How to use MedImageInsight healthcare AI model for medical image embedding generation
Important
The healthcare AI models are intended for research and model development exploration. The models are not designed or intended to be deployed in clinical settings as-is nor for use in the diagnosis or treatment of any health or medical condition, and the individual models’ performances for such purposes have not been established. You bear sole responsibility and liability for any use of the healthcare AI models, including verification of outputs and incorporation into any product or service intended for a medical purpose or to inform clinical decision-making, compliance with applicable healthcare laws and regulations, and obtaining any necessary clearances or approvals.
In this article, you learn how to deploy MedImageInsight from the model catalog as an online endpoint for real-time inference. You also learn to issue a basic call to the API. The steps you take are:
- Deploy the model to a self-hosted managed compute.
- Grant permissions to the endpoint.
- Send test data to the model, receive, and interpret results
MedImageInsight - the medical imaging embedding model
MedImageInsight foundation model for health is a powerful model that can process a wide variety of medical images. These images include X-Ray, CT, MRI, clinical photography, dermoscopy, histopathology, ultrasound, and mammography images. Rigorous evaluations demonstrate MedImageInsight's ability to achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) or human expert-level performance across classification, image-to-image search, and fine-tuning tasks. Specifically, on public datasets, MedImageInsight achieves or exceeds SOTA performance in chest X-ray disease classification and search, dermatology classification and search, Optical coherence tomography (OCT) classification and search, and 3D medical image retrieval. The model also achieves near-SOTA performance for histopathology classification and search.
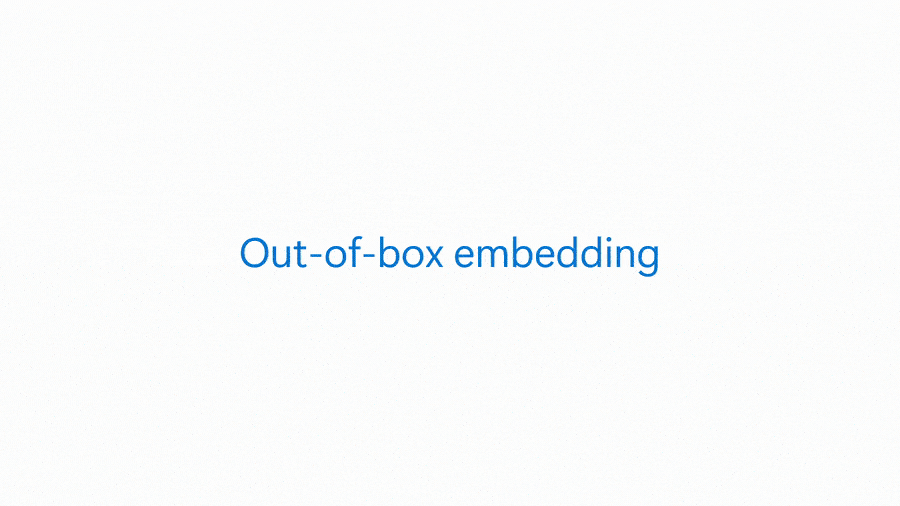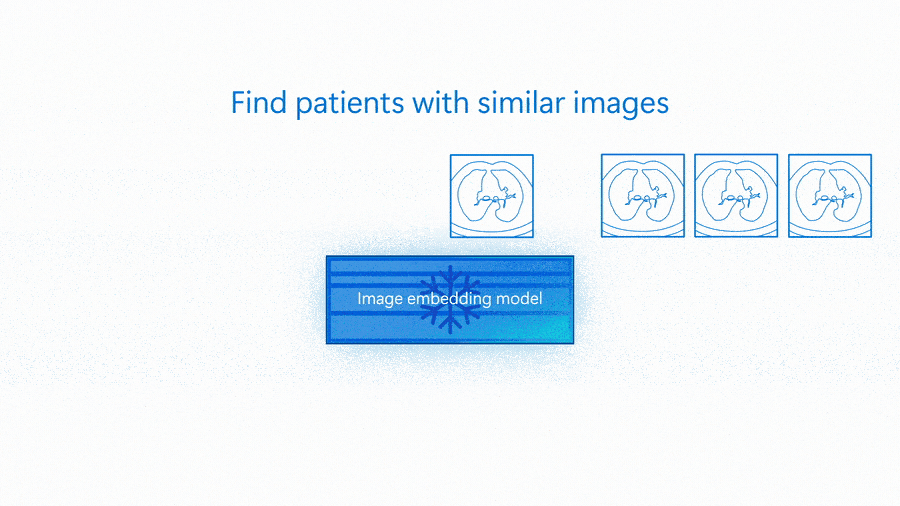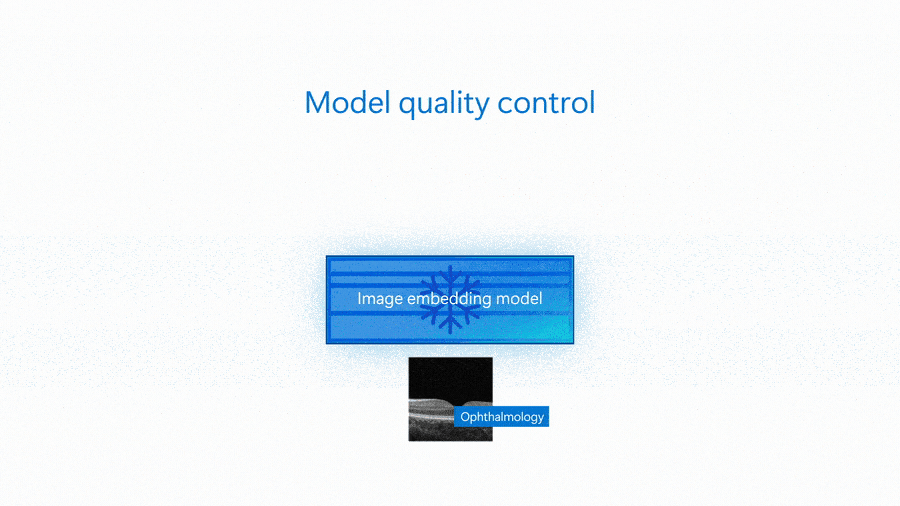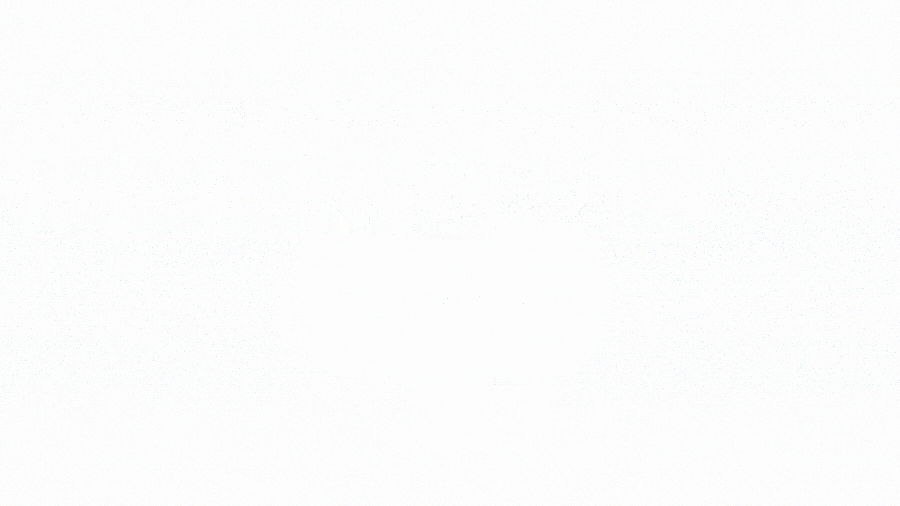
An embedding model is capable of serving as the basis of many different solutions—from classification to more complex scenarios like group matching or outlier detection. The following animation shows an embedding model being used for image similarity search and to detect images that are outliers.
