Monitor queries and improve workload performance with automatic tuning in the Azure portal
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure SQL Database automatically manages data services that constantly monitor your queries and identifies the action that you can perform to improve performance of your workload. You can review recommendations and manually apply them, or let Azure SQL Database automatically apply corrective actions. This is known as automatic tuning mode.
Automatic tuning can be enabled at the server or the database level through:
- The Azure portal
- REST API calls
- T-SQL commands
Note
For Azure SQL Managed Instance, the supported option FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN can only be configured through T-SQL. The Azure portal based configuration and automatic index tuning options described in this article don't apply to Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Configuring automatic tuning options through the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template isn't supported at this time.
Enable automatic tuning on server
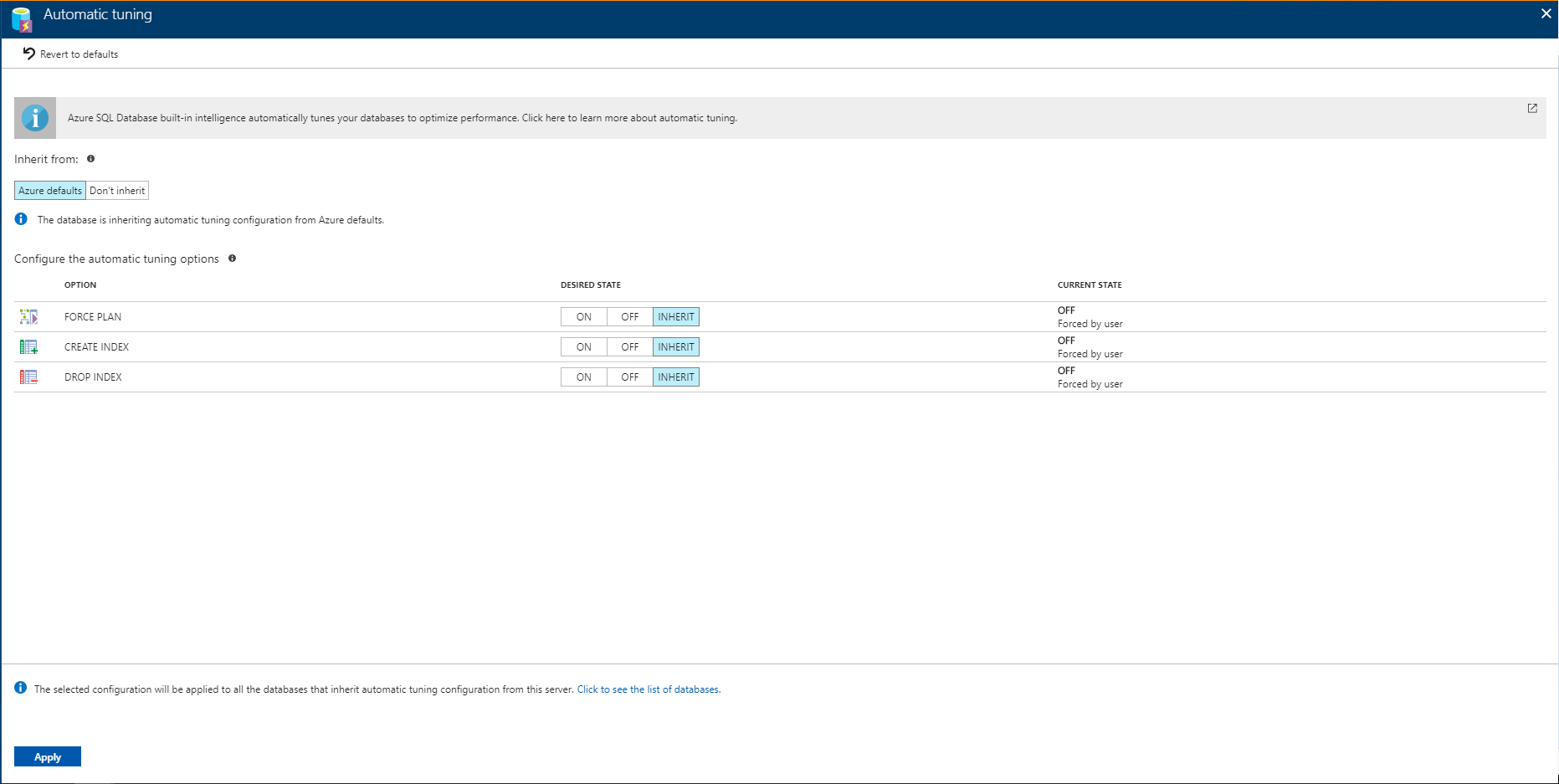
On the server level, you can choose to inherit automatic tuning configuration from "Azure Defaults" or not to inherit the configuration. Azure defaults are FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN enabled, CREATE_INDEX disabled, and DROP_INDEX disabled.
