Migration guide: IBM Db2 to Azure SQL Managed Instance
Applies to:
Azure SQL Managed Instance
This guide teaches you to migrate your IBM Db2 databases to Azure SQL Managed Instance, by using the SQL Server Migration Assistant for Db2.
For other migration guides, see Azure Database Migration Guides.
Prerequisites
To migrate your Db2 database to SQL Managed Instance, you need:
- To verify that your source environment is supported.
- To download SQL Server Migration Assistant (SSMA) for Db2.
- A target instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance.
- Connectivity and sufficient permissions to access both source and target.
Pre-migration
After you have met the prerequisites, you're ready to discover the topology of your environment and assess the feasibility of your migration.
Assess and convert
Create an assessment by using SQL Server Migration Assistant.
To create an assessment, follow these steps:
Open SSMA for Db2.
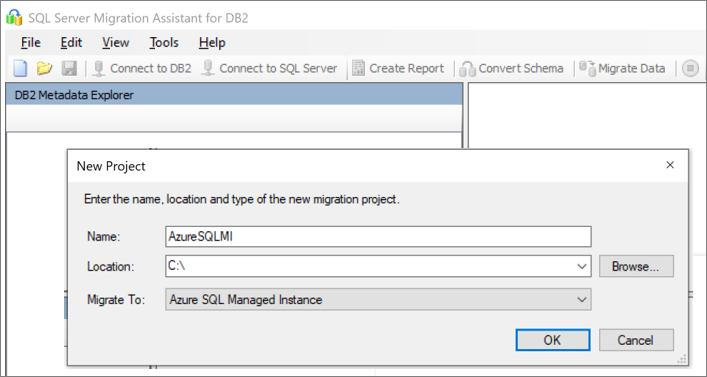
Select File > New Project.
Provide a project name and a location to save your project. Then select Azure SQL Managed Instance as the migration target from the drop-down list, and select OK.
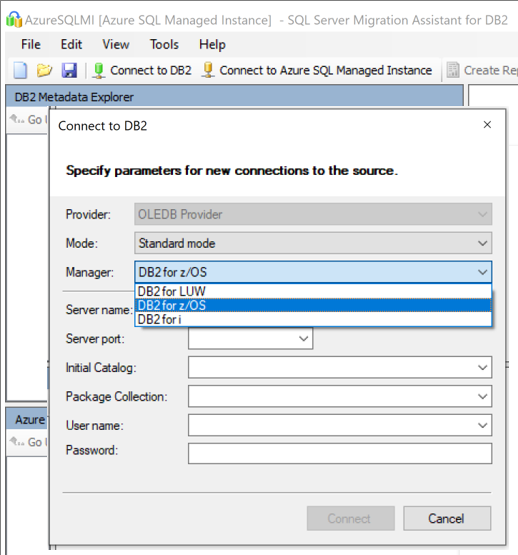
On Connect to Db2, enter values for the Db2 connection details.
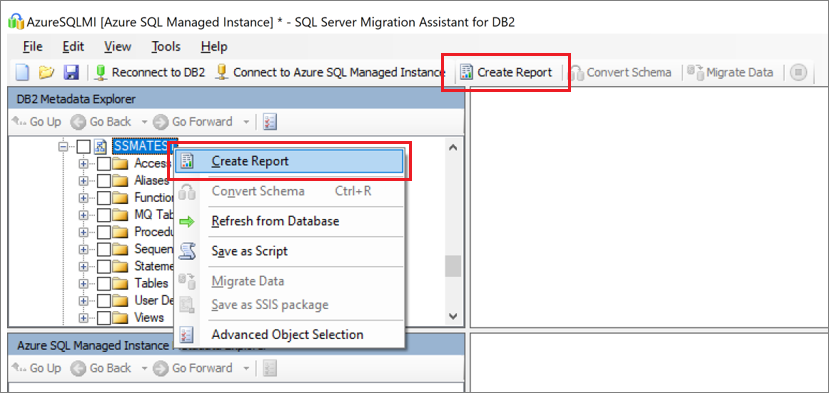
Right-click the Db2 schema you want to migrate, and then choose Create report. This will generate an HTML report. Alternatively, you can choose Create report from the navigation bar after selecting the schema.
