Exchange 2010 Multi-Tenant AutoDiscover and DNS Configuration
The majority of the calls we getting in CSS are autodiscover problems in regards to Multi-Tenant Environments and this is mostly due to incorrectly configured public DNS configuration. As I stated in my other blogs there are two methods to publish the autodiscover records for your tenants. The majority of the customers I do work with are able to get the hosting domain working but end up having problems with the Tenants domain. This article will walk you through configuration your tenant’s autodiscover records using both methods.
Let first go through the difference between the Hosting Organization and Tenant Organization Domain.
**
Hosting Organization**
When you first install Exchange with the hosting switch it will create a top level organization. The Root organization is designed for administrating your Exchange multi-tenant Organization so you will notice that some functionality will not work properly out of the box. If you use the same SMTP domain as your Active directory Domain but it will add additional DNS complexity since this will be in a split DNS configuration.
Tenant Organization
The tenant domain will be your customers smtp domain that you will be hosting on your Exchange Organization. You will be responsible configuring inbound traffic to you Exchange organization for the tenants smtp domain and allow remote access for the tenant subscribers.
In the following scenario we will be using the following domains
Hosting Domain = **Contoso.com
**Tenant Domain = Tenant1.com
You will first want to setup your hosting domain and request a certificate for a public CA. Here you would request your certificate using the New-ExchangeCertificate command and below are some of typical FQDN’s you would request for your certificate.
Autodiscover.contoso.com
Mail.contoso.com
Webmail.contoso.com
The above are the typical public names you will use but will all depend on what you choose to use for your virtual directory ExternalURL’s. As per the naming convention of the FQDN you can easily tell which FQDN will be for what. Now that you requested and imported your Certificate into Exchange using the Import-ExchangeCertificate you will need to configure the ExternalURL’s for your virtual directories.
Autodiscover with IIS Redirection
In our scenario we will configure the autodiscover Externalurl's to use mail.contoso.com to make things simpler. For more information, see Configure Autodiscover Redirection for the Multi-Tenant Organization.
NOTE: This configuration will require 2 public ip addresses for autodiscover redirection to work. The first IP address is for the Exchange Server and the second ip address is for the IIS Redirection Server.
Public DNS Configuration (Exchange Organization)
In this example we are only going to use mail.contoso.com for all your records for Exchange. You will then need to create an A record pointing to the public ip address of your Exchange server. This ip address will point to the public ip address assigned for your Exchange CAS Servers. If your Exchange Server is a CAS/HUB role you can also setup your MX record.
Public IP = 192.168.10.25
Mail.Contoso.Com (A Record) = 192.168.10.25
Contoso.Com (MX Record) = 192.168.10.25
Public DNS configuration (IIS Redirection)
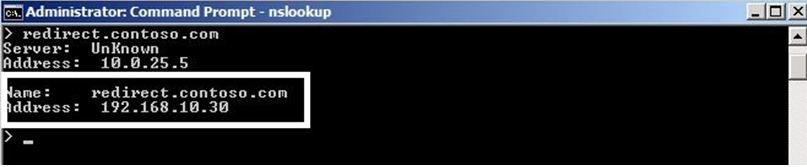
Once you configured your Public records for your Exchange Server you will now need to create an A record for your IIS Redirection Server. In this scenario we will use redirect.contoso.com in your DNS zone that will point to the public ip address assigned for your IIS Redirection servers.
Redirect.contoso.com = 192.168.10.30
Public DNS Configuration (Tenant Organization)
We created a tenant called Tenant1.com in which we will now have to create an autodiscover record for that domain. So now we will have to create a CNAME autodiscover record that will use the redirect.contoso.com A record we just created in your DNS zone.
(CNAME) Autodiscover.Tenant1.com = Redirect.contoso.com
As you can see we are looking up autodiscover.tenant1.com which will now resolve to the redirect.contoso.com record. The outlook client will connect to your IIS server which will then be redirected it to your Exchange Server URL.
