Identity and access management (IAM) architectures provide frameworks for protecting data and resources. Internal networks establish security boundaries in on-premises systems. In cloud environments, perimeter networks and firewalls aren't sufficient for managing access to apps and data. Instead, public cloud systems rely on identity solutions for boundary security.
An identity solution controls access to an organization's apps and data. Users, devices, and applications have identities. IAM components support the authentication and authorization of these and other identities. The process of authentication controls who or what uses an account. Authorization controls what that user can do in applications.
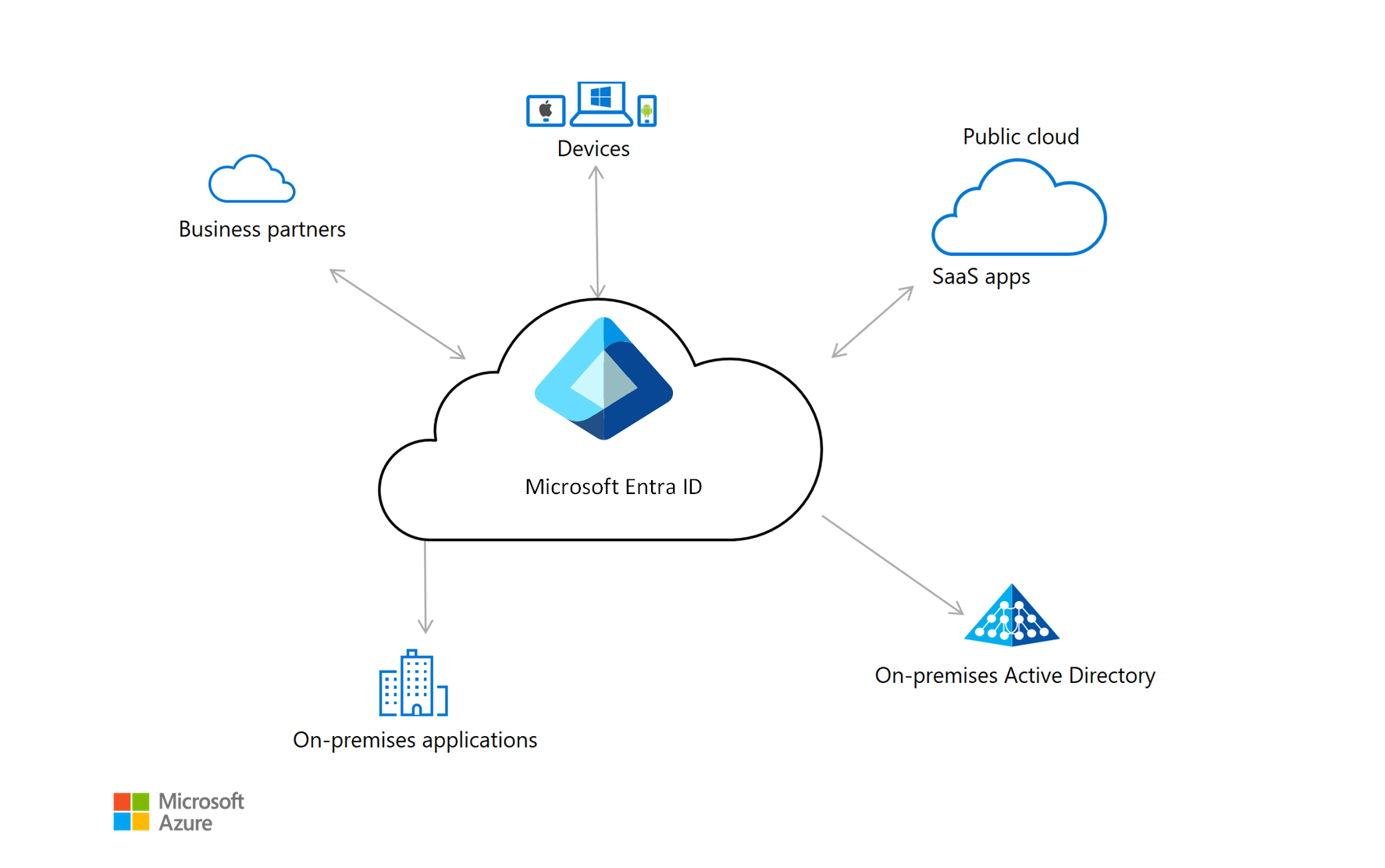
Whether you're just starting to evaluate identity solutions or looking to expand your current implementation, Azure offers many options. One example is Microsoft Entra ID, a cloud service that provides identity management and access control capabilities. To decide on a solution, start by learning about this service and other Azure components, tools, and reference architectures.
