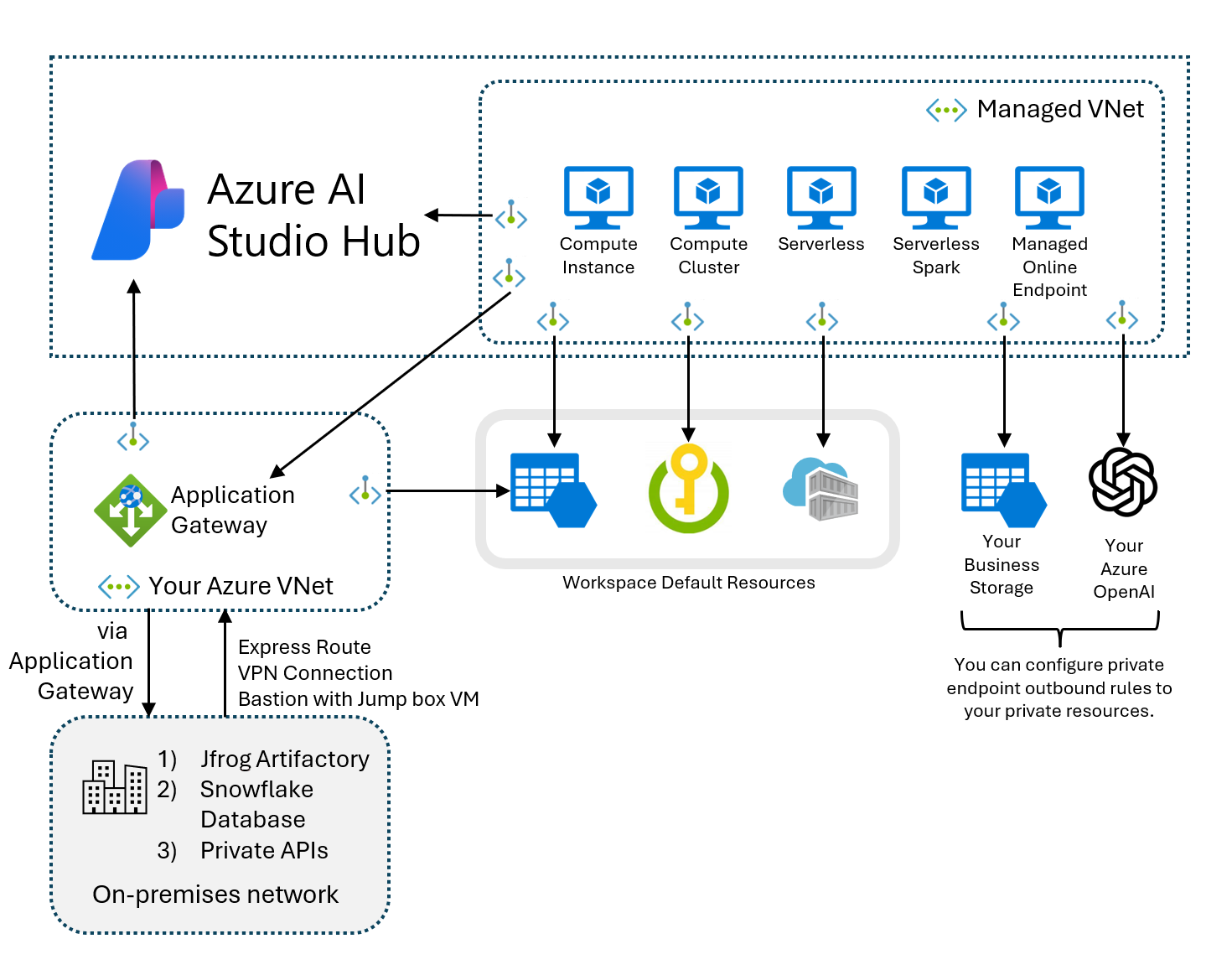
Access on-premises resources from your Azure AI Foundry's managed network (preview)
To access your non-Azure resources located in a different virtual network or located entirely on-premises from your Azure AI Foundry's managed virtual network, an Application Gateway must be configured. Through this Application Gateway, full end to end access can be configured to your resources.
Azure Application Gateway is a load balancer that makes routing decisions based on the URL of an HTTPS request. Azure Machine Learning supports using an application gateway to securely communicate with non-Azure resources. For more on Application Gateway, see What is Azure Application Gateway.
To access on-premises or custom virtual network resources from the managed virtual network, you configure an Application Gateway on your Azure virtual network. The application gateway is used for inbound access to the Azure AI Foundry portal's hub. Once configured, you then create a private endpoint from the Azure AI Foundry hub's managed virtual network to the Application Gateway. With the private endpoint, the full end to end path is secured and not routed through the Internet.
Prerequisites
- Read the How an application gateway works article to understand how the Application Gateway can secure the connection to your non-Azure resources.
- Set up your Azure AI Foundry hub's managed virtual network and select your isolation mode, either Allow Internet Outbound or Allow Only Approved Outbound. For more information, see Managed virtual network isolation.
- Get the private HTTP(S) endpoint of the resource to access.
Supported resources
Application Gateway supports any backend target resource that uses HTTP or HTTPS protocol. Connections to the following resources from the managed virtual network are verified:
- Jfrog Artifactory
- Snowflake Database
- Private APIs
Configure Azure Application Gateway
Follow the Quickstart: Direct web traffic using the portal. To correctly set up your Application Gateway for use with Azure Machine Learning, use the following guidance when creating the Application Gateway:
From the Basics tab:
- Ensure your Application Gateway is in the same region as the selected Azure Virtual Network.
