Add natural language understanding to your bot
APPLIES TO: SDK v4
Note
Language Understanding (LUIS) will be retired on 1 October 2025. Beginning 1 April 2023, you won't be able to create new LUIS resources. A newer version of language understanding is now available as part of Azure AI Language.
Conversational language understanding (CLU), a feature of Azure AI Language, is the updated version of LUIS. For more information about language understanding support in the Bot Framework SDK, see Natural language understanding.
The ability to understand what your user means conversationally and contextually can be a difficult task, but can provide your bot a more natural conversation feel. Language Understanding (LUIS) is a cloud-based API service that enables you to do just that so that your bot can recognize the intent of user messages, allow for more natural language from your user, and better direct the conversation flow.
This topic walks you through adding LUIS to a flight booking application to recognize different intents and entities contained within user input.
Note
The Bot Framework JavaScript, C#, and Python SDKs will continue to be supported, however, the Java SDK is being retired with final long-term support ending in November 2023.
Existing bots built with the Java SDK will continue to function.
For new bot building, consider using Microsoft Copilot Studio and read about choosing the right copilot solution.
For more information, see The future of bot building.
Prerequisites
- A LUIS account.
- A copy of the Core Bot sample in C#, JavaScript, Java, or Python.
- Knowledge of bot basics and natural language processing.
About this sample
This core bot sample shows an example of an airport flight booking application. It uses a LUIS service to recognize the user input and return the top recognized LUIS intent.
The language model contains three intents: Book Flight, Cancel, and None. LUIS will use these intents to understand what the user meant when they send a message to the bot. The language model also defines entities that LUIS can extract from the user's input, such as the origin or destination airport.
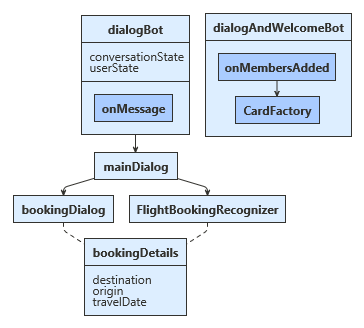
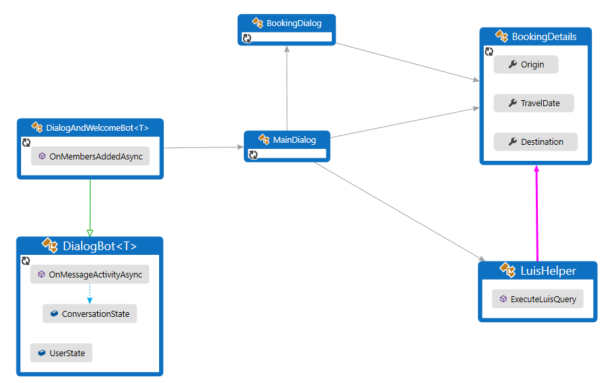
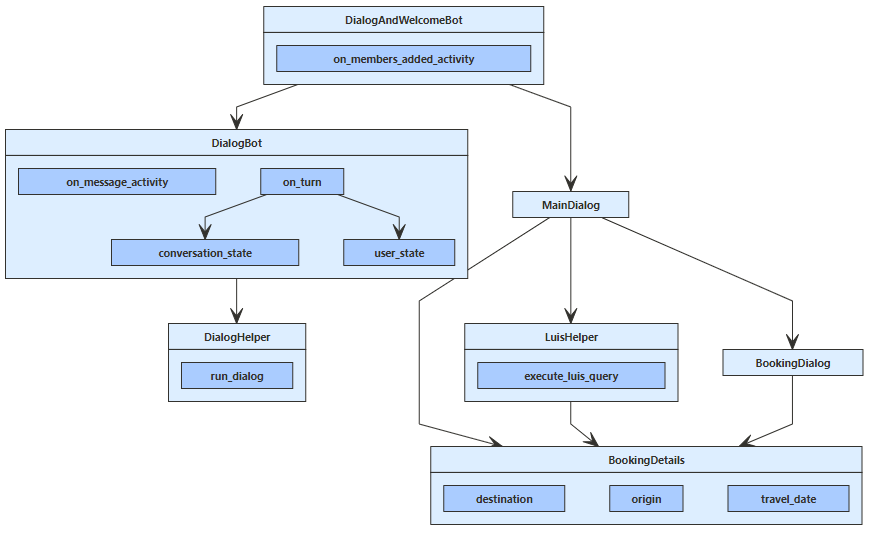
After each processing of user input, DialogBot saves the current state of both UserState and ConversationState. Once all the required information has been gathered, the coding sample creates a demo flight booking reservation. In this article, we'll be covering the LUIS aspects of this sample. However, the general flow of the sample is:
OnMembersAddedAsyncis called when a new user is connected and displays a welcome card.OnMessageActivityAsyncis called for each user input received.
