Overview of change tracking and inventory using Azure Monitoring Agent
Important
- Change Tracking and Inventory using Log Analytics agent has retired on 31 August 2024 and will work on limited support till 01 February 2025. Follow the guidelines for migration from Change Tracking and inventory using Log Analytics to Change Tracking and inventory using Azure Monitoring Agent version
- We recommend that you use Change Tracking with Azure Monitoring Agent with the Change tracking extension version 2.20.0.0 (or above) to access the GA version of this service.
This article explains on the latest version of change tracking support using Azure Monitoring Agent as a singular agent for data collection.
Note
File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is now currently available. If you have FIM configured with either AMA or LA, follow the guidance to migrate from:
What is Change Tracking & Inventory
Azure Change Tracking & Inventory service enhances the auditing and governance for in-guest operations by monitoring changes and providing detailed inventory logs for servers across Azure, on-premises, and other cloud environments.
Change Tracking
a. Monitors changes, including modifications to files, registry keys, software installations, and Windows services or Linux daemons.
b. Provides detailed logs of what and when the changes were made, who made them, enabling you to quickly detect configuration drifts or unauthorized changes.Inventory
a. Collects and maintains an updated list of installed software, operating system details, and other server configurations in linked LA workspace
b. Helps create an overview of system assets, which is useful for compliance, audits, and proactive maintenance.
Support matrix
| Component | Applies to |
|---|---|
| Operating systems | Windows Linux |
| Resource types | Azure VMs Azure Arc-enabled VMs Virtual machines scale set |
| Data types | Windows registry Windows services Linux Daemons |
| Files | Windows Linux |
Key benefits
- Compatibility with the unified monitoring agent - Compatible with the Azure Monitor Agent that enhances security, reliability, and facilitates multi-homing experience to store data.
- Compatibility with tracking tool- Compatible with the Change tracking (CT) extension deployed through the Azure Policy on the client's virtual machine. You can switch to Azure Monitor Agent (AMA), and then the CT extension pushes the software, files, and registry to AMA.
- Multi-homing experience – Provides standardization of management from one central workspace. You can transition from Log Analytics (LA) to AMA so that all VMs point to a single workspace for data collection and maintenance.
- Rules management – Uses Data Collection Rules to configure or customize various aspects of data collection. For example, you can change the frequency of file collection.
Limits
The following table shows the tracked item limits per machine for change tracking and inventory.
| Resource | Limit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| File | 500 | |
| File size | 5 MB | |
| Registry | 250 | |
| Windows software | 250 | Doesn't include software updates. |
| Linux packages | 1,250 | |
| Windows Services | 250 | |
| Linux Daemons | 250 |
Supported operating systems
Change Tracking and Inventory is supported on all operating systems that meet Azure Monitor agent requirements. See supported operating systems for a list of the Windows and Linux operating system versions that are currently supported by the Azure Monitor agent.
To understand client requirements for TLS, see TLS for Azure Automation.
Enable Change Tracking and Inventory
You can enable Change Tracking and Inventory in the following ways:
Manually for non-Azure Arc-enabled machines, Refer to the Initiative Enable Change Tracking and Inventory for Arc-enabled virtual machines in Policy > Definitions > Select Category = ChangeTrackingAndInventory. To enable Change Tracking and Inventory at scale, use the DINE Policy based solution. For more information, see Enable Change Tracking and Inventory using Azure Monitoring Agent (Preview).
For a single Azure VM from the Virtual machine page in the Azure portal. This scenario is available for Linux and Windows VMs.
For multiple Azure VMs by selecting them from the Virtual machines page in the Azure portal.
Tracking file changes
For tracking changes in files on both Windows and Linux, Change Tracking and Inventory uses SHA256 hashes of the files. The feature uses the hashes to detect if changes have been made since the last inventory.
