Simplify network configuration requirements with Azure Arc gateway (Public Preview)
If you use enterprise proxies to manage outbound traffic, the Azure Arc gateway lets you onboard infrastructure to Azure Arc using only seven (7) endpoints. With Azure Arc gateway, you can:
- Connect to Azure Arc by opening public network access to only seven fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
- View and audit all traffic an Azure Connected Machine agent sends to Azure via the Arc gateway.
This article explains how to set up and use Arc gateway (Public Preview).
Important
The Arc gateway feature for Azure Arc-enabled servers is currently in Public Preview in all regions where Azure Arc-enabled servers is present. See the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews for legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, Public Preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
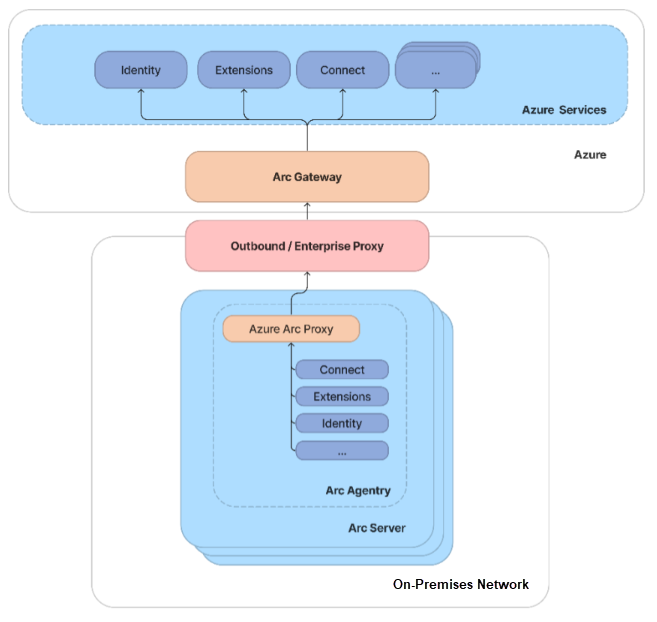
How the Azure Arc gateway works
Azure Arc gateway consists of two main components:
The Arc gateway resource: An Azure resource that serves as a common front-end for Azure traffic. This gateway resource is served on a specific domain. Once the Arc gateway resource is created, the domain is returned to you in the success response.
The Arc Proxy: A new component added to Arc agentry. This component runs as a service called "Azure Arc Proxy" and acts as a forward proxy used by the Azure Arc agents and extensions. No configuration is required on your part for the Arc Proxy. This Proxy is part of Arc core agentry and runs within the context of an Arc-enabled resource.
When the gateway is in place, traffic flows via the following hops: Arc agentry → Arc Proxy → Enterprise proxy → Arc gateway → Target service
Current limitations
During the public preview, the following limitations apply. Consider these factors when planning your configuration.
- TLS Terminating Proxies aren't supported (Public Preview)
- ExpressRoute/Site-to-Site VPN or private endpoints used with the Arc gateway (Public Preview) isn't supported.
- There's a limit of five (5) Arc gateway (Public Preview) resources per Azure subscription.
- The Arc gateway can only be used for connectivity in the Azure public cloud.
Required permissions
To create Arc gateway resources and manage their association with Arc-enabled servers, the following permissions are required:
- Microsoft.HybridCompute/settings/write
- Microsoft.hybridcompute/gateways/read
- Microsoft.hybridcompute/gateways/write
How to use the Arc gateway (Public Preview)
There are four steps to use the Arc gateway:
- Create an Arc gateway resource.
- Ensure the required URLs are allowed in your environment.
- Onboard Azure Arc resources with your Arc gateway resource or configure existing Azure Arc resources to use Arc gateway.
- Verify that the setup succeeded.
Step 1: Create an Arc gateway resource
You can create an Arc gateway resource using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell.
From your browser, sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to the Azure Arc | Azure Arc gateway page, and then select Create.
Select the subscription and resource group where you want the Arc gateway resource to be managed within Azure. An Arc gateway resource can be used by any Arc-enabled resource in the same Azure tenant.
For Name, input the name that for the Arc gateway resource.
