Manage and monitor backed-up SAP ASE databases (preview)
This article describes how to manage the SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE) (Sybase) databases that are running on an Azure virtual machine (VM) by using the Azure Backup service.
Azure Backup allows you to monitor jobs and alerts, trigger an on-demand backup, edit policies, stop and resume database protection, and unregister a VM from backups.
If the backup isn't configured for your SAP ASE databases, see Back up SAP ASE databases on Azure VMs. To learn more about the supported configurations and scenarios, see Support matrix for backup of SAP ASE databases on Azure VMs.
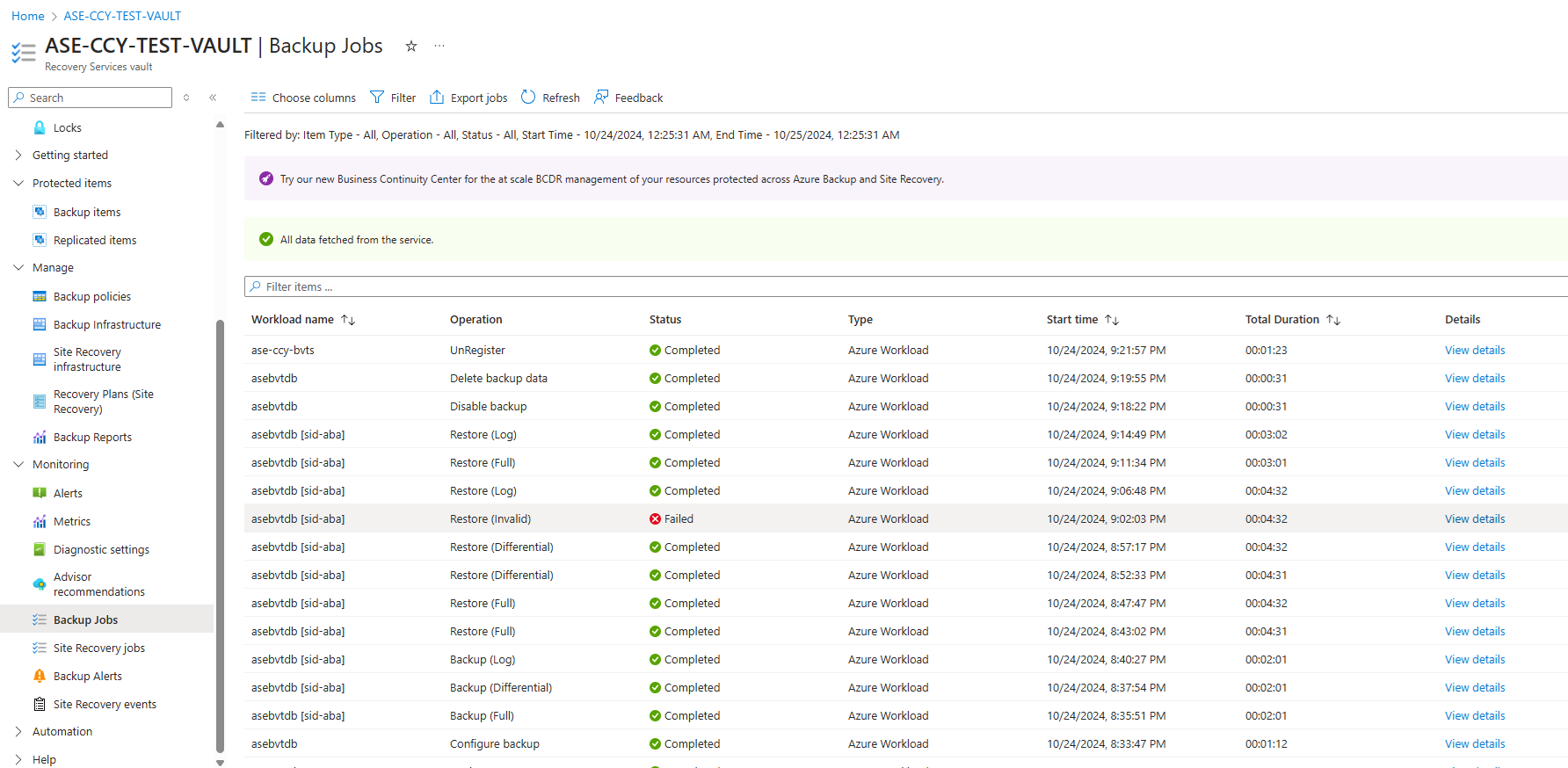
Monitor backup jobs
Azure Backup shows all manually triggered jobs in the Backup jobs section of Recovery Services Vault.
