SSL offloading with Application Gateway for Containers - Ingress API
This document helps set up an example application that uses the Ingress resource from Ingress API:
Background
Application Gateway for Containers enables SSL offloading for better backend performance. See the following example scenario:
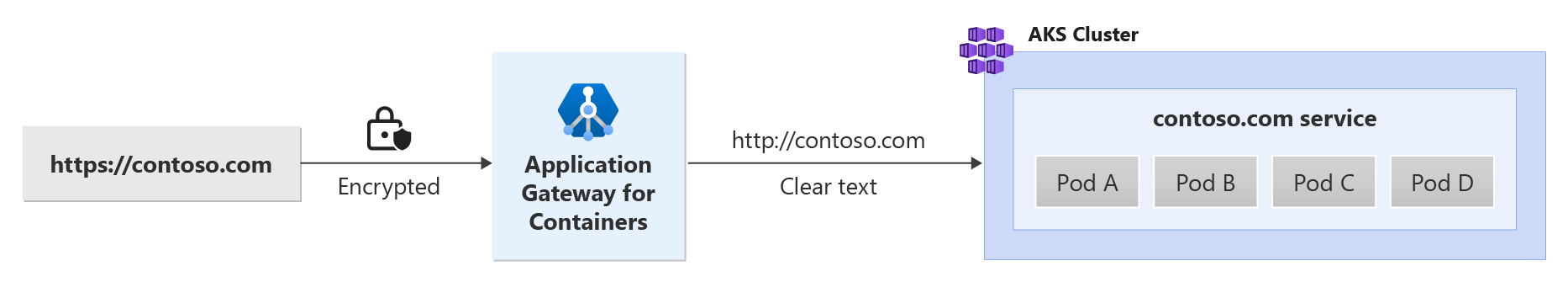
Prerequisites
If you follow the BYO deployment strategy, ensure that you set up your Application Gateway for Containers resources and ALB Controller
If you follow the ALB managed deployment strategy, ensure that you provision your ALB Controller and the Application Gateway for Containers resources via the ApplicationLoadBalancer custom resource.
Deploy a sample HTTPS application: Apply the following deployment.yaml file on your cluster to create a sample web application to demonstrate TLS/SSL offloading.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MicrosoftDocs/azure-docs/refs/heads/main/articles/application-gateway/for-containers/examples/https-scenario/ssl-termination/deployment.yamlThis command creates the following on your cluster:
- a namespace called
test-infra - one service called
echoin thetest-infranamespace - one deployment called
echoin thetest-infranamespace - one secret called
listener-tls-secretin thetest-infranamespace
- a namespace called
Deploy the required Ingress API resources
- Create an Ingress
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-01
namespace: test-infra
annotations:
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-name: alb-test
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-namespace: alb-test-infra
spec:
ingressClassName: azure-alb-external
tls:
- hosts:
- example.com
secretName: listener-tls-secret
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: echo
port:
number: 80
EOF
Note
When the ALB Controller creates the Application Gateway for Containers resources in ARM, it'll use the following naming convention for a frontend resource: fe-<8 randomly generated characters>
If you would like to change the name of the frontend created in Azure, consider following the bring your own deployment strategy.
When the ingress resource is created, ensure the status shows the hostname of your load balancer and that both ports are listening for requests.
kubectl get ingress ingress-01 -n test-infra -o yaml
Example output of successful Ingress creation.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend: FRONTEND_NAME
alb.networking.azure.io/alb-id: /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourcegroups/yyyyyyyy/providers/Microsoft.ServiceNetworking/trafficControllers/zzzzzz
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"networking.k8s.io/v1","kind":"Ingress","metadata":{"annotations":{"alb.networking.azure.io/alb-frontend":"FRONTEND_NAME","alb.networking.azure.io/alb-id":"/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourcegroups/yyyyyyyy/providers/Microsoft.ServiceNetworking/trafficControllers/zzzzzz"},"name"
:"ingress-01","namespace":"test-infra"},"spec":{"ingressClassName":"azure-alb-external","rules":[{"host":"example.com","http":{"paths":[{"backend":{"service":{"name":"echo","port":{"number":80}}},"path":"/","pathType":"Prefix"}]}}],"tls":[{"hosts":["example.com"],"secretName":"listener-tls-secret"}]}}
creationTimestamp: "2023-07-22T18:02:13Z"
generation: 2
name: ingress-01
namespace: test-infra
resourceVersion: "278238"
uid: 17c34774-1d92-413e-85ec-c5a8da45989d
spec:
ingressClassName: azure-alb-external
rules:
- host: example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: echo
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
tls:
- hosts:
- example.com
secretName: listener-tls-secret
status:
loadBalancer:
ingress:
- hostname: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.fzyy.alb.azure.com
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
- port: 443
protocol: TCP
Test access to the application
Now we're ready to send some traffic to our sample application, via the FQDN assigned to the frontend. Use the command below to get the FQDN.
fqdn=$(kubectl get ingress ingress-01 -n test-infra -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname}')
Curling this FQDN should return responses from the backend as configured on the HTTPRoute.
fqdnIp=$(dig +short $fqdn)
curl -vik --resolve example.com:443:$fqdnIp https://example.com
Congratulations, you have installed ALB Controller, deployed a backend application and routed traffic to the application via Ingress on Application Gateway for Containers.