Connect to AWS with the multicloud connector in the Azure portal
The multicloud connector enabled by Azure Arc lets you connect non-Azure public cloud resources to Azure by using the Azure portal. Currently, AWS public cloud environments are supported.
As part of connecting an AWS account to Azure, you deploy a CloudFormation template to the AWS account. This template creates all of the required resources for the connection.
Prerequisites
To use the multicloud connector, you need the appropriate permissions in both AWS and Azure.
AWS prerequisites
To create the connector and to use multicloud inventory, you need the following permissions in AWS:
- AmazonS3FullAccess
- AWSCloudFormationFullAccess
- IAMFullAccess
For Arc onboarding, there are more prerequisites that must be met.
AWS solution permissions
When you upload your CloudFormation template, more permissions are requested, based on the solutions that you selected:
For Inventory, you can choose your permission:
Global Read: Provides read-only access to all resources in the AWS account. When new services are introduced, the connector can scan for those resources without requiring an updated CloudFormation template.
Least Privilege Access: Provides read access to only the resources under the selected services. If you choose to scan for more resources in the future, a new CloudFormation template must be uploaded.
For Arc Onboarding, our service requires EC2 Write access in order to install the Azure Connected Machine agent.
Azure prerequisites
To use the multicloud connector in an Azure subscription, you need the Contributor built-in role.
If this is the first time you're using the service, you need to register these resource providers, which requires Contributor access on the subscription:
- Microsoft.HybridCompute
- Microsoft.HybridConnectivity
- Microsoft.AwsConnector
- Microsoft.Kubernetes
Note
The multicloud connector can work side-by-side with the AWS connector in Defender for Cloud. If you choose, you can use both of these connectors.
Add your public cloud in the Azure portal
To add your AWS public cloud to Azure, use the Azure portal to enter details and generate a CloudFormation template.
In the Azure portal, navigate to Azure Arc.
Under Management, select Multicloud connectors (preview).
In the Connectors pane, select Create.
On the Basics page:
- Select the subscription and resource group in which to create your connector resource.
- Enter a unique name for the connector and select a supported region.
- Provide the ID for the AWS account that you want to connect, and indicate whether it's a single account or an organization account.
- Select Next.
On the Solutions page, select which solutions you'd like to use with this connector and configure them. Select Add to enable Inventory, Arc onboarding, or both.
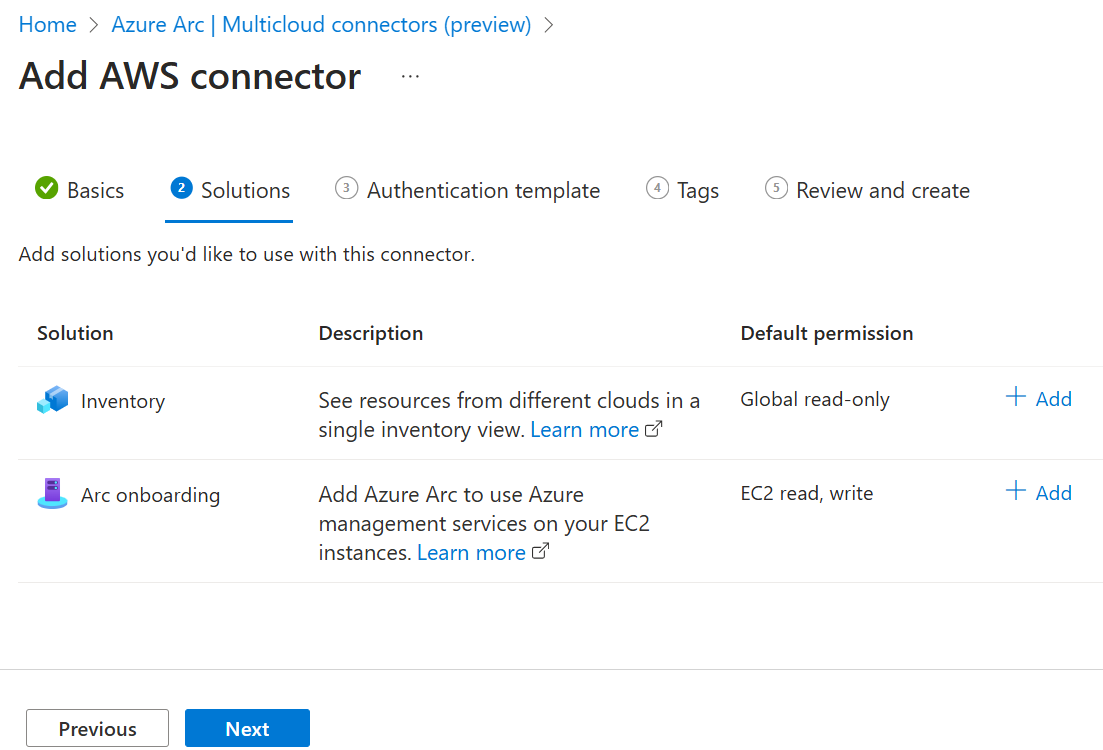
For Inventory, you can modify the following options:
Choose whether or not to enable Add all supported AWS services. By default, this option is enabled, so that all services (available now and services added in the future) are scanned.