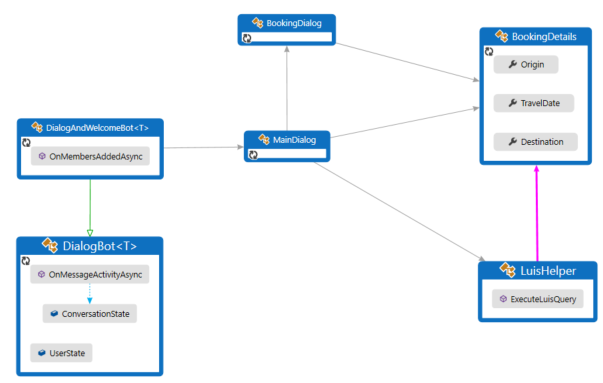
The OnMessageActivityAsync module runs the appropriate dialog through the Run dialog extension method. Then the main dialog calls the LUIS helper to find the top scoring user intent. If the top intent for the user input returns "BookFlight", the helper fills out information from the user that LUIS returned. After that, the main dialog starts the BookingDialog, which acquires additional information as needed from the user such as:
Originthe originating cityTravelDatethe date to book the flightDestinationthe destination city
This article covers how to add LUIS to a bot. For information about using dialogs or state, see how to gather user input using a dialog prompt or save user and conversation data, respectively.
Create a LUIS app in the LUIS portal
- Sign in to the LUIS portal and if needed create an account and authoring resource.
- On the Conversation apps page in LUIS, select Import, then Import as JSON.
- In the Import new app dialog:
- Choose the FlightBooking.json file in the CognitiveModels folder of the sample.
- Enter
FlightBookingas the optional name of the app, and select Done.
- The site may display How to create an effective LUIS app and Upgrade your composite entities dialogs. You can dismiss these dialogs and continue.
- Train your app, then publish your app to the production environment. For more information, see the LUIS documentation on how to train and publish an app.
Why use entities
LUIS entities enable your bot to understand events beyond standard intents. This enables you to gather from users additional information, so your bot can ask questions and respond more intelligently. Along with definitions for the three LUIS intents 'Book Flight', 'Cancel', and 'None', the FlightBooking.json file also contains a set of entities such as 'From.Airport' and 'To.Airport'. These entities allow LUIS to detect and return additional information contained within the user's original input when they request a new travel booking.
Obtain values to connect to your LUIS app
Once your LUIS app is published, you can access it from your bot. You'll need to record several values to access your LUIS app from within your bot. You can retrieve that information using the LUIS portal.
Retrieve application information from the LUIS.ai portal
The settings file (appsettings.json, .env or config.py) acts as the place to bring all service references together in one place. The information you retrieve will be added to this file in the next section.
Select your published LUIS app from luis.ai.
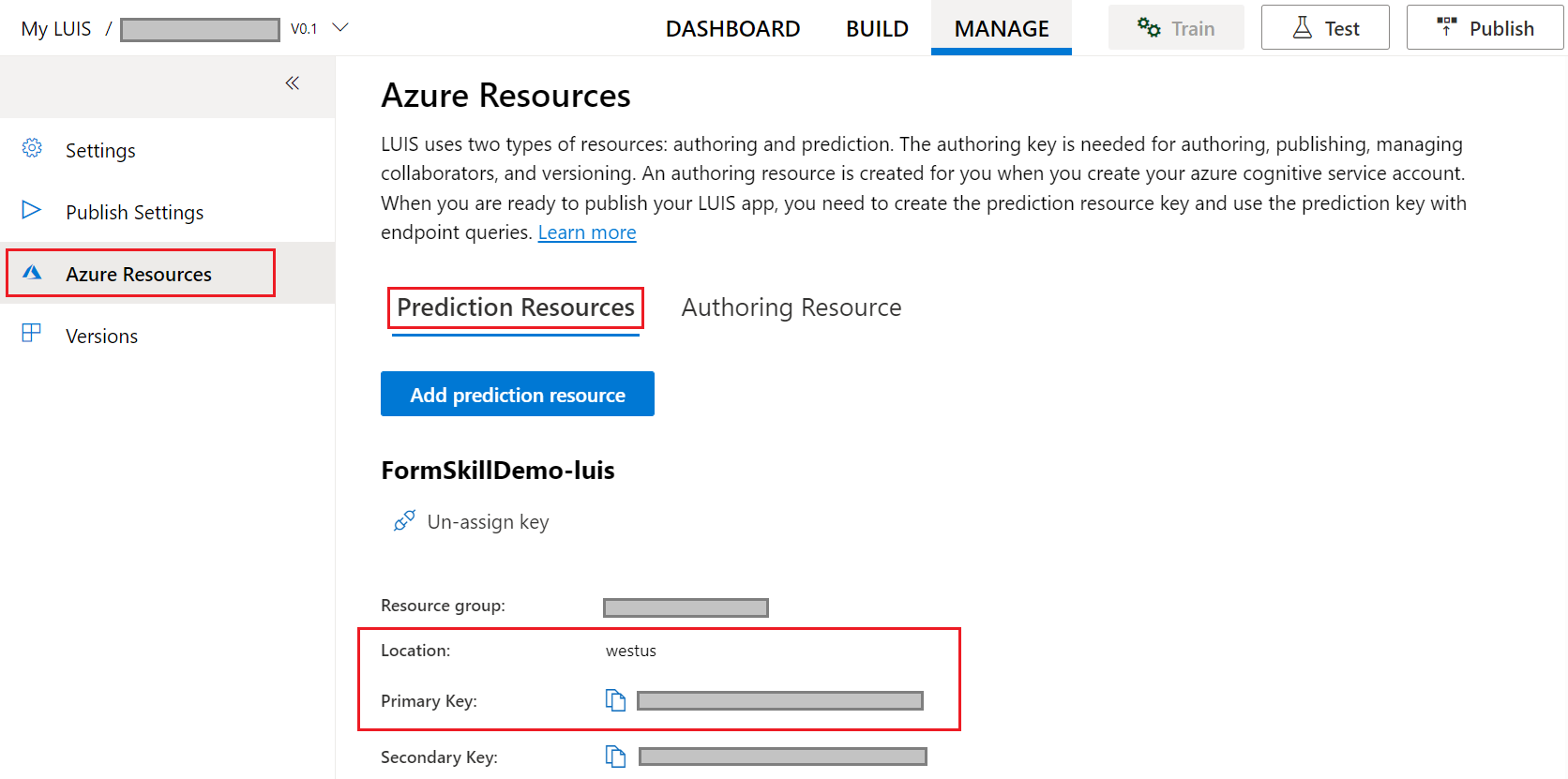
With your published LUIS app open, select the MANAGE tab.
Select the Settings tab on the left side and record the value shown for Application ID as <YOUR_APP_ID>.