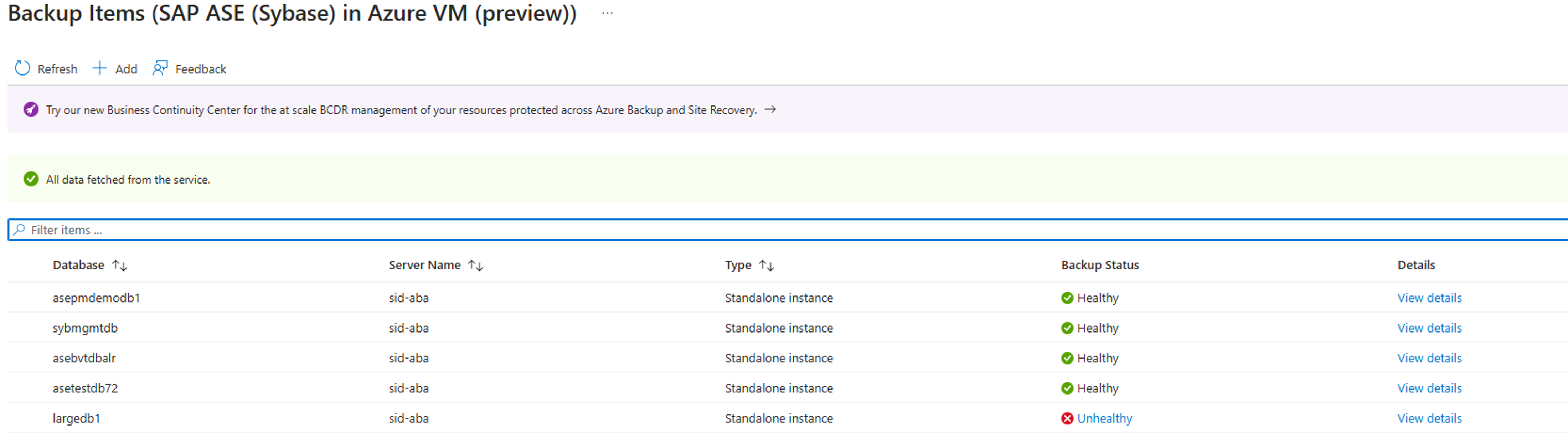
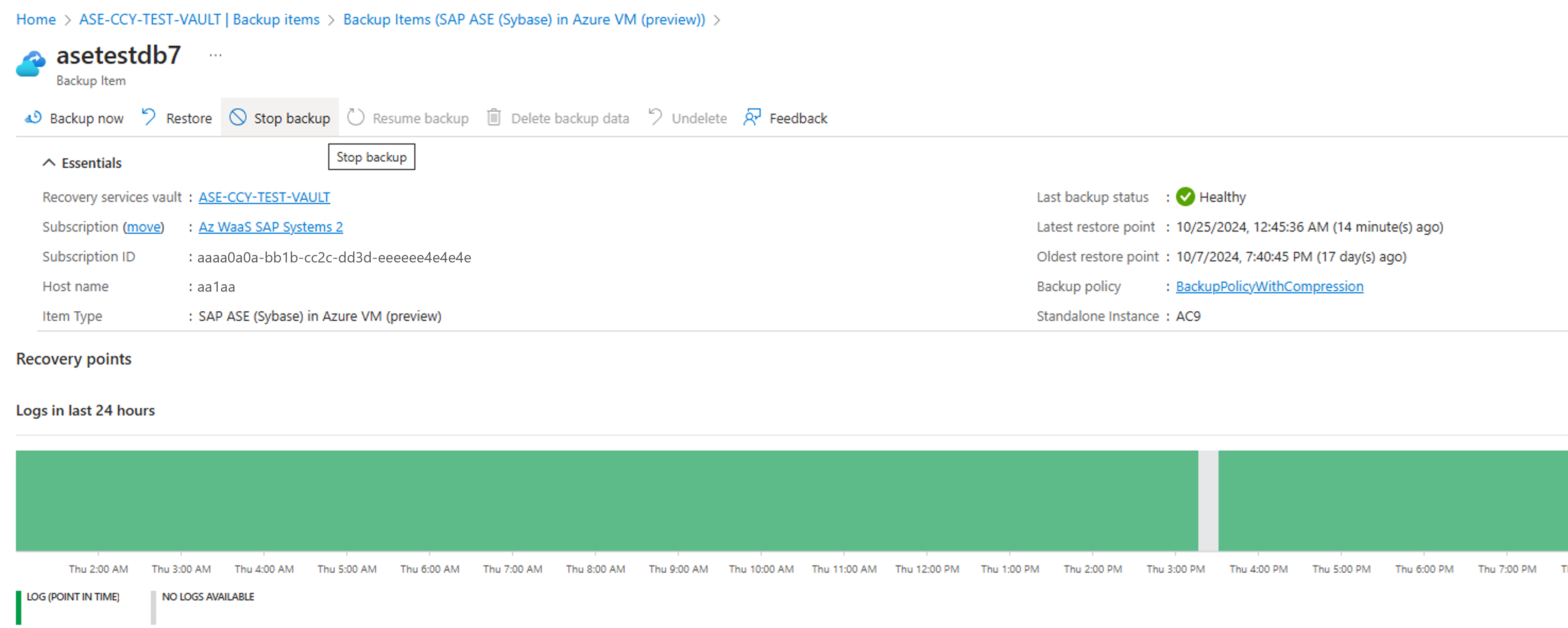
Review backup status
Azure Backup periodically synchronizes the datasource between the extension installed on the VM and Azure Backup service, and shows the backup status in the Azure portal. The following table lists the (four) backup status for a datasource:
| Backup state | Description |
|---|---|
| Healthy | The last backup is successful. |
| Unhealthy | The last backup is failed. |
| NotReachable | Currently, there's no synchronization occurring between the extension on the VM and the Azure Backup service. |
| IRPending | The first backup on the datasource isn't occurred yet. |
Generally, synchronization occurs every hour. However, at the extension level, Azure Backup polls every 5 minutes to check for any changes in the status of the latest backup compared to the previous