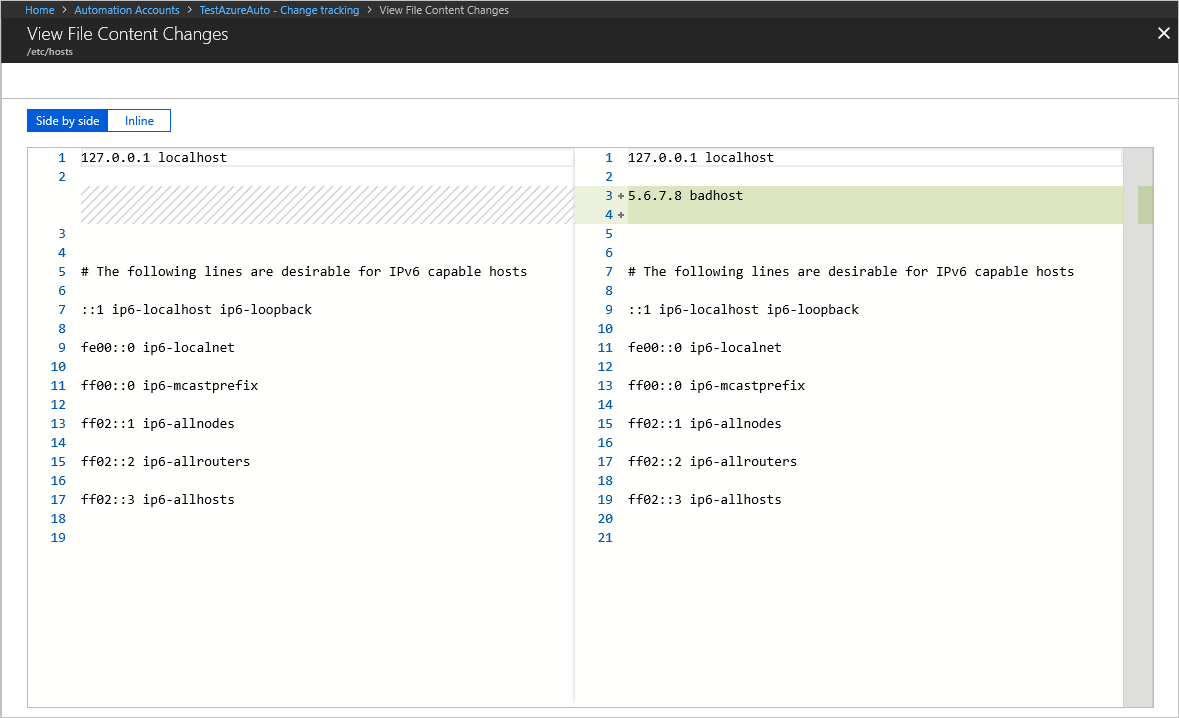
Tracking file content changes
Change Tracking and Inventory allows you to view the contents of a Windows or Linux file. For each change to a file, Change Tracking and Inventory stores the contents of the file in an Azure Storage account. When you're tracking a file, you can view its contents before or after a change. The file content can be viewed either inline or side by side. Learn more.
Tracking of registry keys
Change Tracking and Inventory allows monitoring of changes to Windows registry keys. Monitoring allows you to pinpoint extensibility points where third-party code and malware can activate. The following table lists pre-configured (but not enabled) registry keys. To track these keys, you must enable each one.
