Create and manage a dedicated cluster in Azure Monitor Logs
A dedicated cluster in Azure Monitor enables advanced security and control capabilities, and cost optimization. You can link new, or existing workspaces to the cluster with no interruption to ingestion and query operations.
Advanced capabilities
Capabilities that require dedicated clusters:
- Customer-managed keys - Encrypt data using a key that you provide and control.
- Lockbox - Control Microsoft support engineer access to your data.
- Double encryption - Extra layer of encryption for your data.
- Cross-query optimization - Cross-workspace queries run faster when on the same cluster.
- Cost optimization - Link workspaces in the same region to cluster, and enjoy a commitment tier discount for data ingested from all linked workspaces.
- Availability zones - Protect your data with datacenters in different physical locations, equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. Azure Monitor availability zones covers broader parts of the service and when available in your region, extends your Azure Monitor resilience automatically. Azure Monitor creates dedicated clusters as availability-zone-enabled (
isAvailabilityZonesEnabled: 'true') by default in supported regions. Dedicated clusters Availability zones aren't supported in all regions currently. - Ingest from Azure Event Hubs - Lets you ingest data directly from Event Hubs into a Log Analytics workspace.
Cluster pricing model
Log Analytics dedicated clusters use a commitment tier pricing model starting at 100 GB per day. Ingestion exceeding the commitment tier level is charged based on the per-GB rate. A commitment tier can be increased any time, but has a 31 day commitment period before it can be reduced. See Azure Monitor Logs pricing details for details on commitment tiers.
There are two billing type values that determine the billing attribution for ingested data:
- Cluster (default) - The costs for your cluster are attributed to the cluster resource.
- Workspaces - The costs for your cluster are attributed proportionately to the workspaces in the Cluster, with the cluster resource being billed some of the usage if the total ingested data for the day is under the commitment tier. See Log Analytics Dedicated Clusters to learn more about the cluster pricing model.
Required permissions
To perform cluster-related actions, you need these permissions:
| Action | Permissions or role needed |
|---|---|
| Create a dedicated cluster | Microsoft.Resources/deployments/*and Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/write permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, for example |
| Change cluster properties | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/write permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, for example |
| Link workspaces to a cluster | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/write, Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write, and Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/linkedservices/write permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, for example |
| Check workspace link status | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/read permissions to the workspace, as provided by the Log Analytics Reader built-in role, for example |
| Get clusters or check a cluster's provisioning status | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/read permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Reader built-in role, for example |
| Update commitment tier or billingType in a cluster | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/write permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, for example |
| Grant the required permissions | Owner or Contributor role that has */write permissions, or the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, which has Microsoft.OperationalInsights/* permissions |
| Unlink a workspace from cluster | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/linkedServices/delete permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, for example |
| Delete a dedicated cluster | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/delete permissions, as provided by the Log Analytics Contributor built-in role, for example |
For more information on Log Analytics permissions, see Manage access to log data and workspaces in Azure Monitor.
Resource Manager template samples
This article includes sample Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates to create and configure Log Analytics clusters in Azure Monitor. Each sample includes a template file and a parameters file with sample values to provide to the template.
Note
See Azure Resource Manager samples for Azure Monitor for a list of samples that are available and guidance on deploying them in your Azure subscription.
Template references
Preparation
Cluster commitment tier billing starts once created regardless of data ingestion, and it's recommended to have the following ready before you start:
- Have a subscription where the cluster is created
- Have the list of workspaces that you intend to link to the cluster. They must be in the same region as the cluster.
- Conclude the billing type and attribution, whether to the cluster (default), or to linked workspaces proportionally.
- Verify your permissions to create a cluster and to link workspaces
Note
- Creating a cluster and linking workspaces are performed in asynchronous operations that can take a few hours to complete
- Linking or unlinking workspaces from a cluster have no effect on ingestion, or queries during the operations.
Create a dedicated cluster
Provide the following properties when creating a new dedicated cluster:
- ClusterName: Must be unique for the resource group.
- ResourceGroupName: Use a central IT resource group because many teams in the organization usually share clusters. For more design considerations, review Design a Log Analytics workspace configuration.
- Location
- SkuCapacity: You can set the commitment tier to 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 25000 or 50000 GB per day. The minimum commitment tier supported in CLI is 500 GB currently. Use REST to configure lower commitment tiers with minimum of 100 GB. For more information on cluster costs, see Dedicated clusters.
