Monitor a single Azure Local system with Insights
Applies to: Azure Local 2311.2 and later
This article describes how to use Insights to monitor a single Azure Local system. For multiple Azure Local systems, see Monitor multiple Azure Local systems with Insights.
Insights is a feature of Azure Monitor that quickly gets you started monitoring your Azure Local system. You can view key metrics, health, and usage information regarding cluster, nodes, virtual machines, and storage.
Take a few moments to watch the video walkthrough on Insights for Azure Local:
Benefits
Insights for Azure Local offers the following benefits:
Managed by Azure. Insights is managed by Azure and accessed through the Azure portal, ensuring it's always up to date. There's no need for database or special software setup.
Scalability. Insights is capable of loading over 400 cluster information sets across multiple subscriptions simultaneously. There are no limitations on cluster, domain, or physical location.
Customizability. The Insight's experience is built on top of Azure Monitor workbook templates. This allows you to change the views and queries, modify or set thresholds that align with your specific limits, and then save these customizations into a workbook. You can then pin charts in the workbooks to the Azure dashboards.
Prerequisites
Here are the prerequisites of using Insights for Azure Local:
You must have access to an Azure Local system that is deployed and registered.
The managed identity for the Azure resource must be enabled. For more information, see Enabled enhanced management.
Enable Insights
Enabling Insights helps you monitor all the Azure Local systems currently associated with the Log Analytics workspace by providing useful health metrics. Insights installs the Azure Monitor Agent and helps you to configure data collection rules (DCRs) for monitoring your Azure Local system.
To enable Insights at scale, see Enable Insights for Azure Local at scale using Azure policies.
Follow these steps to enable Insights from the Azure portal:
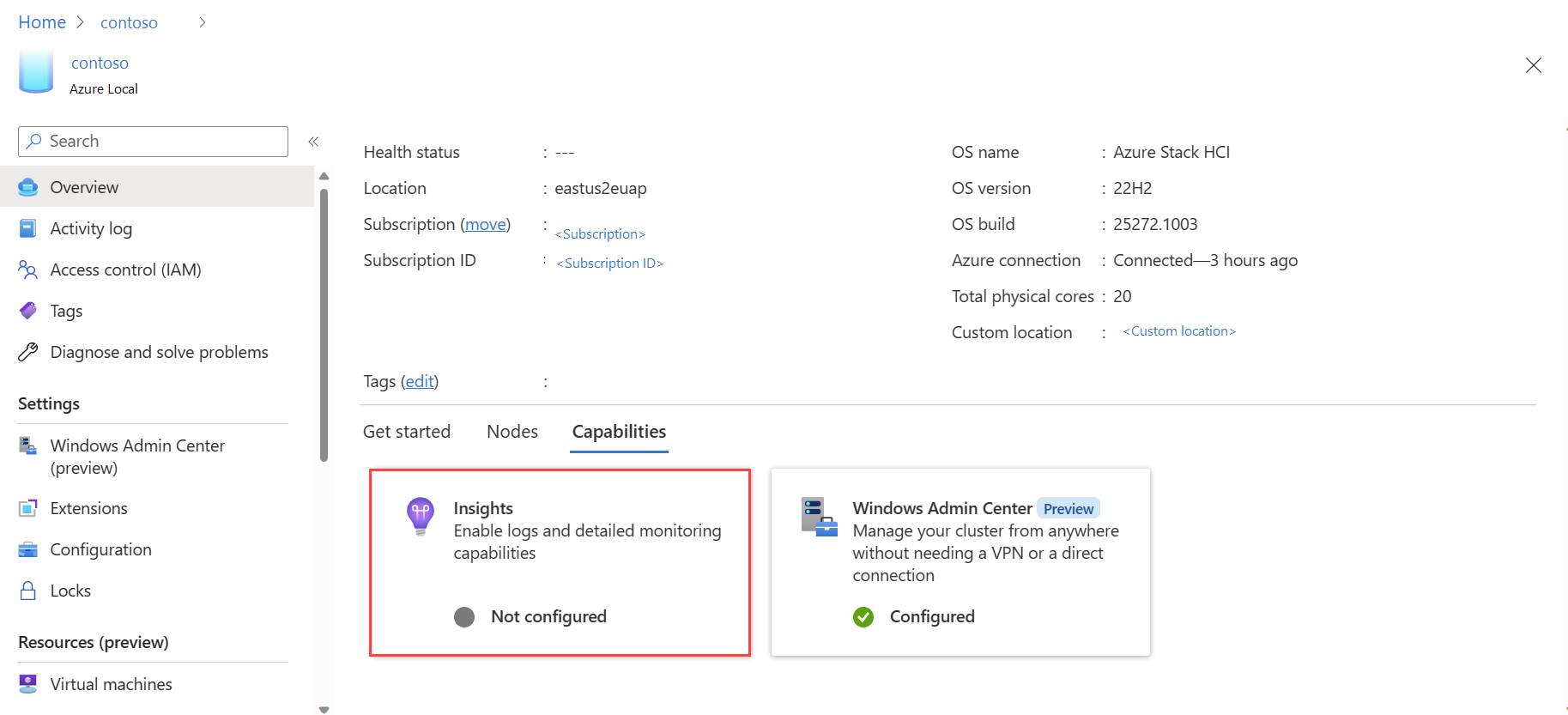
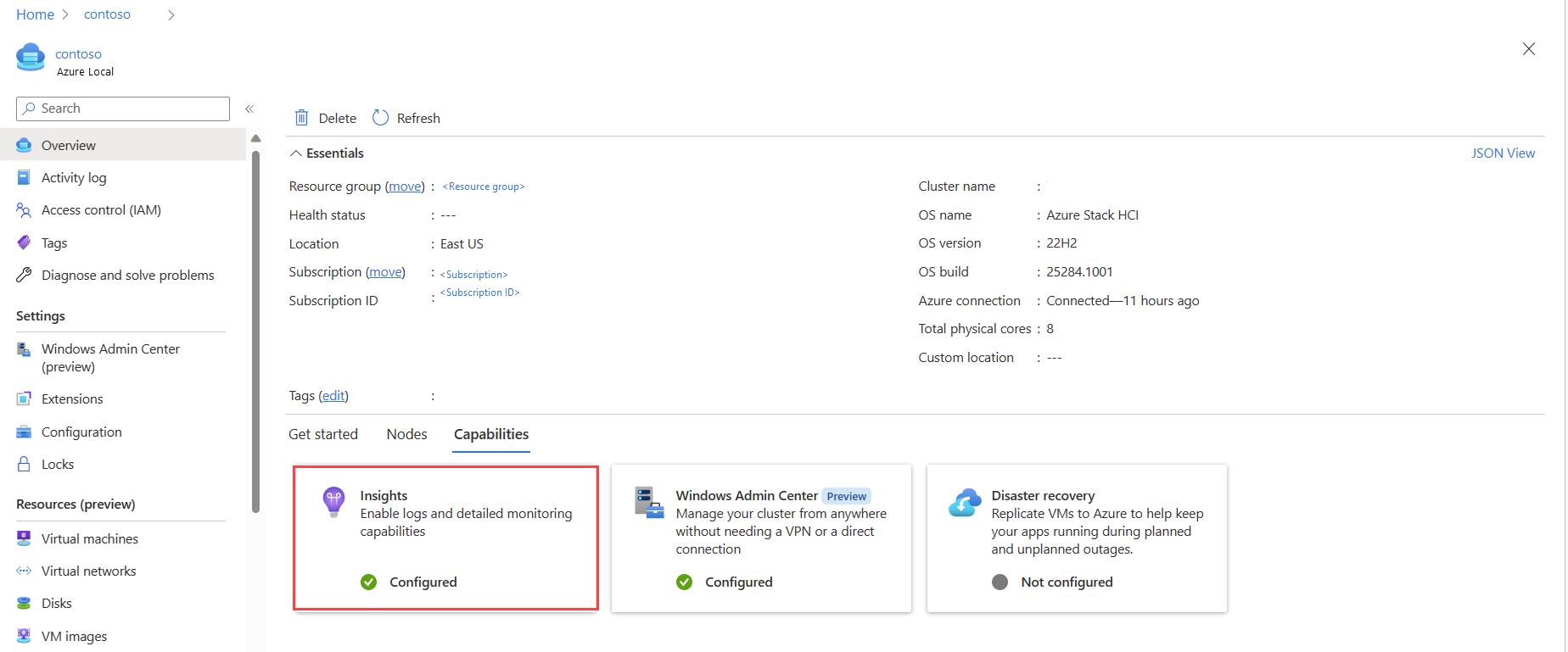
In the Azure portal, browse to your Azure Local resource page, then select your system. Under the Capabilities tab, select Insights.
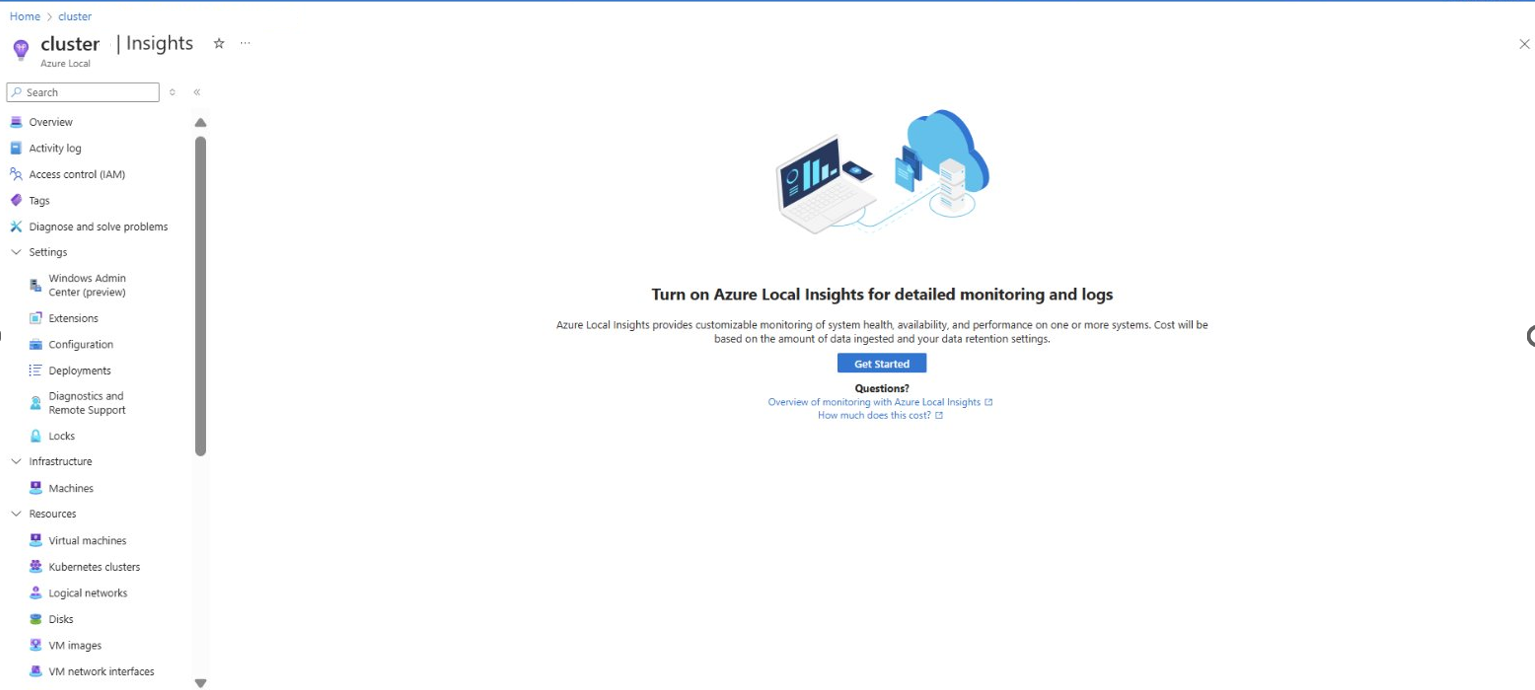
On the Insights page, select Get Started.