| Registry Key | Purpose |
|---|---|
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Group Policy\Scripts\Startup |
Monitors scripts that run at startup. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Group Policy\Scripts\Shutdown |
Monitors scripts that run at shutdown. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run |
Monitors keys that are loaded before the user signs in to the Windows account. The key is used for 32-bit applications running on 64-bit computers. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Active Setup\Installed Components |
Monitors changes to application settings. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\Directory\ShellEx\ContextMenuHandlers |
Monitors context menu handlers that hook directly into Windows Explorer and usually run in-process with explorer.exe. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Classes\Directory\Shellex\CopyHookHandlers |
Monitors copy hook handlers that hook directly into Windows Explorer and usually run in-process with explorer.exe. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ShellIconOverlayIdentifiers |
Monitors for icon overlay handler registration. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\ShellIconOverlayIdentifiers |
Monitors for icon overlay handler registration for 32-bit applications running on 64-bit computers. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Browser Helper Objects |
Monitors for new browser helper object plugins for Internet Explorer. Used to access the Document Object Model (DOM) of the current page and to control navigation. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Browser Helper Objects |
Monitors for new browser helper object plugins for Internet Explorer. Used to access the Document Object Model (DOM) of the current page and to control navigation for 32-bit applications running on 64-bit computers. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Extensions |
Monitors for new Internet Explorer extensions, such as custom tool menus and custom toolbar buttons. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Extensions |
Monitors for new Internet Explorer extensions, such as custom tool menus and custom toolbar buttons for 32-bit applications running on 64-bit computers. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Drivers32 |
Monitors 32-bit drivers associated with wavemapper, wave1 and wave2, msacm.imaadpcm, .msadpcm, .msgsm610, and vidc. Similar to the [drivers] section in the system.ini file. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Drivers32 |
Monitors 32-bit drivers associated with wavemapper, wave1 and wave2, msacm.imaadpcm, .msadpcm, .msgsm610, and vidc for 32-bit applications running on 64-bit computers. Similar to the [drivers] section in the system.ini file. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\KnownDlls |
Monitors the list of known or commonly used system DLLs. Monitoring prevents people from exploiting weak application directory permissions by dropping in Trojan horse versions of system DLLs. |
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\Notify |
Monitors the list of packages that can receive event notifications from winlogon.exe, the interactive logon support model for Windows. |
Recursion support
Change Tracking and Inventory supports recursion, which allows you to specify wildcards to simplify tracking across directories. Recursion also provides environment variables to allow you to track files across environments with multiple or dynamic drive names. The following list includes common information you should know when configuring recursion:
Wildcards are required for tracking multiple files.
You can use wildcards only in the last segment of a file path, for example, c:\folder\file* or /etc/*.conf.
If an environment variable has an invalid path, validation succeeds but the path fails during execution.
You should avoid general path names when setting the path, as this type of setting can cause too many folders to be traversed.
Change Tracking and Inventory data collection
The next table shows the data collection frequency for the types of changes supported by Change Tracking and Inventory. Inventory logs will be populated every 10 hours by default for all data types. Additionally, when there is a change registered for any of the data types, the inventory and change logs will be generated for this instance.
| Change Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Windows registry | 50 minutes |
| Windows file | 30 to 40 minutes |
| Linux file | 15 minutes |
| Windows services | 10 minutes to 30 minutes Default: 30 minutes |
| Windows software | 30 minutes |
| Linux software | 5 minutes |
| Linux Daemons | 5 minutes |
The following table shows the tracked item limits per machine for Change Tracking and Inventory.
| Resource | Limit |
|---|---|
| File | 500 |
| Registry | 250 |
| Windows software (not including hotfixes) | 250 |
| Linux packages | 1250 |
| Windows Services | 250 |
| Linux Daemons | 500 |
Windows services data
Prerequisites
To enable tracking of Windows Services data, you must upgrade CT extension and use extension more than or equal to 2.11.0.0
- az vm extension set --publisher Microsoft.Azure.ChangeTrackingAndInventory --version 2.11.0 --ids /subscriptions/<subscriptionids>/resourceGroups/<resourcegroupname>/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/<vmname> --name ChangeTracking-Windows --enable-auto-upgrade true
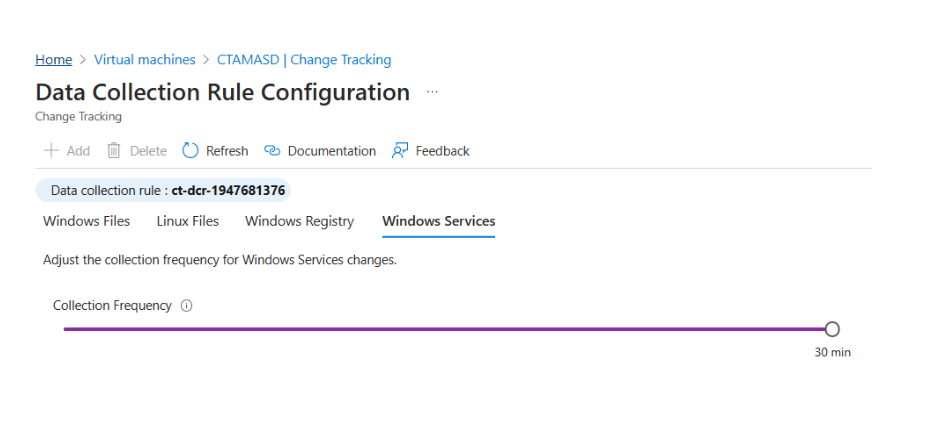
Configure frequency
The default collection frequency for Windows services is 30 minutes. To configure the frequency,
- under Edit Settings, use a slider on the Windows services tab.
