Improve performance by compressing files in Azure CDN
Important
Azure CDN Standard from Microsoft (classic) will be retired on September 30, 2027. To avoid any service disruption, it's important that you migrate your Azure CDN Standard from Microsoft (classic) profiles to Azure Front Door Standard or Premium tier by September 30, 2027. For more information, see Azure CDN Standard from Microsoft (classic) retirement.
Azure CDN from Edgio was retired on January 15, 2025. For more information, see Azure CDN from Edgio retirement FAQ.
File compression is a simple and effective method to improve file transfer speed and increase page-load performance by reducing a file's size before it's sent from the server. File compression can reduce bandwidth costs and provide a more responsive experience for your users.
There are two ways to enable file compression:
- Enable compression on your origin server. In this case, Azure CDN passes along the compressed files and delivers them to clients that request them.
- Enable compression directly on the CDN POP servers (compression on the fly). In this case, the CDN compresses the files and serves them to the end users, even if they don't get compressed by the origin server.
Important
Azure Content Delivery Network configuration changes can take up to 10 minutes to propagate through the network:
If you're setting up compression for the first time for your CDN endpoint, consider waiting 1-2 hours before you troubleshoot to ensure the compression settings have propagated to the POPs.
Enabling compression
The standard and premium CDN tiers provide the same compression functionality, but the user interface differs. For more information about the differences between standard and premium CDN tiers, see Azure CDN Overview.
From the CDN profile page, select the CDN endpoint you want to manage.
The CDN endpoint page opens.
Select Compression.
The compression page opens.
Select On to turn on compression.
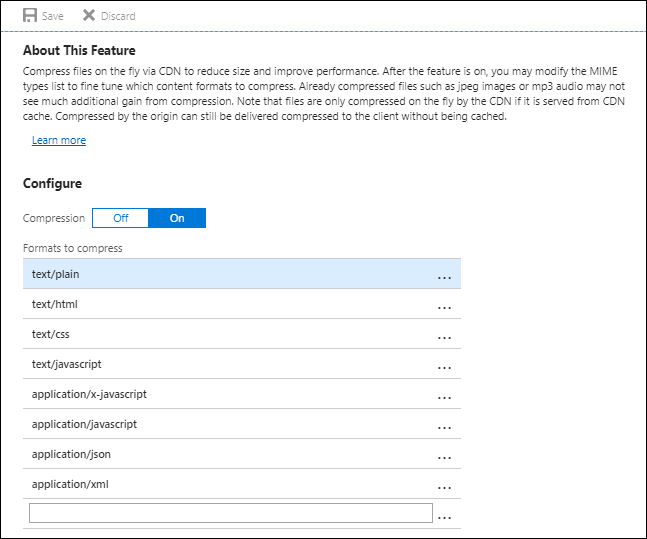
Use the default MIME types, or modify the list by adding or removing MIME types.
Tip
Although it is possible, it is not recommended to apply compression to compressed formats. For example, ZIP, MP3, MP4, or JPG.
After making your changes, select Save.
Compression rules
Only files that meet the following criteria are eligible for compression:
- Be of a MIME type that has been configured for compression
- Have only "identity" Content-Encoding headers in the origin response
- Be larger than 1 KB
- Be smaller than 8 MB
Only the following compression encodings are supported:
- gzip (GNU zip)
- brotli
If the request supports more than one compression type, brotli compression takes precedence.
When a request for an asset specifies gzip compression and the request results in a cache miss, Azure CDN performs gzip compression of the asset directly on the POP server. Afterward, the compressed file is served from the cache.
If the origin uses Chunked Transfer Encoding (CTE) to send data to the CDN POP, then compression isn't supported.
Compression behavior tables
The following tables describe Azure CDN compression behavior for every scenario:
Compression is disabled or file is ineligible for compression
| Client-requested format (via Accept-Encoding header) | Cached-file format | The CDN response to the client | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressed | Compressed | Compressed | |
| Compressed | Uncompressed | Uncompressed | |
| Compressed | Not cached | Compressed or Uncompressed | The origin response determines whether CDN performs a compression. |
| Uncompressed | Compressed | Uncompressed | |
| Uncompressed | Uncompressed | Uncompressed | |
| Uncompressed | Not cached | Uncompressed |
Compression is enabled and file is eligible for compression
| Client-requested format (via Accept-Encoding header) | Cached-file format | CDN response to the client | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressed | Compressed | Compressed | CDN transcodes between supported formats. Azure CDN from Microsoft doesn't support transcoding between formats and instead fetches data from origin, compresses, and caches separately for the format. |
| Compressed | Uncompressed | Compressed | CDN performs a compression. |
| Compressed | Not cached | Compressed | CDN performs a compression if the origin returns an uncompressed file. Files with the Cache-Control: no-cache header are never compressed. |
| Uncompressed | Compressed | Uncompressed | CDN performs a decompression. Azure CDN from Microsoft doesn't support decompression and instead fetches data from origin and caches separately for uncompressed clients. |
| Uncompressed | Uncompressed | Uncompressed | |
| Uncompressed | Not cached | Uncompressed |
Media Services CDN Compression
For endpoints enabled for Media Services CDN streaming, compression is enabled by default for the following MIME types:
- application/vnd.ms-sstr+XML
- application/dash+XML
- application/vnd.Apple.mpegurl
- application/f4m+XML