Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
When working with a database it is common to request data that is spread across multiple tables. To retrieve data from two different tables we can use either a correlated subquery or a JOIN operation. In this tutorial we compare correlated subqueries and the JOIN syntax before looking at how to create a TableAdapter that includes a JOIN in its main query.
Introduction
With relational databases the data we are interested in working with is often spread across multiple tables. For example, when displaying product information we likely want to list each product s corresponding category and supplier s names. The Products table has CategoryID and SupplierID values, but the actual category and supplier names are in the Categories and Suppliers tables, respectively.
To retrieve information from another, related table, we can either use correlated subqueries or JOINs. A correlated subquery is a nested SELECT query that references columns in the outer query. For example, in the Creating a Data Access Layer tutorial we used two correlated subqueries in the ProductsTableAdapter s main query to return the category and supplier names for each product. A JOIN is a SQL construct that merges related rows from two different tables. We used a JOIN in the Querying Data with the SqlDataSource Control tutorial to display category information alongside each product.
The reason we have abstained from using JOIN s with the TableAdapters is because of limitations in the TableAdapter s wizard to auto-generate corresponding INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements. More specifically, if the TableAdapter s main query contains any JOIN s, the TableAdapter cannot auto-create the ad-hoc SQL statements or stored procedures for its InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties.
In this tutorial we will briefly compare and contrast correlated subqueries and JOIN s before exploring how to create a TableAdapter that includes JOIN s in its main query.
Comparing and Contrasting Correlated Subqueries andJOIN s
Recall that the ProductsTableAdapter created in the first tutorial in the Northwind DataSet uses correlated subqueries to bring back each product s corresponding category and supplier name. The ProductsTableAdapter s main query is shown below.
SELECT ProductID, ProductName, SupplierID, CategoryID,
QuantityPerUnit, UnitPrice, UnitsInStock, UnitsOnOrder,
ReorderLevel, Discontinued,
(SELECT CategoryName FROM Categories WHERE Categories.CategoryID =
Products.CategoryID) as CategoryName,
(SELECT CompanyName FROM Suppliers WHERE Suppliers.SupplierID =
Products.SupplierID) as SupplierName
FROM Products
The two correlated subqueries - (SELECT CategoryName FROM Categories WHERE Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID) and (SELECT CompanyName FROM Suppliers WHERE Suppliers.SupplierID = Products.SupplierID) - are SELECT queries that return a single value per product as an additional column in the outer SELECT statement s column list.
Alternatively, a JOIN can be used to return each product s supplier and category name. The following query returns the same output as the above one, but uses JOIN s in place of subqueries:
SELECT ProductID, ProductName, Products.SupplierID, Products.CategoryID,
QuantityPerUnit, UnitPrice, UnitsInStock, UnitsOnOrder,
ReorderLevel, Discontinued,
Categories.CategoryName,
Suppliers.CompanyName as SupplierName
FROM Products
LEFT JOIN Categories ON
Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID
LEFT JOIN Suppliers ON
Suppliers.SupplierID = Products.SupplierID
A JOIN merges the records from one table with records from another table based on some criteria. In the above query, for example, the LEFT JOIN Categories ON Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID instructs SQL Server to merge each product record with the category record whose CategoryID value matches the product s CategoryID value. The merged result allows us to work with the corresponding category fields for each product (such as CategoryName).
Note
JOIN s are commonly used when querying data from relational databases. If you are new to the JOIN syntax or need to brush up a bit on its usage, I d recommend the SQL Join tutorial at W3 Schools. Also worth reading are the JOIN Fundamentals and Subquery Fundamentals sections of the SQL Books Online.
Since JOIN s and correlated subqueries can both be used to retrieve related data from other tables, many developers are left scratching their heads and wondering which approach to use. All of the SQL gurus I ve talked to have said roughly the same thing, that it doesn t really matter performance-wise as SQL Server will produce roughly identical execution plans. Their advice, then, is to use the technique that you and your team are most comfortable with. It merits noting that after imparting this advice these experts immediately express their preference of JOIN s over correlated subqueries.
