Java REST SDK Developers Guide (preview)
The Azure Maps Java SDK can be integrated with Java applications and libraries to build maps-related and location-aware applications. The Azure Maps Java SDK contains APIs for Search, Route, Render, Geolocation, Traffic, Timezone, and Weather. These APIs support operations such as searching for an address, routing between different coordinates, obtaining the geo-location of a specific IP address etc.
Note
Azure Maps Java SDK is baselined on Java 8, with testing and forward support up until the latest Java long-term support release (currently Java 18). For the list of Java versions for download, see Java Standard Versions.
Prerequisites
- An Azure Maps account
- A Subscription key or other form of authentication
- Java Version 8 or above
- Maven (any version). For more information, see Get started with Azure SDK and Apache Maven.
Tip
You can create an Azure Maps account programmatically, Here's an example using the Azure CLI:
az maps account create --kind "Gen2" --account-name "myMapAccountName" --resource-group "<resource group>" --sku "G2"
Create a Maven project
The following PowerShell code snippet demonstrates how to use PowerShell to create a maven project. First, run the maven command to create a maven project:
mvn archetype:generate "-DgroupId=groupId" "-DartifactId=DemoProject" "-DarchetypeArtifactId=maven-archetype-quickstart" "-DarchetypeVersion=1.4" "-DinteractiveMode=false"
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
-DGroupId |
Group ID uniquely identifies your project across all projects |
-DartifactId |
Project name. It's created as a new folder. |
-DarchetypeArtifactId |
project type. maven-archetype-quickstart results in a sample project. |
-DinteractiveMode |
Setting to false results in a blank Java project with default options. |
Install the packages
To use the Azure Maps Java SDK, you need to install all required packages. Each service in Azure Maps is available in its own package. The Azure Maps services include Search, Render, Traffic, Weather, etc. You only need to install the packages for the service or services used in your project.
Once the maven project is created, there should be a pom.xml file with basic information such as group ID, name, artifact ID. Next, add a dependency for each of the Azure Maps services, as the following example demonstrates:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-maps-search</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-maps-route</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-maps-render</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-maps-traffic</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-maps-weather</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-maps-timezone</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta.1</version>
</dependency>
Run mvn clean install on your project, then create a java file named demo.java and import what you need from Azure maps into the file:
cd DemoProject
New-Item demo.java
Tip
If running mvn clean install results in an error, try running mvn clean install -U.
Azure Maps services
Create and authenticate a MapsSearchClient
The client object used to access the Azure Maps Search APIs require either an AzureKeyCredential object to authenticate when using an Azure Maps subscription key or a TokenCredential object with the Azure Maps client ID when authenticating using Microsoft Entra ID. For more information on authentication, see Authentication with Azure Maps.
Using a Microsoft Entra credential
You can authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID using the Azure Identity library. To use the DefaultAzureCredential provider, you need to add the mvn dependency in the pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-identity</artifactId>
</dependency>
You need to register the new Microsoft Entra application and grant access to Azure Maps by assigning the required role to your service principal. For more information, see Host a daemon on non-Azure resources. The Application (client) ID, a Directory (tenant) ID, and a client secret are returned. Copy these values and store them in a secure place. You need them in the following steps.
Set the values of the Application (client) ID, Directory (tenant) ID, and client secret of your Microsoft Entra application, and the map resource's client ID as environment variables:
| Environment Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| AZURE_CLIENT_ID | Application (client) ID in your registered application |
| AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET | The value of the client secret in your registered application |
| AZURE_TENANT_ID | Directory (tenant) ID in your registered application |
| MAPS_CLIENT_ID | The client ID in your Azure Map account |
Now you can create environment variables in PowerShell to store these values:
$Env:AZURE_CLIENT_ID="<client-id>"
A$Env:AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET="<client-secret>"
$Env:AZURE_TENANT_ID="<tenant-id>"
$Env:MAPS_CLIENT_ID="<maps-client-id>"
After setting up the environment variables, you can use them in your program to instantiate the AzureMapsSearch client:
import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredential;
import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClient;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClientBuilder;
public class Demo {
public static void main( String[] args) {
MapsSearchClientBuilder builder = new MapsSearchClientBuilder();
DefaultAzureCredential tokenCredential = new DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder().build();
builder.credential(tokenCredential);
builder.mapsClientId(System.getenv("MAPS_CLIENT_ID"));
MapsSearchClient client = builder.buildClient();
}
}
Important
The other environment variables created in the previous code snippet, while not used in the code sample, are required by are required by DefaultAzureCredential(). If you do not set these environment variables correctly, using the same naming conventions, you will get run-time errors. For example, if your AZURE_CLIENT_ID is missing or invalid you will get an InvalidAuthenticationTokenTenant error.