Choose the AWS Services for which you want to scan and import resources. By default, all available services are selected.
Choose your permissions. If Add all supported AWS services is checked, you must have Global read access.
Choose whether or not to enable periodic sync. By default, this option is enabled so that the connector scans your AWS account regularly. If you uncheck the box, your AWS account is scanned only once.
If Enable periodic sync is checked, confirm or change the Recur every selection to specify how often your AWS account are scanned.
Choose whether or not to enable Include all supported AWS regions. By selecting this option, all current and future AWS regions are scanned.
Choose which regions to scan for resources in your AWS account. By default, all available regions are selected. If you selected Include all supported AWS regions, all regions must be selected.
When you have finished making selections, select Save to return to the Solutions page.
For Arc onboarding:
- Select a Connectivity method to determine whether the Connected Machine agent should connect to the internet via a public endpoint or by proxy server. If you select Proxy server, provide a Proxy server URL to which the EC2 instance can connect.
- Choose whether or not to enable periodic sync. By default, this option is enabled so that the connector scans your AWS account regularly. If you uncheck the box, your AWS account is scanned only once.
- If Enable periodic sync is checked, confirm or change the Recur every selection to specify how often your AWS account are scanned.
- Choose whether or not to enable Include all supported AWS regions. By selecting this option, all current and future AWS regions are scanned.
- Choose which regions to scan for EC2 instances in your AWS account. By default, all available regions are selected. If you selected Include all supported AWS regions, all regions must be selected.
- Choose to filter for EC2 instances by AWS tag. If you enter a tag value here, only EC2 instances that contain that tag are onboarded to Arc. By leaving this value empty, all EC2 Instances discovered are onboarded to Arc.
On the Authentication template page, download the CloudFormation template that you'll upload to AWS. This template is created based on the information you provided in Basics and the solutions you selected. You can upload the template right away, or wait until you finish adding your public cloud.
On the Tags page, enter any tags you'd like to use.
On the Review and create page, confirm your information, then select Create.
If you didn't upload your template during this process, follow the steps in the next section to do so.
Upload CloudFormation template to AWS
After you save the CloudFormation template generated in the previous section, you need to upload it to your AWS public cloud. If you upload the template before you finish connecting your AWS cloud in the Azure portal, your AWS resources are scanned immediately. If you complete the Add public cloud process in the Azure portal before uploading the template, it takes a bit longer to scan your AWS resources and make them available in Azure.
Create stack
Follow these steps to create a stack and upload your template:
Open the AWS CloudFormation console and select Create stack.
Select Template is ready, then select Upload a template file. Select Choose file and browse to select your template. Then select Next.
In Specify stack details, enter a stack name.
