Customize the user interface with HTML templates in Azure Active Directory B2C
Before you begin, use the Choose a policy type selector at the top of this page to choose the type of policy you’re setting up. Azure Active Directory B2C offers two methods to define how users interact with your applications: through predefined user flows or through fully configurable custom policies. The steps required in this article are different for each method.
Branding and customizing the user interface that Azure Active Directory B2C (Azure AD B2C) displays to your customers helps provide a seamless user experience in your application. These experiences include signing up, signing in, profile editing, and password resetting. This article introduces the methods of user interface (UI) customization.
Tip
If you want to modify only the banner logo, background image, and background color of your user flow pages, you can try the Company branding feature.
Custom HTML and CSS overview
Azure AD B2C runs code in your customer's browser by using Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS). At runtime, content is loaded from a URL you specify in your user flow or custom policy. Each page in the user experience loads its content from the URL you specify for that page. After content is loaded from your URL, it's merged with an HTML fragment inserted by Azure AD B2C, and then the page is displayed to your customer.
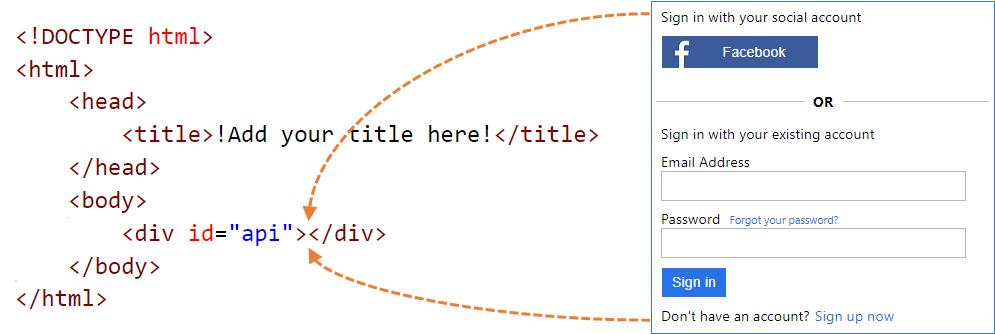
Custom HTML page content
Create an HTML page with your own branding to serve your custom page content. This page can be a static *.html page, or a dynamic page like .NET, Node.js, or PHP,however, Azure B2C does not support any view engines. Any server-side rendering of the dynamic page must be performed by a dedicated web application.
Your custom page content can contain any HTML elements, including CSS and JavaScript, but can't include insecure elements like iframes. The only required element is a div element with id set to api, such as this one <div id="api"></div> within your HTML page.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Product Brand Name</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="api"></div>
</body>
</html>
Customize the default Azure AD B2C pages
Instead of creating your custom page content from scratch, you can customize Azure AD B2C's default page content.
The following table lists the default page content provided by Azure AD B2C. Download the files and use them as a starting point for creating your own custom pages. See Sample templates to learn how you can download and use the sample templates.
| Page | Description | Templates |
|---|---|---|
| Unified sign-up or sign-in | This page handles the user sign-up and sign-in process. Users can use enterprise identity providers, social identity providers such as Facebook, Microsoft account, or local accounts. | Classic, Ocean Blue, and Slate Gray. |
| Sign-in (only) | The sign-in page is also known as the Identity provider selection. It handles the user sign-in with local account, or federated identity providers. Use this page to allow sign-in without the ability to sign up. For example before user can edit their profile. | Classic, Ocean Blue, and Slate Gray. |
| Self-Asserted | Most interactions in Azure AD B2C where the user is expected to provide input are self-asserted. For example, a sign-up page, sign-in page, or password reset page. Use this template as a custom page content for a social account sign-up page, a local account sign-up page, a local account sign-in page, password reset, edit profile, block page and more. The self-asserted page can contain various input controls, such as: a text input box, a password entry box, a radio button, single-select drop-down boxes, and multi-select check boxes. | Classic, Ocean Blue, and Slate Gray. |
| Multi-factor authentication | On this page, users can verify their phone numbers (by using text or voice) during sign-up or sign-in. | Classic, Ocean Blue, and Slate Gray. |
| Error | This page is displayed when an exception or an error is encountered. | Classic, Ocean Blue, and Slate Gray. |
Hosting the page content
When using your own HTML and CSS files to customize the UI, host your UI content on any publicly available HTTPS endpoint that supports CORS. For example, Azure Blob storage, Azure App Services, web servers, CDNs, AWS S3, or file sharing systems.
Guidelines for using custom page content
Use an absolute URL when you include external resources like media, CSS, and JavaScript files in your HTML file.