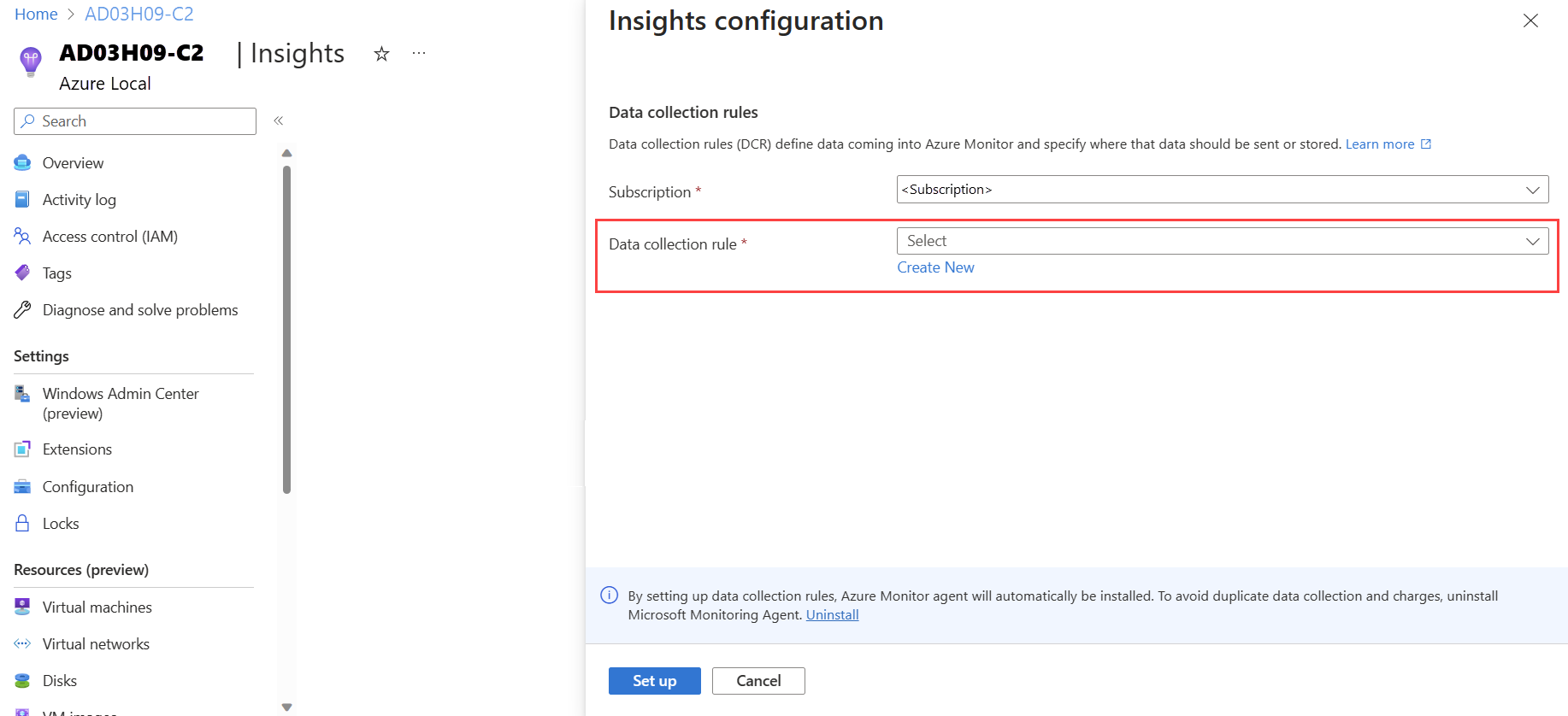
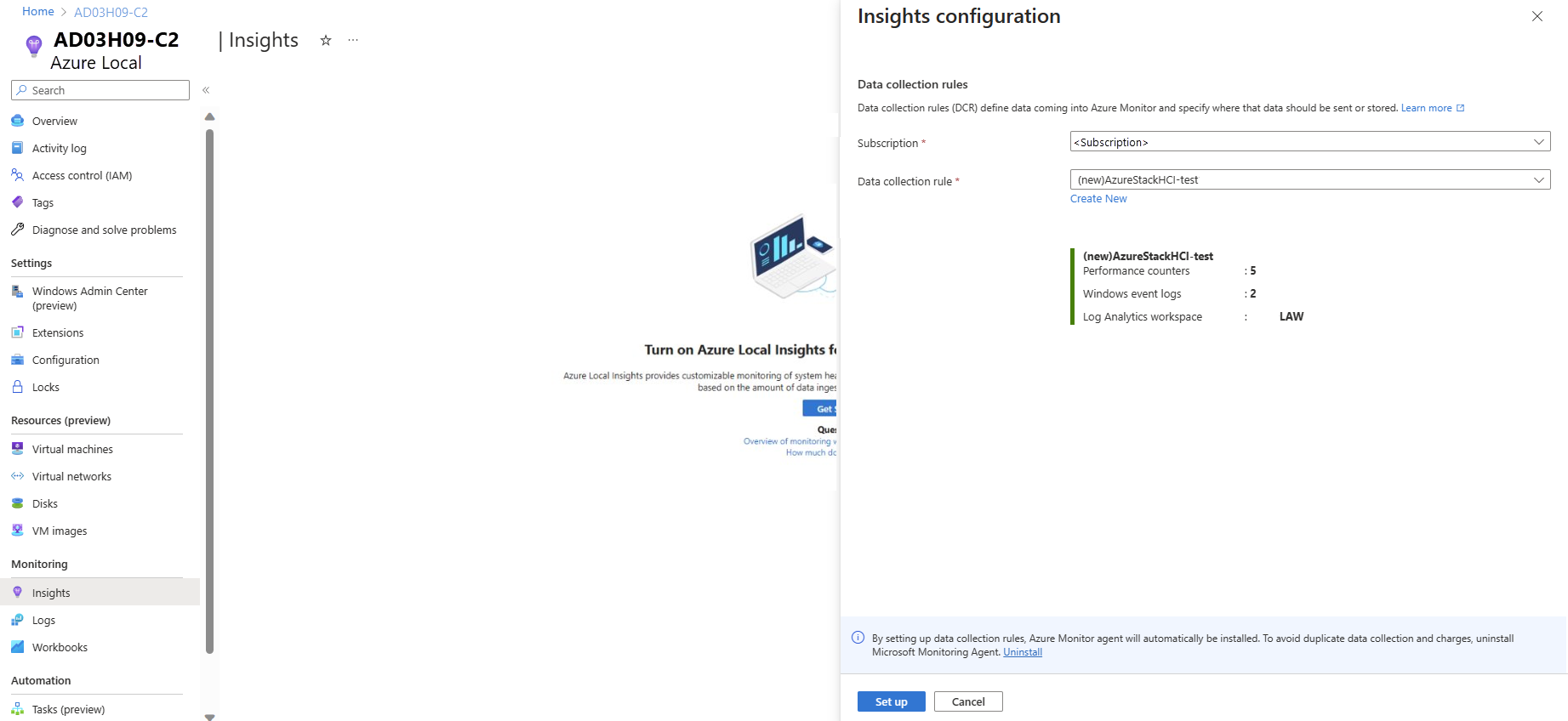
On the Insights configuration page, select an existing DCR from the Data collection rule dropdown. The DCR specifies the event logs and performance counters that need to be collected and stores it in a Log Analytics workspace. Insights creates a default DCR if one doesn't already exist. Only the DCRs that are enabled for Insights are included.