one. For example, if the previous backup is successful but the latest backup is failed, Azure Backup syncs the backup status in the Azure portal accordingly to Healthy or Unhealthy.
If no data sync occurs to the Azure Backup service for more than 2 hours, Azure Backup shows the backup status as NotReachable. This scenario might occur if the VM is shut down for an extended period or there's a network connectivity issue on the VM, causing the synchronization to cease. Once the VM is operational again and the extension services restart, the data sync operation to the service resumes, and the backup status changes to Healthy or Unhealthy based on the status of the last backup.
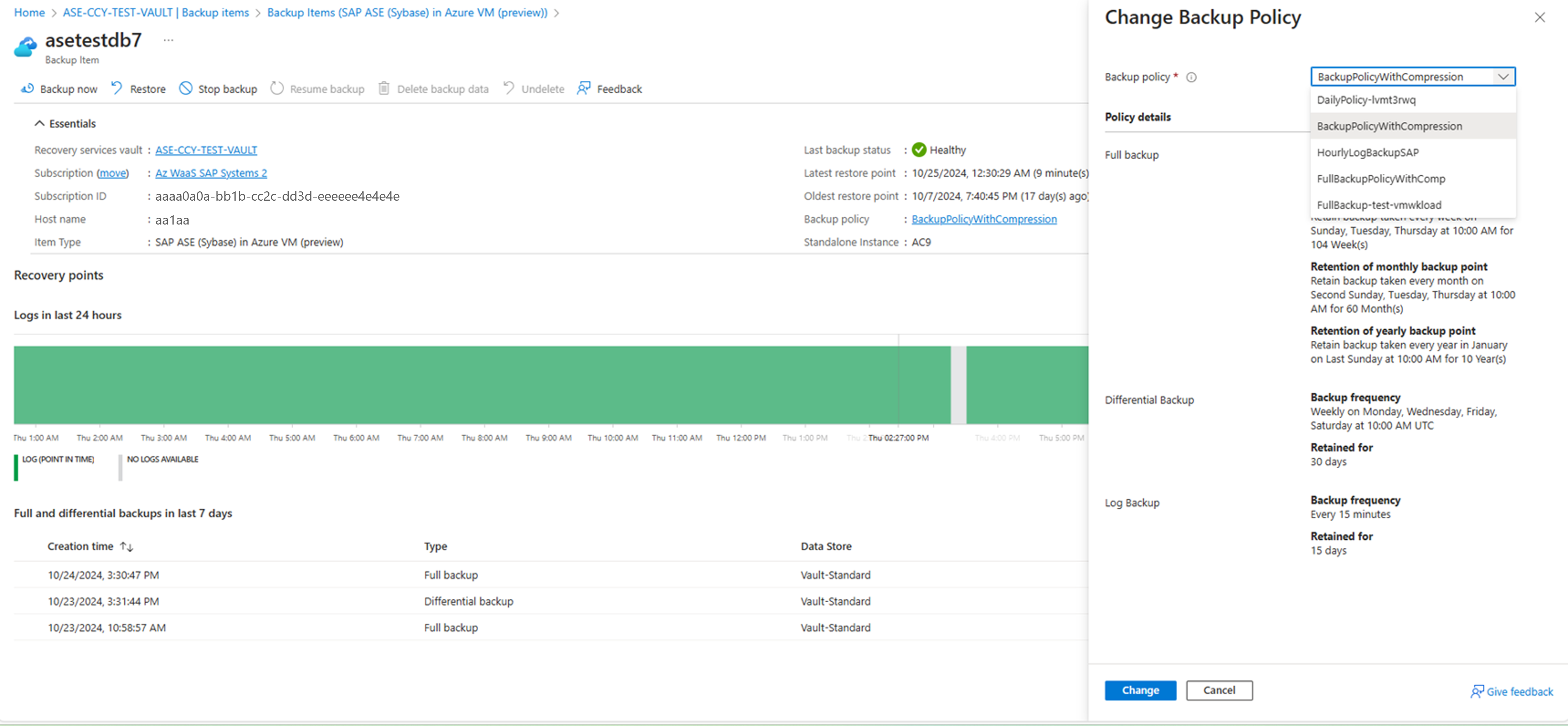
Change Backup policy
You can change the underlying policy for an SAP ASE backup items > View details > Backup policy > Change Backup Policy.