Review the HTML report to understand conversion statistics and any errors or warnings. You can also open the report in Excel to get an inventory of Db2 objects and the effort required to perform schema conversions. The default location for the report is in the report folder within SSMAProjects.
For example:
drive:\<username>\Documents\SSMAProjects\MyDb2Migration\report\report_<date>.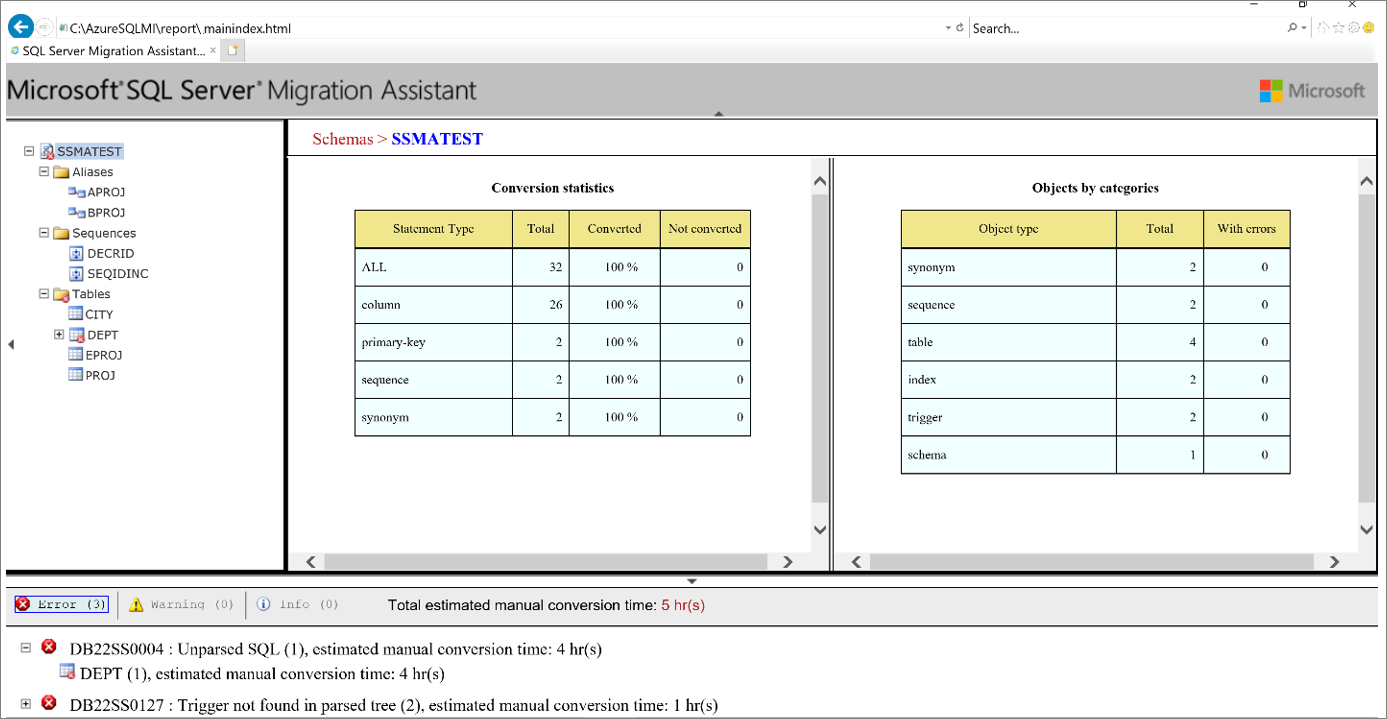
Validate data types
Validate the default data type mappings, and change them based on requirements if necessary. To do so, follow these steps:
Select Tools from the menu.
Select Project Settings.
Select the Type mappings tab.

You can change the type mapping for each table by selecting the table in the Db2 Metadata Explorer.
