Validate resiliency of MongoDB cluster on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
After deploying the MongoDB cluster on AKS using the Percona Operator for MongoDB and installing mongo-express on your cluster to interact with MongoDB, you test the resiliency of the MongoDB cluster in several scenarios. This tutorial builds upon the MongoDB cluster deployment and MongoDB cluster validation covered in previous guides.
Build and run a sample client application for MongoDB
The following steps show how to build a sample client application for MongoDB and push the Docker image of the application to an Azure Container Registry. The sample client application uses the Locust load testing framework to simulate a workload on the MongoDB cluster. This application inserts documents into the MongoDB cluster and measures the time taken for each document insertion operation. The application uses Faker library to generate random names and departments for the employee documents. You can expand this class to implement more complex operations.
Create a new directory using the following command:
mkdir mongodb-locust-client cd mongodb-locust-clientCreate
requirements.txtfile in themongodb-locust-clientdirectory using the following command:cat > requirements.txt <<EOF locust pymongo Faker EOFCreate
locustfile.pyin themongodb-locust-clientdirectory using the following command:cat > locustfile.py <<EOF import os import random import logging import time import uuid from locust import User, task, constant_throughput, events, tag, between from pymongo import MongoClient from pymongo.errors import ServerSelectionTimeoutError from pymongo.errors import ConnectionFailure from faker import Faker # Set up Faker for generating random names and departments fake = Faker() # Configure logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # List of department names for random selection department_keywords = [ "Accounting", "Marketing", "Human Resources", "Sales", "Research and Development", "IT", "Customer Support", "Legal", "Operations", "Finance", "Product Management", "Public Relations", "Engineering", "Data Science", "Business Development" ] class MongoDBLocust(User): # Set constant throughput (requests per second) wait_time = constant_throughput(20) # MongoDB connection details (make sure these are set correctly in your environment) host = "${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-mongos.mongodb.svc.cluster.local" port = "27017" username = os.getenv('MONGODB_USERNAME') password = os.getenv('MONGODB_PASSWORD') def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super(MongoDBLocust, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs) self.client = MongoDBClient(self.username, self.password) # Initialize MongoDB client def on_stop(self): """Called when the simulated user stops, to close the MongoDB client.""" self.client.close() @task @tag("insert") def insert_document(self): """Task to insert a document into MongoDB.""" self.client.insert_document("insert_document") class MongoDBClient(object): """MongoDB client for managing database interactions.""" def __init__(self, username, password): # Set MongoDB connection parameters self.host = "${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-mongos.mongodb.svc.cluster.local" self.port = "27017" self.username = username self.password = password self.client = MongoClient(f"mongodb://{self.username}:{self.password}@{self.host}:{self.port}/") self.db = self.client['employeeDB'] self.collection = self.db['employees'] self.document_id = None # Placeholder for the inserted document ID def insert_document(self, task_name, command='INSERT'): """Insert a document into MongoDB and measure the time.""" employee_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) start_time = time.time() logger.info(f"{employee_id} - Start Time -> start_time: {start_time}") try: # Create a new fake employee document new_document = { 'Id': str(uuid.uuid4()), 'EmployeeId': employee_id, 'FirstName': fake.first_name(), 'LastName': fake.last_name(), 'Department': random.choice(department_keywords) } # Insert the document result = self.collection.insert_one(new_document) self.document_id = str(result.inserted_id) # Store the document ID for future reads # Measure the time taken for the MongoDB operation (in milliseconds) total_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000 # Convert to ms logger.info(f"{employee_id} - Task - {task_name} -> total_time: {total_time} ms") # Fire the event to report the request events.request.fire( request_type=command, name=task_name, response_time=total_time, response_length=len(str(result)) # Length of the result returned by the operation ) except Exception as e: total_time = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000 # Time taken with error logger.error(f"{employee_id} - Error in {task_name}: {e} -> total_time: {total_time} ms") events.request.fire( request_type=command, name=task_name, response_time=total_time, response_length=0, # No response in case of error exception=e ) logger.info(f"{employee_id} - End Time -> end time: {time.time()}") def close(self): """Close the MongoDB connection.""" self.client.close() EOFCreate a Dockerfile in the
mongodb-locust-clientdirectory using the following command. The Dockerfile creates a Docker image for the sample client application, uses thepython:3.10-slim-bullseyeimage as the base image, and installs the required dependencies for the application.cat > Dockerfile <<EOF # Use a slim Python image as the base FROM python:3.10-slim-bullseye # Install wget and gnupg RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y wget gnupg # Add MongoDB GPG Key and repository RUN wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-6.0.asc | tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/mongodb.asc && \ echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/debian bullseye/mongodb-org/6.0 main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-6.0.list # Update APT sources and install MongoDB Shell (mongosh) RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y mongodb-mongosh # Copy your application files COPY requirements.txt ./ COPY locustfile.py ./ # Install Python dependencies RUN pip install --upgrade pip && pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt EOFBuild the Docker image for the sample client application using the
az acr buildcommand. Make sure you replace$MY_ACR_REGISTRYwith the name of your Azure Container Registry.az acr build --image mongodb-locust-client --registry $MY_ACR_REGISTRY .