Azure portal
To enable automatic tuning on a server in Azure SQL Database, navigate to the server in the Azure portal and then select Automatic tuning in the menu.
Select the automatic tuning options you want to enable and select Apply.
Automatic tuning options on a server are applied to all databases on this server. By default, all databases inherit configuration from their parent server, but this can be overridden and specified for each database individually.
REST API
To find out more about using a REST API to enable automatic tuning on a server, see Server automatic tuning UPDATE and GET HTTP methods.
Configuring automatic tuning options through the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template isn't supported at this time.
Enable automatic tuning on an individual database
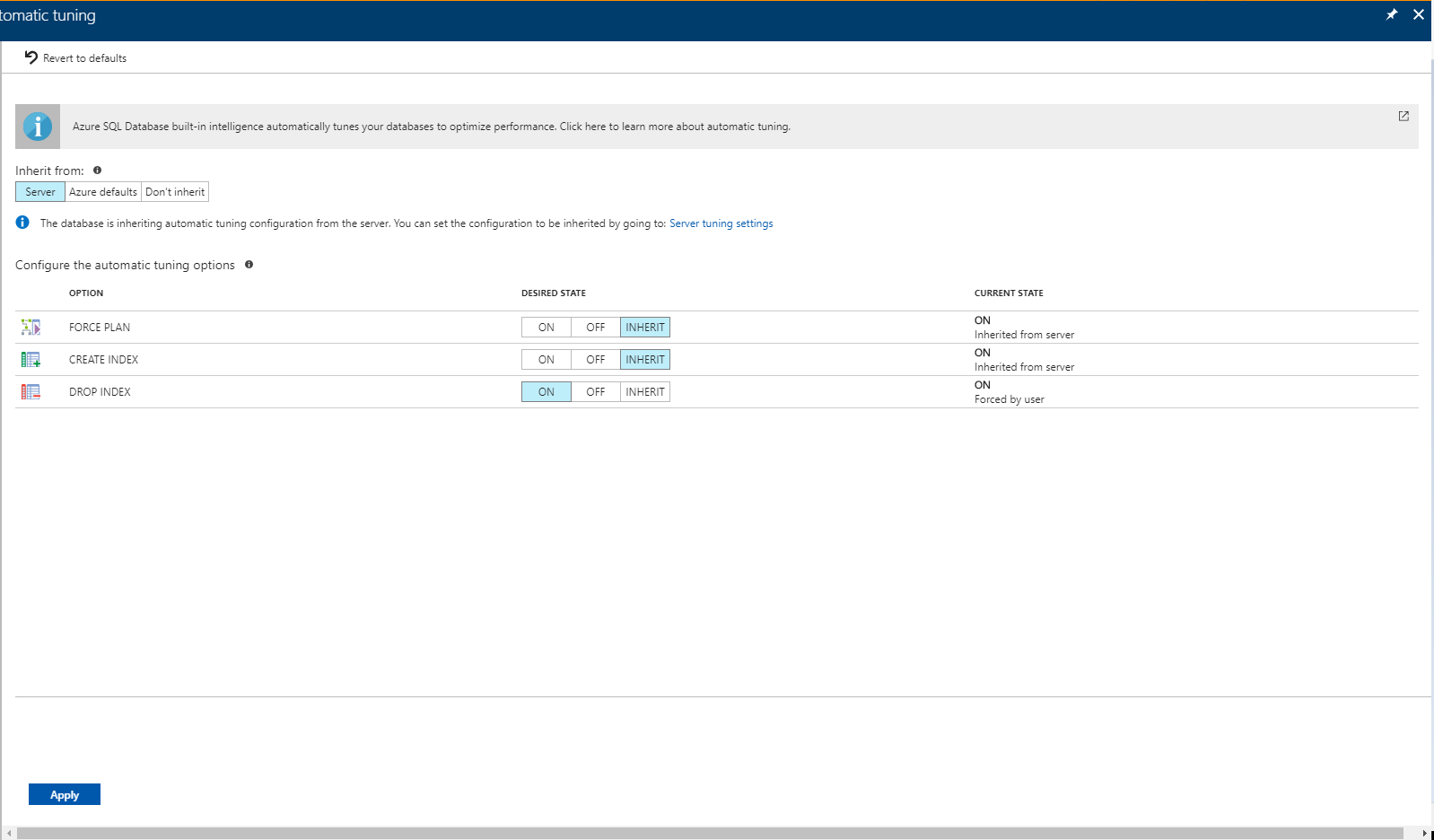
Azure SQL Database enables you to individually specify the automatic tuning configuration for each database. On the database level you can choose to inherit automatic tuning configuration from the parent server, "Azure Defaults" or not to inherit the configuration. These defaults are as follows:
FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLANis enabledCREATE_INDEXis disabledDROP_INDEXis disabled
Tip
The general recommendation is to manage the automatic tuning configuration at server level so the same configuration settings can be applied on every database automatically. Configure automatic tuning on an individual database only if you need that database to have different settings than others inheriting settings from the same server.