Select Azure Resources, then Prediction Resource. Record the value shown for Location as <YOUR_REGION> and Primary Key as <YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY>.
Alternatively, you can use the region and primary key for your authoring resource.
Update the settings file
Add the information required to access your LUIS app including application ID, authoring key, and region into the appsettings.json file. In the previous step, you retrieved these values from your published LUIS app. The API host name should be in the format <your region>.api.cognitive.microsoft.com.
appsetting.json
Warning
It looks like the sample you are looking for has moved! Rest assured we are working on resolving this.
Configure your bot to use your LUIS app
Be sure that the Microsoft.Bot.Builder.AI.Luis NuGet package is installed for your project.
To connect to the LUIS service, the bot pulls the information you added to the appsetting.json file. The FlightBookingRecognizer class contains code with your settings from the appsetting.json file and queries the LUIS service by calling RecognizeAsync method.
FlightBookingRecognizer.cs
Warning
It looks like the sample you are looking for has moved! Rest assured we are working on resolving this.
The FlightBookingEx.cs contains the logic to extract From, To and TravelDate; it extends the partial class FlightBooking.cs used to store LUIS results when calling FlightBookingRecognizer.RecognizeAsync<FlightBooking> from the MainDialog.cs.
CognitiveModels\FlightBookingEx.cs
Warning
It looks like the sample you are looking for has moved! Rest assured we are working on resolving this.
LUIS is now configured and connected for your bot.
Test the bot
Download and install the latest Bot Framework Emulator
Run the sample locally on your machine. If you need instructions, refer to the
READMEfile for the C# Sample, JS Sample or Python Sample.In the Emulator, type a message such as "travel to paris" or "going from paris to berlin". Use any utterance found in the file FlightBooking.json for training the intent "Book flight".
If the top intent returned from LUIS resolves to "Book flight", your bot will ask more questions until it has enough information stored to create a travel booking. At that point it will return this booking information back to your user.
At this point, the code bot logic will reset and you can continue to create more bookings.
Additional information
For more about LUIS, see the LUIS documentation:
- What is Language Understanding (LUIS)?
- Create a new LUIS app in the LUIS portal
- Design with intent and entity models
- Migrate to V3 Authoring APIS
- Migrate to V3 Prediction APIs
Tip
Different parts of the SDK define separate entity classes or elements. For message entities, see Entities and activity types.