For Location, input the region where the Arc gateway resource should live. An Arc gateway resource can be used by any Arc-enabled Resource in the same Azure tenant.
Select Next.
On the Tags page, specify one or more custom tags to support your standards.
Select Review & Create.
Review your input details, and then select Create.
The gateway creation process takes 9-10 minutes to complete.
Step 2: Ensure the required URLs are allowed in your environment
When the resource is created, the success response includes the Arc gateway URL. Ensure your Arc gateway URL and all URLs in the following table are allowed in the environment where your Arc resources live. The required URLs are:
| URL | Purpose |
|---|---|
| [Your URL Prefix].gw.arc.azure.com | Your gateway URL (This URL can be obtained by running az arcgateway list after you create your gateway Resource) |
| management.azure.com | Azure Resource Manager Endpoint, required for Azure Resource Manager control channel |
| login.microsoftonline.com | Microsoft Entra ID’s endpoint, for acquiring Identity access tokens |
| gbl.his.arc.azure.com | The cloud service endpoint for communicating with Azure Arc agents |
| <region>.his.arc.azure.com | Used for Arc’s core control channel |
| packages.microsoft.com | Required to acquire Linux based Arc agentry payload, only needed to connect Linux servers to Arc |
Step 3a: Onboard Azure Arc resources with your Arc gateway resource.
Generate the installation script.
Follow the instructions at Quickstart: Connect hybrid machines with Azure Arc-enabled servers to create a script that automates the downloading and installation of the Azure Connected Machine agent and establishes the connection with Azure Arc.
Important
When generating the onboarding script, select Proxy Server under Connectivity method to reveal the dropdown for Gateway resource.
Run the installation script to onboard your servers to Azure Arc.
In the script, the Arc gateway resource's ARM ID is shown as
--gateway-id.
Step 3b: Configure existing Azure Arc resources to use Arc gateway
You can configure existing Azure Arc resources to use Arc gateway by using the Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell.
On the Azure portal, go to the Azure Arc - Azure Arc gateway page.
Select the Arc gateway Resource to associate with your Arc-enabled server.
Go to the Associated Resources page for your gateway resource.
Select Add.
Select the Arc-enabled resource to associate with your Arc gateway resource.
Select Apply.
Update your Arc-enabled server to use Arc gateway by running
azcmagent config set connection.type gateway.
Step 4: Verify that the setup succeeded
On the onboarded server, run the following command: azcmagent show
The result should indicate the following values:
- Agent Status should show as Connected.
- Using HTTPS Proxy should show as http://localhost:40343.
- Upstream Proxy should show as your enterprise proxy (if you set one). Gateway URL should reflect your gateway resource's URL.
Additionally, to verify successful set-up, you can run the following command: azcmagent check
The result should indicate that the connection.type is set to gateway, and the Reachable column should indicate true for all URLs.
Associate a machine with a new Arc gateway
To associate a machine with a new Arc gateway:
On the Azure portal, go to the Azure Arc - Azure Arc gateway page.
Select the new Arc gateway Resource to associate with the machine.
Go to the Associated Resources page for your gateway resource.
Select Add.
Select the Arc-enabled machine to associate with the new Arc gateway resource.
Select Apply.
Update your Arc-enabled server to use Arc gateway by running
azcmagent config set connection.type gateway.
Remove Arc gateway association (to use the direct route instead)
Set the connection type of the Arc-enabled Server to "direct” instead of “gateway" by running the following command:
azcmagent config set connection.type directNote
If you take this step, all Azure Arc network requirements must be met in your environment to continue leveraging Azure Arc.
Detach the Arc gateway resource from the machine:
On the Azure portal, go to the Azure Arc - Azure Arc gateway page.
Select the Arc gateway Resource.
Go to the Associated Resources page for your gateway resource and select the server.
Select Remove.
Delete an Arc gateway resource
Note
This operation can take 4 to 5 minutes to complete.
On the Azure portal, go to the Azure Arc - Azure Arc gateway page.
Select the Arc gateway Resource.
Select Delete.
Troubleshooting
You can audit your Arc gateway’s traffic by viewing the Azure Arc proxy logs.