- Managed identity: Clusters support two managed identity types:
System-assigned managed identity - Generated automatically with the cluster creation when identity
typeis set to "SystemAssigned". This identity can be used later to grant storage access to your Key Vault for wrap and unwrap operations.Identity in Cluster's REST Call
{ "identity": { "type": "SystemAssigned" } }User-assigned managed identity - Lets you configure a customer-managed key at cluster creation, when granting it permissions in your Key Vault before cluster creation.
Identity in Cluster's REST Call
{ "identity": { "type": "UserAssigned", "userAssignedIdentities": { "subscriptions/<subscription-id>/resourcegroups/<resource-group-name>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/UserAssignedIdentities/<cluster-assigned-managed-identity>" } } }
After you create your cluster resource, you can edit properties such as sku, keyVaultProperties, or billingType. See more details below.
Deleted clusters take two weeks to be completely removed. You can have up to seven clusters per subscription and region - five active, and two deleted in the past two weeks.
Note
Creating a cluster involves multiple resources and the operation typically completes in two hours. A dedicated cluster is billed once provisioned regardless of data ingestion and it's recommended to prepare the deployment to expedite the provisioning and workspaces link to the cluster. Verify the following:
- A list of initial workspaces to be linked to the cluster is identified
- You have permissions to the subscription intended for the cluster and any workspace to be linked
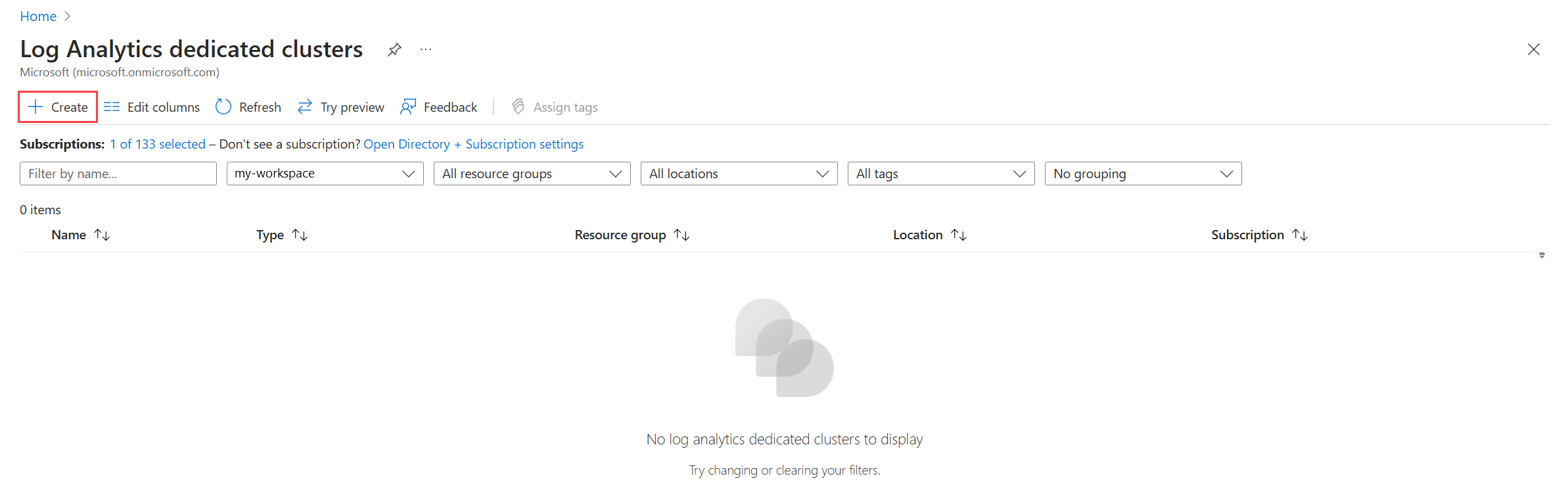
Click Create in the Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal. You will be prompted for details such as the name of the cluster and the commitment tier.
Check cluster provisioning status
The provisioning of the Log Analytics cluster takes a while to complete. Use one of the following methods to check the ProvisioningState property. The value is ProvisioningAccount while provisioning and Succeeded when completed.
The portal will provide a status as the cluster is being provisioned.
Link a workspace to a cluster
Note
- Linking a workspace can be performed only after the completion of the Log Analytics cluster provisioning.
- Linking a workspace to a cluster involves syncing multiple backend components and cache hydration, which typically completes in two hours.
