Review two-node storage reference pattern components for Azure Local
Applies to: Azure Local 2311.2 and later
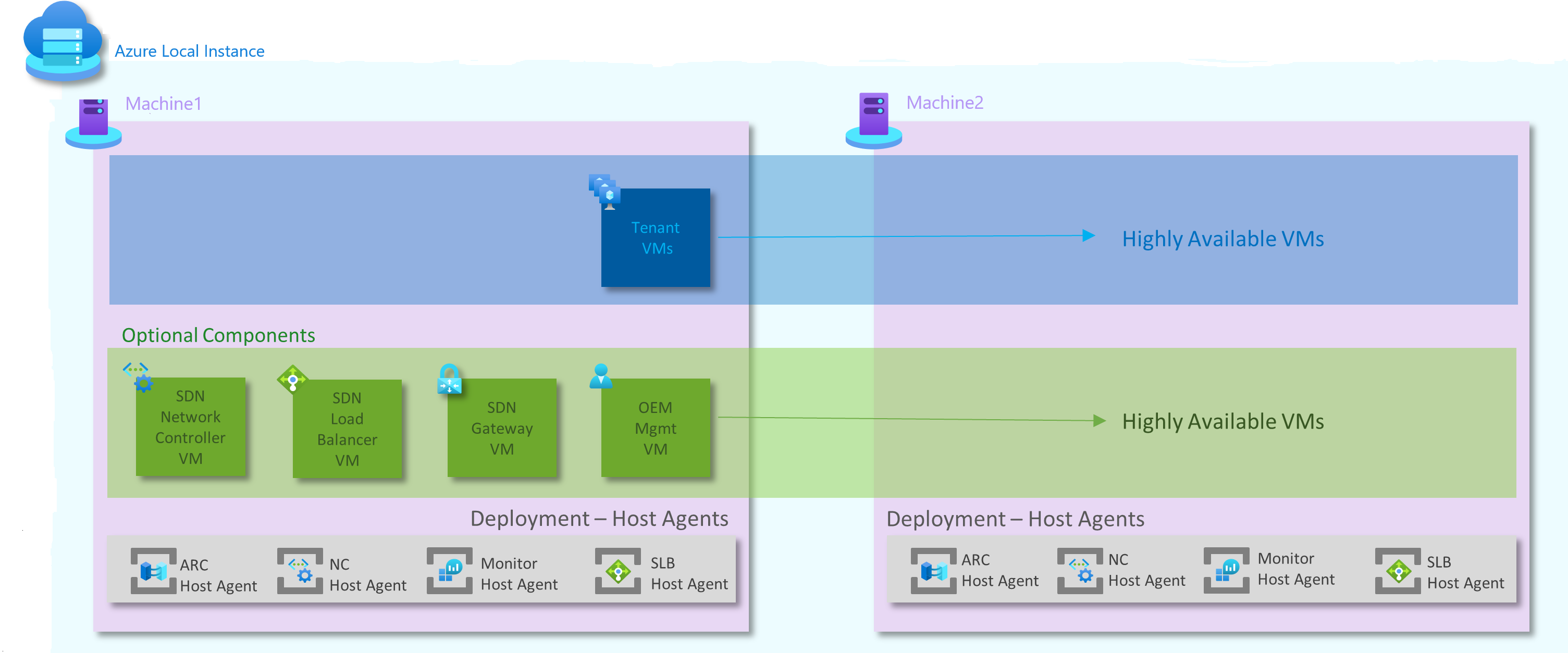
In this article, you'll learn about which network components get deployed for two-node reference patterns, as shown below:
VM components
The following table lists all the components running on VMs for two-node network patterns:
| Component | Number of VMs | OS disk size | Data disk size | vCPUs | Memory |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network Controller | 1 | 100 GB | 30 GB | 4 | 4 GB |
| SDN Software Load Balancers (SLB) | 1 | 60 GB | 30 GB | 16 | 8 GB |
| SDN Gateways | 1 | 60 GB | 30 GB | 8 | 8 GB |
| OEM Management | OEM defined | OEM defined | OEM defined | OEM defined | OEM defined |
| Total | 3 + OEM | 270 GB + OEM | 90 GB + OEM | 32 + OEM | 28 GB + OEM |
Default components
Network Controller VM
The Network Controller VM is deployed optionally. If Network Controller VM isn't deployed, the default access network access policies won't be available. Additionally, it's needed if you have any of the following requirements:
Create and manage virtual networks. Connect virtual machines (VMs) to virtual network subnets.
Configure and manage micro-segmentation for VMs connected to virtual networks or traditional VLAN-based networks.
Attach virtual appliances to your virtual networks.
Configure Quality of Service (QoS) policies for VMs attached to virtual networks or traditional VLAN-based networks.
Optional components
The following are optional components. For more information on Software Defined Networking (SDN), see Plan a Software Defined Network infrastructure.
SDN Load Balancer VM
The SDN Software Load Balancer (SLB) VM is used to evenly distribute customer network traffic among multiple VMs. It enables multiple machines to host the same workload, providing high availability and scalability. It's also used to provide inbound Network Address Translation (NAT) services for inbound access to virtual machines, and outbound NAT services for outbound connectivity.
SDN Gateway VM
The SDN Gateway VM is used for routing network traffic between a virtual network and another network, either local or remote. Gateways can be used to:
Create secure site-to-site IPsec connections between SDN virtual networks and external customer networks over the internet.
Create Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) connections between SDN virtual networks and external networks. The difference between site-to-site connections and GRE connections is that the latter isn't an encrypted connection. For more information about GRE connectivity scenarios, see GRE Tunneling in Windows Server.
Create Layer 3 connections between SDN virtual networks and external networks. In this case, the SDN gateway simply acts as a router between your virtual network and the external network.
Host service and agent components
The following components run as services or agents on the host machine:
Arc host agent: Enables you to manage your Windows and Linux computers hosted outside of Azure on your corporate network or other cloud providers.
Network Controller host agent: Allows Network Controller to manage the goal state of the data plane, and to receive notification of events as the configuration of the data plane changes.
Monitor host agent: Orchestrator-managed agent used for emitting observability (telemetry and diagnostics) pipeline data that upload to Geneva (Azure Storage).
Software Load Balancer host agent: Listens for policy updates from the Network Controller. In addition, this agent programs agent rules into the SDN-enabled Hyper-V virtual switches that are configured on the local computer.
Next steps
Learn about Two-node deployment IP requirements.