Convert schema
To convert the schema, follow these steps:
(Optional) Add dynamic or ad hoc queries to statements. Right-click the node, and then choose Add statements.
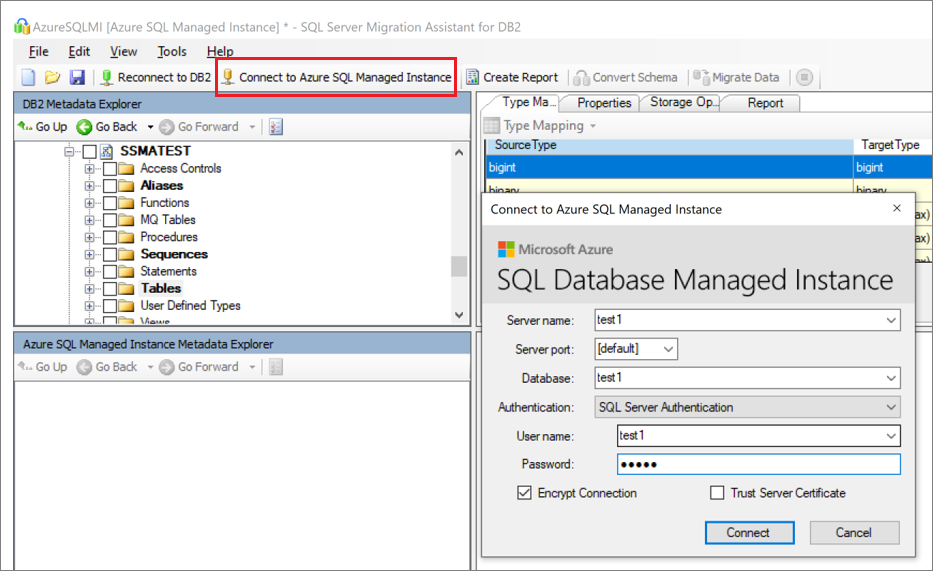
Select Connect to Azure SQL Managed Instance.
- Enter connection details to connect to Azure SQL Managed Instance.
- Choose your target database from the drop-down list, or provide a new name, in which case a database will be created on the target server.
- Provide authentication details.
- Select Connect.
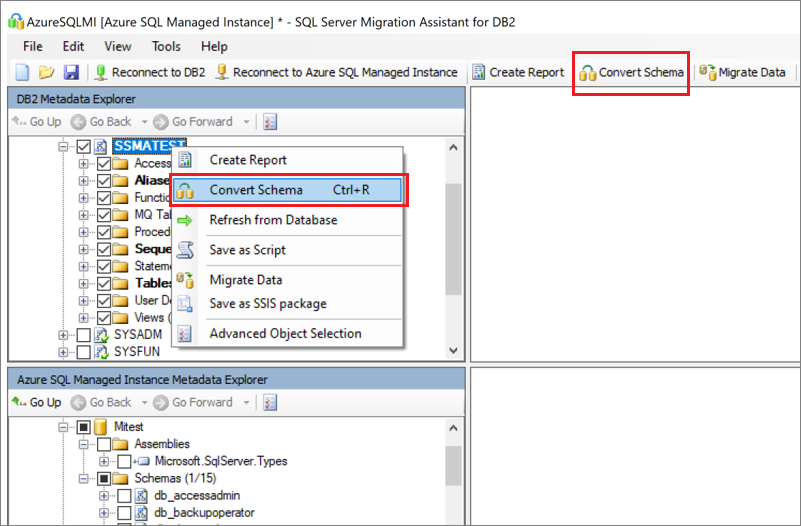
Right-click the schema, and then choose Convert Schema. Alternatively, you can choose Convert Schema from the top navigation bar after selecting your schema.
After the conversion completes, compare and review the structure of the schema to identify potential problems. Address the problems based on the recommendations.