- When linking a Log Analytics workspace, the workspace billing plan in changed to LACluster, and you should remove the SKU in the workspace template to prevent a conflict during workspace deployment.
- Other than the billing aspects that are governed by the cluster plan, all workspace configurations and query aspects remain unchanged during and after the link.
You need 'write' permissions to both the workspace and the cluster resource for the workspace link operation:
- In the workspace: Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write
- In the cluster resource: Microsoft.OperationalInsights/clusters/write
Once a Log Analytics workspace is linked to a dedicated cluster, new data sent to the workspace is ingested to your dedicated cluster, while previously ingested data remains in the Log Analytics cluster. Linking a workspace has no effect on workspace operation, including ingestion and query experiences. The Log Analytics query engine stitches data from old and new clusters automatically, and the results of queries are complete.
Clusters are regional and can be linked to up to 1,000 workspaces located in the same region as the cluster. A workspace can't be linked to a cluster more than twice a month, to prevent data fragmentation.
Linked workspaces can be in different subscriptions than the subscription the cluster is located in. The workspace and cluster can be in different tenants if Azure Lighthouse is used to map both of them to a single tenant.
When a dedicated cluster is configured with a customer-managed key (CMK), the newly ingested data is encrypted with your key, while older data remains encrypted with a Microsoft-managed key (MMK). The key configuration is abstracted by Log Analytics and the query across old and new data encryptions is performed seamlessly.
Use the following steps to link a workspace to a cluster. You can use automation for linking multiple workspaces:
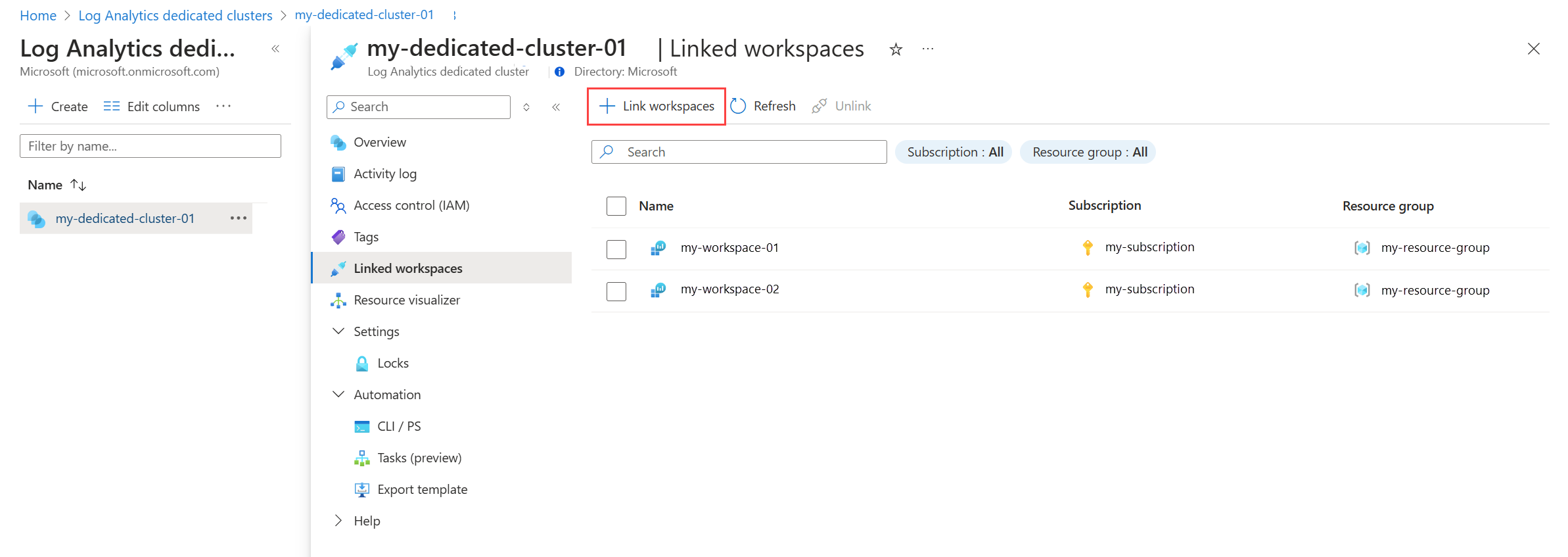
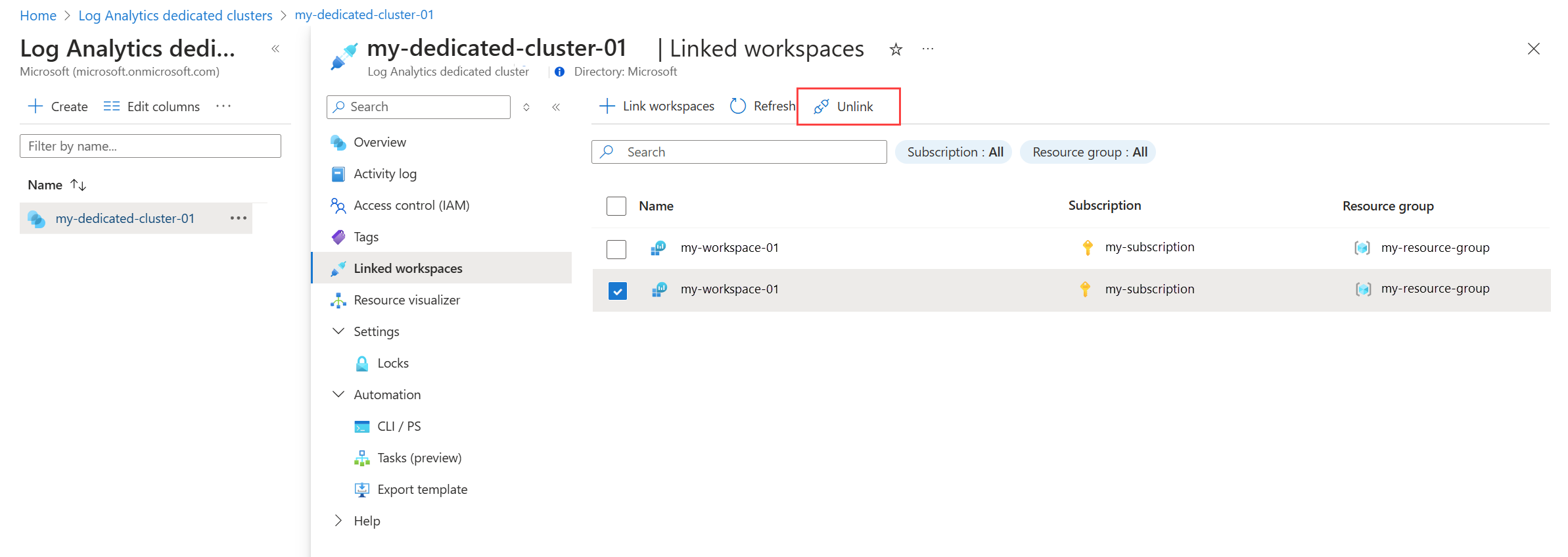
Select your cluster from Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal and then click Linked workspaces to view all workspaces currently linked to the dedicated cluster. Click Link workspaces to link additional workspaces.
Check workspace link status
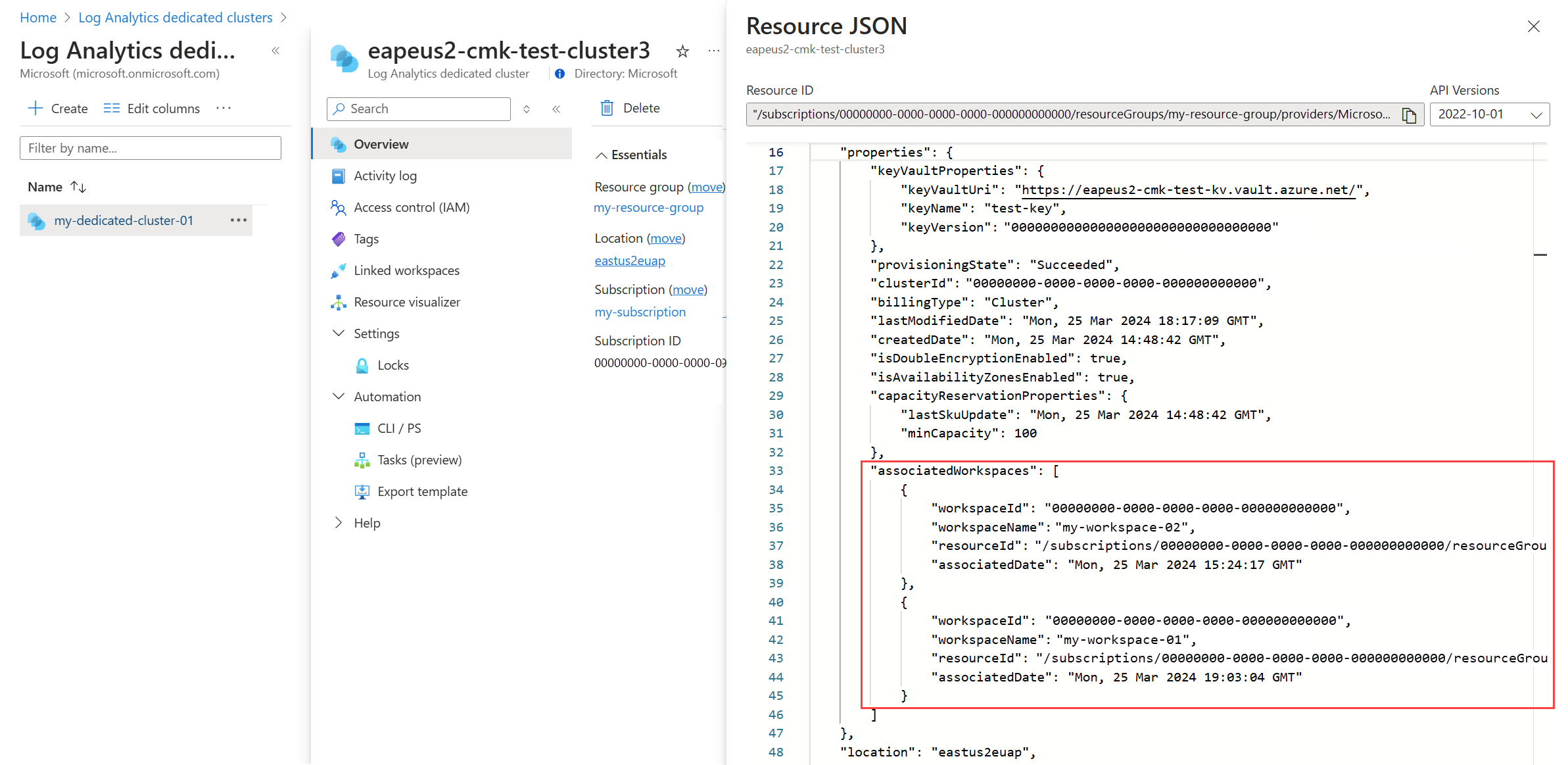
The workspace link operation can take up to 90 minutes to complete. You can check the status on both the linked workspaces and the cluster. When completed, the workspace resources will include the clusterResourceId property under features, and the cluster will include linked workspaces under associatedWorkspaces section.
When a cluster is configured with a customer-managed key, data ingested to the workspaces after the link operation is complete will be stored encrypted with your key.
On the Overview page for your dedicated cluster, select JSON View. The associatedWorkspaces section lists the workspaces linked to the cluster.
Change cluster properties
After you create your cluster resource and it's fully provisioned, you can edit cluster properties using CLI, PowerShell or REST API. Properties you can set after the cluster is provisioned include:
- keyVaultProperties - Contains the key in Azure Key Vault with the following parameters: KeyVaultUri, KeyName, KeyVersion. See Update cluster with Key identifier details.
- Identity - The identity used to authenticate to your Key Vault. This can be System-assigned or User-assigned.
- billingType - Billing attribution for the cluster resource and its data. Includes on the following values:
- Cluster (default) - The costs for your cluster are attributed to the cluster resource.
- Workspaces - The costs for your cluster are attributed proportionately to the workspaces in the Cluster, with the cluster resource being billed some of the usage if the total ingested data for the day is under the commitment tier. See Log Analytics Dedicated Clusters to learn more about the cluster pricing model.
Important
A single cluster update should not include both identity and key identifier details in the same operation. If you need to update both, the update should be in two consecutive operations.