When building a Data Access Layer using Typed DataSets, the tools work better when using subqueries. In particular, the TableAdapter s wizard will not auto-generate corresponding INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements if the main query contains any JOIN s, but will auto-generate these statements when correlated subqueries are used.
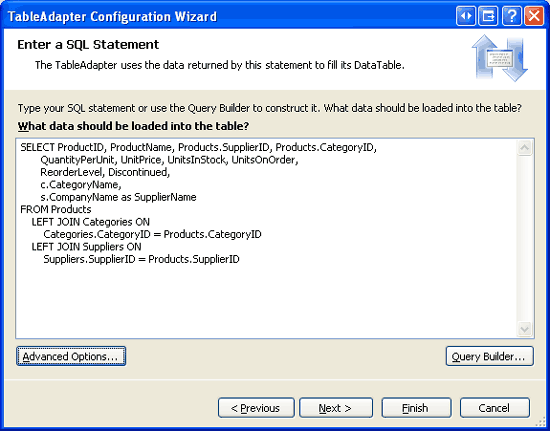
To explore this shortcoming, create a temporary Typed DataSet in the ~/App_Code/DAL folder. During the TableAdapter Configuration wizard, choose to use ad-hoc SQL statements and enter the following SELECT query (see Figure 1):
SELECT ProductID, ProductName, Products.SupplierID, Products.CategoryID,
QuantityPerUnit, UnitPrice, UnitsInStock, UnitsOnOrder,
ReorderLevel, Discontinued,
Categories.CategoryName,
Suppliers.CompanyName as SupplierName
FROM Products
LEFT JOIN Categories ON
Categories.CategoryID = Products.CategoryID
LEFT JOIN Suppliers ON
Suppliers.SupplierID = Products.SupplierID
Figure 1: Enter a Main Query that Contains JOIN s (Click to view full-size image)
By default, the TableAdapter will automatically create INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements based on the main query. If you click the Advanced button you can see that this feature is enabled. Despite this setting, the TableAdapter will not be able to create the INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements because the main query contains a JOIN.
Figure 2: Enter a Main Query that Contains JOIN s
Click Finish to complete the wizard. At this point your DataSet s Designer will include a single TableAdapter with a DataTable with columns for each of the fields returned in the SELECT query s column list. This includes the CategoryName and SupplierName, as Figure 3 shows.
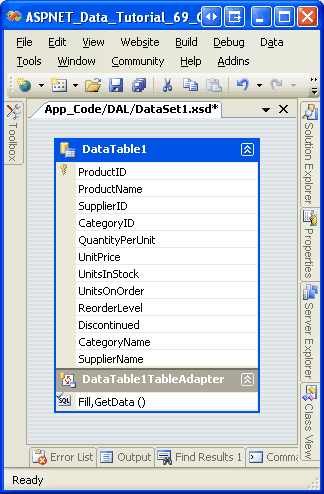
Figure 3: The DataTable Includes a Column for Each Field Returned in the Column List
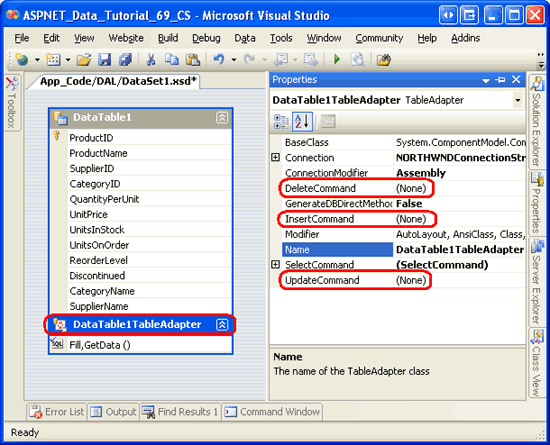
While the DataTable has the appropriate columns, the TableAdapter lacks values for its InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties. To confirm this, click on the TableAdapter in the Designer and then go to the Properties window. There you will see that the InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties are set to (None) .