Prerequisites
To use the MedImageInsight model, you need the following prerequisites:
A model deployment
Deployment to a self-hosted managed compute
MedImageInsight model can be deployed to our self-hosted managed inference solution, which allows you to customize and control all the details about how the model is served. You can deploy the model through the catalog UI (in Azure AI Foundry or Azure Machine Learning studio) or deploy programmatically.
To deploy the model through the UI:
Go to the catalog.
Search for MedImageInsight and select the model card.
On the model's overview page, select Deploy.
If given the option to choose between serverless API deployment and deployment using a managed compute, select Managed Compute.
Fill out the details in the deployment window.
Note
For deployment to a self-hosted managed compute, you must have enough quota in your subscription. If you don't have enough quota available, you can use our temporary quota access by selecting the option I want to use shared quota and I acknowledge that this endpoint will be deleted in 168 hours.
Select Deploy.
To deploy the model programmatically, see How to deploy and inference a managed compute deployment with code.
Work with an embedding model
In this section, you consume the model and make basic calls to it.
Use REST API to consume the model
Consume the MedImageInsight embedding model as a REST API, using simple GET requests or by creating a client as follows:
from azure.ai.ml import MLClient
from azure.identity import DeviceCodeCredential
credential = DefaultAzureCredential()
ml_client_workspace = MLClient.from_config(credential)
In the deployment configuration, you get to choose the authentication method. This example uses Azure Machine Learning token-based authentication. For more authentication options, see the corresponding documentation page. Also, note that the client is created from a configuration file that is created automatically for Azure Machine Learning virtual machines (VMs). Learn more on the corresponding API documentation page.
Make basic calls to the model
Once the model is deployed, use the following code to send data and retrieve embeddings.
import base64
import json
import os
endpoint_name = "medimageinsight"
deployment_name = "medimageinsight-v1"
sample_image_xray = os.path.join(image_path)
def read_image(image_path):
with open(image_path, "rb") as f:
return f.read()
data = {
"input_data": {
"columns": ["image", "text"],
# IMPORTANT: Modify the index as needed
"index": [0],
"data": [
[
base64.encodebytes(read_image(sample_image_xray)).decode("utf-8"),
"x-ray chest anteroposterior Pneumonia",
]
],
},
"params": {"get_scaling_factor": True},
}
# Create request json
request_file_name = "sample_request_data.json"
with open(request_file_name, "w") as request_file:
json.dump(data, request_file)
response = ml_client_workspace.online_endpoints.invoke(
endpoint_name=endpoint_name,
deployment_name=deployment_name,
request_file=request_file_name,
)
Use MedImageInsight REST API
MedImageInsight model assumes a simple single-turn interaction where one request produces one response.