Get all clusters in resource group
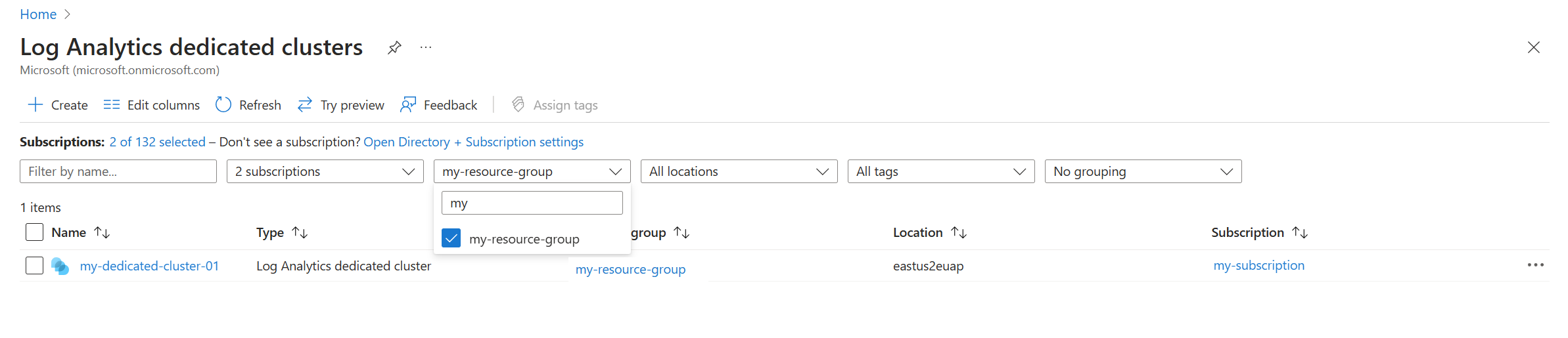
From the Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal, select the Resource group filter.
Get all clusters in subscription
From the Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal, select the Subscription filter.
Update commitment tier in cluster
When the data volume to linked workspaces changes over time, you can update the Commitment Tier level appropriately to optimize cost. The tier is specified in units of Gigabytes (GB) and can have values of 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 25000, 50000 GB per day. You don't have to provide the full REST request body, but you must include the SKU.
During the commitment period, you can change to a higher commitment tier, which restarts the 31-day commitment period. You can't move back to pay-as-you-go or to a lower commitment tier until after you finish the commitment period.
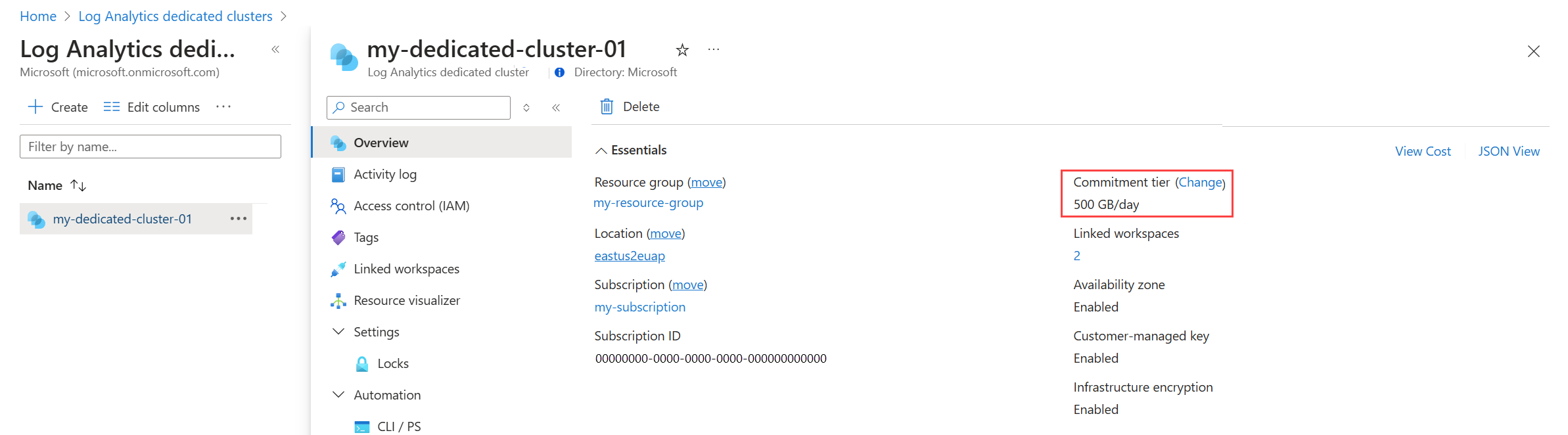
Select your cluster from Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal and then click Change next to Commitment tier
Unlink a workspace from cluster
You can unlink a workspace from a cluster at any time. The workspace pricing tier is changed to per-GB, data ingested to the cluster before the unlink operation remains in the cluster, and new data sent to the workspace gets ingested to Log Analytics cluster.
Warning
Unlinking a workspace does not move workspace data out of the cluster. Any data collected for workspace while linked to cluster, remains in cluster for the retention period defined in workspace, and accessible as long as cluster isn't deleted.