Making policy modifications affects all the associated backup items and triggers corresponding configure protection jobs.
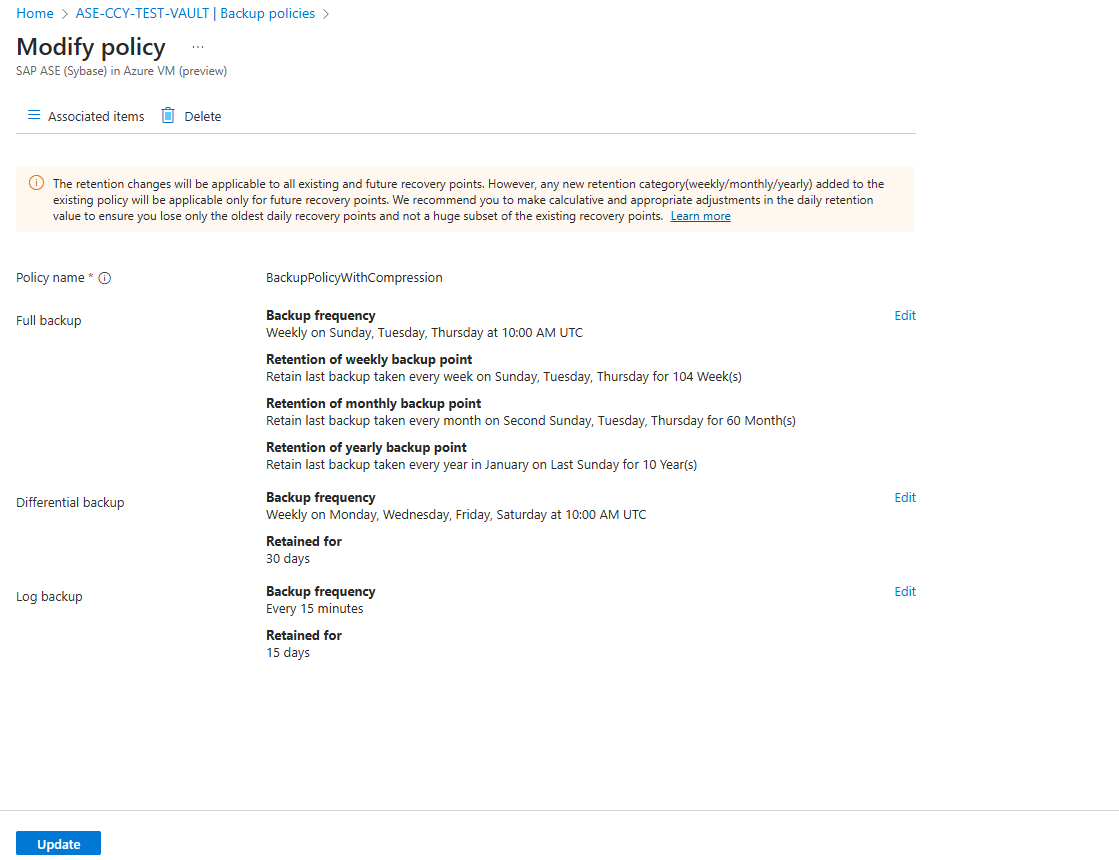
Edit a Policy
To modify the policy to change backup types, frequencies, and retention range, follow these steps:
Note
Any change in the retention period will be applied to both the new recovery points and, retroactively, to all the older recovery points.
Modifying the backup policy affects all the associated backup items and triggers the corresponding configure protection jobs.
