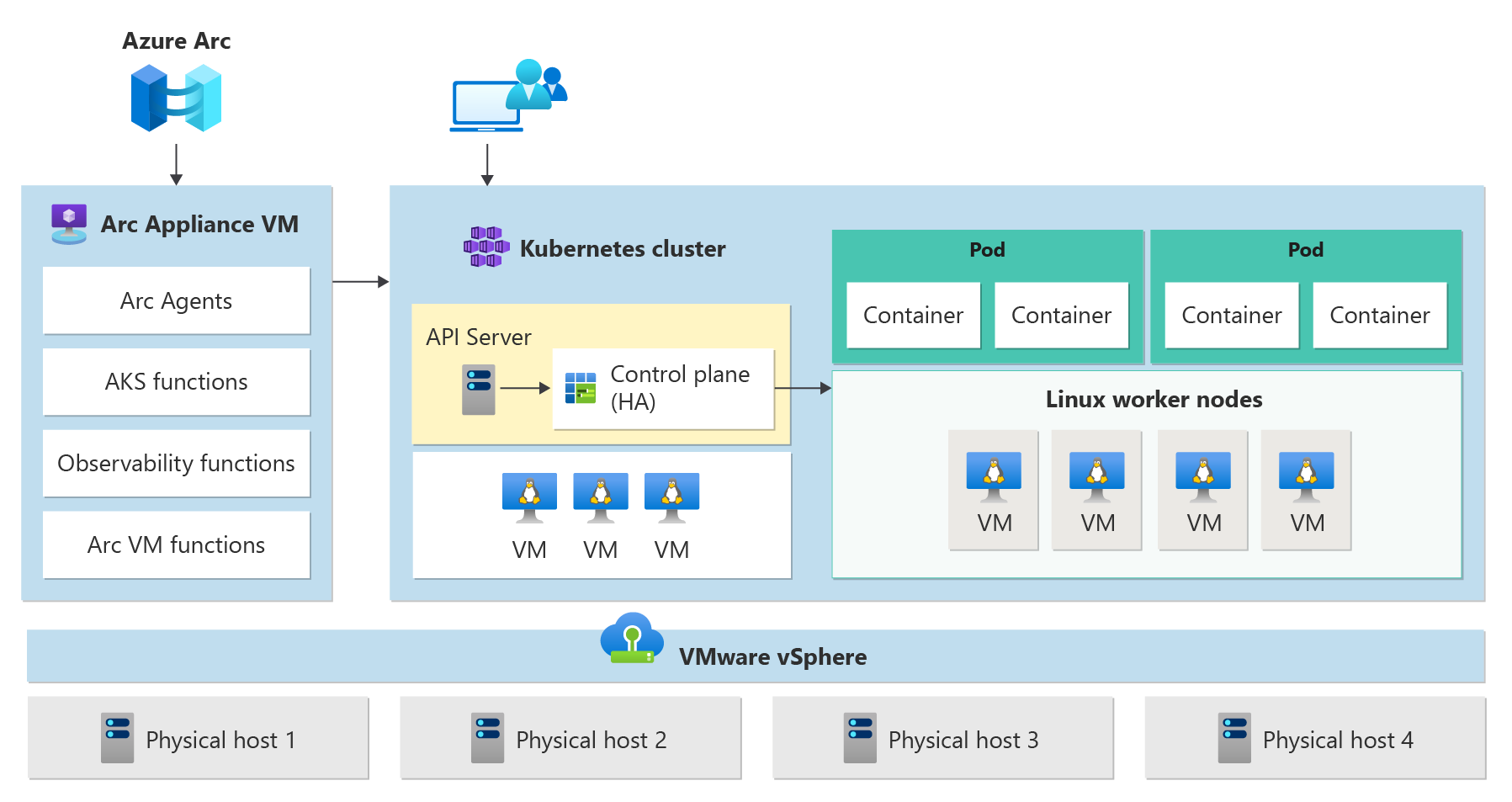
AKS Arc on VMware (preview) and workload cluster architecture
Applies to: AKS enabled by Azure Arc on VMware (preview)
This article provides an overview of the cluster architecture and key infrastructure components of Kubernetes, such as the control plane and worker nodes, for AKS enabled by Azure Arc on VMware.