(Optional) You can also create a new DCR by selecting Create New on the Insights configuration page.
Important
We strongly recommend that you don't create your own DCR. The DCR created by Insights includes a special data stream required for its operation. You can edit this DCR to collect more data, such as Windows and Syslog events. The DCRs created through AMA installation will have a prefix
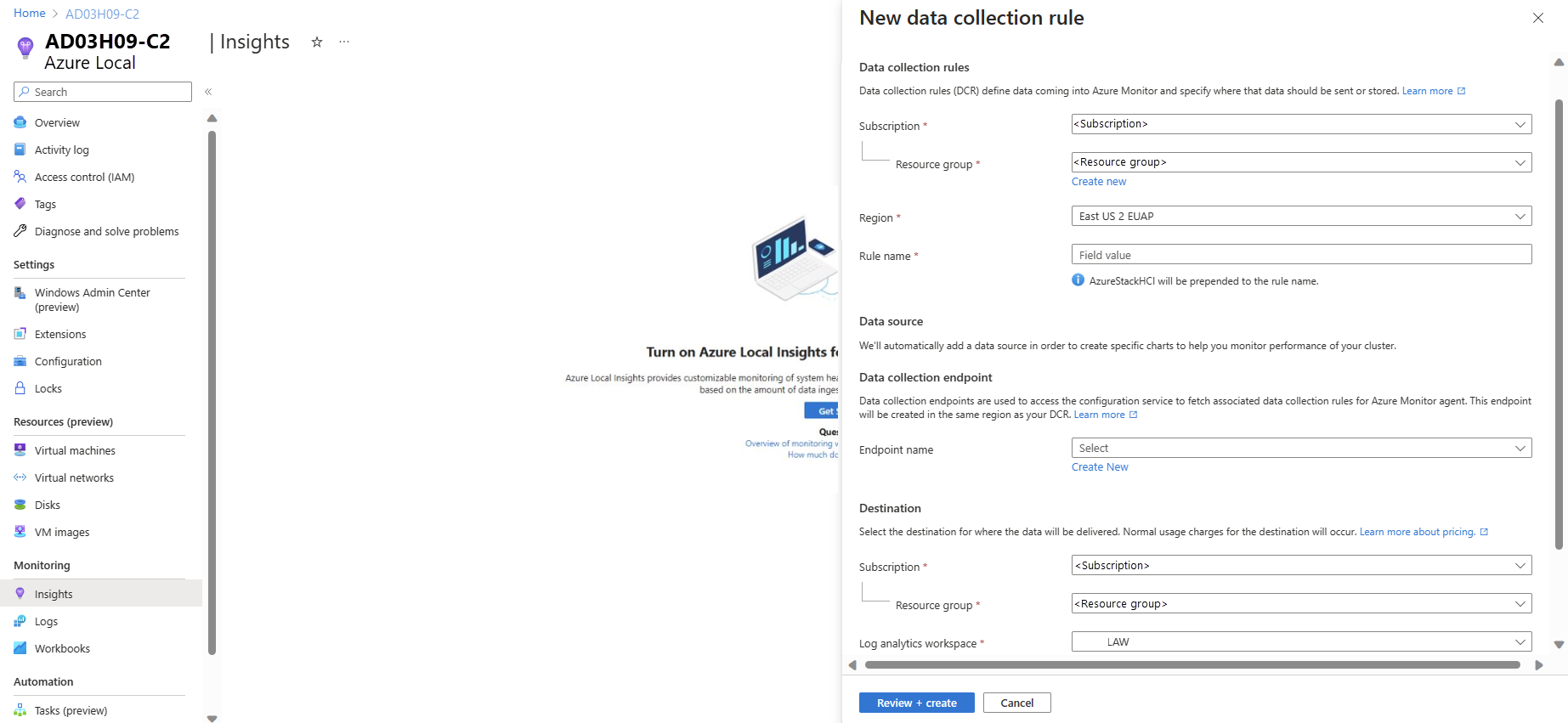
AzureStackHCI-attached with the DCR name.On the New data collection rule page, specify the subscription, DCR name, and data collection endpoint (DCE) name. DCEs are used to access the configuration service to fetch associated DCRs for Azure Monitor Agent. For more information about DCE, see Data collection endpoints in Azure Monitor.
Note
If you're using private links on the agent, you must add DCEs. For more information about AMA network settings, see Define Azure Monitor Agent network settings.
Select the Review + create button.
If a DCR isn't already created for the unmonitored cluster, then one is created with performance counters enabled and the Windows event log channel enabled.
Review the final screen with a summary of DCR name, number of event logs, performance counters, and name of the Log Analytics workspace in which data is stored. Select Set up.
After selecting Set up, you're redirected to the Extensions page, where you can see the status of your agent installation. By configuring Insights, AMA is automatically installed on all nodes of the cluster.