Configure IIS Redirection
You will now have to Setup the Autodiscover redirection site using the following Steps for IIS7. Please note the Prerequisites for configuring the AutoDiscover redirection which is also in the provided article.
Prerequisites: You must be running Internet Information Services (IIS) 7. **The Client Access Server and the Domain Controller can't be the same server. **
This is where most administrators make the first mistake when building their environment. When setting up locally on the same server you will break Remote Powershell and you will still get the certificate prompt.
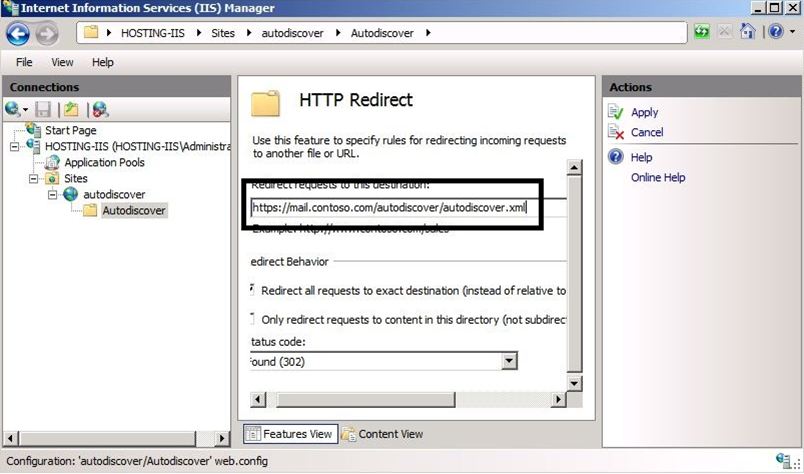
Here is a snapshot of the Autodiscover Virtual directory configured to redirect incoming requests to mail.contoso.com.
At this point when the outlook client connects to your IIS server using http://Autodiscover.tenant1.com, the request will be redirected to the exact URL **https://mail.contoso.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml**. Because the URL matches the already assigned certificate name you will not get a certificate error.
Autodiscover with SRV Record
Using SRV records is more optimal since you will only require a single public ip address which will point to your Exchange Server. You will not require a second ip address or an IIS Server to perform any redirection. All you will need to do is create a SRV record for you tenant that will point to your Exchange Servers DNS name. In this scenario we will create a SRV record that will point to mail.contoso.com. To create a SRV record using a windows server you can use KB940881.
Public DNS Configuration
In this example we are going to create a public SRV record for our tenant1.com domain.
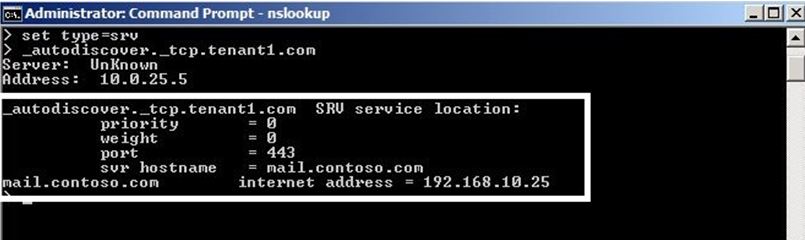
You can use Nslookup against a public dns server to verify if the record is correctly configured.
1) In the command prompt type nslookup
2) Type set type=srv
3) Type _autodiscover._tcp.tenant1.com
Conclusion
The easiest way to configure autodiscover for you tenants is by creating SRV records. You will only require one public ip address and there is no need to bring up any additional server to perform the IIS redirect. The only problem is that some DNS providers do not have the ability to create SRV records in which you will have to use the IIS redirection method.
This article is in reference to Exchange 2010 Multi-tenant deployments when the Exchange organization was installed with the /hosting switch. Please reference Exchange Server 2010 Hosting Deployment to determine if your Exchange organization has been deployed in /hosting mode.
Exchange 2010 Multi-Tenant Hosting Wiki
- Ed Bringas