Introduction to identity on Azure
If you're new to IAM, the best place to start is Microsoft Learn. This free online platform offers videos, tutorials, and hands-on training for various products and services.
The following resources can help you learn the core concepts of IAM.
Learning paths
- Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals: Describe the capabilities of Microsoft Identity and access management solutions
- Implement Microsoft identity – Associate
- SC-300: Implement an identity management solution
- MS-500 part 1 - Implement and manage identity and access
Modules
Path to production
After you've covered the fundamentals of identity management, the next step is to develop your solution.
Design
To explore options for identity solutions, consult these resources:
For a comparison of three services that provide access to a central identity, see Compare self-managed Active Directory Domain Services, Microsoft Entra ID, and managed Microsoft Entra Domain Services.
For information on associating billing offers with a Microsoft Entra tenant, see Azure billing offers and Active Directory tenants.
To evaluate options for an identity and access foundation, see Azure identity and access management design area.
To explore ways to organize resources that you deploy to the cloud, see Resource organization.
For a comparison of various authentication options, see Choose the right authentication method for your Microsoft Entra hybrid identity solution.
For a comprehensive hybrid identity solution, see How Microsoft Entra ID delivers cloud-governed management for on-premises workloads.
To learn how Microsoft Entra Connect integrates on-premises directories with Microsoft Entra ID, see What is Microsoft Entra Connect?.
Implementation
When you've decided on an approach, implementation comes next. For deployment recommendations, see these resources:
For a series of articles and code samples for a multitenant solution, see Identity management in multitenant applications.
For information on deploying Microsoft Entra ID, see these resources:
To learn how to use Microsoft Entra ID to secure a single-page application, see the tutorials at Register a Single-page application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Best practices
With capabilities like automation, self-service, and single sign-on, Microsoft Entra ID can boost productivity. For general information on benefitting from this service, see Four steps to a strong identity foundation with Microsoft Entra ID.
To check whether your Microsoft Entra implementation aligns with the Azure Security Benchmark version 2.0, see Azure security baseline for Microsoft Entra ID.
Some solutions use private endpoints in tenants to connect to Azure services. To see guidelines for security issues regarding private endpoints, see Limit cross-tenant private endpoint connections in Azure.
For recommendations for the following scenarios, see Integrate on-premises AD domains with Microsoft Entra ID:
- Giving your organization's remote users access to your Azure web apps
- Implementing self-service capabilities for end users
- Using an on-premises network and a virtual network that aren't connected by a virtual private network (VPN) tunnel or ExpressRoute circuit
For general information and guidelines on migrating applications to Microsoft Entra ID, see these articles:
Suite of baseline implementations
These reference architectures provide baseline implementations for various scenarios:
- Create an AD DS resource forest in Azure
- Deploy AD DS in an Azure virtual network
- Extend on-premises AD FS to Azure
Stay current with identity
Microsoft Entra ID receives improvements on an ongoing basis.
- To stay on top of recent developments, see What's new in Microsoft Entra ID?.
- For a roadmap showing new key features and services, see Azure updates.
Additional resources
The following resources provide practical recommendations and information for specific scenarios.
Microsoft Entra ID in educational environments
- Introduction to Microsoft Entra tenants
- Design a multi-directory architecture for large institutions
- Design Tenant Configuration
- Design authentication and credential strategies
- Design an account strategy
- Design identity governance
- Updated Guidance for Microsoft 365 EDU Deployment during COVID-19