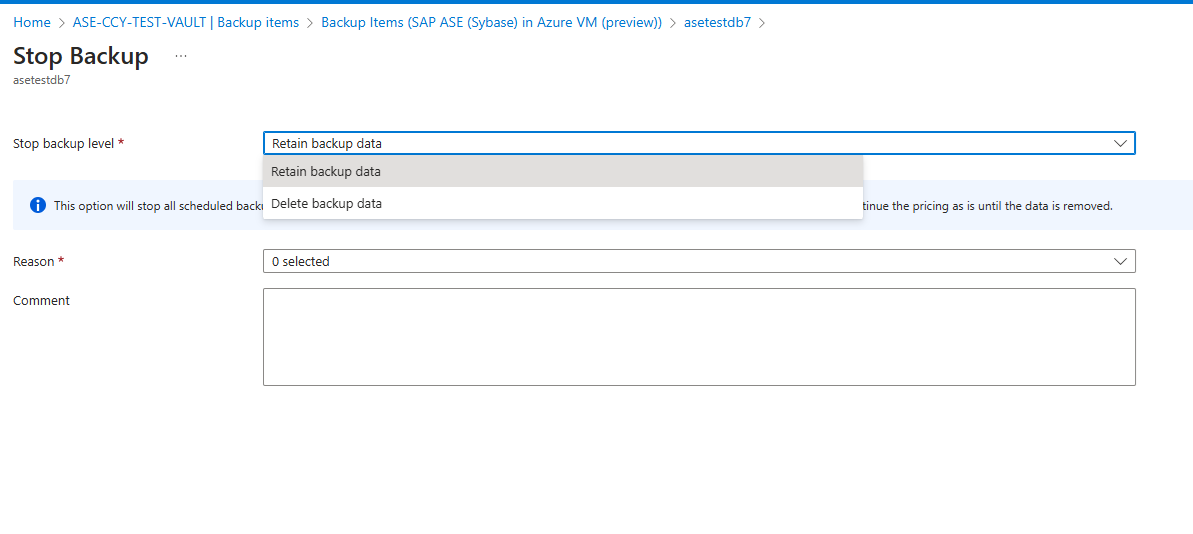
Stop protection for an SAP ASE database or ASE instance
There are two ways to stop protection of an SAP ASE database:
Delete backup data -Stop all future backup jobs and delete all recovery points.
Retain backup data -Stop all future backup jobs and leave the recovery points intact.
Note
If you choose to leave recovery points:
- All recovery points remain intact forever, and all pruning jobs stop at stop protection with retain data.
- You incur charges for the protected instance and the consumed storage.
- If you delete a data source without stopping backups, new backups fail.
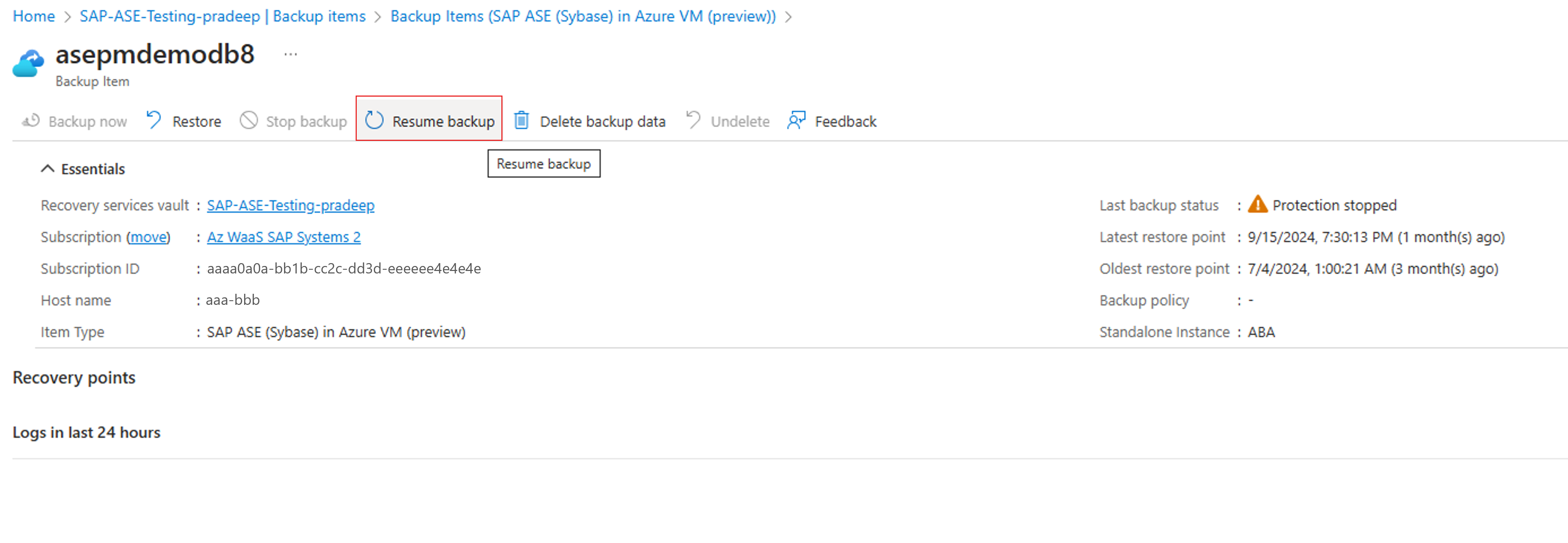
Resume protection for an SAP ASE database
When you stop protection for an SAP ASE database, if you select the Retain Backup Data option, you can later resume protection. If you don't retain the backed-up data, you can't resume protection.