Test the MongoDB cluster on AKS
Create MongoDB Locust client pod
In the following section, you create a MongoDB Locust client pod in your AKS cluster. This pod uses the Docker image you built earlier to simulate a workload on the MongoDB cluster. The following spec uses password and username from the external secret created in the earlier tutorial.
Create the MongoDB Locust client pod using the
kubectl applycommand.kubectl apply -n mongodb -f - <<EOF apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: mongodb-locust-client labels: app: mongodb-locust-client spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: mongodb-locust-client template: metadata: labels: app: mongodb-locust-client spec: nodeSelector: kubernetes.azure.com/agentpool: "systempool" # Ensure pods are scheduled on the system node pool containers: - name: mongodb-locust-client image: $MY_ACR_REGISTRY.azurecr.io/mongodb-locust-client command: ["locust", "-f", "/locustfile.py", "--host=http://${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-mongos.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017/"] env: - name: MONGODB_USERNAME valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: ${AKS_MONGODB_SECRETS_NAME} # Name of your external secret key: MONGODB_DATABASE_ADMIN_USER # Key for the admin username - name: MONGODB_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: ${AKS_MONGODB_SECRETS_NAME} # Name of your external secret key: MONGODB_DATABASE_ADMIN_PASSWORD # Key for the admin password EOFExample output:
deployment.apps/mongodb-locust-client createdGet the name of the MongoDB client pod using the
kubectl get podscommand.kubectl get pods -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACEExample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE ... // Additional pods mongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745 1/1 Running 0 5d8h ... // Additional podsMake note of the name of the pod with the
mongodb-locust-clientprefix. This pod connects to the MongoDB cluster to execute the MongoDB commands.
Port forward the MongoDB Locust client pod
Port forward the port 8089 to access the Locust web interface on your local machine using the
kubectl port-forwardcommand. Make sure you replacemongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745with the name of the MongoDB client pod you created in the previous section.kubectl -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACE port-forward mongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745 8089:8089
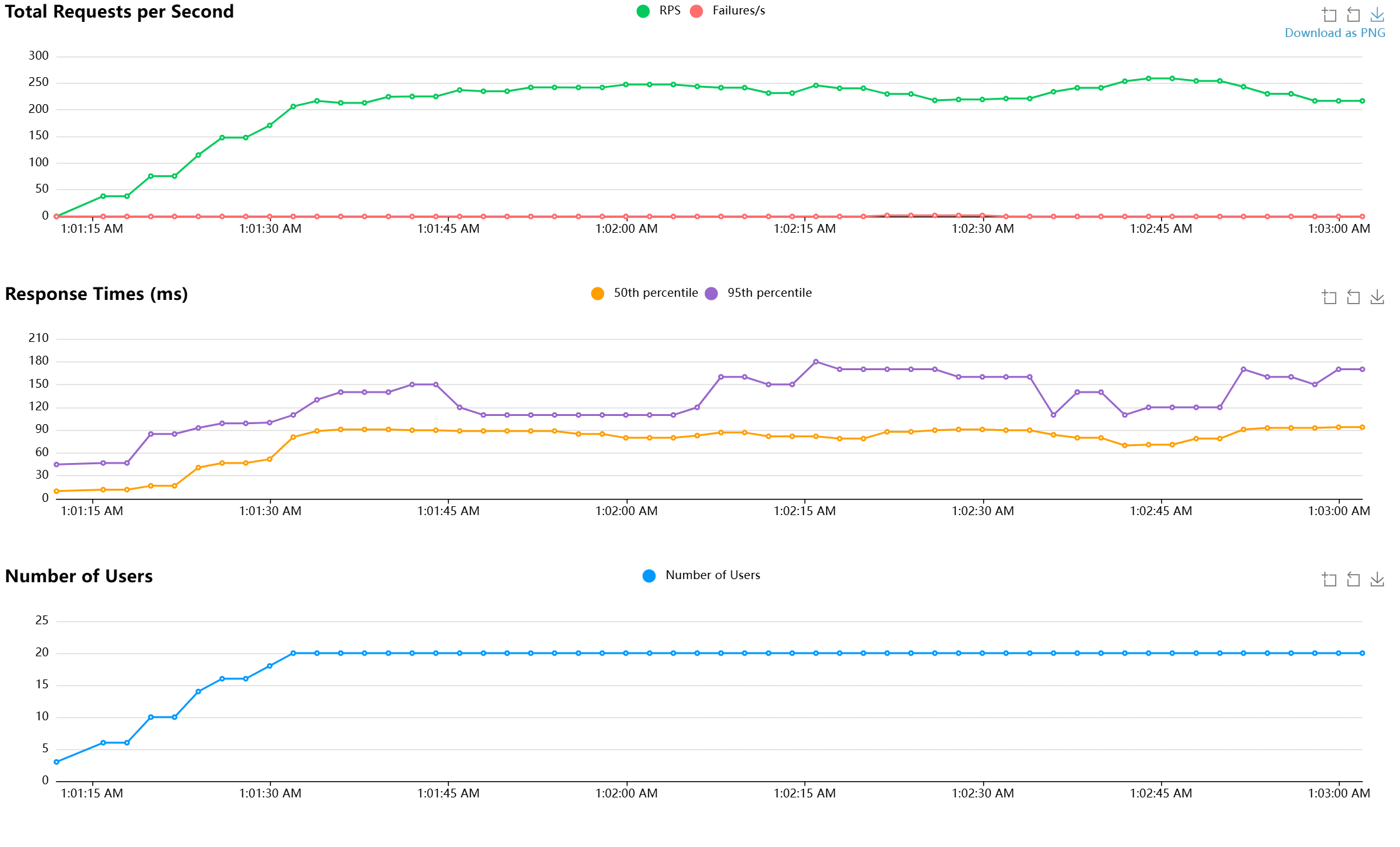