Azure portal
To enable automatic tuning on a single database, navigate to the database in the Azure portal and select Automatic tuning.
Individual automatic tuning settings can be separately configured for each database. You can manually configure an individual automatic tuning option, or specify that an option inherits its settings from the server.
Once you select your desired configuration, select Apply.
REST API
To find out more about using a REST API to enable automatic tuning on a single database, see Azure SQL Database automatic tuning UPDATE and GET HTTP methods.
Configuring automatic tuning options through the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template isn't supported at this time.
T-SQL
To enable automatic tuning on a single database via T-SQL, connect to the database and execute the following query:
ALTER DATABASE current SET AUTOMATIC_TUNING = AUTO | INHERIT | CUSTOM
Setting automatic tuning to AUTO applies Azure defaults. Setting it to INHERIT, automatic tuning configuration is inherited from the parent server. If you choose CUSTOM, you must manually configure automatic tuning.
To configure individual automatic tuning options via T-SQL, connect to the database and execute the following query:
ALTER DATABASE CURRENT SET AUTOMATIC_TUNING (
FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN = ON,
CREATE_INDEX = ON,
DROP_INDEX = OFF
);
Setting the individual tuning option to ON overrides any setting that database inherited, and enables the tuning option. Setting it to OFF also overrides any setting that database inherited and disables the tuning option. Automatic tuning options for which DEFAULT is specified inherit the automatic tuning configuration from the server level settings.
Important
For active geo-replication, automatic tuning must be configured on the primary database only. Automatically applied tuning actions, such as creating or deleting an index, are automatically replicated to geo-secondaries. Trying to enable automatic tuning via T-SQL on the read-only secondary results in a failure, as having a different tuning configuration on the read-only secondary isn't supported.
To find out more abut T-SQL options to configure automatic tuning, see ALTER DATABASE SET Options.
Troubleshooting
Automated recommendation management is disabled
If you see error messages that automated recommendation management was disabled, or disabled by the system, the most common causes are:
- Query Store isn't enabled, or
- Query Store is in read-only mode for a specified database, or
- Query Store stopped running because it ran out of allocated storage space.
The following steps can be considered to rectify this issue:
Clean up the Query Store, or modify the data retention period to "auto" by using T-SQL, or increase Query Store maximum size. See how to configure recommended retention and capture policy for Query Store.
Use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and follow these steps:
- Connect to the Azure SQL database.
- Right-click on the database.
- Go to Properties and select Query Store.
- Change the Operation Mode to Read-Write.
- Change the Store Capture Mode to Auto.
- Change the Size Based Cleanup Mode to Auto.
Permissions
For Azure SQL Database, managing automatic tuning in Azure portal, or using PowerShell or REST API requires membership in built-in Azure role-based access control (RBAC) roles.
To manage automatic tuning, the minimum required permission to grant to the user is membership in the SQL Database contributor role. You can also consider using higher privilege roles such as SQL Server Contributor, Contributor, and Owner.
For permissions required to manage automatic tuning with T-SQL, see Permissions for ALTER DATABASE.
Configure automatic tuning e-mail notifications
To receive automated email notifications on recommendations made by the automatic tuning, see the automatic tuning e-mail notifications guide.