Figure 4: The InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand Properties are Set to (None) (Click to view full-size image)
To work around this shortcoming, we can manually provide the SQL statements and parameters for the InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties via the Properties window. Alternatively, we could start by configuring the TableAdapter s main query to not include any JOIN s. This will allow the INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements to be auto-generated for us. After completing the wizard, we could then manually update the TableAdapter s SelectCommand from the Properties window so that it includes the JOIN syntax.
While this approach works, it is very brittle when using ad-hoc SQL queries because any time the TableAdapter s main query is re-configured through the wizard, the auto-generated INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements are recreated. That means all of the customizations we later made would be lost if we right-clicked on the TableAdapter, chose Configure from the context menu, and completed the wizard again.
The brittleness of the TableAdapter s auto-generated INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements is, fortunately, limited to ad-hoc SQL statements. If your TableAdapter uses stored procedures, you can customize the SelectCommand, InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, or DeleteCommand stored procedures and re-run the TableAdapter Configuration wizard without having to fear that the stored procedures will be modified.
Over the next several steps we will create a TableAdapter that, initially, uses a main query that omits any JOIN s so that the corresponding insert, update, and delete stored procedures will be auto-generated. We will then update the SelectCommand so that uses a JOIN that returns additional columns from related tables. Finally, we'll create a corresponding Business Logic Layer class and demonstrate using the TableAdapter in an ASP.NET web page.
Step 1: Creating the TableAdapter Using a Simplified Main Query
For this tutorial we will add a TableAdapter and strongly-typed DataTable for the Employees table in the NorthwindWithSprocs DataSet. The Employees table contains a ReportsTo field that specified the EmployeeID of the employee s manager. For example, employee Anne Dodsworth has a ReportTo value of 5, which is the EmployeeID of Steven Buchanan. Consequently, Anne reports to Steven, her manager. Along with reporting each employee s ReportsTo value, we might also want to retrieve the name of their manager. This can be accomplished using a JOIN. But using a JOIN when initially creating the TableAdapter precludes the wizard from automatically generating the corresponding insert, update, and delete capabilities. Therefore, we will start by creating a TableAdapter whose main query does not contain any JOIN s. Then, in Step 2, we will update the main query stored procedure to retrieve the manager s name via a JOIN.
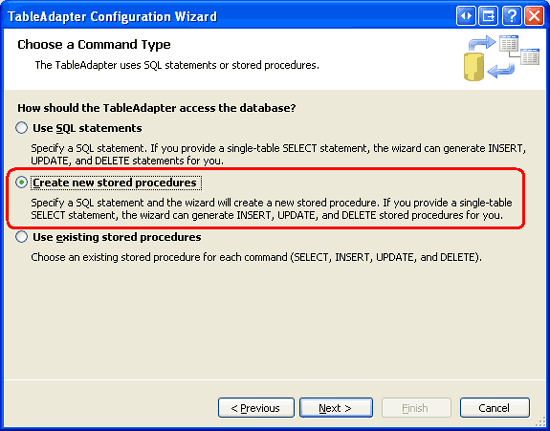
Start by opening the NorthwindWithSprocs DataSet in the ~/App_Code/DAL folder. Right-click on the Designer, select the Add option from the context menu, and pick the TableAdapter menu item. This will launch the TableAdapter Configuration wizard. As Figure 5 depicts, have the wizard create new stored procedures and click Next. For a refresher on creating new stored procedures from the TableAdapter s wizard, consult the Creating New Stored Procedures for the Typed DataSet s TableAdapters tutorial.
Figure 5: Select the Create new stored procedures Option (Click to view full-size image)
Use the following SELECT statement for the TableAdapter s main query:
SELECT EmployeeID, LastName, FirstName, Title, HireDate, ReportsTo, Country
FROM Employees
Since this query does not include any JOIN s, the TableAdapter wizard will automatically create stored procedures with corresponding INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements, as well as a stored procedure for executing the main query.
