Repair a node on Azure Local
Applies to: Azure Local 2311.2 and later
This article describes how to repair a node on your Azure Local instance. In this article, each server is referred to as a node.
About repair nodes
Azure Local is a hyperconverged system that allows you to repair nodes from existing systems. You may need to repair a node in a system if there's a hardware failure.
Before you repair a node, make sure to check with your solution provider, which components on the node are field replacement units (FRUs) that you can replace yourself and which components would require a technician to replace.
Parts that support hot swap typically don't require you to reimage the node unlike the non hot-swappable components such as motherboard do. Consult your hardware manufacturer to determine which component replacements would require you to reimage the node. For more information, see Component replacement.
Repair node workflow
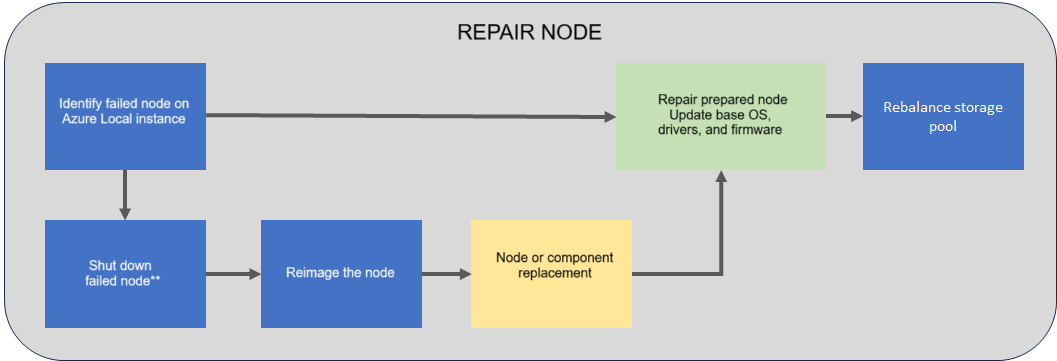
The following flow diagram shows the overall process to repair a node.
*Node may not be in a state where shutdown is possible or necessary*
To repair an existing node, follow these high-level steps:
If possible, shut down the node that you want to repair. Depending on the state of the node, a shutdown may not be possible or necessary.
Reimage the node that needs to be repaired.
Run the repair node operation. The Azure Stack HCI Operating System, drivers, and firmware are updated as part of the repair operation.
The storage is automatically rebalanced on the reimaged node. Storage rebalance is a low priority task that can run for multiple days depending on the number of nodes and the storage used.
Supported scenarios
Repairing a node reimages a node and brings it back to the system with the previous name and configuration.
Repairing a single node results in a redeployment with the option to persist the data volumes. Only the system volume is deleted and newly provisioned during deployment.
Important
Make sure that you always have backups for your workloads and do not rely on the system resiliency only. This is especially critical in single-node scenarios.
Resiliency settings
In this release, for a repair node operation, specific tasks aren't performed on the workload volumes that you created after the deployment. For a repair node operation, only the required infrastructure volumes and the workload volumes are restored and surfaced as cluster shared volumes (CSVs).
The other workload volumes that you created after the deployment are still retained and you can discover these volumes by running the Get-VirtualDisk cmdlet. You'll need to manually unlock the volume (if the volume has BitLocker enabled), and create a CSV (if needed).
Hardware requirements
When repairing a node, the system validates the hardware of the new, incoming node and ensures that the node meets the hardware requirements before it's added to the system.
| Component | Compliance check |
|---|---|
| CPU | Validate the new node has the same number of or more CPU cores. If the CPU cores on the incoming node don't meet this requirement, a warning is presented. The operation is however allowed. |
| Memory | Validate the new node has the same amount of or more memory installed. If the memory on the incoming node doesn't meet this requirement, a warning is presented. The operation is however allowed. |
| Drives | Validate that the new node has the same number of data drives available for Storage Spaces Direct. If the number of drives on the incoming node doesn't meet this requirement, an error is reported and the operation is blocked. |
Node replacement
You may replace the entire node:
- With a new node that has a different serial number compared to the old node.