Queries aren't affected when workspace is unlinked and service performs cross-cluster queries seamlessly. If cluster was configured with Customer-managed key (CMK), data ingested to workspace while was linked, remains encrypted with your key and accessible, while your key and permissions to Key Vault remain.
Note
- There is a limit of two link operations for a specific workspace within a month to prevent data distribution across clusters. Contact support if you reach the limit.
- Unlinked workspaces are moved to a Pay-As-You-Go pricing tier.
Use the following commands to unlink a workspace from cluster:
Select your cluster from Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal and then click Linked workspaces to view all workspaces currently linked to the dedicated cluster. Select any workspaces you want to unlink and click Unlink.
Delete cluster
You need to have write permissions on the cluster resource.
A cluster deletion operation should be done with caution, since the operation is non-recoverable. All ingested data to the cluster from linked workspaces gets permanently deleted.
The cluster's billing stops when the cluster is deleted, regardless of the 31-day commitment period defined in cluster.
If you delete a cluster that has linked workspaces, the workspaces get automatically unlinked from the cluster, they are moved to a pay-as-you-go pricing tier, and new data sent to the workspaces is ingested to Log Analytics clusters instead. You can query a workspace across the time range before it was linked to the cluster, and after the unlink, and the service performs cross-cluster queries seamlessly.
Note
- There is a limit of seven clusters per subscription and region, five active, plus two that were deleted in past two weeks.
- A cluster's name remains reserved two weeks after deletion, and can't be used for creating a new cluster.
Use the following commands to delete a cluster:
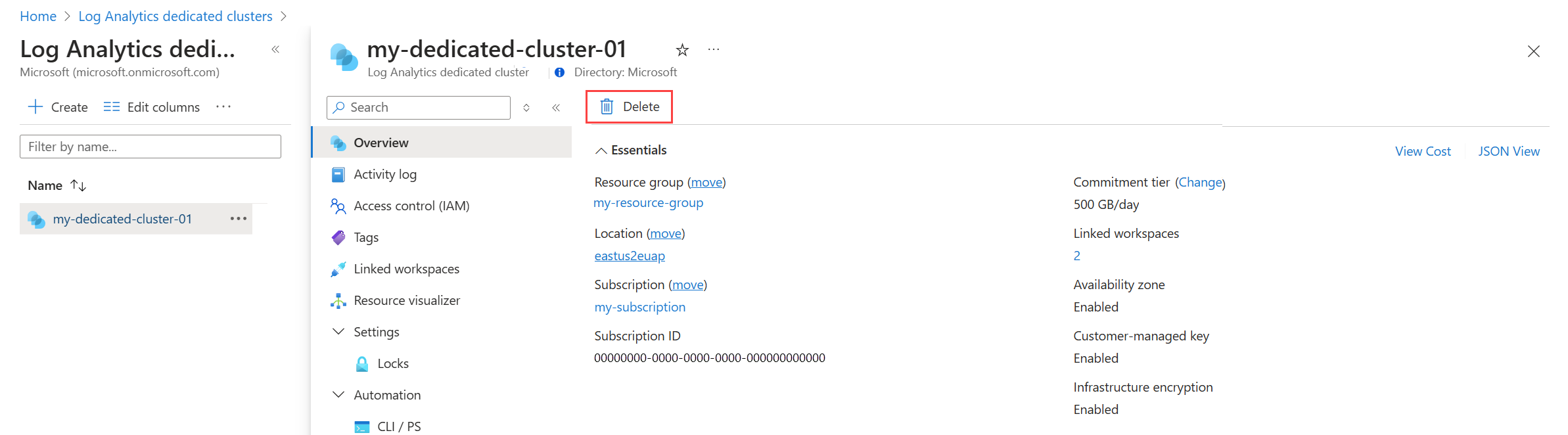
Select your cluster from Log Analytics dedicated clusters menu in the Azure portal and then click Delete.
Change managed identity type
The identity type can be changed after the cluster is created with no interruption to ingestion or queries with the following considerations:
- Updating SystemAssigned to UserAssigned - Grant UserAssign identity in Key Vault, then update identity type in cluster
- Updating UserAssigned to SystemAssigned - Since System-assigned managed identity created after updating cluster identity type with SystemAssigned, the following steps must be followed:
- Update cluster to remove the key - set keyVaultUri, keyName, and keyVersion to value ""
- Update cluster identity type to SystemAssigned
- Update Key Vault and grant permissions to the identity
- Update key in cluster
Limits and constraints
A maximum of five active clusters can be created in each region and subscription.