To resume protection for an SAP ASE database, follow these steps:
Open the backup item, and then select Resume backup.
On the Backup policy menu, select a policy, and then select Save.
Unregister an SAP ASE instance
Unregister an SAP ASE instance after you disable protection but before you delete the vault.
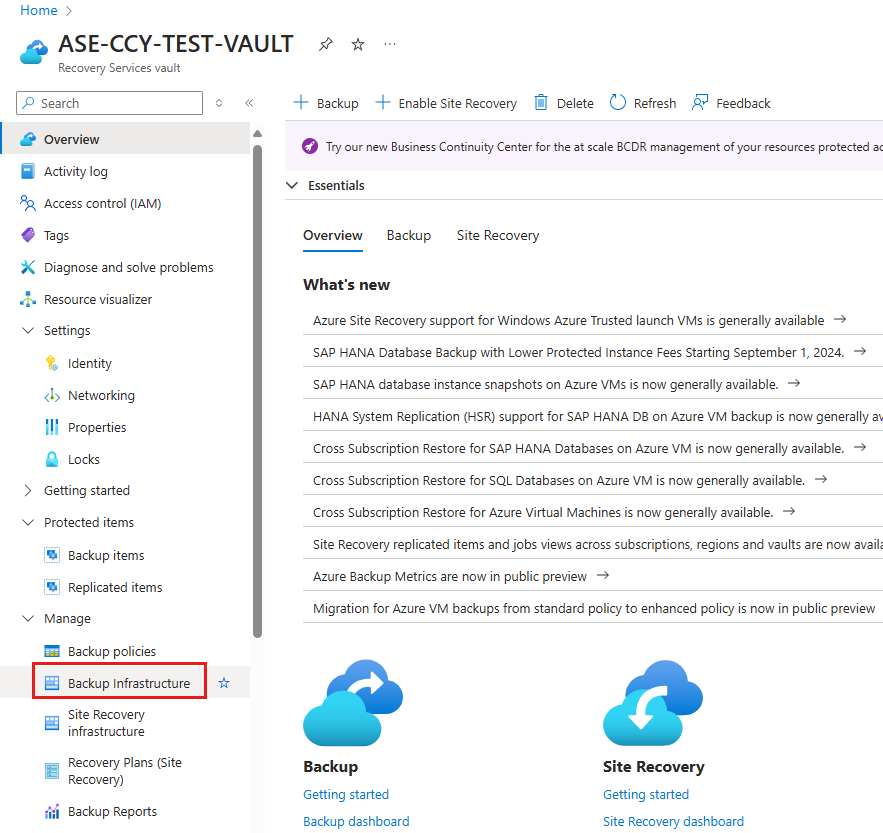
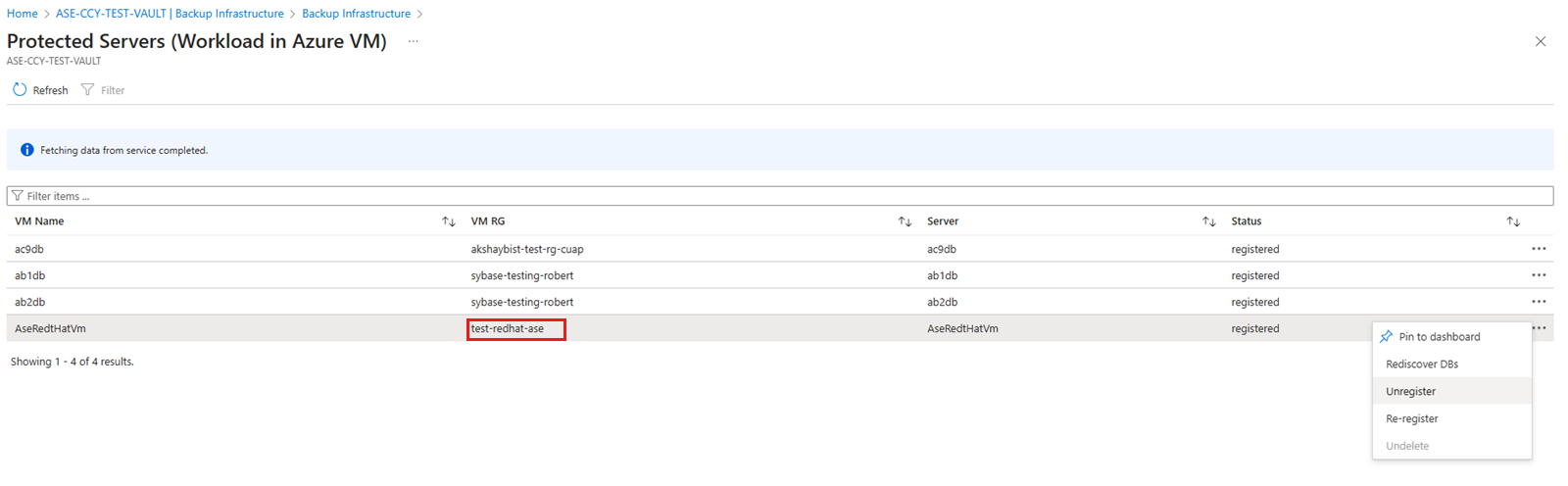
To unregister an SAP ASE instance, follow these steps:
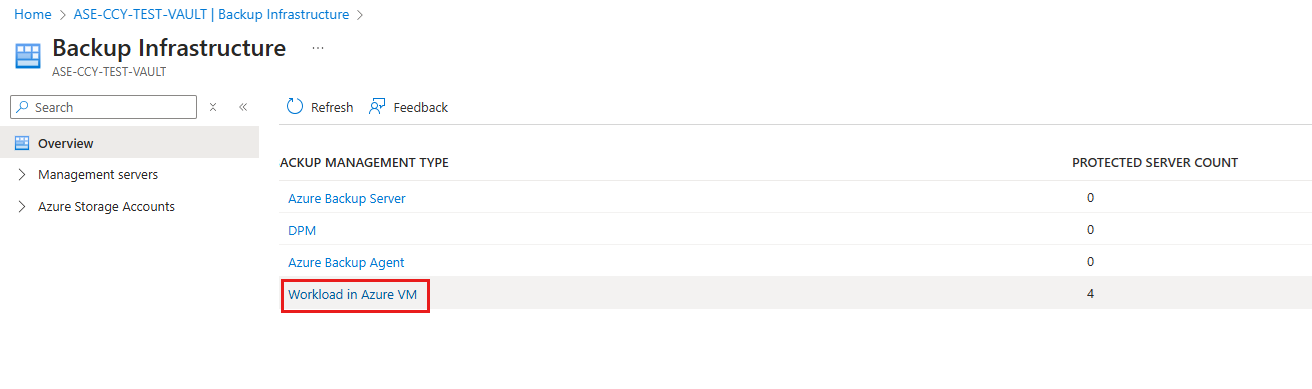
In the Recovery Services vault, under Manage, select Backup Infrastructure.
On the Backup Infrastructure blade, for BACKUP MANAGEMENT TYPE, select Workload in Azure VM.
On the Protected Servers blade, select the instance to unregister. To delete the vault, you must unregister all servers and instances.
Configure striping for higher backup throughput for SAP ASE databases
Striping is designed to enhance backup efficiency further by allowing data to be streamed through multiple backup channels simultaneously. This operation is beneficial for large databases, where the time required to complete a backup can be significant. If you distribute the data across multiple stripes, striping significantly reduces backup time, allowing for more efficient use of both storage and network resources. The striping process provides 30-40% increase in throughput performance and we recommend you testing the striping configuration before making changes on production.
Enable striping for SAP ASE databases
During the execution of the preregistration script, you can control the enable-striping parameter by setting it to true or false depending on your need. Additionally, a new configuration parameter, stripesCount, is introduced, which defaults to 4 but can be modified to suit your requirements.
Recommended configuration
For databases smaller than 4 TB, we suggest using a stripe count of 4. This configuration provides an optimal balance between performance and resource utilization, ensuring a smooth and efficient backup process.
Change the database stripe count
There're two ways to modify the stripe count:
Pre-registration script: Run the preregistration script and specify your preferred value using the stripes-count parameter.
Note
This parameter is optional.
Configuration file: Manually update the stripesCount value in the configuration file at the following path: /opt/msawb/etc/config/SAPAse/config.json
Learn more about the SAP database deployment.
Note
Setting the above ASE parameters will lead to increased memory and CPU utilization. We recommend that you monitor the memory consumption and CPU utilization, as overutilization can impact the backup and other ASE operations negatively.
Enable SAP ASE native compression from Azure Backup
Data compression in SAP ASE reduces storage consumption, accelerates backup and restore times, and enhances overall performance. It is supported for full, differential, and log backups, offering multiple compression levels to balance between performance and storage savings based on your priorities.