Cluster architecture
An Azure Kubernetes Service cluster has the following components:
- Arc Resource Bridge (also known as the Arc appliance) provides the core orchestration mechanism and interface for deploying and managing one or more workload clusters.
- Workload clusters (also known as target clusters) are where containerized applications are deployed.
AKS Arc uses a set of predefined configuration options to deploy Kubernetes clusters effectively and with scalability in mind. A deployment operation creates multiple Linux virtual machines and joins them together to create one or more Kubernetes clusters.
Arc Resource Bridge
The Arc Resource Bridge connects a private cloud (for example, Azure Local, VMWare/vSphere, or SCVMM) to Azure and enables on-premises resource management from Azure. Once connected, you can configure the container orchestration platform in AKS on a vSphere environment, which is the VMware virtualization platform. The two main components of vSphere are ESXi and vCenter.
Azure Arc Resource Bridge provides the line of sight to private clouds required to manage resources such as Kubernetes clusters on-premises through Azure. Arc Resource Bridge includes the following core AKS Arc components:
- AKS Arc cluster extensions: A cluster extension is the on-premises equivalent of an Azure Resource Manager resource provider. Just as the Microsoft.ContainerService resource provider manages AKS clusters in Azure, the Microsoft.HybridContainerService resource provider enables the AKS Arc cluster extension to manage Kubernetes clusters via Azure when added to your Arc Resource Bridge.
- Custom location: A custom location is the on-premises equivalent of an Azure region and is an extension of the Azure location construct. Custom locations provide a way for tenant administrators to use their data center with the right extensions installed, as target locations for deploying Azure service instances.
- vCenter resource: VMware vCenter is server management software that provides a centralized platform for controlling vSphere environments. The Arc Resource Bridge and AKS extensions communicate with the vCenter through the cluster API provided by vSphere (CAPv), facilitating the creation of workload clusters. Each of the custom location resources maps to an instance of vCenter. As you connect your vCenter to Azure, you also register your vCenter as an Azure resource, which is the vCenter resource.
For an architectural overview of the Azure Arc Resource Bridge, see the Azure Arc Resource Bridge overview. For each Azure Arc Resource Bridge, you can manage multiple vCenter instances by creating vCenter resources with the corresponding custom locations. There is a one-to-one mapping relationship between vCenter resources and custom locations.
Workload clusters
A workload cluster has many components, as described in the following sections.
Control plane
- API server: The API server enables interaction with the Kubernetes API. This component provides the interaction for management tools, such as Azure CLI, or kubectl.
- Etcd: Etcd is a distributed key-value store that stores data required for lifecycle management of the cluster. It stores the control plane state.
Load balancer
The main purpose of a load balancer is to distribute traffic across multiple nodes in a Kubernetes cluster. This load balancing can help prevent downtime and improve overall performance of applications.
The AKS Arc on VMware preview supports the following options to deploy a load balancer for your Kubernetes cluster:
- Bring your own third party load balancer.
Worker nodes
To run your applications and supporting services, you need a Kubernetes node. An AKS workload cluster has one or more worker nodes. Worker nodes act as virtual machines (VMs) that run the Kubernetes node components and host the pods and services that make up the application workload.
There are core Kubernetes workload components that you can deploy on AKS workload clusters, such as pods and deployments.
Warning
During the preview, the creation and management of Windows node pools is not supported.
Lifecycle management
Azure Arc is automatically enabled on all your Kubernetes clusters that are created using AKS Arc. You can use your Microsoft Entra identity for connecting to your clusters from anywhere. Azure Arc enables you to use familiar tools like the Azure CLI and Azure Resource Manager templates to create and manage your Kubernetes clusters.
Next steps
- To understand the supported deployment scale for running AKS Arc on VMware, see the supported deployment scale.
- If your vCenter is not connected to Azure Arc and you want to add the AKS extension, see the Quickstart: Connect VMware vCenter Server to Azure Arc using the help script.
- If you already connected vCenter to Azure Arc and you want to add the AKS extension, see how to enable Kubernetes Extension for AKS Arc Operators.