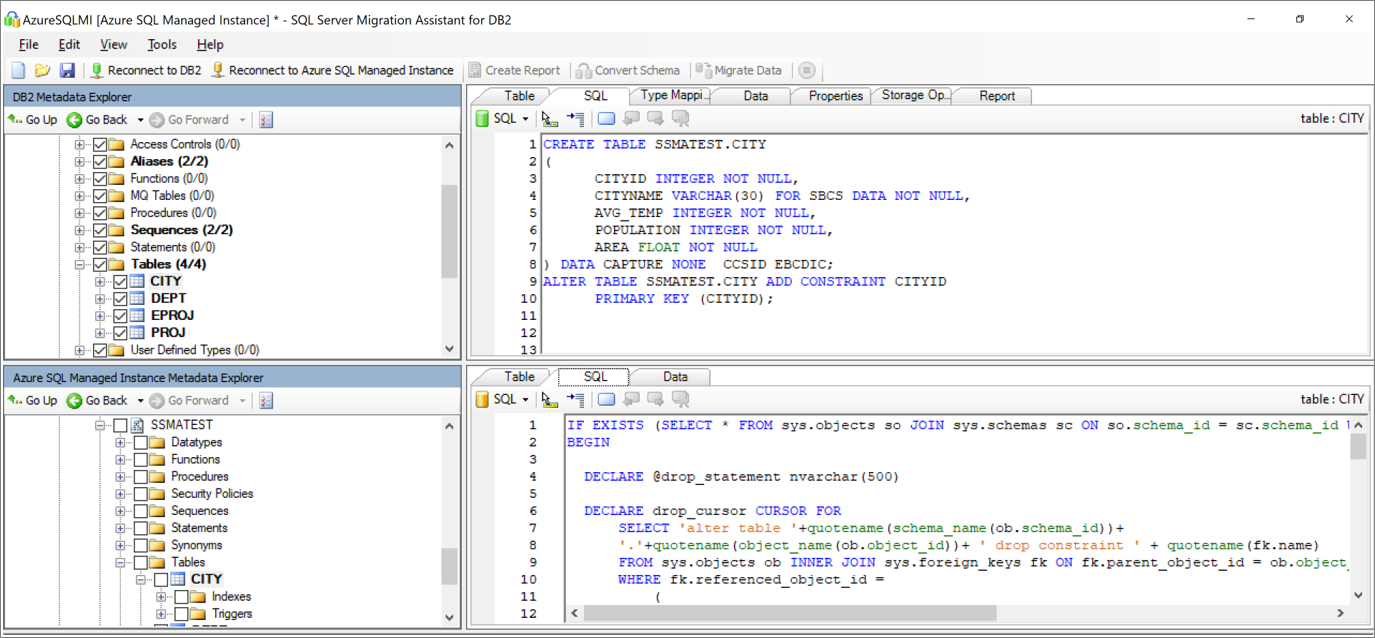
In the Output pane, select Review results. In the Error list pane, review errors.
Save the project locally for an offline schema remediation exercise. From the File menu, select Save Project. This gives you an opportunity to evaluate the source and target schemas offline, and perform remediation before you can publish the schema to SQL Managed Instance.
Migrate
After you have completed assessing your databases and addressing any discrepancies, the next step is to execute the migration process.
To publish your schema and migrate your data, follow these steps:
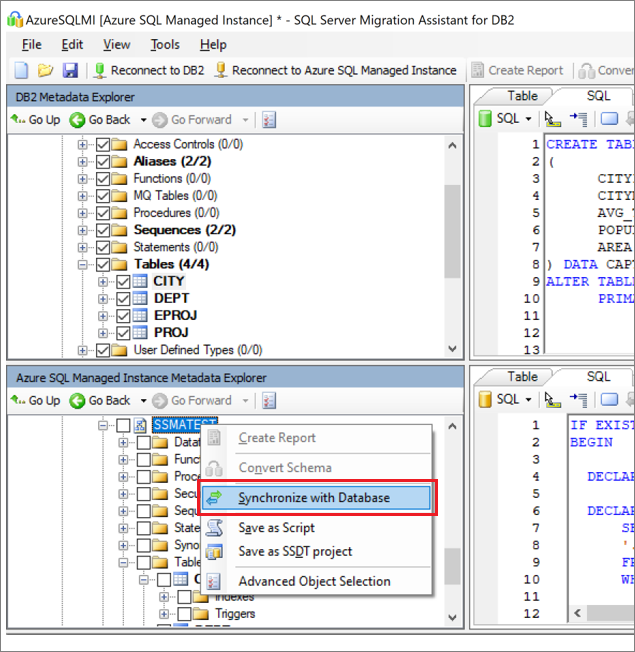
Publish the schema. In Azure SQL Managed Instance Metadata Explorer, from the Databases node, right-click the database. Then select Synchronize with Database.