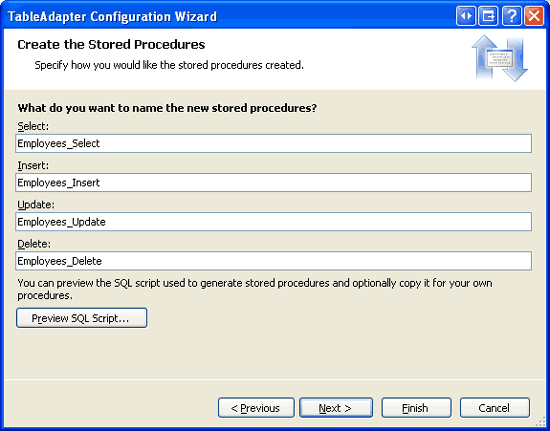
The following step allows us to name the TableAdapter s stored procedures. Use the names Employees_Select, Employees_Insert, Employees_Update, and Employees_Delete, as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Name the TableAdapter s Stored Procedures (Click to view full-size image)
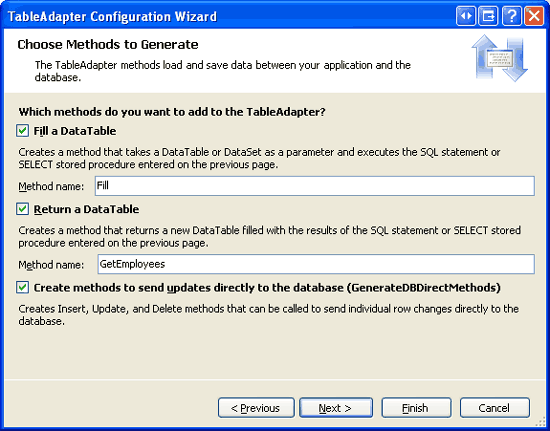
The final step prompts us to name the TableAdapter s methods. Use Fill and GetEmployees as the method names. Also be sure to leave the Create methods to send updates directly to the database (GenerateDBDirectMethods) checkbox checked.
Figure 7: Name the TableAdapter s Methods Fill and GetEmployees (Click to view full-size image)
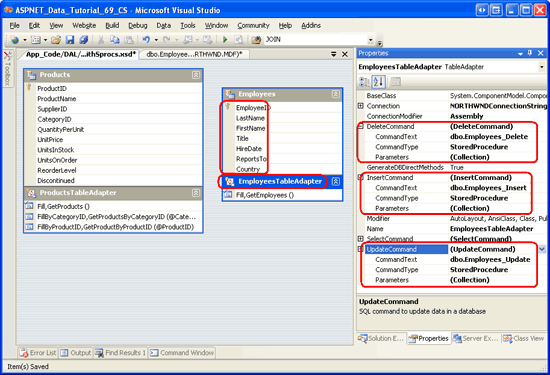
After completing the wizard, take a moment to examine the stored procedures in the database. You should see four new ones: Employees_Select, Employees_Insert, Employees_Update, and Employees_Delete. Next, inspect the EmployeesDataTable and EmployeesTableAdapter just created. The DataTable contains a column for each field returned by the main query. Click on the TableAdapter and then go to the Properties window. There you will see that the InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties are correctly configured to call the corresponding stored procedures.
Figure 8: The TableAdapter Includes Insert, Update, and Delete Capabilities (Click to view full-size image)
With the insert, update, and delete stored procedures automatically created and the InsertCommand, UpdateCommand, and DeleteCommand properties correctly configured, we are ready to customize the SelectCommand s stored procedure to return additional information about each employee s manager. Specifically, we need to update the Employees_Select stored procedure to use a JOIN and return the manager s FirstName and LastName values. After the stored procedure has been updated, we will need to update the DataTable so that it includes these additional columns. We'll tackle these two tasks in Steps 2 and 3.