Go to your Azure Local resource page, and then select your system. Insights now shows as Configured on the Capabilities tab:
Data collection rules
When you enable Insights on a machine with the Azure Monitor Agent, you must specify a DCR to use. For more information about DCRs, see Data collection rules in Azure Monitor.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
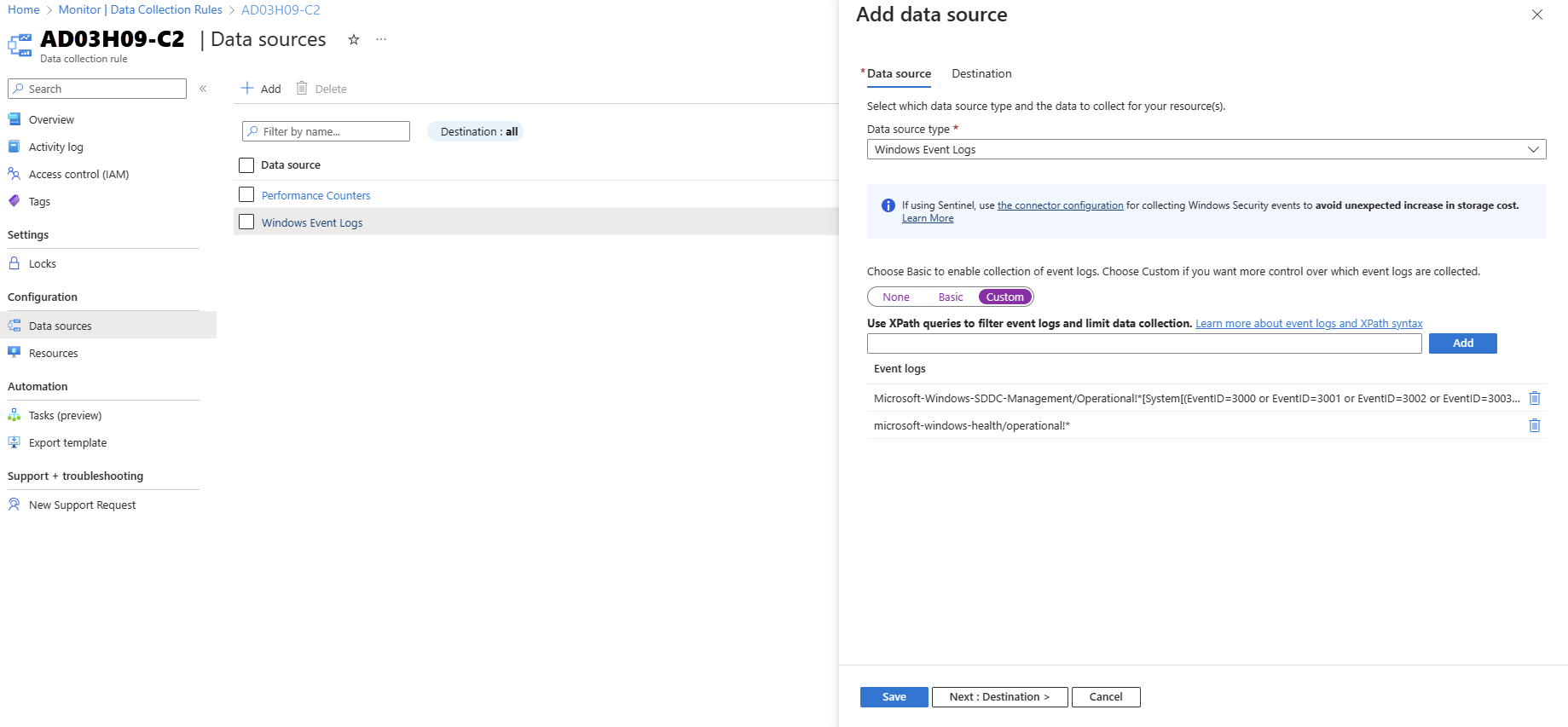
| Performance Counters | Specifies what data performance counters to collect from the operating system. This option is required for all computers. These performance counters are used to populate the visualizations in the Insights workbook. Currently, Insights workbook uses five performance counters - Memory()\Available Bytes, Network Interface()\Bytes Total/sec, Processor(_Total)\% Processor Time, RDMA Activity()\RDMA Inbound Bytes/sec, and RDMA Activity()\RDMA Outbound Bytes/sec |
| Event Log Channel | Specifies which Windows event logs to collect from the operating system. This option is required for all computers. Windows event logs are used to populate the visualizations in the Insights workbook. Currently, data is collected through two Windows event log channels: - microsoft-windows-health/operational and microsoft-windows-sddc-management/operational |
| Log Analytics workspace | Workspace to store the data. Only workspaces with Insights are listed. |
Event channel
The Microsoft-windows-sddc-management/operational and Microsoft-windows-health/operational Windows event channel is added to your Log Analytics workspace under Windows event logs.
By collecting these logs, Insights shows the health status of the individual nodes, drives, volumes, and VMs. By default, five performance counters are added.
