Multiparty computing or privacy-preserving computation allows parties in a business relationship to share data, do computations, and arrive at a mutual result without divulging their private data. Azure services can help you build a multiparty computing solution. The solution can include cloud-based and on-premises resources.
Multiparty computing has the following attributes:
- More than one company or organization is involved.
- The parties are independent.
- The parties don't trust one another with all their data.
- All parties access a common computing and data storage platform.
- Some processes must be private for some of the parties involved.
Azure multiparty computing
This section describes multiparty computing options that are available by using Azure services.
Blockchain with Azure Virtual Machines
You can run ledger software by using Azure Virtual Machines. Create as many virtual machines as you need, and connect them in a blockchain network.
Deploying your own virtual machines allows you to customize your solution. The approach includes management overhead, such as updates, high availability, and business continuity requirements. You might have multiple organizations and multiple cloud accounts. Connecting the individual nodes can be complicated.
Deployment templates are available on Azure for most blockchain ledgers for virtual machines.
Blockchain on Kubernetes
Because most blockchain ledgers support deploying into Docker containers, you can use Kubernetes to manage the containers. Azure has a managed Kubernetes offering called Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) that you can use to deploy and configure your blockchain nodes.
AKS implementations come with a managed service for the virtual machines that power the AKS cluster. Your organization must still manage your AKS clusters and any networking or storage options in your architecture.
Deployment templates are available on Azure for most blockchain ledgers for AKS.
Blockchain as a service
Azure supports third-party services that run ledger software on Azure. The service provider manages the infrastructure. They handle maintenance and updates. High availability and consortium management are included in the service.
ConsenSys offers Quorum on Azure. Quorum is an open-source protocol layer that supports Ethereum-based applications.
Other offerings might be available in the future.
Azure confidential ledger
Azure confidential ledger is a managed service built on the Confidential Consortium Framework. It implements a permissioned blockchain network of nodes within Azure confidential computing. Confidential ledger builds on existing encryption.
- Existing encryption:
- Data at rest. Encrypt inactive data when stored in blob storage or a database.
- Data in transit. Encrypt data that's flowing between public or private networks.
- Confidential computing:
- Data in use. Encrypt data that's in use, while in memory and during computation.
Confidential computing allows encryption of data in the main memory. Confidential computing lets you process data from multiple sources without exposing the input data to other parties. This type of secure computation supports multiparty computing scenarios where data protection is mandatory in every step. Examples might be money laundering detection, fraud detection, and secure analysis of healthcare data.
Data stored in confidential ledger is immutable and tamper-proof in the append-only ledger. The ledger is also independently verifiable. Confidential ledger uses secure enclaves for a decentralized blockchain network and requires a minimal trusted computing base.
Azure SQL Database ledger
Azure SQL Database ledger allows participants to verify the data integrity of centrally housed data without the network consensus of a blockchain network. For some centralized solutions, trust is important, but decentralized infrastructure isn't necessary. This approach avoids complexity and performance implications of such an infrastructure.
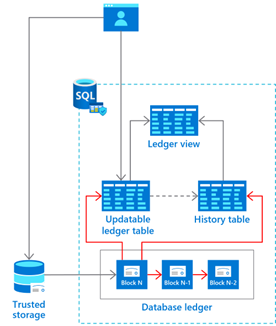
Ledger provides tamper-evidence capabilities for your database. These capabilities allow you to cryptographically attest that your data hasn't been tampered with.
Ledger helps protect data from any attacker or high-privileged user, including database, system, and cloud administrators. Historical data is preserved. If a row is updated in the database, its previous value is maintained in a history table. This capability offers protection without any application changes.
Ledger is a feature of SQL Database. It can be enabled in any existing SQL Database.
Compare options
Use the following tables to compare options so that you can make informed decisions.
Confidential ledger and SQL Database ledger
This table compares confidential ledger with SQL Database ledger.
| Capabilities | SQL Database ledger | Confidential ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized system that requires tamper evidence | Yes | No |
| Decentralized system that requires data to be tamper proof | No | Yes |
| Protects relational data from tampering | Yes | No |
| Protects unstructured data from tampering | No | Yes |
| Secure off-chain store of chain data in a blockchain | Yes | No |
| Secure off-chain store for files referenced to from a blockchain | No | Yes |
| Relational data is queryable | Yes | No |
| Unstructured stored data is queryable | No | Yes |
Confidential ledger and Azure Blob Storage
The immutable storage feature of Azure Blob Storage ensures that data written to it can be read but never changed. This table compares that technology with confidential ledger.
| Capabilities | Confidential ledger | Immutable storage |
|---|---|---|
| Confidential hardware enclaves | Yes | No |
| Append-only data integrity | Yes | Yes, limited to intervals |
| In-use data encryption | Yes | No |
| Blockchain ledger proof | Yes | No |
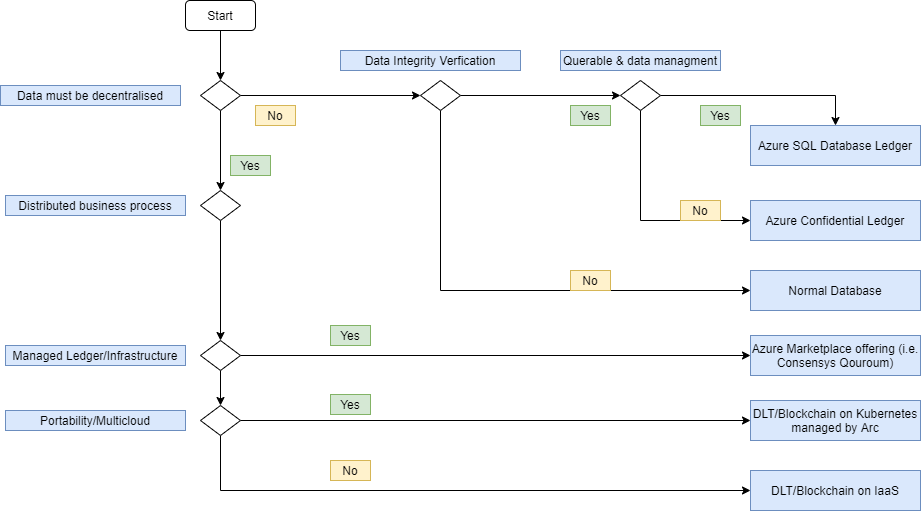
Multiparty computing decision
This diagram summarizes options for multiparty computing with Azure services.
Next steps
- Azure confidential ledger
- Azure SQL Database ledger
- Azure Virtual Machines
- Azure Kubernetes Service
- Azure SQL Database
- Authenticate Azure confidential ledger nodes
- Azure confidential ledger architecture