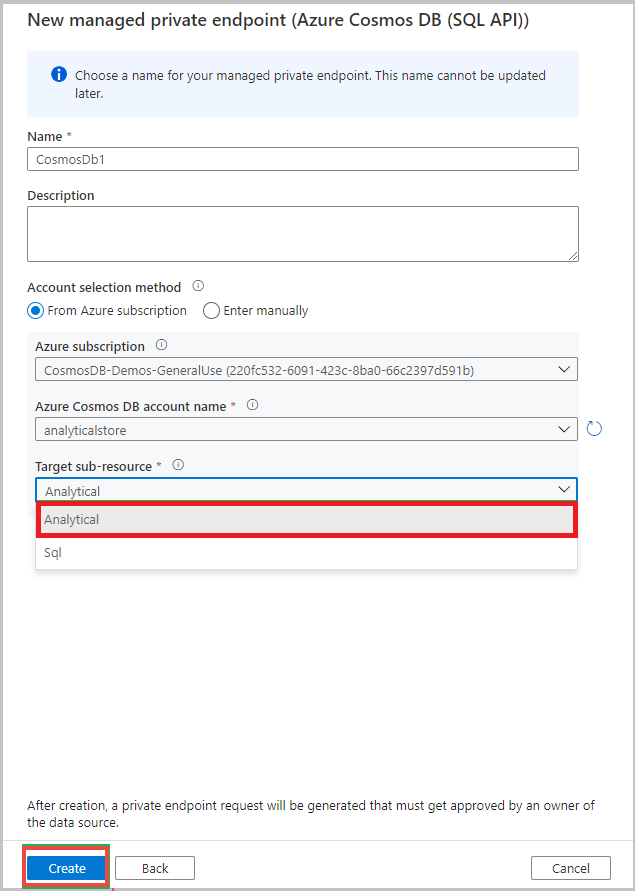
After creating, go to the private endpoint name and select Manage approvals in Azure portal.
Navigate to your Azure Cosmos DB account, select the private endpoint, and select Approve.
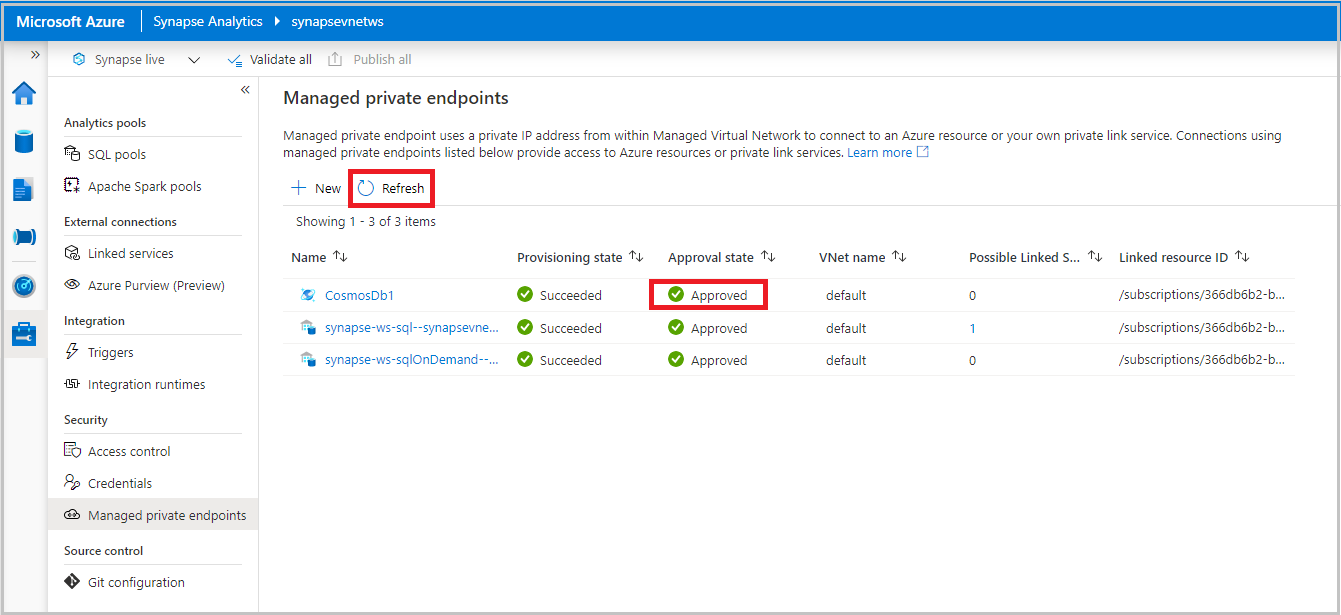
Navigate back to Synapse Analytics workspace and click Refresh on the Managed private endpoints pane. Verify that private endpoint is in Approved state.