Migrate the data. Right-click the database or object you want to migrate in Db2 Metadata Explorer, and choose Migrate data. Alternatively, you can select Migrate Data from the navigation bar. To migrate data for an entire database, select the check box next to the database name. To migrate data from individual tables, expand the database, expand Tables, and then select the check box next to the table. To omit data from individual tables, clear the check box.
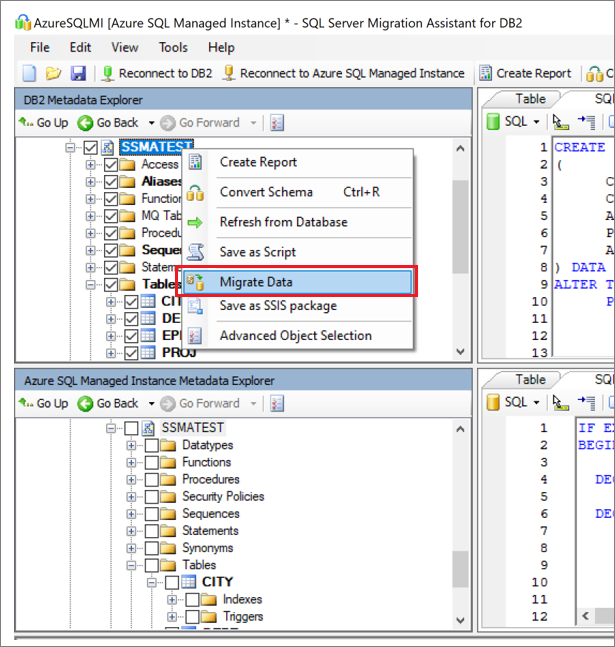
Provide connection details for both Db2 and SQL Managed Instance.
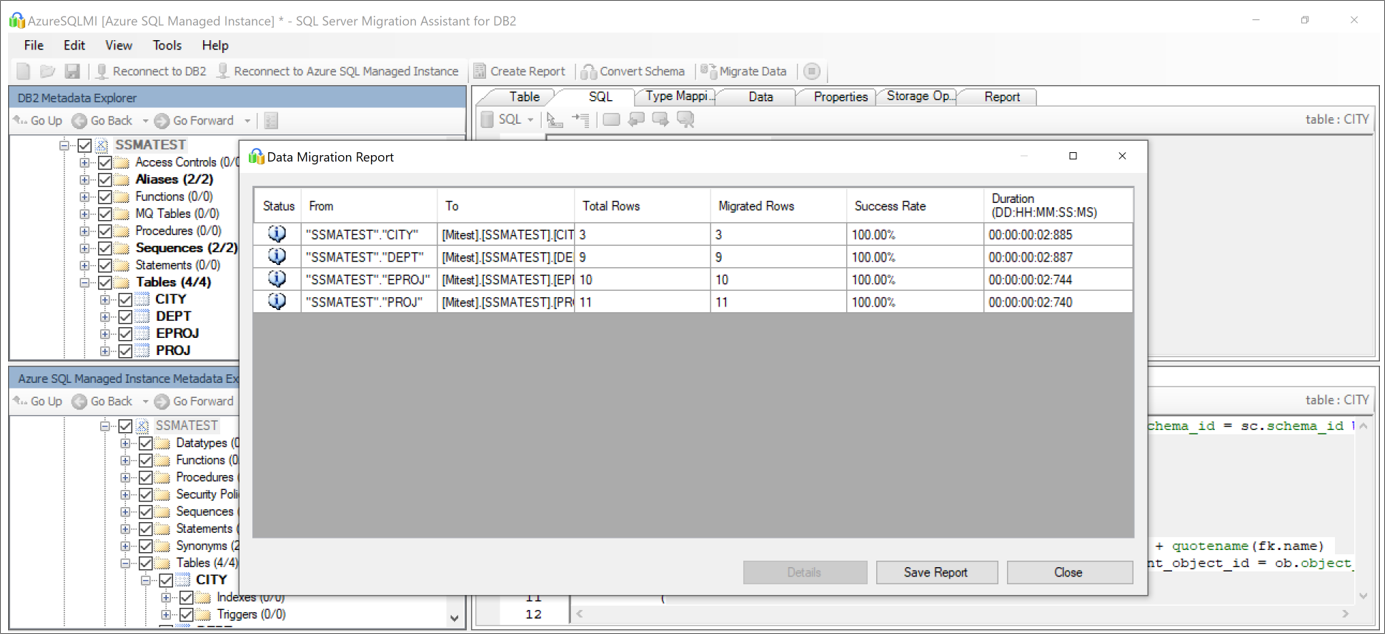
After migration completes, view the Data Migration Report.
Connect to your instance of Azure SQL Managed Instance by using SQL Server Management Studio. Validate the migration by reviewing the data and schema:
Post-migration
After the migration is complete, you need to go through a series of post-migration tasks to ensure that everything is functioning as smoothly and efficiently as possible.
Remediate applications
After the data is migrated to the target environment, all the applications that formerly consumed the source need to start consuming the target. Accomplishing this will in some cases require changes to the applications.
Perform tests
Testing consists of the following activities:
- Develop validation tests: To test database migration, you need to use SQL queries. You must create the validation queries to run against both the source and the target databases. Your validation queries should cover the scope you have defined.
- Set up the test environment: The test environment should contain a copy of the source database and the target database. Be sure to isolate the test environment.
- Run validation tests: Run the validation tests against the source and the target, and then analyze the results.
- Run performance tests: Run performance tests against the source and the target, and then analyze and compare the results.
Advanced features
Be sure to take advantage of the advanced cloud-based features offered by Azure SQL Managed Instance, such as built-in high availability, threat detection, and monitoring and tuning your workload.
Some SQL Server features are only available when the database compatibility level is changed to the latest compatibility level.