- With the current node after you reimage it.
The following scenarios are supported during node replacement:
| Node | Disk | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| New node | New disks | Yes |
| New node | Current disks | Yes |
| Current node (reimaged) | Current disks reformatted ** | No |
| Current node (reimaged) | New disks | Yes |
| Current node (reimaged) | Current disks | Yes |
**Disks that have been used by Storage Spaces Direct require proper cleaning. Reformatting isn't sufficient. See how to Clean drives.
Important
If you replace a component during node repair, you don't need to replace or reset data drives. If you replace a drive or reset it, then the drive won't be recognized once the node joins the system.
Component replacement
On your Azure Local instance, non hot-swappable components include the following items:
- Motherboard/baseboard management controller (BMC)/video card
- Disk controller/host bus adapter (HBA)/backplace
- Network adapter
- Graphics processing unit
- Data drives (drives that don't support hot swap, for example PCI-e add-in cards)
The actual replacement steps for non hot-swappable components vary based on your original equipment manufacturer (OEM) hardware vendor. See your OEM vendor's documentation if a node repair is required for non hot-swappable components.
Prerequisites
Before you repair a node, you must ensure that:
AzureStackLCMUseris active in Active Directory. For more information, see Prepare the Active Directory.- Signed in as
AzureStackLCMUseror another user with equivalent permissions. - Credentials for the
AzureStackLCMUserhaven't changed.
If needed, take the node that you have identified for repair offline. Follow the steps here:
Repair a node
This section describes how to repair a node using PowerShell, monitor the status of the Repair-Server operation and troubleshoot, if there are any issues.
Make sure that you have reviewed the prerequisites.
Follow these steps on the node you're trying to repair.
Sign into the Azure portal with Azure Stack HCI Administrator role permissions.
Go to the resource group used to deploy your Azure Local instance. In the resource group, identify the Azure Arc machine resource for the faulty node that you wish to repair.
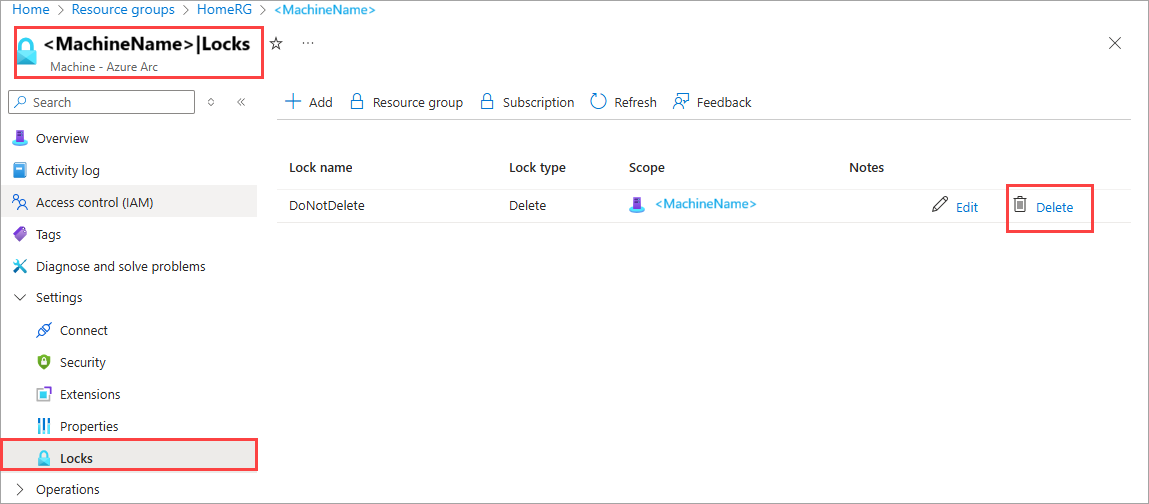
In the Azure Arc machine resource, go to Settings > Locks. In the right-pane, you see a resource lock.