Performance counters
By default, five performance counters are added:
The following table describes the performance counters that are monitored:
| Performance counters | Description |
|---|---|
| Memory(*)\Available Bytes | Available Bytes is the amount of physical memory, in bytes, immediately available for allocation to a process or for system use. |
| Network Interface(*)\Bytes Total/sec | The rate at which bytes are sent and received over each network adapter, including framing characters. Bytes Total/sec is a sum of Bytes Received/sec and Bytes Sent/sec. |
| Processor(_Total)% Processor Time | The percentage of elapsed time that all of process threads used the processor to execution instructions. |
| RDMA Activity(*)\RDMA Inbound Bytes/sec | Rate of data received over RDMA by the network adapter per second. |
| RDMA Activity(*)\RDMA Outbound Bytes/sec | Rate of data sent over RDMA by the network adapter per second. |
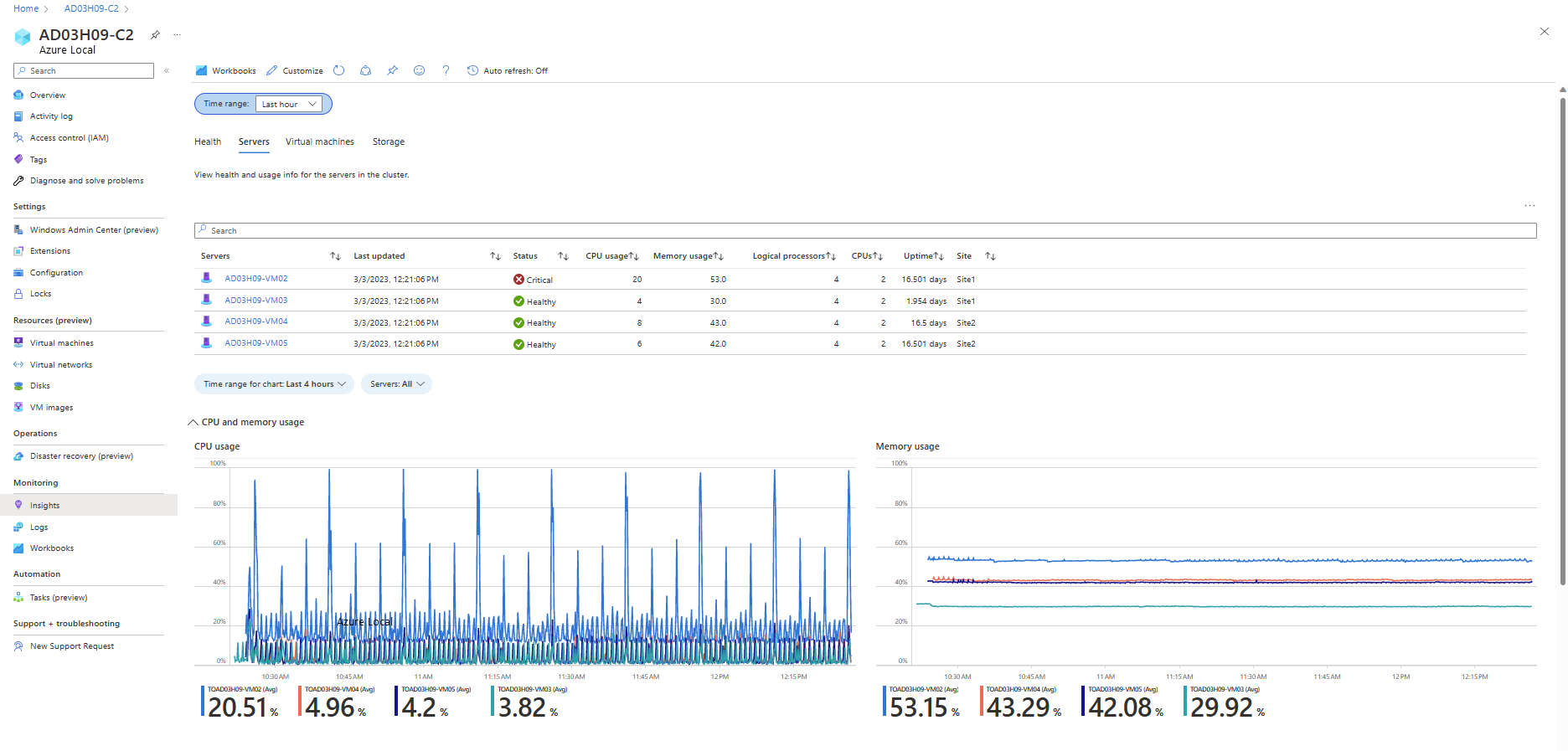
After you enable Insights, it can take up to 15 minutes to collect the data. When the process is finished, you're able to see a rich visualization of the health of your cluster from the Insights menu on the left pane:
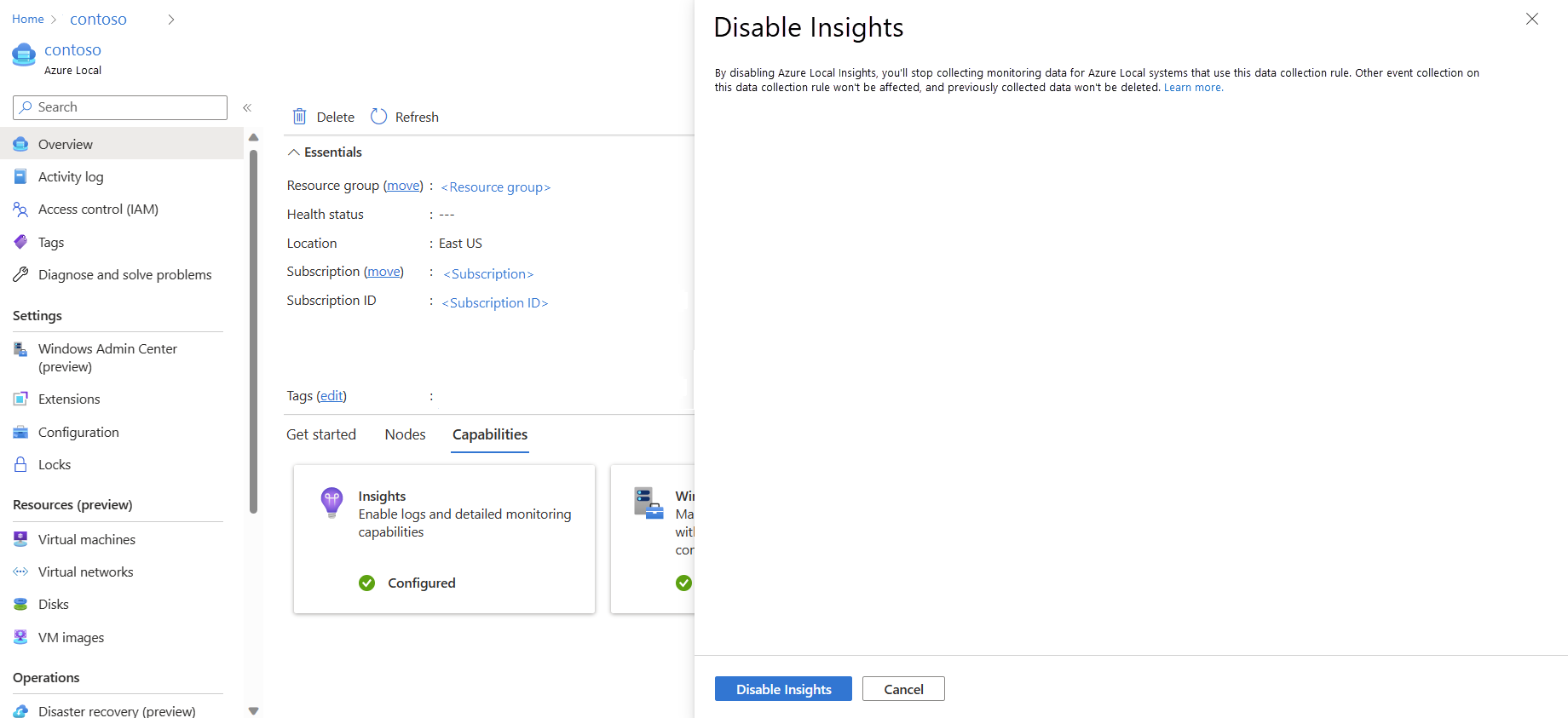
Disable Insights
To disable Insights, follow these steps:
When you disable the Insights feature, the association between the data collection rule and the cluster is deleted and the Health Service and SDDC Management logs are no longer collected; however, existing data isn't deleted. If you'd like to delete that data, go into your DCR and Log Analytics workspace and delete the data manually.