- Azure AI Foundry only supports IPv4 for Application Gateway.
- With your Azure Virtual Network, select one dedicated subnet for your Application Gateway. No other resources can be deployed in this subnet.
From the Frontends tab, Application Gateway doesn't support private Frontend IP address only so Public IP addresses need to be selected or a new one created. Private IP addresses for the resources that the gateway connects to can be added within the range of the subnet you selected on the Basics tab.
From the Backends tab, you can add your backend target to a backend pool. You can manage your backend targets by creating different backend pools. Request routing is based on the pools. You can add backend targets such as a Snowflake database.
From the Configuration tab, you configure how requests are received with the frontend IPs and routed to the backend.
In the Listener section:
- You can create a listener with either HTTP or HTTPS protocol and specify the port you want it to listen to. If you want two listeners listening on the same front-end IP address and routing to different backend pools, you need to choose different ports. Incoming requests are differentiated based on ports.
- If you want end-to-end TLS encryption, select HTTPS listener and upload your own certificate for Application Gateway to decrypt request received by listener. For more information, see Enabling end to end TLS on Azure Application Gateway.
- If you want a fully private backend target without any public network access, DO NOT setup a listener on the public frontend IP address and its associated routing rule. Application Gateway only forwards requests that listeners receive at the specific port. If you want to avoid adding public frontend IP listener by mistake, see Network security rules to fully lock down public network access.
In the Backend targets section, if you want to use HTTPS and Backend server's certificate is NOT issued by a well-known CA, you must upload the Root certificate (.CER) of the backend server. For more on configuring with a root certificate, see Configure end-to-end TLS encryption using the portal.
Once the Application Gateway resource is created, navigate to the new Application Gateway resource in the Azure portal. Under Settings, select, Private link to enable a virtual network to privately access the Application Gateway through a private endpoint connection. The Private link configuration isn't created by default.
- Select + Add to add the Private Link configuration, and then use the following values to create the configuration:
- Name: Provide a name for your private link configuration
- Private link subnet: Select a subnet in your virtual network.
- Frontend IP Configuration:
appGwPrivateFrontendIpIPv4
- To verify the Private link is set up correctly, navigate to the Private endpoint connections tab and select + Private endpoint. On the Resource tab, the Target sub-resource should be the name of your private Frontend IP configuration,
appGwPrivateFrontendIpIPv4. If no value appears in the Target sub-resource, then the Application Gateway listener wasn't configured correctly. For more on setting up Private link in Application Gateway, see Configure Azure Application Gateway Private Link.
- Select + Add to add the Private Link configuration, and then use the following values to create the configuration:
Configure private link
Now that your Application Gateway's front-end IP and backend pools are created, you can now configure the private endpoint from the managed virtual network to your Application Gateway. in the Azure portal, navigate to your Azure AI Foundry hub's Networking tab. Select Workspace managed outbound access, + Add user-defined outbound rules.
In the Workspace Outbound rules form, select the following to create your private endpoint:
- Rule name: Provide a name for your private endpoint to Application Gateway.
- Destination Type: Private Endpoint
- Subscription and Resource Group: Select the Subscription and Resource Group where your Application Gateway is deployed
- Resource Type:
Microsoft.Network/applicationGateways - Resource name: The name of your Application Gateway resource.
- Sub resource:
appGwPrivateFrontendIpIPv4 - FQDNs: These FQDNs are the aliases that you want to use inside the Azure AI Foundry portal. They're resolved to the managed private endpoint's private IP address targeting Application Gateway. You might include multiple FQDNs depending on how many resources you would like to connect to with the Application Gateway.
Note
- If you are using HTTPS listener with certificate uploaded, make sure the FQDN alias matches with the certificate's CN (Common Name) or SAN (Subject Alternative Name) otherwise HTTPS call will fail with SNI (Server Name Indication).
- The provided FQDNs must have at least three labels in the name to properly create the private DNS zone of thee private endpoint for Application Gateway.
- The FQDNs field is editable after the private endpoint creation through SDK or CLI. The field is not editable in the Azure portal.
- Dynamic sub-resource naming is not supported for the private Frontend IP configuration. The Frontend IP name must be
appGwPrivateFrontendIpIPv4.
Configure using Python SDK and Azure CLI
To create a private endpoint to Application Gateway with SDK, see Azure SDK for Python.
To create a private endpoint to Application Gateway with the Azure CLI, use the az ml workspace outbound-rule set command. Set properties as needed for your configuration. For more information, see Configure a managed network.
Limitations
- Application Gateway supports only HTTP(s) endpoints in the Backend pool. There's no support for non-HTTP(s) network traffic. Ensure your resources support HTTP(S) protocol.
- To connect to Snowflake using the Application Gateway, you should add your own FQDN outbound rules to enable package/driver download and OCSP validation.
- The Snowflake JDBC driver uses HTTPS calls, but different drivers might have different implementations. Check if your resource uses HTTP(S) protocol or not.
- For more information on limitations, see Frequently asked questions about Application Gateway.
Application Gateway Errors
For errors related to the Application Gateway connection to your backend resources, follow the existing Application Gateway documentation based on the errors you receive:
- Troubleshoot backend health issues in Application Gateway
- Troubleshooting bad gateway errors in Application Gateway
- HTTP response codes in Application Gateway
- Understanding disabled listeners