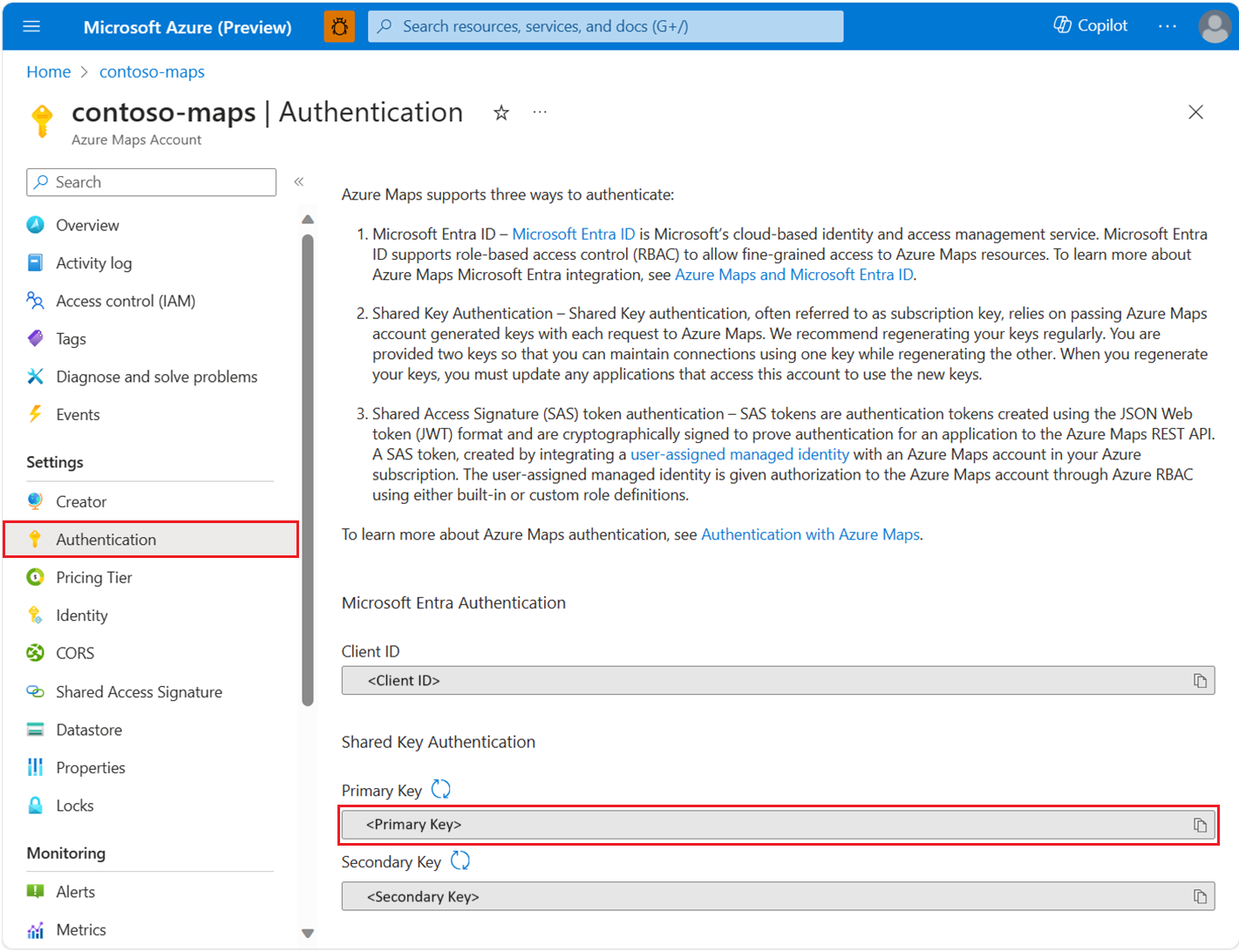
Using a subscription key credential
You can authenticate with your Azure Maps subscription key. Your subscription key can be found in the Authentication section in the Azure Maps account as shown in the following screenshot:
Now you can create environment variables in PowerShell to store the subscription key:
$Env:SUBSCRIPTION_KEY="<subscription-key>"
Once your environment variable is created, you can access it in your code:
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClient;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClientBuilder;
public class Demo {
public static void main( String[] args) {
// Use Azure Maps subscription key authentication
MapsSearchClientBuilder builder = new MapsSearchClientBuilder();
AzureKeyCredential keyCredential = new AzureKeyCredential(System.getenv("SUBSCRIPTION_KEY"));
builder.credential(keyCredential);
MapsSearchClient client = builder.buildClient();
}
}
Fuzzy search an entity
The following code snippet demonstrates how, in a simple console application, to import the azure-maps-search package and perform a fuzzy search on "Starbucks" near Seattle:
import java.io.IOException;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.models.GeoPosition;
// Enable the 2 imports below if you want to use AAD authentication
// import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredential;
// import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClient;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClientBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.FuzzySearchOptions;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.SearchAddressResult;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.SearchAddressResultItem;