Current limitations
Change Tracking and Inventory using Azure Monitoring Agent doesn't support or has the following limitations:
- Recursion for Windows registry tracking
- Network file systems
- Different installation methods
- *.exe files stored on Windows
- The Max File Size column and values are unused in the current implementation.
- If you are tracking file changes, it is limited to a file size of 5 MB or less.
- If the file size appears >1.25MB, then FileContentChecksum is incorrect due to memory constraints in the checksum calculation.
- If you try to collect more than 2500 files in a 30-minute collection cycle, Change Tracking and Inventory performance might be degraded.
- If network traffic is high, change records can take up to six hours to display.
- If you modify a configuration while a machine or server is shut down, it might post changes belonging to the previous configuration.
- Collecting Hotfix updates on Windows Server 2016 Core RS3 machines.
- Linux daemons might show a changed state even though no change has occurred. This issue arises because of how the
SvcRunLevelsdata in the Azure Monitor ConfigurationChange table is written. - Change Tracking extension doesn't support any hardening standards for any Linux Operating systems or Distros.
Support for alerts on configuration state
A key capability of Change Tracking and Inventory is alerting on changes to the configuration state of your hybrid environment. Many useful actions are available to trigger in response to alerts. For example, actions on Azure functions, Automation runbooks, webhooks, and the like. Alerting on changes to the c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts file for a machine is one good application of alerts for Change Tracking and Inventory data. There are many more scenarios for alerting as well, including the query scenarios defined in the next table.
| Query | Description |
|---|---|
| ConfigurationChange | where ConfigChangeType == "Files" and FileSystemPath contains " c:\windows\system32\drivers\" |
Useful for tracking changes to system-critical files. |
| ConfigurationChange | where FieldsChanged contains "FileContentChecksum" and FileSystemPath == "c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts" |
Useful for tracking modifications to key configuration files. |
| ConfigurationChange | where ConfigChangeType == "WindowsServices" and SvcName contains "w3svc" and SvcState == "Stopped" |
Useful for tracking changes to system-critical services. |
| ConfigurationChange | where ConfigChangeType == "Daemons" and SvcName contains "ssh" and SvcState!= "Running" |
Useful for tracking changes to system-critical services. |
| ConfigurationChange | where ConfigChangeType == "Software" and ChangeCategory == "Added" |
Useful for environments that need locked-down software configurations. |
| ConfigurationData | where SoftwareName contains "Monitoring Agent" and CurrentVersion!= "8.0.11081.0" |
Useful for seeing which machines have outdated or noncompliant software version installed. This query reports the last reported configuration state, but doesn't report changes. |
| ConfigurationChange | where RegistryKey == @"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\QualityCompat" |
Useful for tracking changes to crucial antivirus keys. |
| ConfigurationChange | where RegistryKey contains @"HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\SYSTEM\\CurrentControlSet\\Services\\SharedAccess\\Parameters\\FirewallPolicy" |
Useful for tracking changes to firewall settings. |
Next steps
- To enable from the Azure portal, see Enable Change Tracking and Inventory from the Azure portal.