Migration assets
For additional assistance, see the following resources, which were developed in support of a real-world migration project engagement:
| Asset | Description |
|---|---|
| Data workload assessment model and tool | This tool provides suggested "best fit" target platforms, cloud readiness, and application/database remediation level for a given workload. It offers simple, one-click calculation and report generation that helps to accelerate large estate assessments by providing and automated and uniform target platform decision process. |
| Db2 zOS data assets discovery and assessment package | After running the SQL script on a database, you can export the results to a file on the file system. Several file formats are supported, including *.csv, so that you can capture the results in external tools such as spreadsheets. This method can be useful if you want to easily share results with teams that do not have the workbench installed. |
| IBM Db2 LUW inventory scripts and artifacts | This asset includes a SQL query that hits IBM Db2 LUW version 11.1 system tables and provides a count of objects by schema and object type, a rough estimate of "raw data" in each schema, and the sizing of tables in each schema, with results stored in a CSV format. |
| IBM Db2 to SQL MI - Database Compare utility | The Database Compare utility is a Windows console application that you can use to verify that the data is identical both on source and target platforms. You can use the tool to efficiently compare data down to the row or column level in all or selected tables, rows, and columns. |
The Data SQL Engineering team developed these resources. This team's core charter is to unblock and accelerate complex modernization for data platform migration projects to Microsoft's Azure data platform.
Next steps
For Microsoft and third-party services and tools to assist you with various database and data migration scenarios, see Service and tools for data migration.
To learn more about Azure SQL Managed Instance, see:
To learn more about the framework and adoption cycle for cloud migrations, see:
For details on how to perform data access layer A/B testing, see Database Experimentation Assistant.