If you selected the Arc Onboarding solution, fill out the following details in the Stack parameters:
EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignment: Specifies whether IAM roles used for SSM tasks are automatically assigned to EC2 instances. By default this option is set to true, and all discovered EC2 machines will have the IAM role assigned. If you set this option to false, you must manually assign the IAM role to the EC2 instances that you want onboarded to Arc.
EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignmentSchedule: Specifies whether the EC2 IAM Role used for SSM tasks should be autoassigned periodically. By default, this option is set to enable, meaning that any EC2 machines discovered in the future will have the IAM role automatically assigned. If you set this option to disable, you must manually assign the IAM role to any newly deployed EC2 that you want onboarded to Azure Arc.
EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignmentScheduleInterval: Specifies the periodic interval for autoassignment of the EC2 IAM Role used for SSM tasks (for example, 15 minutes, 6 hours, or 1 day). If you set the EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignment to true and EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignmentSchedule to enable, you can choose how often you want to scan for new EC2 instances to be assigned the IAM role. The default interval is 1 day.
EC2SSMIAMRolePolicyUpdateAllowed: Specifies whether existing EC2 IAM roles used for SSM tasks are allowed to update with required permission policies if they're missing. By default, this option is set to true. If you choose to set to false, you must manually add this IAM role permission to the EC2 instance.
Otherwise, leave the other options set to their default settings and select Next.
In Configure stack options, leave the options set to their default settings and select Next.
In Review and create, confirm that the information is correct, select the acknowledgment checkbox, and then select Submit.
Create StackSet
If your AWS account is an organization account, you also need to create a StackSet and upload your template again. To do so:
Open the AWS CloudFormation console and select StackSets, then select Create StackSet.
Select Template is ready, then select Upload a template file. Select Choose file and browse to select your template. Then select Next.
In Specify stack details, enter
AzureArcMultiCloudStacksetas the StackSet nameIf you selected the Arc Onboarding solution, fill out the following details in the Stack parameters:
EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignment: Specifies whether IAM roles used for SSM tasks are automatically assigned to EC2 instances. By default this option is set to true, and all discovered EC2 machines will have the IAM role assigned. If you set this option to false, you must manually assign the IAM role to the EC2 instances that you want onboarded to Arc.
EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignmentSchedule: Specifies whether the EC2 IAM Role used for SSM tasks should be autoassigned periodically. By default, this option is set to enable, meaning that any EC2 machines discovered in the future will have the IAM role automatically assigned. If you set this option to disable, you must manually assign the IAM role to any newly deployed EC2 instance that you want onboarded to Arc.
EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignmentScheduleInterval: Specifies the periodic interval for autoassignment of the EC2 IAM Role used for SSM tasks (such as, 15 minutes, 6 hours, or 1 day). If you set the EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignment to true and EC2SSMIAMRoleAutoAssignmentSchedule to enable, you can choose how often you want to scan for new EC2 instances to be assigned the IAM role. The default interval is 1 day.
EC2SSMIAMRolePolicyUpdateAllowed: Specifies whether existing EC2 IAM roles used for SSM tasks are allowed to update with required permission policies if they're missing. By default, this option is set to true. If you choose to set to false, you must manually add this IAM role permission to the EC2 instance.
Otherwise, leave the other options set to their default settings and select Next.
In Configure stack options, leave the options set to their default settings and select Next.
In Set deployment options, enter the ID for the AWS account where the StackSet will be deployed, and select any AWS region to deploy the stack. Leave the other options set to their default settings and select Next.
In Review, confirm that the information is correct, select the acknowledgment checkbox, and then select Submit.
Confirm deployment
After you complete the Add public cloud option in Azure and upload your template to AWS, your connector and selected solutions are created. On average, it takes about one hour for your AWS resources to become available in Azure. If you upload the template after creating the public cloud in Azure, it may take a bit more time before you see the AWS resources.
AWS resources are stored in a resource group using the naming convention aws_yourAwsAccountId, with permissions inherited from its subscription. Scans run regularly to update these resources, based on your Enable periodic sync selections.
Next steps
- Query your inventory with the multicloud connector Inventory solution.
- Learn how to use the multicloud connector Arc onboarding solution.