Create Windows Server containers
Applies to: Azure Local, version 23H2
This article describes how to use Azure CLI to deploy a node pool to an existing AKS cluster that runs Windows Server containers. It also describes how to deploy an ASP.NET sample application in a Windows Server container to the cluster.
Prerequisites
Create an AKS cluster following the instructions in How to create AKS clusters.
Add a node pool
By default, a Kubernetes cluster is created with a node pool that can run Linux containers. You must add another node pool that can run Windows Server containers alongside the Linux node pool.
Add a node pool with Windows container hosts using the az aksarc nodepool add command with the parameter --os-type Windows. If the operating system SKU isn't specified, the node pool is set to the default OS based on the Kubernetes version of the cluster. Windows Server 2022 is the default operating system for Kubernetes versions 1.25.0 and higher. Windows Server 2019 is the default OS for earlier versions.
- To use Windows Server 2019, specify the following parameters:
os-typeset toWindows.os-skuset toWindows2019.
- To use Windows Server 2022, specify the following parameters:
os-typeset toWindows.os-skuset toWindows2022(optional).
The following command creates a new node pool named $mynodepool and adds it to $myAKSCluster with one Windows Server 2022 node:
az aksarc nodepool add --resource-group $myResourceGroup --cluster-name $myAKSCluster --name $mynodepool --node-count 1 --os-type Windows --os-sku Windows2022
Connect to the AKS cluster
Now you can connect to your Kubernetes cluster by running the az connectedk8s proxy command from your local machine. Make sure you sign in to Azure before running this command. If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, select the appropriate subscription ID using the az account set command.
This command downloads the kubeconfig of your Kubernetes cluster to your local machine and opens a proxy connection channel to your on-premises Kubernetes cluster. The channel is open for as long as this command runs. Let this command run for as long as you want to access your cluster. If the command times out, close the CLI window, open a new one, then run the command again.
You must have Contributor permissions on the resource group that hosts the AKS cluster in order to run the following command successfully:
az connectedk8s proxy --name $aksclustername --resource-group $resource_group --file .\aks-arc-kube-config
Expected output:
Proxy is listening on port 47011
Merged "aks-workload" as current context in .\aks-arc-kube-config
Start sending kubectl requests on 'aks-workload' context using kubeconfig at .\aks-arc-kube-config
Press Ctrl+C to close proxy.
Keep this session running and connect to your Kubernetes cluster from a different terminal/command prompt. Verify that you can connect to your Kubernetes cluster by running the kubectl get command. This command returns a list of the cluster nodes:
kubectl get node -A --kubeconfig .\aks-arc-kube-config
The following example output shows the node created in the previous steps. Make sure the node status is Ready:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
moc-lesdc78871d Ready control-plane 6d8h v1.26.3
moc-lupeeyd0f8c Ready <none> 6d8h v1.26.3
moc-ww2c8d5ranw Ready <none> 7m18s v1.26.3
Deploy the application
A Kubernetes manifest file defines a cluster's desired state, such as which container images to run.
You can use a YAML manifest to create all the objects needed to run the ASP.NET sample application in a Windows Server container. This manifest includes a Kubernetes deployment for the ASP.NET sample application and a Kubernetes service to access the application from the internet.
The ASP.NET sample application is provided as part of the .NET Framework samples and runs in a Windows Server container. AKS requires Windows Server containers to be based on images of Windows Server 2019 or greater. The Kubernetes manifest file must also define a node selector to ensure your ASP.NET sample application's pods are scheduled on a node that can run Windows Server containers.
Create a file named sample.yaml and copy in the following YAML definition:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: sample labels: app: sample spec: replicas: 1 template: metadata: name: sample labels: app: sample spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": windows containers: - name: sample image: mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/framework/samples:aspnetapp resources: limits: cpu: 1 memory: 800M ports: - containerPort: 80 selector: matchLabels: app: sample --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: sample spec: type: LoadBalancer ports: - protocol: TCP port: 80 selector: app: sampleFor a breakdown of YAML manifest files, see Deployments and YAML manifests.
Deploy the application using the kubectl apply command and specify the name of your YAML manifest:
kubectl apply -f sample.yaml --kubeconfig .\\aks-arc-kube-config
The following example output shows that the deployment and service were created successfully:
deployment.apps/sample created
service/sample created
Test the application
When the application runs, a Kubernetes service exposes the application front end to the internet. This process can take a few minutes to complete. Occasionally, the service can take longer than a few minutes to provision. Allow up to 10 minutes for provisioning.