Use Apache Spark for Azure Synapse Analytics
If you created an Azure Synapse workspace with data-exfiltration protection turned on, the outbound access from Synapse Spark to Azure Cosmos DB accounts will be blocked, by default. Also, if the Azure Cosmos DB already has an existing private endpoint, Synapse Spark will be blocked from accessing it.
To allow access to Azure Cosmos DB data:
If you are using Azure Synapse Link to query Azure Cosmos DB data, add a managed analytical private endpoint for the Azure Cosmos DB account.
If you are using batch writes/reads and/or streaming writes/reads to transactional store, add a managed SQL or MongoDB private endpoint for the Azure Cosmos DB account. In addition, you should also set connectionMode to Gateway as shown in the following code snippet:
# Write a Spark DataFrame into an Azure Cosmos DB container # To select a preferred lis of regions in a multi-region account, add .option("spark.cosmos.preferredRegions", "<Region1>, <Region2>") YOURDATAFRAME.write\ .format("cosmos.oltp")\ .option("spark.synapse.linkedService", "<your-Cosmos-DB-linked-service-name>")\ .option("spark.cosmos.container","<your-Cosmos-DB-container-name>")\ .option("spark.cosmos.write.upsertEnabled", "true")\ .option("spark.cosmos.connection.mode", "Gateway")\ .mode('append')\ .save()
Using Synapse serverless SQL pools
Synapse serverless SQL pools use multitenant capabilities that are not deployed into managed virtual network. If the Azure Cosmos DB account has an existing private endpoint, Synapse serverless SQL pool will be blocked from accessing the account, due to network isolation checks on the Azure Cosmos DB account.
To configure network isolation for this account from a Synapse workspace:
Allow the Synapse workspace to access the Azure Cosmos DB account by specifying
NetworkAclBypassResourceIdsetting on the account.Using PowerShell
Update-AzCosmosDBAccount -Name MyCosmosDBDatabaseAccount -ResourceGroupName MyResourceGroup -NetworkAclBypass AzureServices -NetworkAclBypassResourceId "/subscriptions/subId/resourceGroups/rgName/providers/Microsoft.Synapse/workspaces/wsName"Using Azure CLI
az cosmosdb update --name MyCosmosDBDatabaseAccount --resource-group MyResourceGroup --network-acl-bypass AzureServices --network-acl-bypass-resource-ids "/subscriptions/subId/resourceGroups/rgName/providers/Microsoft.Synapse/workspaces/wsName"Note
Azure Cosmos DB account and Azure Synapse Analytics workspace should be under same Microsoft Entra tenant.
You can now access the account from serverless SQL pools, using T-SQL queries over Azure Synapse Link. However, to ensure network isolation for the data in analytical store, you must add an analytical managed private endpoint for this account. Otherwise, the data in the analytical store will not be blocked from public access.
Important
If you are using Azure Synapse Link and need network isolation for your data in analytical store, you must map the Azure Cosmos DB account into Synapse workspace using Analytical managed private endpoint.
Next steps
- Get started with querying analytical store with Azure Synapse Spark 3
- Get started with querying analytical store with Azure Synapse Spark 2
- Get started with querying analytical store with Azure Synapse serverless SQL pools