public class Demo {
public static void main( String[] args) throws IOException {
MapsSearchClientBuilder builder = new MapsSearchClientBuilder();
// Instantiate with key credential. Get SUBSCRIPTION_KEY from environment variable:
AzureKeyCredential keyCredential = new AzureKeyCredential(System.getenv("SUBSCRIPTION_KEY"));
builder.credential(keyCredential);
// Or you can also instantiate with token credential:
// DefaultAzureCredential tokenCredential = new DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder().build();
// builder.credential(tokenCredential);
// builder.mapsClientId(System.getenv("MAPS_CLIENT_ID"));
MapsSearchClient client = builder.buildClient();
// Fuzzy search with options:
SearchAddressResult results = client.fuzzySearch(new FuzzySearchOptions("starbucks", new GeoPosition(-122.34255, 47.61010)));
// Print the search results:
for (SearchAddressResultItem item : results.getResults()) {
MapsSearchAddress address = item.getAddress();
GeoPosition coordinate = item.getPosition();
System.out.format(
"* %s, %s\\n" +
" %s %s %s\\n" +
" Coordinate: (%.4f, %.4f)\\n",
address.getStreetNumber(), address.getStreetName(),
address.getMunicipality(), address.getCountryCode(), address.getPostalCode(),
coordinate.getLatitude(), coordinate.getLongitude());
}
}
}
This code snippet demonstrates how to create a MapsSearchClient object using Azure credentials. Start by instantiating AzureKeyCredential using your Azure Maps subscription key, then passes the credentials to instantiate MapsSearchClient. MapsSearchClient methods such as FuzzySearch can use the point of interest (POI) name "Starbucks" and coordinates GeoPosition(-122.31, 47.61).