Access the Locust web interface
Access the Locust web interface by navigating to
http://localhost:8089in your web browser. The Locust web interface allows you to configure the number of users and the spawned rate for the load test. You can also view the statistics of the load test in real-time.
Connect to the MongoDB shell and identify the primary member
Connect to the MongoDB client pod using the following command. Make sure you replace
mongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745with the name of the MongoDB client pod you created earlier.kubectl -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACE exec -it mongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745 -- /bin/bashOnce you're connected to the pod, use the following command to connect to the MongoDB shell. Make sure you replace
${MY_CLUSTER_NAME},${databaseAdmin}and${databaseAdminPassword}with the values you obtained from the previous tutorial.mongosh --host ${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-rs0-0.${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local --port 27017 -u ${databaseAdmin} -p ${databaseAdminPassword} --authenticationDatabase adminOnce you're connected to the MongoDB shell, use the following command to identify the primary MongoDB replica set:
rs.status()Example output:
{ set: 'rs0', ... // Additional details members: [ { _id: 0, name: 'cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-0.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017', health: 1, state: 2, stateStr: 'SECONDARY', uptime: 207037, ... // Additional details for the first member }, { _id: 1, name: 'cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017', health: 1, state: 1, stateStr: 'PRIMARY', uptime: 207033, ... // Additional details for the second member }, { _id: 2, name: 'cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-2.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017', health: 1, state: 2, stateStr: 'SECONDARY', uptime: 207033, ... // Additional details for the third member } ], ... }From the output, make note of the member with the
PRIMARYstate. In this example, the member withname: cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1is the primary member of the MongoDB replica set. You delete the primary member in the next step to simulate a MongoDB pod failure.
Resiliency testing scenarios
While the database script continues to execute in first terminal window, in the second terminal window, you can use the following scripts to simulate the failure scenarios and observe the behavior of the MongoDB cluster.