A maximum of seven clusters allowed per subscription and region, five active, plus two that were deleted in the past 2 weeks.
A maximum of 1,000 Log Analytics workspaces can be linked to a cluster.
A maximum of two workspace link operations on particular workspace is allowed in 30 day period.
Moving a cluster to another resource group or subscription isn't currently supported.
Moving a cluster to another region isn't supported.
A cluster update shouldn't include both identity and key identifier details in the same operation. In case you need to update both, the update should be in two consecutive operations.
Lockbox isn't currently available in China.
Lockbox can't currently be applied to tables with the Auxiliary plan.
Double encryption is configured automatically for clusters created from October 2020 in supported regions. You can verify if your cluster is configured for double encryption by sending a GET request on the cluster and observing that the
isDoubleEncryptionEnabledvalue istruefor clusters with Double encryption enabled.- If you create a cluster and get an error "region-name doesn't support Double Encryption for clusters.", you can still create the cluster without Double encryption by adding
"properties": {"isDoubleEncryptionEnabled": false}in the REST request body. - The double encryption setting can't be changed after the cluster has been created.
- If you create a cluster and get an error "region-name doesn't support Double Encryption for clusters.", you can still create the cluster without Double encryption by adding
Deleting a workspace is permitted while linked to a cluster. If you decide to recover the workspace during the soft-delete period, the workspace returns to its previous state and remains linked to cluster.
During the commitment period, you can change to a higher commitment tier, which restarts the 31-day commitment period. You can't move back to pay-as-you-go or to a lower commitment tier until after you finish the commitment period.
Troubleshooting
If you get a conflict error when creating a cluster, it might have been deleted in the past 2 weeks and is still in the deletion process. The cluster name remains reserved during the 2-week deletion period and you can't create a new cluster with that name.
If you update your cluster while the cluster is in the provisioning or updating state, the update will fail.
Some operations are long and can take a while to complete. These are cluster create, cluster key update and cluster delete. You can check the operation status by sending a GET request to the cluster or workspace and observe the response. For example, an unlinked workspace won't have the clusterResourceId under features.
If you attempt to link a Log Analytics workspace that's already linked to another cluster, the operation will fail.
Error messages
Cluster Create
- 400--Cluster name isn't valid. Cluster name can contain characters a-z, A-Z, 0-9 and a length of 3-63.
- 400--The body of the request is null or in bad format.
- 400--SKU name is invalid. Set SKU name to capacityReservation.
- 400--Capacity was provided but SKU isn't capacityReservation. Set SKU name to capacityReservation.
- 400--Missing Capacity in SKU. Set Capacity value to 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 25000, 50000 GB per day.
- 400--Capacity is locked for 30 days. Decreasing capacity is permitted 30 days after update.
- 400--No SKU was set. Set the SKU name to capacityReservation and Capacity value to 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000, 10000, 25000, 50000 GB per day.
- 400--Operation can't be executed now. Async operation is in a state other than succeeded. Cluster must complete its operation before any update operation is performed.
Cluster Update
- 400--Cluster is in deleting state. Async operation is in progress. Cluster must complete its operation before any update operation is performed.
- 400--KeyVaultProperties isn't empty but has a bad format. See key identifier update.
- 400--Failed to validate key in Key Vault. Could be due to lack of permissions or when key doesn't exist. Verify that you set key and access policy in Key Vault.
- 400--Key isn't recoverable. Key Vault must be set to Soft-delete and Purge-protection. See Key Vault documentation
- 400--Operation can't be executed now. Wait for the Async operation to complete and try again.
- 400--Cluster is in deleting state. Wait for the Async operation to complete and try again.
Cluster Get
- 404--Cluster not found, the cluster might have been deleted. If you try to create a cluster with that name and get a conflict, the cluster is in deletion process.
Cluster Delete
- 409--Can't delete a cluster while in provisioning state. Wait for the Async operation to complete and try again.
Workspace link
- 404--Workspace not found. The workspace you specified doesn't exist or was deleted.
- 409--Workspace link or unlink operation in process.
- 400--Cluster not found, the cluster you specified doesn't exist or was deleted.
Workspace unlink
- 404--Workspace not found. The workspace you specified doesn't exist or was deleted.
- 409--Workspace link or unlink operation in process.
Next steps
- Learn about Log Analytics dedicated cluster billing.
- Learn about proper design of Log Analytics workspaces.
- Get other sample templates for Azure Monitor.