Execute the program from the project folder in the command line:
java .\demo.java
You should see a list of Starbucks address and coordinate results:
* 1912, Pike Place
Seattle US 98101
Coordinate: (47.6102, -122.3425)
* 2118, Westlake Avenue
Seattle US 98121
Coordinate: (47.6173, -122.3378)
* 2601, Elliott Avenue
Seattle US 98121
Coordinate: (47.6143, -122.3526)
* 1730, Howell Street
Seattle US 98101
Coordinate: (47.6172, -122.3298)
* 220, 1st Avenue South
Seattle US 98104
Coordinate: (47.6003, -122.3338)
* 400, Occidental Avenue South
Seattle US 98104
Coordinate: (47.5991, -122.3328)
* 1600, East Olive Way
Seattle US 98102
Coordinate: (47.6195, -122.3251)
* 500, Mercer Street
Seattle US 98109
Coordinate: (47.6250, -122.3469)
* 505, 5Th Ave S
Seattle US 98104
Coordinate: (47.5977, -122.3285)
* 425, Queen Anne Avenue North
Seattle US 98109
Coordinate: (47.6230, -122.3571)
Search an address
Call the SearchAddress method to get the coordinate of an address. Modify the Main program from the sample as follows:
import java.io.IOException;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.models.GeoPosition;
// Enable the 2 imports below if you want to use AAD authentication
// import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredential;
// import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClient;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClientBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.SearchAddressOptions;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.SearchAddressResult;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.SearchAddressResultItem;
public class Demo {
public static void main( String[] args) throws IOException {
MapsSearchClientBuilder builder = new MapsSearchClientBuilder();
// Instantiate with key credential:
AzureKeyCredential keyCredential = new
AzureKeyCredential(System.getenv("SUBSCRIPTION_KEY"));
builder.credential(keyCredential);
// Or you can also instantiate with token credential:
// DefaultAzureCredential tokenCredential = new DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder().build();
// builder.credential(tokenCredential);
// builder.mapsClientId(System.getenv("MAPS_CLIENT_ID"));
MapsSearchClient client = builder.buildClient();
client.searchAddress(new SearchAddressOptions("15127 NE 24th Street, Redmond, WA 98052"));
// Search address with options and return top 5 results:
SearchAddressResult results = client.searchAddress(new SearchAddressOptions("1
Main Street").setCoordinates(new GeoPosition(-74.011454,
40.706270)).setRadiusInMeters(40000).setTop(5));
// Print results:
if (results.getResults().size() > 0) {
SearchAddressResultItem item = results.getResults().get(0);
System.out.format("The coordinates is (%.4f, %.4f)",
item.getPosition().getLatitude(), item.getPosition().getLongitude());
}
}
}
In this sample, the client.SearchAddress method returns results ordered by confidence score and prints the coordinates of the first result.
Batch reverse search
Azure Maps Search also provides some batch query methods. These methods return Long Running Operations (LRO) objects. The requests might not return all the results immediately, so users can choose to wait until completion or query the result periodically as demonstrated in the batch reverse search method:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.azure.core.credential.AzureKeyCredential;
import com.azure.core.models.GeoPosition;
// Enable the 2 imports below if you want to use AAD authentication
// import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredential;
// import com.azure.identity.DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClient;
import com.azure.maps.search.MapsSearchClientBuilder;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.BatchReverseSearchResult;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.ReverseSearchAddressBatchItem;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.ReverseSearchAddressOptions;
import com.azure.maps.search.models.ReverseSearchAddressResultItem;
public class Demo{
public static void main( String[] args) throws IOException {
MapsSearchClientBuilder builder = new MapsSearchClientBuilder();
// Instantiate with key credential:
AzureKeyCredential keyCredential = new
AzureKeyCredential(System.getenv("SUBSCRIPTION_KEY"));
builder.credential(keyCredential);
// Or you can also instantiate with token credential:
// DefaultAzureCredential tokenCredential = new DefaultAzureCredentialBuilder().build();
// builder.credential(tokenCredential);
// builder.mapsClientId(System.getenv("MAPS_CLIENT_ID"));
MapsSearchClient client = builder.buildClient();
List<ReverseSearchAddressOptions> reverseOptionsList = new ArrayList<>();
reverseOptionsList.add(new ReverseSearchAddressOptions(new GeoPosition(2.294911, 48.858561)));
reverseOptionsList.add(new ReverseSearchAddressOptions(new GeoPosition(-122.34255, 47.61010)));
reverseOptionsList.add(new ReverseSearchAddressOptions(new GeoPosition(-122.33817, 47.61559)).setRadiusInMeters(5000));
BatchReverseSearchResult batchReverseSearchResult =
client.beginReverseSearchAddressBatch(reverseOptionsList).getFinalResult();
for (ReverseSearchAddressBatchItem item : batchReverseSearchResult.getBatchItems()) {
for (ReverseSearchAddressResultItem result : item.getResult().getAddresses()) {
System.out.println(result.getAddress().getFreeformAddress());
}
}
}
}