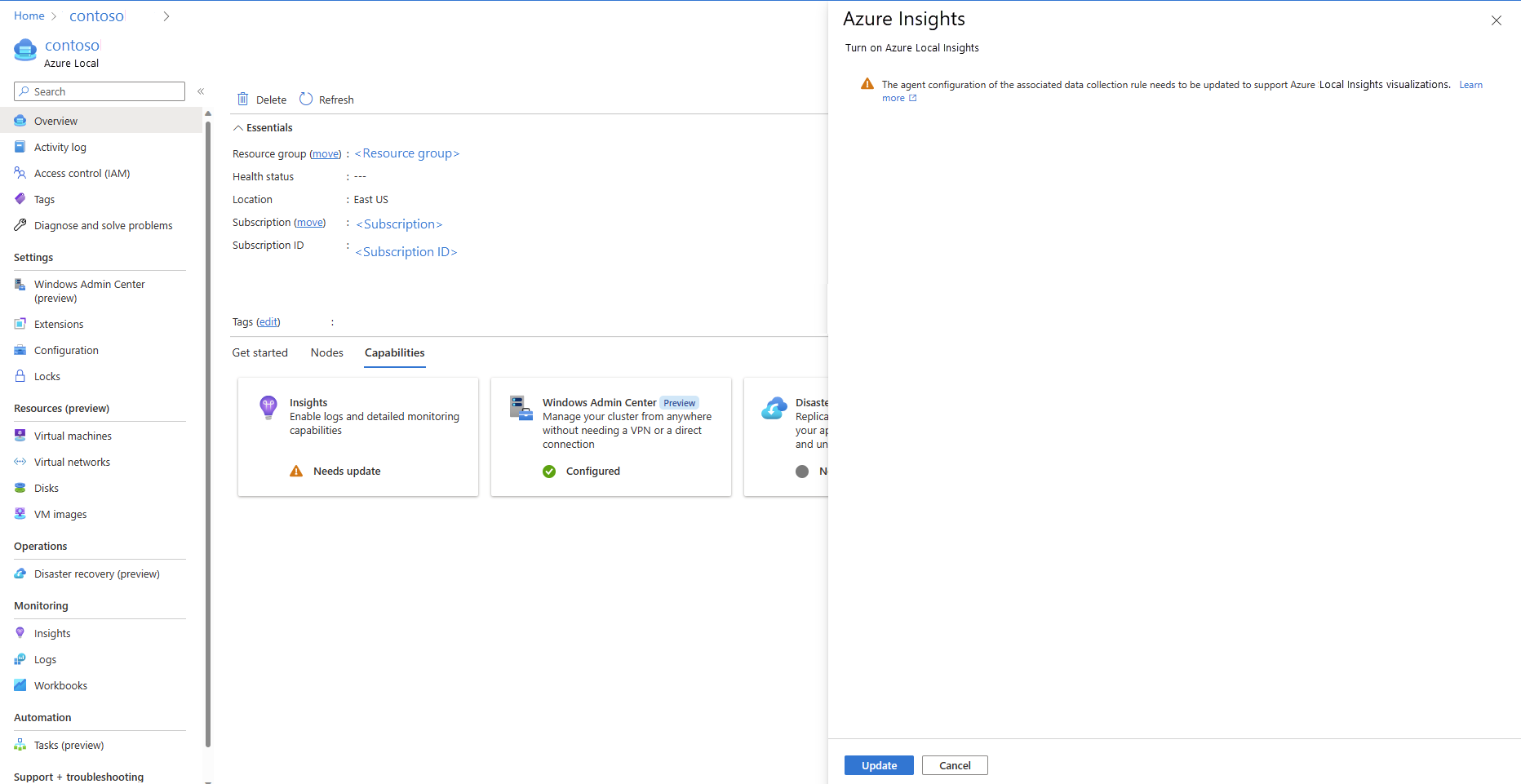
Update Insights
The Insights tile shows a Needs update message in the following cases:
- A data collection rule is changed.
- A health event from the Windows events log is deleted.
- Any of the five performance counters from the Log Analytics workspace are deleted.
To enable Insights again, follow these steps:
Troubleshoot
This section gives guidance for resolving the issues with using Insights for Azure Local.
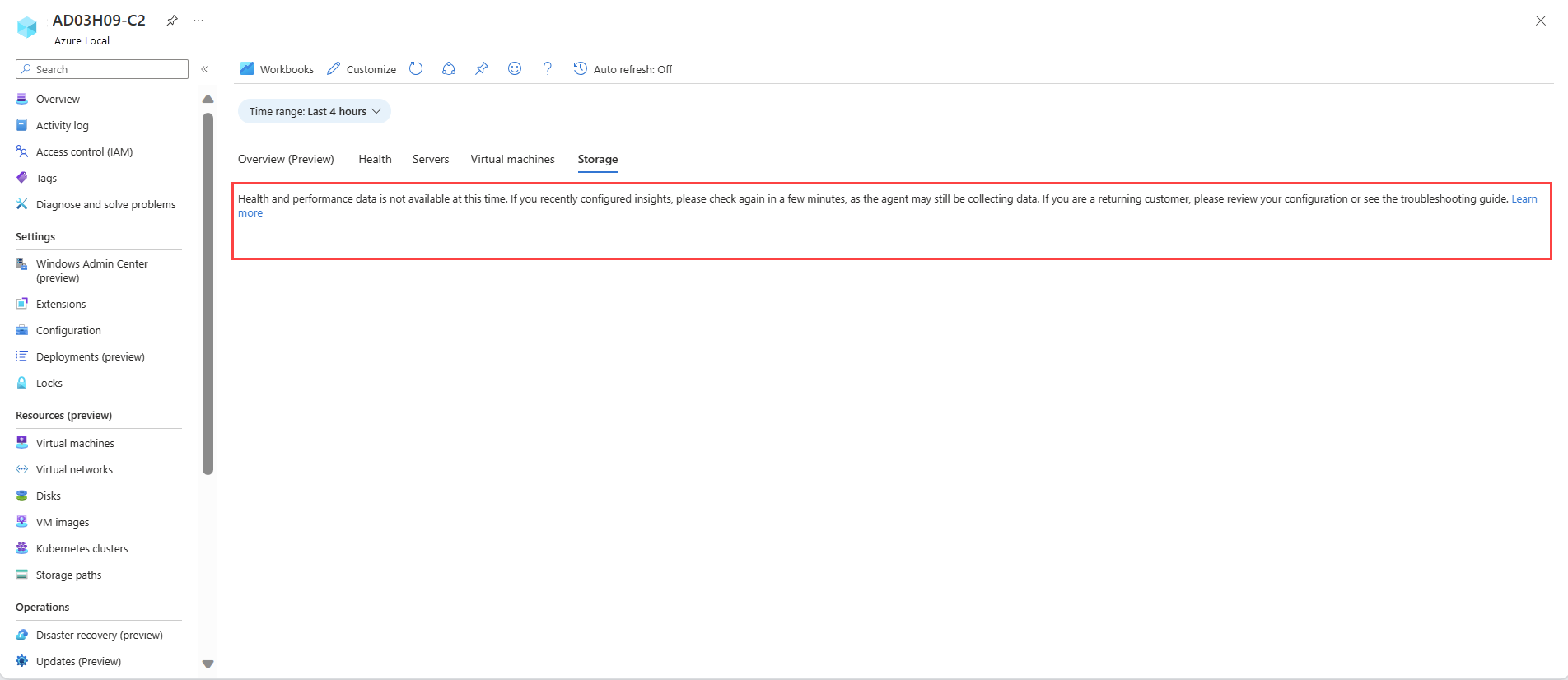
Troubleshoot blank Workbooks page with no data populated
Issue. You see a blank Workbooks page with no data populated, as shown in the following screenshot:
Possible causes. There could be several causes for this issue, such as recent configuration of Insights or improper configuration of the associated DCR.