Select the lock and then select the trash can icon to delete the lock.
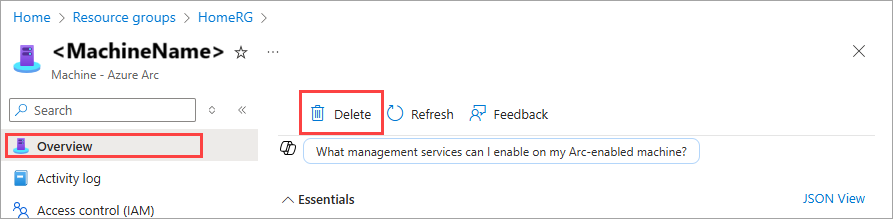
On the Overview page of the Azure Arc machine resource, in the right-pane, select Delete. This action should delete the faulty machine node.
Install the operating system and required drivers on the node you wish to repair. Follow the steps in Install the Azure Stack HCI Operating System, version 23H2.
Note
If you deployed your Azure Local instance using custom storage IPs, you must manually assign IPs to the storage network adapters after the node is repaired.
Register the node with Arc. Follow the steps in Register with Arc and set up permissions.
Note
You must use the same parameters as the existing nodes to register with Arc. For example: Resource Group name, Region, Subscription, and Tenant.
Assign the following permissions to the repaired node:
- Azure Local Device Management Role
- Key Vault Secrets User For more information, see Assign permissions to the node.
Follow these steps on another node that is a member of the same Azure Local instance.
If you are running a version prior to 2405.3, you must run the following command to clean up conflicting files:
Get-ChildItem -Path "$env:SystemDrive\NugetStore" -Exclude Microsoft.AzureStack.Solution.LCMControllerWinService*,Microsoft.AzureStack.Role.Deployment.Service* | Remove-Item -Recurse -ForceSign into the node that is already a member of the system, with the domain user credentials that you provided during the deployment of the system. Run the following command to repair the incoming node:
$Cred = Get-Credential Repair-Server -Name "<Name of the new node>" -LocalAdminCredential $CredNote
The node name must be the NetBIOS name. The parameter
LocalAdminCredentialby default, is the builtin Administrator account created by the Windows OS installation.Make a note of the operation ID as output by the
Repair-Servercommand. You use this later to monitor the progress of theRepair-Serveroperation.
Monitor operation progress
To monitor the progress of the add node operation, follow these steps:
Run the following cmdlet and provide the operation ID from the previous step.
$ID = "<Operation ID>" Start-MonitoringActionplanInstanceToComplete -actionPlanInstanceID $IDAfter the operation is complete, the background storage rebalancing job will continue to run. Wait for the storage rebalance job to complete. To verify the progress of this storage rebalancing job, use the following cmdlet:
Get-VirtualDisk|Get-StorageJobIf the storage rebalance job is complete, the cmdlet won't return an output.
Recovery scenarios
Following recovery scenarios and the recommended mitigation steps are tabulated for repairing a node:
| Scenario description | Mitigation | Supported? |
|---|---|---|
| Repair node operation failed. | To complete the operation, investigate the failure. Rerun the failed operation using Repair-Server -Rerun. |
Yes |
| Repair node operation succeeded partially but had to start with a fresh operation system install. | In this scenario, the orchestrator (also known as Lifecycle Manager) has already updated its knowledge store with the new node. Use the repair node scenario. | Yes |
Troubleshooting
If you experience failures or errors while repairing a node, you can capture the output of the failures in a log file.
Sign in with the domain user credentials that you provided during the deployment of the system. Capture the issue in the log files.
Get-ActionPlanInstance -ActionPlanInstanceID $ID |out-file log.txtTo rerun the failed operation, use the following cmdlet:
Repair-Server -Rerun
Next steps
Learn more about how to Add a node.