Request schema
Request payload is a JSON formatted string containing the following parameters:
| Key | Type | Required/Default | Allowed values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
input_data |
[object] |
Y | An object containing the input data payload | |
params |
[object] |
Nnull |
An object containing parameters passed to the model |
The input_data object contains the following fields:
| Key | Type | Required/Default | Allowed values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
columns |
list[string] |
Y | "text", "image" |
An object containing the strings mapping data to inputs passed to the model. |
index |
integer |
Y | 0 - 1024 | Count of inputs passed to the model. You're limited by how much data can be passed in a single POST request, which depends on the size of your images. Therefore, you should keep this number in the dozens |
data |
list[list[string]] |
Y | "" | The list contains the items passed to the model which is defined by the index parameter. Each item is a list of two strings. The order is defined by the columns parameter. The text string contains text to embed. The image strings are the image bytes encoded using base64 and decoded as utf-8 string |
The params object contains the following fields:
| Key | Type | Required/Default | Allowed values | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
get_scaling_factor |
boolean |
NTrue |
"True" OR "False" |
Whether the model should return "temperature" scaling factor. This factor is useful when you're planning to compare multiple cosine similarity values in an application like classification. It's essential for correct implementation of "zero-shot" type of scenarios. For usage, refer to the zero-shot classification example linked in the Classification techniques section. |
Request example
A simple inference requesting embedding of a single string
{
"input_data": {
"columns": [
"image",
"text"
],
"index":[0],
"data": [
["", "a quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog"]
]
},
"params": {}
}
Request for embedding of an image and a string, requesting for return of the scaling factor
{
"input_data": {
"columns": ["image", "text"],
"index": [0],
"data": [
[
"iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAIAAAACCAYAAABytg0kAAAAAXNSR0IArs4c6QAAAARnQU1BAACx\njwv8YQUAAAAJcEhZcwAAFiUAABYlAUlSJPAAAAAbSURBVBhXY/gUoPS/fhfDfwaGJe///9/J8B8A\nVGwJ5VDvPeYAAAAASUVORK5CYII=\n",
"x-ray chest anteroposterior Pleural Effusion"
]
]
},
"params": {
"get_scaling_factor": "true"
}
}
Response schema
Response payload is a JSON formatted string containing the following fields:
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
image_features |
list[list[float]] |
If requested, list of vectors, one per each submitted image. |
text_features |
list[list[float]] |
If requested, list of vectors, one per each submitted text string. |
scaling_factor |
float |
If requested, the scaling factor |
Response example
A simple inference requesting embedding of a single string
{
"image_features": [[0.029661938548088074, -0.027228673920035362, ... , -0.0328846238553524]],
"text_features": [[0.0028937323950231075, 0.004354152828454971, -0.0227945726364851, ..., 0.002080598147585988]],
"scaling_factor": 4.516357
}
Other implementation considerations
The maximum number of tokens processed in the input string is 77. Anything past 77 tokens would be cut off before being passed to the model. The model is using a Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) tokenizer which uses about three Latin characters per token.
The submitted text is embedded into the same latent space as the image. As a result, strings describing medical images of certain body parts obtained with certain imaging modalities are embedded close to such images. Also, when building systems on top of a MedImageInsight model, you should make sure that all your embedding strings are consistent with one another (word order and punctuation). For best results with base model, strings should follow the pattern <image modality> <anatomy> <exam parameters> <condition/pathology>., for example: x-ray chest anteroposterior Atelectasis..
If you're fine-tuning the model, you can change these parameters to better suit your application needs.
Supported image formats
The deployed model API supports images encoded in PNG format.
When the model receives the images, it does preprocessing that involves compressing and resizing the images to 512x512 pixels.
The preferred compression format is lossless PNG, containing either an 8-bit monochromatic or RGB image. For optimization purposes, you can perform resizing on the client side to reduce network traffic.
Learn more from samples
MedImageInsight is a versatile model that can be applied to a wide range of tasks and imaging modalities. For more specific examples of solving various tasks with MedImageInsight, see the following interactive Python notebooks.
Getting started
- Deploying and Using MedImageInsight: Learn how to deploy the MedImageInsight model programmatically and issue an API call to it.
Classification techniques
Building a Zero-Shot Classifier: Discover how to use MedImageInsight to create a classifier without the need for training or large amount of labeled ground truth data.
Enhancing Classification with Adapter Networks: Improve classification performance by building a small adapter network on top of MedImageInsight.
Advanced applications
Inferring MRI Acquisition Parameters from Pixel Data: Understand how to extract MRI exam acquisition parameters directly from imaging data.
Scalable MedImageInsight Endpoint Usage: Learn how to generate embeddings of medical images at scale using the MedImageInsight API while handling potential network issues gracefully.