Step 2: Customizing the Stored Procedure to Include aJOIN
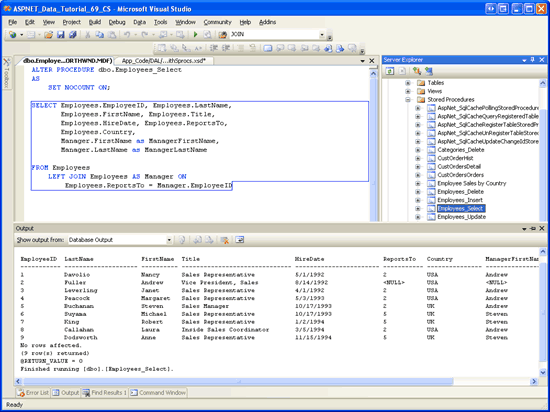
Start by going to the Server Explorer, drilling down into the Northwind database s Stored Procedures folder, and opening the Employees_Select stored procedure. If you do not see this stored procedure, right-click on the Stored Procedures folder and choose Refresh. Update the stored procedure so that it uses a LEFT JOIN to return the manager s first and last name:
SELECT Employees.EmployeeID, Employees.LastName,
Employees.FirstName, Employees.Title,
Employees.HireDate, Employees.ReportsTo,
Employees.Country,
Manager.FirstName as ManagerFirstName,
Manager.LastName as ManagerLastName
FROM Employees
LEFT JOIN Employees AS Manager ON
Employees.ReportsTo = Manager.EmployeeID
After updating the SELECT statement, save the changes by going to the File menu and choosing Save Employees_Select. Alternatively, you can click the Save icon in the toolbar or hit Ctrl+S. After saving your changes, right-click on the Employees_Select stored procedure in the Server Explorer and choose Execute. This will run the stored procedure and show its results in the Output window (see Figure 9).
Figure 9: The Stored Procedures Results are Displayed in the Output Window (Click to view full-size image)
Step 3: Updating the DataTable s Columns
At this point, the Employees_Select stored procedure returns ManagerFirstName and ManagerLastName values, but the EmployeesDataTable is missing these columns. These missing columns can be added to the DataTable in one of two ways:
- Manually - right-click on the DataTable in the DataSet Designer and, from the Add menu, choose Column. You can then name the column and set its properties accordingly.
- Automatically - the TableAdapter Configuration wizard will update the DataTable s columns to reflect the fields returned by the
SelectCommandstored procedure. When using ad-hoc SQL statements, the wizard will also remove theInsertCommand,UpdateCommand, andDeleteCommandproperties since theSelectCommandnow contains aJOIN. But when using stored procedures, these command properties remain intact.
We have explored manually adding DataTable columns in previous tutorials, including Master/Detail Using a Bulleted List of Master Records with a Details DataList and Uploading Files, and we will look at this process again in more detail in our next tutorial. For this tutorial, however, let s use the automatic approach via the TableAdapter Configuration wizard.
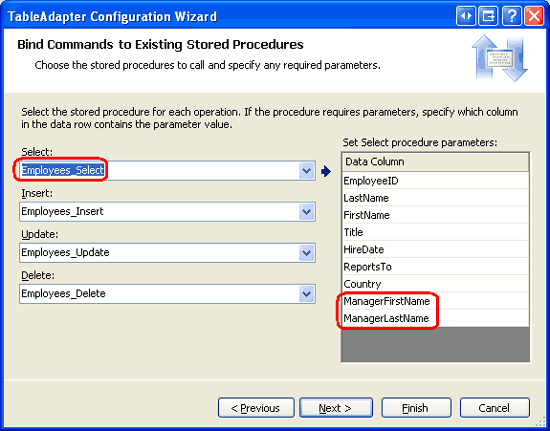
Start by right-clicking on the EmployeesTableAdapter and selecting Configure from the context menu. This brings up the TableAdapter Configuration wizard, which lists the stored procedures used for selecting, inserting, updating, and deleting, along with their return values and parameters (if any). Figure 10 shows this wizard. Here we can see that the Employees_Select stored procedure now returns the ManagerFirstName and ManagerLastName fields.