Scenario 1: Simulate deletion of statefulSet
List all stateful sets using the
kubectl getcommand.kubectl get sts -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACEExample output:
NAME READY AGE cluster-aks-mongodb-cfg 3/3 5d21h cluster-aks-mongodb-mongos 3/3 5d18h cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0 3/3 3h26mDelete the stateful set named
cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0using thekubectl deletecommand.kubectl delete sts -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACE cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0Once the stateful set is deleted, check the Locust test dashboard to observe the behavior of the MongoDB cluster.
Get the logs of the Percona Operator pod using the
kubectl logscommand. Make sure you replace<percona-operator-pod>with the name of your Percona Operator pod.kubectl logs -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACE <percona-operator-pod>You should see the Percona Operator recreates the stateful set and the MongoDB cluster returns to normal operation, as shown in the following example output:
... 2024-11-29T13:48:07.427Z ERROR failed to reconcile cluster {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "2e037504-d213-4bf7-a2b8-5af396b2d16c", "replset": "rs0", "error": "dial: ping mongo: server selection error: context deadline exceeded, current topology: { Type: ReplicaSetNoPrimary, ... ... 2024-11-29T13:48:37.678Z INFO Warning: Reconciler returned both a non-zero result and a non-nil error. The result will always be ignored if the error is non-nil and the non-nil error causes reqeueuing with exponential backoff. For more details, see: https://pkg.go.dev/sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/reconcile#Reconciler {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "2e037504-d213-4bf7-a2b8-5af396b2d16c"} 2024-11-29T13:48:37.678Z ERROR Reconciler error {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "2e037504-d213-4bf7-a2b8-5af396b2d16c", "error": "create pbm object: create PBM connection to cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-0. cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017,cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster. local:27017,cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-2.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017: create mongo connection: ping: server selection error: server selection timeout, ... ... 2024-11-29T13:48:38.210Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "2d970945-86b2-4c10-a610-7f7c42ad9a9f", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 1} 2024-11-29T13:48:38.437Z INFO Cluster state changed {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "2d970945-86b2-4c10-a610-7f7c42ad9a9f", "previous": "error", "current": "initializing"} 2024-11-29T13:48:38.955Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "f2f803cb-d5f4-4851-9a05-71d46d95ca6d", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 1} 2024-11-29T13:48:40.102Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "76accdff-7d7a-4ba8-9914-ff8793226dd5", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 1} 2024-11-29T13:48:43.964Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "c49f50e7-881e-469c-bdf5-aaf925436097", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 1} 2024-11-29T13:48:49.736Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "5b52ce2e-e07e-43e8-8ca0-b6850a4d8823", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 1} 2024-11-29T13:48:55.560Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "95a26aff-b022-4543-a22e-0d50ea292190", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 2} 2024-11-29T13:48:56.466Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "9f64bdb1-e616-44ab-a480-7eaf813db73e", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 2} 2024-11-29T13:49:01.279Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "0281130b-b13e-4ab2-bd68-0b4cb6d01c84", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 2} 2024-11-29T13:49:07.027Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "a3caedd1-ead3-406b-8ce3-056c7cd875dc", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 2} 2024-11-29T13:49:12.783Z INFO Waiting for the pods {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "8a82eb0c-8b26-4542-a4b5-f7e13e030d1e", "replset": "rs0", "size": 3, "pods": 2} 2024-11-29T13:49:28.521Z ERROR failed to reconcile cluster {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "22fc8c4d-30d5-4bf6-b405-720533f1d8d2", "replset": "rs0", "error": "dial: ping mongo: server selection error: context deadline exceeded, current topology: { Type: ReplicaSetNoPrimary, ... ... 2024-11-29T13:49:32.472Z INFO Fixing member tags {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "8ff97dc9-b024-4cd9-b411-c3ffaf225e14", "replset": "rs0"} 2024-11-29T13:49:39.065Z ERROR failed to reconcile cluster {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "28438ddb-77a1-48b0-8390-277c4687a97b", "replset": "rs0", "error": "create system users: failed to get mongo client: ping mongo: connection() error occurred during connection handshake: dial tcp: lookup cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb. svc.cluster.local on 10.0.0.10:53: no such host", ... ... 2024-11-29T13:49:40.424Z ERROR failed to reconcile cluster {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "cfec8e33-d0c9-4adf-afe9-bc6dcbf711ba", "replset": "rs0", "error": "dial: ping mongo: connection() error occurred during connection handshake: ... ... 2024-11-29T13:49:45.433Z INFO Cluster state changed {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "0765ea5f-52d8-44e2-a680-c7d082dd88e1", "previous": "initializing", "current": "ready"}