Monitor progress using the kubectl get service command with the
--watchargument.kubectl get service sample --watch --kubeconfig .\aks-arc-kube-configInitially, the output shows the EXTERNAL-IP for the sample service as pending:
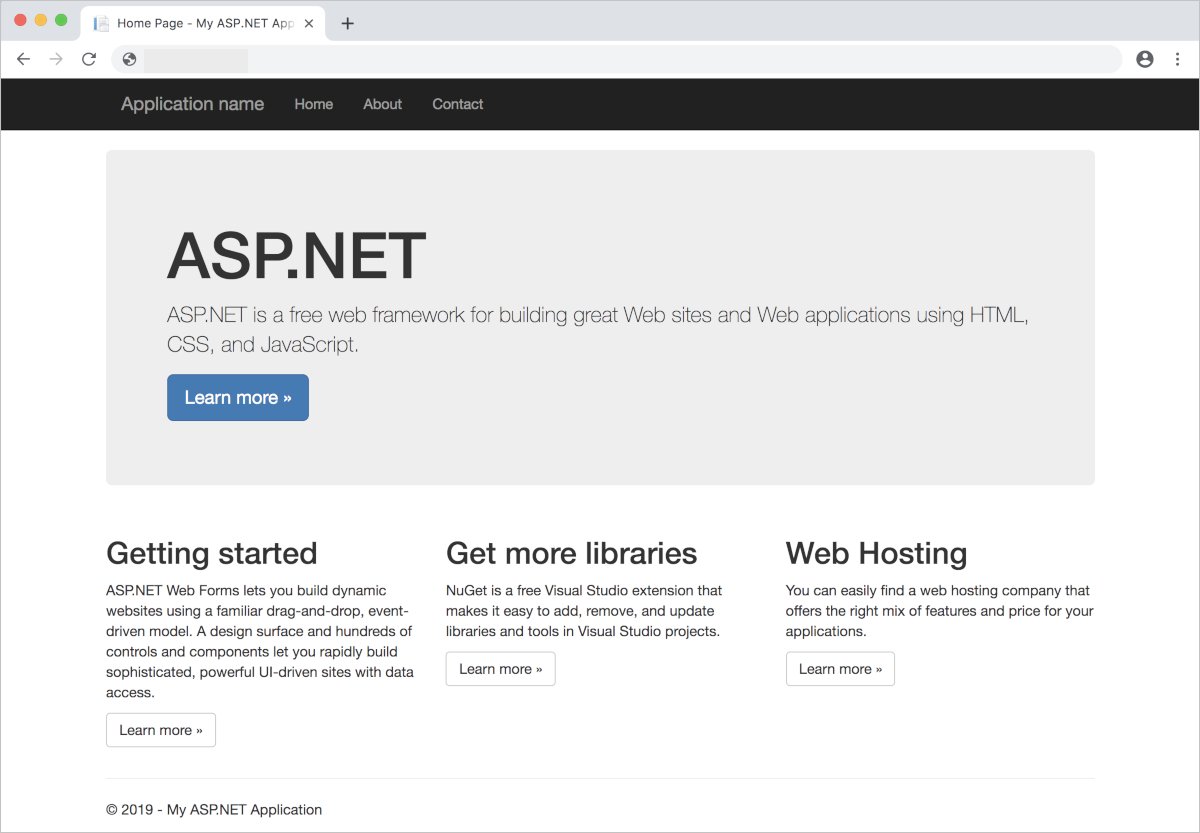
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE sample LoadBalancer 10.0.37.27 <pending> 80:30572/TCP 6sWhen the EXTERNAL-IP address changes from pending to an IP address, use CTRL-C to stop the kubectl watch process. The following example output shows a valid public IP address assigned to the service:
sample LoadBalancer 10.0.37.27 52.179.23.131 80:30572/TCP 2mSee the sample app in action by opening a web browser to the external IP address and port of the sample service.
If you receive a connection timeout when trying to load the page, you should verify that the sample app is ready using the
kubectl get pods --watchcommand. Sometimes, the Windows container isn't started by the time your external IP address is available.
Delete node pool
Delete the node pool using the az akshybrid nodepool delete command:
az aksarc nodepool delete -g $myResourceGroup --cluster-name $myAKSCluster --name $mynodepool --no-wait