Using page layout version 1.2.0 and above, you can add the
data-preload="true"attribute in your HTML tags to control the load order for CSS and JavaScript. Withdata-preload="true", the page is constructed before being shown to the user. This attribute helps prevent the page from "flickering" by preloading the CSS file, without the un-styled HTML being shown to the user. The following HTML code snippet shows the use of thedata-preloadtag.<link href="https://path-to-your-file/sample.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" data-preload="true"/>We recommend that you start with the default page content and build on top of it.
You can include JavaScript in your custom content.
Supported browser versions are:
- Internet Explorer 11, 10, and Microsoft Edge
- Limited support for Internet Explorer 9 and 8
- Google Chrome 42.0 and above
- Mozilla Firefox 38.0 and above
- Safari for iOS and macOS, version 12 and above
Due to security restrictions, Azure AD B2C doesn't support
frame,iframe, orformHTML elements.
Localize content
You localize your HTML content by enabling language customization in your Azure AD B2C tenant. Enabling this feature allows Azure AD B2C to set the HTML page language attribute and pass the OpenID Connect parameter ui_locales to your endpoint.
Single-template approach
During page load, Azure AD B2C sets the HTML page language attribute with the current language. For example, <html lang="en">. To render different styles per the current language, use the CSS :lang selector along with your CSS definition.
The following example defines the following classes:
imprint-en- Used when the current language is English.imprint-de- Used when the current language is German.imprint- Default class that is used when the current language is not English or German.
.imprint-en:lang(en),
.imprint-de:lang(de) {
display: inherit !important;
}
.imprint {
display: none;
}
The following HTML elements will be shown or hidden according to the page language:
<a class="imprint imprint-en" href="Link EN">Imprint</a>
<a class="imprint imprint-de" href="Link DE">Impressum</a>
Multi-template approach
The language customization feature allows Azure AD B2C to pass the OpenID Connect parameter ui_locales to your endpoint. Your content server can use this parameter to provide language-specific HTML pages.
Note
Azure AD B2C doesn't pass OpenID Connect parameters, such as ui_locales, to the exception pages.
Content can be pulled from different places based on the locale that's used. In your CORS-enabled endpoint, you set up a folder structure to host content for specific languages. You call the right one if you use the wildcard value {Culture:RFC5646}.
For example, your custom page URI might look like:
https://contoso.blob.core.windows.net/{Culture:RFC5646}/myHTML/unified.html
You can load the page in French by pulling content from:
https://contoso.blob.core.windows.net/fr/myHTML/unified.html
Custom page content walkthrough
Here's an overview of the process:
- Prepare a location to host your custom page content (a publicly accessible, CORS-enabled HTTPS endpoint).
- Download and customize a default page content file, for example
unified.html. - Publish your custom page content your publicly available HTTPS endpoint.
- Set cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) for your web app.
- Point your policy to your custom policy content URI.
Prerequisites
- Create a user flow so users can sign up and sign in to your application.
- Register a web application.
- Complete the steps in Get started with custom policies in Active Directory B2C. This tutorial guides you how to update custom policy files to use your Azure AD B2C tenant configuration.
- Register a web application.
1. Create your HTML content
Create a custom page content with your product's brand name in the title.
Copy the following HTML snippet. It's well-formed HTML5 with an empty element called <div id="api"></div> located within the <body> tags. This element indicates where Azure AD B2C content is to be inserted.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>My Product Brand Name</title> </head> <body> <div id="api"></div> </body> </html>Paste the copied snippet in a text editor
Use CSS to style the UI elements that Azure AD B2C inserts into your page. The following example shows a simple CSS file that also includes settings for the sign-up injected HTML elements:
h1 { color: blue; text-align: center; } .intro h2 { text-align: center; } .entry { width: 400px ; margin-left: auto ; margin-right: auto ; } .divider h2 { text-align: center; } .create { width: 400px ; margin-left: auto ; margin-right: auto ; }Save the file as customize-ui.html.
Note
HTML form elements will be removed due to security restrictions if you use login.microsoftonline.com. If you want to use HTML form elements in your custom HTML content, use b2clogin.com.
2. Create an Azure Blob storage account
In this article, we use Azure Blob storage to host our content. You can choose to host your content on a web server, but you must enable CORS on your web server.
Note
In an Azure AD B2C tenant, you can't provision Blob storage. You must create this resource in your Microsoft Entra tenant.
To host your HTML content in Blob storage, use the following steps:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- If you have access to multiple tenants, select the Settings icon in the top menu to switch to your Microsoft Entra ID tenant from the Directories + subscriptions menu.
- In the Azure portal, search for and select Storage accounts
- Select + Create.
- Select a Subscription for your storage account.
- Create a Resource group or select an existing one.
- Enter a unique Storage account name for your storage account.
- Select the geographical Region for your storage account.
- Performance can remain Standard.
- Redundancy can remain Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
- Select Review + create and wait a few seconds for Microsoft Entra ID to run a validation.