Figure 10: The Wizard Shows the Updated Column List for the Employees_Select Stored Procedure (Click to view full-size image)
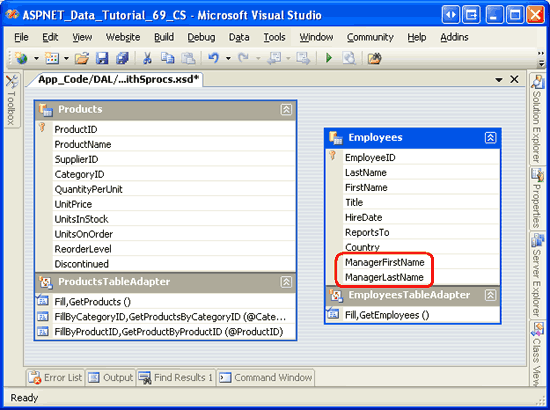
Complete the wizard by clicking Finish. Upon returning to the DataSet Designer, the EmployeesDataTable includes two additional columns: ManagerFirstName and ManagerLastName.
Figure 11: The EmployeesDataTable Contains Two New Columns (Click to view full-size image)
To illustrate that the updated Employees_Select stored procedure is in effect and that the insert, update, and delete capabilities of the TableAdapter are still functional, let s create a web page that allows users to view and delete employees. Before we create such a page, however, we need to first create a new class in the Business Logic Layer for working with employees from the NorthwindWithSprocs DataSet. In Step 4, we will create an EmployeesBLLWithSprocs class. In Step 5, we will use this class from an ASP.NET page.
Step 4: Implementing the Business Logic Layer
Create a new class file in the ~/App_Code/BLL folder named EmployeesBLLWithSprocs.cs. This class mimics the semantics of the existing EmployeesBLL class, only this new one provides fewer methods and uses the NorthwindWithSprocs DataSet (instead of the Northwind DataSet). Add the following code to the EmployeesBLLWithSprocs class.
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using NorthwindWithSprocsTableAdapters;
[System.ComponentModel.DataObject]
public class EmployeesBLLWithSprocs
{
private EmployeesTableAdapter _employeesAdapter = null;
protected EmployeesTableAdapter Adapter
{
get
{
if (_employeesAdapter == null)
_employeesAdapter = new EmployeesTableAdapter();
return _employeesAdapter;
}
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Select, true)]
public NorthwindWithSprocs.EmployeesDataTable GetEmployees()
{
return Adapter.GetEmployees();
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Delete, true)]
public bool DeleteEmployee(int employeeID)
{
int rowsAffected = Adapter.Delete(employeeID);
// Return true if precisely one row was deleted, otherwise false
return rowsAffected == 1;
}
}
The EmployeesBLLWithSprocs class s Adapter property returns an instance of the NorthwindWithSprocs DataSet s EmployeesTableAdapter. This is used by the class s GetEmployees and DeleteEmployee methods. The GetEmployees method calls the EmployeesTableAdapter s corresponding GetEmployees method, which invokes the Employees_Select stored procedure and populates its results in an EmployeeDataTable. The DeleteEmployee method similarly calls the EmployeesTableAdapter s Delete method, which invokes the Employees_Delete stored procedure.
Step 5: Working with the Data in the Presentation Layer
With the EmployeesBLLWithSprocs class complete, we re ready to work with employee data through an ASP.NET page. Open the JOINs.aspx page in the AdvancedDAL folder and drag a GridView from the Toolbox onto the Designer, setting its ID property to Employees. Next, from the GridView s smart tag, bind the grid to a new ObjectDataSource control named EmployeesDataSource.