To view Arc proxy logs on Windows:
- Run
azcmagent logsin PowerShell. - In the resulting .zip file, the logs are located in the
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\ArcProxyfolder.
To view Arc proxy logs on Linux:
- Run
sudo azcmagent logsand share the resulting file. - In the resulting log file, the logs are located in the
/usr/local/arcproxy/logs/folder.
Additional scenarios
During Public Preview, Arc gateway covers the endpoints required for onboarding a server, as well as a portion of endpoints required for additional Arc-enabled scenarios. Based on the scenario(s) you adopt, additional endpoints must be allowed in your proxy.
Scenarios that don’t require additional endpoints
- Windows Admin Center
- SSH
- Extended Security Updates
- Microsoft Defender
- Azure Extension for SQL Server
Scenarios that require additional endpoints
Endpoints listed with the following scenarios must be allowed in your enterprise proxy when using Arc gateway:
Azure Arc-enabled Data Services
*.ods.opinsights.azure.com
*.oms.opinsights.azure.com
*.monitoring.azure.com
Azure Monitor Agent
<log-analytics-workspace-id>.ods.opinsights.azure.com
<data-collection-endpoint>.<virtual-machine-region-name>.ingest.monitor.azure.com
Azure Key Vault Certificate Sync
- <vault-name>.vault.azure.net
Azure Automation Hybrid Runbook Worker extension
- *.azure-automation.net
Windows OS Update Extension / Azure Update Manager
- Your environment must meet all the prerequisites for Windows Update
Known issues
Following is a description of currently known issues for the Arc gateway.
Refresh needed after Azure Connected Machine agent onboarding
When using the onboarding script (or the azcmagent connect command) to onboard a server with the gateway resource ID specified, the resource will successfully use Arc gateway. However, due to a known bug (with a fix currently underway), the Arc-enabled server won't display as an Associated Resource in Azure portal unless the resource’s settings are refreshed. Use the following procedure to perform this refresh:
In the Azure portal, navigate to the Azure Arc | Arc gateway page.
Select the Arc gateway resource to associate with your Arc-enabled server.
Navigate to the Associated Resources page for your gateway resource.
Select Add.
Select the Arc-enabled resource to associate with your Arc gateway resource and select Apply.
Arc proxy refresh needed after detaching a gateway resource from the machine
When detaching an Arc gateway resource from a machine, you must refresh the Arc proxy to clear the Arc gateway configuration. To do so, perform the following procedure:
Stop arc proxy.
- Windows:
Stop-Service arcproxy - Linux:
sudo systemctl stop arcproxyd
- Windows:
Delete the
cloudconfig.jsonfile.- Windows: "C:\ProgramData\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\Config\cloudconfig.json"
- Linux: "/var/opt/azcmagent/cloudconfig.json"
Start arc proxy.
- Windows:
Start-Service arcproxy - Linux:
sudo systemctl start arcproxyd
- Windows:
Restart himds (optional, but recommended).
- Windows:
Restart-Service himds - Linux:
sudo systemctl restart himdsd
- Windows:
Refresh needed for machines re-enabled without gateway
If an Arc-enabled machine with an Arc gateway is deleted from Azure Arc and re-Arc-enabled without an Arc gateway, a refresh is needed to update its status in the Azure portal.
Important
This issue occurs only when the resource is re-Arc-enabled with the same ARM ID as its initial enablement.
In this scenario, the machine incorrectly displays in Azure portal as a resource associated with the Arc gateway. To prevent this, if you intend to Arc-enable a machine without an Arc gateway that was previously Arc-enabled with an Arc gateway, you must update the Arc gateway association after onboarding. To do so, use the following procedure:
In the Azure portal, navigate to the Azure Arc | Arc gateway page.
Select the Arc gateway resource.
Navigate to the Associated Resources page for your gateway resource.
Select the server, and then select Remove.
Manual gateway association required post-deletion
If an Arc gateway is deleted while a machine is still connected to it, Azure portal must be used to associate the machine with any other Arc gateway resources.
To avoid this issue, detach all Arc-enabled resources from an Arc gateway before deleting the gateway resource. If you encounter this error, use Azure portal to associate the machine with a new Arc gateway resource.