- Select Create to create the storage account. After the deployment is completed, the storage account page opens automatically or you need to select Go to resource.
2.1 Create a container
To create a public container in Blob storage, perform the following steps:
- Under Settings in the leftmost menu, select Configuration.
- Enable Allow Blob anonymous access.
- Select Save.
- Under Data storage in the left-hand menu, select Containers.
- Select + Container.
- For Name, enter root. The name can be a name of your choosing, for example contoso, but we use root in this example for simplicity.
- For Public access level, select Blob. By selecting the Blob option, you allow an anonymous public read-only access for this container.
- Select Create to create the container.
- Select root to open the new container.
2.2 Upload your custom page content files
- Select Upload.
- Select the folder icon next to Select a file.
- Navigate to and select customize-ui.html, which you created earlier in the Page UI customization section.
- If you want to upload to a subfolder, expand Advanced and enter a folder name in Upload to folder.
- Select Upload.
- Select the customize-ui.html blob that you uploaded.
- To the right of the URL text box, select the Copy to clipboard icon to copy the URL to your clipboard.
- In web browser, navigate to the URL you copied to verify the blob you uploaded is accessible. If it's inaccessible, for example if you encounter a
ResourceNotFounderror, make sure the container access type is set to blob.
3. Configure CORS
Configure Blob storage for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing by performing the following steps:
- Navigate to your storage account.
- In the left-hand menu, under Settings, select Resource sharing (CORS).
- For Allowed origins, enter
https://your-tenant-name.b2clogin.com. Replaceyour-tenant-namewith the name of your Azure AD B2C tenant. For example,https://fabrikam.b2clogin.com. Use all lowercase letters when entering your tenant name. - For Allowed Methods, select both
GETandOPTIONS. - For Allowed Headers, enter an asterisk (*).
- For Exposed Headers, enter an asterisk (*).
- For Max age, enter 200.
- At the top of the page, select Save.
3.1 Test CORS
Validate that you're ready by performing the following steps:
- Repeat the configure CORS step. For Allowed origins, enter
https://www.test-cors.org - Navigate to www.test-cors.org
- For the Remote URL box, paste the URL of your HTML file. For example,
https://your-account.blob.core.windows.net/root/azure-ad-b2c/unified.html - Select Send Request.
The result should be
XHR status: 200. If you receive an error, make sure that your CORS settings are correct. You might also need to clear your browser cache or open an in-private browsing session by pressing Ctrl+Shift+P.
Learn more about how to create and manage Azure storage accounts.
4. Update the user flow
- If you have access to multiple tenants, select the Settings icon in the top menu to switch to your Azure AD B2C tenant from the Directories + subscriptions menu.
- In the Azure portal, search for and select Azure AD B2C.
- In the left-hand menu, select User flows, and then select the B2C_1_signupsignin1 user flow.
- Select Page layouts, and then under Unified sign-up or sign-in page, select Yes for Use custom page content.
- In Custom page URI, enter the URI for the custom-ui.html file that you recorded earlier.
- At the top of the page, select Save.
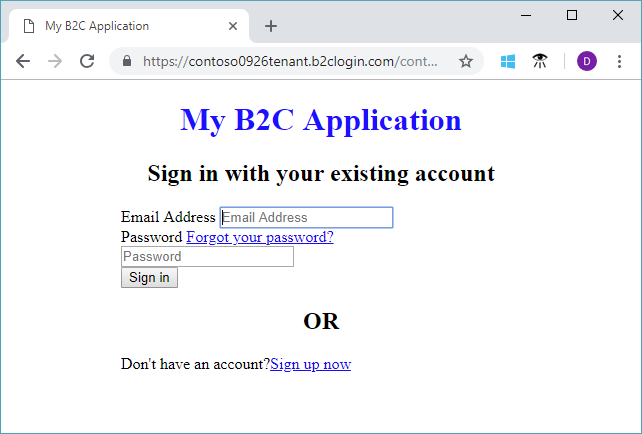
5. Test the user flow
- In your Azure AD B2C tenant, select User flows and select the B2C_1_signupsignin1 user flow.
- At the top of the page, select Run user flow.
- At the pane on right side, select the Run user flow button.
You should see a page similar to the following example with the elements centered based on the CSS file that you created:
4. Modify the extensions file
To configure UI customization, copy the ContentDefinition and its child elements from the base file to the extensions file:
Open the base file of your policy. For example,
SocialAndLocalAccounts/TrustFrameworkBase.xml. This base file is one of the policy files included in the custom policy starter pack, which you should have obtained in the prerequisite, Get started with custom policies.Search for and copy the entire contents of the ContentDefinitions element.
Open the extension file. For example, TrustFrameworkExtensions.xml. Search for the BuildingBlocks element. If the element doesn't exist, add it.
Paste the entire contents of the ContentDefinitions element that you copied as a child of the BuildingBlocks element.