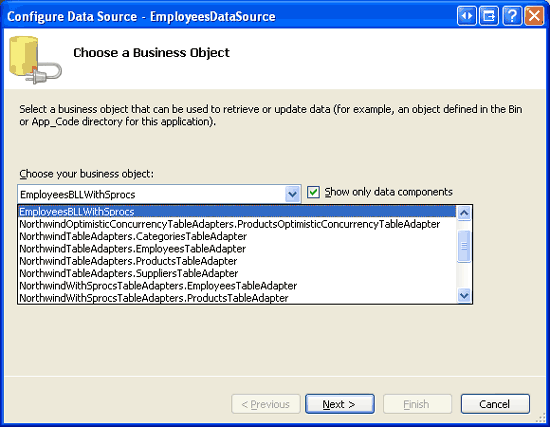
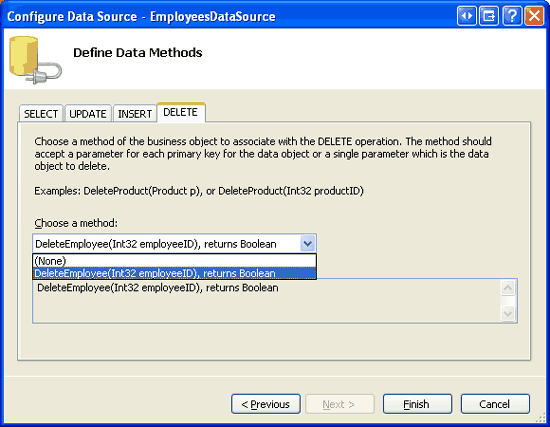
Configure the ObjectDataSource to use the EmployeesBLLWithSprocs class and, from the SELECT and DELETE tabs, ensure that the GetEmployees and DeleteEmployee methods are selected from the drop-down lists. Click Finish to complete the ObjectDataSource s configuration.
Figure 12: Configure the ObjectDataSource to Use the EmployeesBLLWithSprocs Class (Click to view full-size image)
Figure 13: Have the ObjectDataSource Use the GetEmployees and DeleteEmployee Methods (Click to view full-size image)
Visual Studio will add a BoundField to the GridView for each of the EmployeesDataTable s columns. Remove all of these BoundFields except for Title, LastName, FirstName, ManagerFirstName, and ManagerLastName and rename the HeaderText properties for the last four BoundFields to Last Name, First Name, Manager s First Name, and Manager s Last Name, respectively.
To allow users to delete employees from this page we need to do two things. First, instruct the GridView to provide deleting capabilities by checking the Enable Deleting option from its smart tag. Second, change the ObjectDataSource s OldValuesParameterFormatString property from the value set by the ObjectDataSource wizard (original_{0}) to its default value ({0}). After making these changes, your GridView and ObjectDataSource s declarative markup should look similar to the following:
<asp:GridView ID="Employees" runat="server" AutoGenerateColumns="False"
DataKeyNames="EmployeeID" DataSourceID="EmployeesDataSource">
<Columns>
<asp:CommandField ShowDeleteButton="True" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="Title"
HeaderText="Title"
SortExpression="Title" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="LastName"
HeaderText="Last Name"
SortExpression="LastName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="FirstName"
HeaderText="First Name"
SortExpression="FirstName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="ManagerFirstName"
HeaderText="Manager's First Name"
SortExpression="ManagerFirstName" />
<asp:BoundField DataField="ManagerLastName"
HeaderText="Manager's Last Name"
SortExpression="ManagerLastName" />
</Columns>
</asp:GridView>
<asp:ObjectDataSource ID="EmployeesDataSource" runat="server"
DeleteMethod="DeleteEmployee" OldValuesParameterFormatString="{0}"
SelectMethod="GetEmployees" TypeName="EmployeesBLLWithSprocs">
<DeleteParameters>
<asp:Parameter Name="employeeID" Type="Int32" />
</DeleteParameters>
</asp:ObjectDataSource>
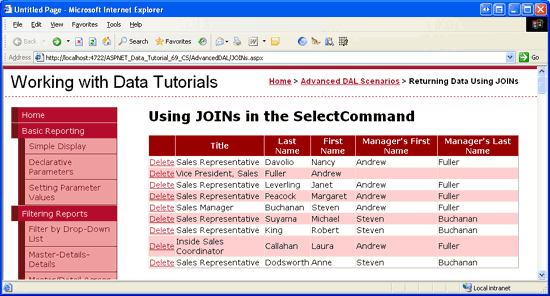
Test out the page by visiting it through a browser. As Figure 14 shows, the page will list each employee and his or her manager s name (assuming they have one).