Solution. To troubleshoot the issue, perform the following steps in sequence:
- If you recently configured Insights, wait for up to one hour for AMA to gather data.
- Verify the configuration of the associated DCR. Make sure that event channels and performance counters are added as data sources to the associated DCR, as described in the Data Collection Rules section.
- If the issue persists after performing the above steps, and you still don't see any data, contact customer support for assistance.
For more detailed troubleshooting guidance, see Troubleshooting guidance for the Azure Monitor Agent.
Insights visualizations
Once Insights is enabled, the following tables provide details about all resources.
Health
Provides health faults on a cluster.
| Metric | Description | Unit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fault | A short description of health faults. On clicking the link, a side panel opens with more information. | No unit | PoolCapacityThresholdExceeded |
| Faulting resource type | The type of resource that encountered a fault. | No unit | StoragePool |
| Faulting resource ID | Unique ID for the resource that encountered a health fault. | Unique ID | {a0a0a0a0-bbbb-cccc-dddd-e1e1e1e1e1e1}: SP:{b1b1b1b1-cccc-dddd-eeee-f2f2f2f2f2f2} |
| Severity | Severity of fault could be warning or critical. | No unit | Warning |
| Initial fault time | Timestamp of when the node was last updated. | Datetime | 4/9/2022, 12:15:42 PM |
Nodes
| Metric | Description | Unit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | The names of the nodes in the cluster. | No unit | VM-1 |
| Last updated | The date and time of when the node was last updated. | Datetime | 4/9/2022, 12:15:42 PM |
| Status | The health status of the nodes in the cluster. | It can be healthy, warning, critical, and other | Healthy |
| CPU usage | The % of time the process has used the CPU. | Percent | 56% |
| Memory usage | Memory usage of the node process is equal to counter Process\Private Bytes plus the size of memory-mapped data. | Percent | 16% |
| Logical processors | The number of logical processors. | Count | 2 |
| CPUs | The number of CPUs. | Count | 2 |
| Uptime | The time during which a machine, especially a computer, is in operation. | Timespan | 2.609 hr. |
| Site | The name of the site to which the node belongs. | Site name | SiteA |
| Domain name | The local domain to which the node belongs. | No unit | Contoso.local |
Virtual machines
Provides the state of the virtual machines on each node in the cluster. A VM can be in one of the following states: Running, Stopped, Failed, or Other (Unknown, Starting, Snapshotting, Saving, Stopping, Pausing, Resuming, Paused, Suspended).
| Metric | Description | Unit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | The name of the node. | No unit | Sample-VM-1 |
| Last Updated | This gives the date and time of when the node was last updated | Datetime | 4/9/2022, 12:24:02 PM |
| Total VMs | The number of VMs in a node. | Count | 0 of 0 running |
| Running | The number of VMs running in a node. | Count | 2 |
| Stopped | The number of VMs stopped in a node. | Count | 3 |
| Failed | The number of VMs failed in a node. | Count | 2 |
| Other | If VM is in one of the following states (Unknown, Starting, Snapshotting, Saving, Stopping, Pausing, Resuming, Paused, Suspended), it's considered as "Other." | Count | 2 |
Storage
The following table provides the health of volumes and drives in the cluster:
| Metric | Description | Unit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volumes | The name of the volume | No unit | ClusterPerformanceHistory |
| Last updated | The date and time of when the storage was last updated. | Datetime | 4/14/2022, 2:58:55 PM |
| Status | The status of the volume. | Healthy, warning, critical, and other. | Healthy |
| Total capacity | The total capacity of the device in bytes during the reporting period. | Bytes | 2.5 GB |
| Available capacity | The available capacity in bytes during the reporting period. | Bytes | 20B |
| Iops | Input/output operations per second. | Per second | 45/s |
| Throughput | Number of bytes per second the Application Gateway has served. | Bytes per second | 5B/s |
| Latency | The time it takes for the I/O request to be completed. | Second | 0.0016 s |
| Resiliency | The capacity to recover from failures. Maximizes data availability. | No unit | Three Way Mirror |
| Deduplication | The process of reducing the physical number of bytes of data that needs to be stored on disk. | Available or not | Yes/No |
| File system | The type of filesystem. | No unit | ReFS |
Azure Monitor pricing
When you enable monitoring visualization, logs are collected from:
- Health Management (Microsoft-windows-health/operational).
- SDDC Management (Microsoft-Windows-SDDC-Management/Operational; Event ID: 3000, 3001, 3002, 3003, 3004).
You're billed based on the amount of data ingested and the data retention settings of your Log Analytics workspace.
Azure Monitor has pay-as-you-go pricing, and the first 5 GB per billing account per month is free. Because pricing can vary due to multiple factors, such as the region of Azure you're using, visit the Azure Monitor pricing calculator for the most up-to-date pricing calculations.