Search for the ContentDefinition element that contains
Id="api.signuporsignin"in the XML that you copied.Change the value of LoadUri to the URL of the HTML file that you uploaded to storage. For example,
https://your-storage-account.blob.core.windows.net/your-container/customize-ui.html.Your custom policy should look like the following code snippet:
<BuildingBlocks> <ContentDefinitions> <ContentDefinition Id="api.signuporsignin"> <LoadUri>https://your-storage-account.blob.core.windows.net/your-container/customize-ui.html</LoadUri> <RecoveryUri>~/common/default_page_error.html</RecoveryUri> <DataUri>urn:com:microsoft:aad:b2c:elements:unifiedssp:1.0.0</DataUri> <Metadata> <Item Key="DisplayName">Signin and Signup</Item> </Metadata> </ContentDefinition> </ContentDefinitions> </BuildingBlocks>Save the extensions file.
5. Upload and test your updated custom policy
5.1 Upload the custom policy
- If you have access to multiple tenants, select the Settings icon in the top menu to switch to your Azure AD B2C tenant from the Directories + subscriptions menu.
- Search for and select Azure AD B2C.
- Under Policies, select Identity Experience Framework.
- Select Upload custom policy.
- Upload the extensions file that you previously changed.
5.2 Test the custom policy by using Run now
- Select the policy that you uploaded, and then select Run now.
- You should be able to sign up by using an email address.
Configure dynamic custom page content URI
By using Azure AD B2C custom policies, you can send a parameter in the URL path, or a query string. By passing the parameter to your HTML endpoint, you can dynamically change the page content. For example, you can change the background image on the Azure AD B2C sign-up or sign-in page, based on a parameter that you pass from your web or mobile application. The parameter can be any claim resolver, such as the application ID, language ID, or custom query string parameter, such as campaignId.
Sending query string parameters
To send query string parameters, in the relying party policy, add a ContentDefinitionParameters element as shown below.
<RelyingParty>
<DefaultUserJourney ReferenceId="SignUpOrSignIn" />
<UserJourneyBehaviors>
<ContentDefinitionParameters>
<Parameter Name="campaignId">{OAUTH-KV:campaignId}</Parameter>
<Parameter Name="lang">{Culture:LanguageName}</Parameter>
<Parameter Name="appId">{OIDC:ClientId}</Parameter>
</ContentDefinitionParameters>
</UserJourneyBehaviors>
...
</RelyingParty>
In your content definition, change the value of LoadUri to https://<app_name>.azurewebsites.net/home/unified. Your custom policy ContentDefinition should look like the following code snippet:
<ContentDefinition Id="api.signuporsignin">
<LoadUri>https://<app_name>.azurewebsites.net/home/unified</LoadUri>
...
</ContentDefinition>
When Azure AD B2C loads the page, it makes a call to your web server endpoint:
https://<app_name>.azurewebsites.net/home/unified?campaignId=123&lang=fr&appId=00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444
Dynamic page content URI
Content can be pulled from different places based on the parameters used. In your CORS-enabled endpoint, set up a folder structure to host content. For example, you can organize the content in following structure. Root folder/folder per language/your html files. For example, your custom page URI might look like:
<ContentDefinition Id="api.signuporsignin">
<LoadUri>https://contoso.blob.core.windows.net/{Culture:LanguageName}/myHTML/unified.html</LoadUri>
...
</ContentDefinition>
Azure AD B2C sends the two letter ISO code for the language, fr for French:
https://contoso.blob.core.windows.net/fr/myHTML/unified.html
Sample templates
You can find sample templates for UI customization here:
git clone https://github.com/azure-ad-b2c/html-templates
This project contains the following templates:
To use the sample:
Clone the repo on your local machine. Choose a template folder
/AzureBlue,/MSA, or/classic.Upload all the files under the template folder and the
/srcfolder, to Blob storage as described in the previous sections.Next, open each
\*.htmlfile in the template folder. Then replace all instances ofhttps://login.microsoftonline.comURLs, with the URL you uploaded in step 2. For example:From:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/templates/src/fonts/segoeui.WOFFTo:
https://your-storage-account.blob.core.windows.net/your-container/templates/src/fonts/segoeui.WOFFSave the
\*.htmlfiles and upload them to the Blob storage.Now modify the policy, pointing to your HTML file, as mentioned previously.
If you see missing fonts, images, or CSS, check your references in the extensions policy and the
\*.htmlfiles.
Use company branding assets in custom HTML
To use company branding assets in a custom HTML, add the following tags outside the <div id="api"> tag. The image source is replaced with that of the background image and banner logo.
<img data-tenant-branding-background="true" />
<img data-tenant-branding-logo="true" alt="Company Logo" />
Next steps
Learn how to enable client-side JavaScript code.