Figure 14: The JOIN in the Employees_Select Stored Procedure Returns the Manager s Name (Click to view full-size image)
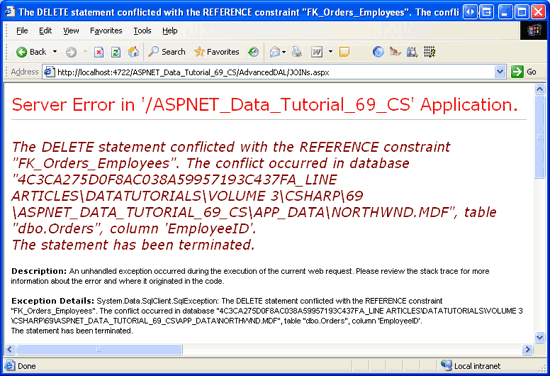
Clicking the Delete button starts the deleting workflow, which culminates in the execution of the Employees_Delete stored procedure. However, the attempted DELETE statement in the stored procedure fails because of a foreign key constraint violation (see Figure 15). Specifically, each employee has one or more records in the Orders table, causing the delete to fail.
Figure 15: Deleting an Employee That has Corresponding Orders Results in a Foreign Key Constraint Violation (Click to view full-size image)
To allow an employee to be deleted you could:
- Update the foreign key constraint to cascade deletes,
- Manually delete the records from the
Orderstable for the employee(s) you want to delete, or - Update the
Employees_Deletestored procedure to first delete the related records from theOrderstable before deleting theEmployeesrecord. We discussed this technique in the Using Existing Stored Procedures for the Typed DataSet s TableAdapters tutorial.
I leave this as an exercise for the reader.
Summary
When working with relational databases, it is common for queries to pull their data from multiple, related tables. Correlated subqueries and JOIN s provide two different techniques for accessing data from related tables in a query. In previous tutorials we most commonly made use of correlated subqueries because the TableAdapter cannot auto-generate INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements for queries involving JOIN s. While these values can be provided manually, when using ad-hoc SQL statements any customizations will be overwritten when the TableAdapter Configuration wizard is completed.
Fortunately, TableAdapters created using stored procedures do not suffer from the same brittleness as those created using ad-hoc SQL statements. Therefore, it is feasible to create a TableAdapter whose main query uses a JOIN when using stored procedures. In this tutorial we saw how to create such a TableAdapter. We started by using a JOIN-less SELECT query for the TableAdapter s main query so that the corresponding insert, update, and delete stored procedures would be auto-created. With the TableAdapter s initial configuration complete, we augmented the SelectCommand stored procedure to use a JOIN and re-ran the TableAdapter Configuration wizard to update the EmployeesDataTable s columns.
Re-running the TableAdapter Configuration wizard automatically updated the EmployeesDataTable columns to reflect the data fields returned by the Employees_Select stored procedure. Alternatively, we could have added these columns manually to the DataTable. We will explore manually adding columns to the DataTable in the next tutorial.
Happy Programming!
About the Author
Scott Mitchell, author of seven ASP/ASP.NET books and founder of 4GuysFromRolla.com, has been working with Microsoft Web technologies since 1998. Scott works as an independent consultant, trainer, and writer. His latest book is Sams Teach Yourself ASP.NET 2.0 in 24 Hours. He can be reached at mitchell@4GuysFromRolla.com. or via his blog, which can be found at http://ScottOnWriting.NET.
Special Thanks To
This tutorial series was reviewed by many helpful reviewers. Lead reviewers for this tutorial were Hilton Geisenow, David Suru, and Teresa Murphy. Interested in reviewing my upcoming MSDN articles? If so, drop me a line at mitchell@4GuysFromRolla.com.