Manage database compression
You can enable or disable compression in the following scenarios:
Backup Policy Creation: Configure compression while setting up a backup policy for the database.
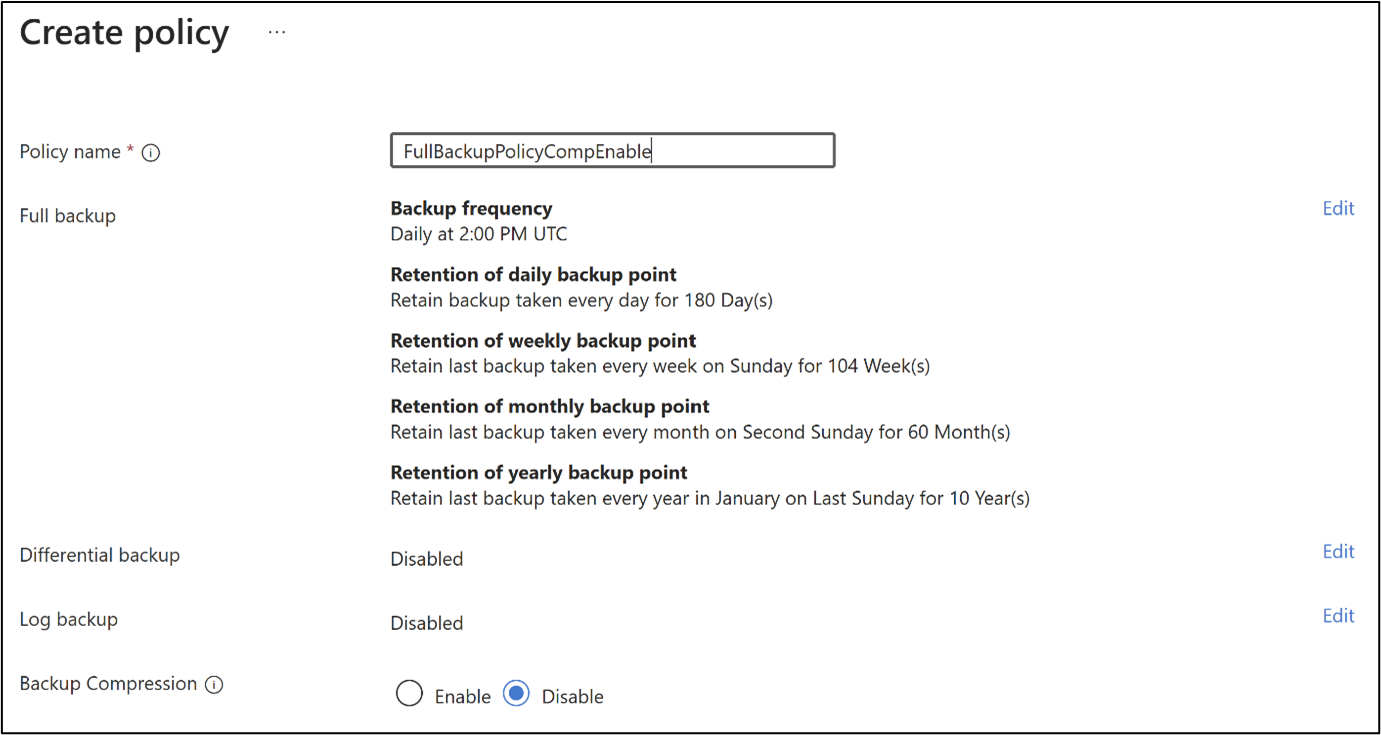
Ad Hoc Backup: Enable or disable compression when performing an on-demand backup.

Review compression levels
SAP ASE supports various compression levels, allowing you to choose based on your specific needs:
- Levels 1-3: Optimized for faster compression and decompression, prioritizing performance.
- Levels 4-6: A balanced approach between performance and storage efficiency.
- Levels 7-9: Maximizes storage savings with increased CPU usage.
- Level 100: Specialized for certain data types.
- Level 101: Advanced compression designed for improved performance with specific data patterns.
Recommended setup
For best results, we recommend using compression level 101. When the preregistration script runs, it adds the compressionLevel parameter to the configuration file, with the default set to 101. You can modify this based on your needs.
Change the compression Level
There are two ways to update the compression level:
Pre-registration script: Run the script with the compression-level parameter and specify your desired value.
Note
This parameter is optional.
Configuration file: Manually update the compressionLevel value in the configuration file at the following path: /opt/msawb/etc/config/SAPAse/config.json
Note
If you set the given ASE parameters, the memory and CPU utilization increase. We recommend that you monitor the memory consumption and CPU utilization as overutilization might negatively impact the backup and other ASE operations.