Scenario 2: Simulate a MongoDB pod failure
Identify the primary MongoDB replica set and then delete it using the
kubectl deletecommand to simulate a MongoDB pod failure. Make sure you replacecluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1with the primary member name from the output of thers.status()command.kubectl delete pod cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1 -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACEThe MongoDB replica set should elect a new primary member to continue serving the requests. You can verify the new primary member by connecting to the MongoDB shell and executing the
rs.status()command. Connect to the MongoDB client pod using the following command. Make sure you replacemongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745with the pod name from the output of the previous command.kubectl -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACE exec -it mongodb-locust-client-564695f8f-q6745 -- /bin/bashOnce you're connected to the pod, connect to the MongoDB shell using the following command. Make sure you replace
${MY_CLUSTER_NAME},${databaseAdmin}and${databaseAdminPassword}with the values you obtained in the previous tutorial.mongosh --host ${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-rs0-0.${MY_CLUSTER_NAME}-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local --port 27017 -u ${databaseAdmin} -p ${databaseAdminPassword} --authenticationDatabase adminOnce you're connected to the MongoDB shell, use the following command to identify the primary MongoDB replica set:
rs.status()Example output:
{ set: 'rs0', ... // Additional details members: [ { _id: 0, name: 'cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-0.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017', health: 1, state: 2, stateStr: 'PRIMARY', uptime: 207037, ... // Additional details for the first member }, { _id: 1, name: 'cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-1.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017', health: 1, state: 1, stateStr: 'SECONDARY', uptime: 207033, ... // Additional details for the second member }, { _id: 2, name: 'cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0-2.cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0.mongodb.svc.cluster.local:27017', health: 1, state: 2, stateStr: 'SECONDARY', uptime: 207033, ... // Additional details for the third member } ], ... }You should see that the member with the
PRIMARYstate changed toSECONDARY, and another member with theSECONDARYstate changed toPRIMARY:Get the logs of the Percona Operator pod using the
kubectl logscommand. Make sure you replace<percona-operator-pod>with the name of your Percona Operator pod.kubectl logs -n $AKS_MONGODB_NAMESPACE <percona-operator-pod>You should see the Percona Operator recreates the stateful set and the MongoDB cluster returns to normal operation, as shown in the following example output:
... 2024-11-29T14:02:17.151Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "b1b1b1b1-cccc-dddd-eeee-f2f2f2f2f2f2", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:17.189Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "b1b1b1b1-cccc-dddd-eeee-f2f2f2f2f2f2", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:17.405Z INFO Cluster state changed {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "b1b1b1b1-cccc-dddd-eeee-f2f2f2f2f2f2", "previous": "ready", "current": "initializing"} 2024-11-29T14:02:18.448Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "c2c2c2c2-dddd-eeee-ffff-a3a3a3a3a3a3", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:18.489Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "c2c2c2c2-dddd-eeee-ffff-a3a3a3a3a3a3", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:23.359Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "d3d3d3d3-eeee-ffff-aaaa-b4b4b4b4b4b4", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:23.402Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "d3d3d3d3-eeee-ffff-aaaa-b4b4b4b4b4b4", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:29.341Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "e4e4e4e4-ffff-aaaa-bbbb-c5c5c5c5c5c5", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:02:29.377Z INFO StatefulSet is not up to date {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "e4e4e4e4-ffff-aaaa-bbbb-c5c5c5c5c5c5", "sts": "cluster-aks-mongodb-rs0"} 2024-11-29T14:03:01.246Z INFO Cluster state changed {"controller": "psmdb-controller", "object": {"name":"cluster-aks-mongodb","namespace":"mongodb"}, "namespace": "mongodb", "name": "cluster-aks-mongodb", "reconcileID": "f5f5f5f5-aaaa-bbbb-cccc-d6d6d6d6d6d6", "previous": "initializing", "current": "ready"}
Next step
Azure Kubernetes Service