How to recover SQL data from a dropped table without backup
Sometimes, you find yourself in a situation when you delete rows or entire tables from the database that you should not have deleted. If you've just deleted some data or a table from the SQL database, there is no need to panic. There is a good news! You can recover SQL data from a dropped table, even without backup. Let’s see how to do so.
You must know that each data change occurs within a transaction and then goes through the transaction log. If you have performed an update or a deletion, then these data changes are passed through the transaction log. Even if you haven't explicitly opened a transaction, SQL Server will open one (implicit) for you.
At this point, you will have already understood where we are going to look for the deleted data: the transaction log.
You can read the content of the SQL Server transaction log via the undocumented T-SQL function fn_dblog. You can use this function by optionally passing two parameters, called start and end LSN (log sequence number). LSN is a uniquely incrementing three-part value used to maintain the sequence of the transaction log records in the database. Keep in mind that each transaction (explicit or implicit) has its own unique number.
You must also know that there is another similar function, called fn_dump_dblog. This function returns the same results but can also read, in addition to the online transaction log file, the SQL Server transaction log backup.
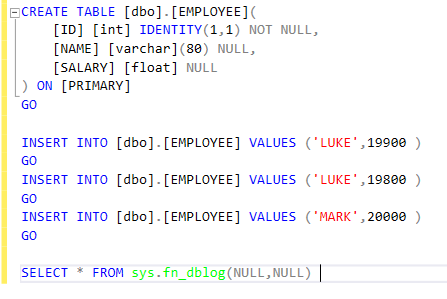
As an example, we will create a table and populate it with some data, then see what this function fn_dblog gives.
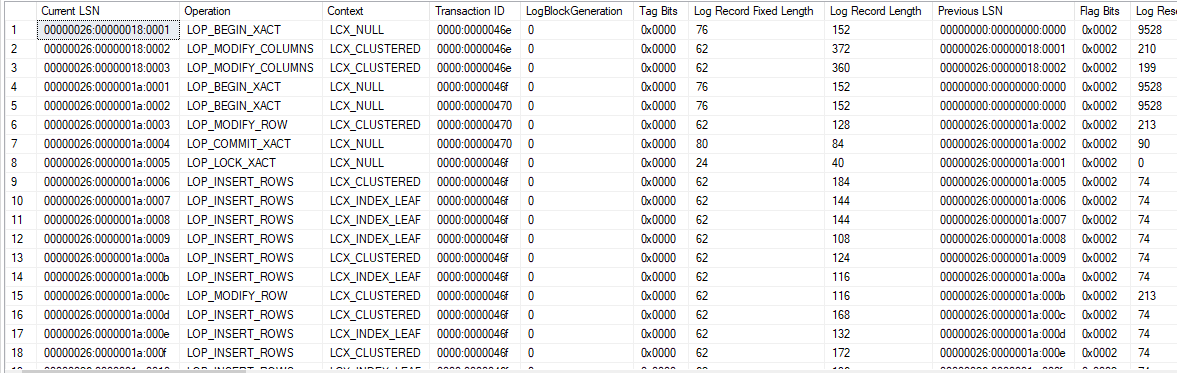
After running these T-SQL commands, you can see that over 500 rows have appeared in the transaction log file.
The transaction log file has many columns but the current LSN, the operation, and the transaction ID columns are very important.
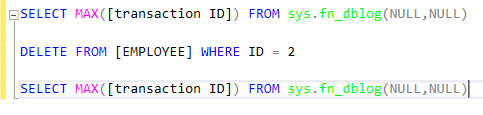
Let’s try now to delete a row.
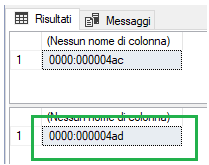
You will see there is a new transaction ID. SQL Server has opened an implicit one.
Now, take a look at the transaction log with this T-SQL command:
Here is the output of this command:
There are three rows:
- The first row represents the opening of the transaction.
- The second row, where the operation column has the value LOP_DELETE_ROWS, represents the deleted row.
- The third row represents the closing of the transaction.
Now, look at the columns: RowLog Contents 0 - RowLog Contents 5.
The first value is “0x3000100002000000000000000056D34003000001001B004C554B45.” Now, to view the deleted data, you just need to decode the hexadecimal strings contained in the RowLog fields.
It is not such a simple process. Here, we will only show you schematically the format used to store the data.
The first 2 bytes, called “Status Bits A” and “Status Bits B”, are the bitmaps containing the information about the row.
We have these two values:
- 30 is the Status Bits A
- 00 is the Status Bits B
The next 2 bytes contain an offset. This value is used to find number of columns. The value of “1000” must be read from right to left. So, the real value is 0001.
The next 2 bytes (highlighted with yellow in the image above) contain a value of “02000000”. This value is nothing else but the ID of the deleted row. You must read the data byte-by-byte from right to left. So, the ID is equal to 00000002. This indicates that the deleted row ID is 2.
The next 6 bytes (highlighted with light blue in the image above) contain the value for the column SALARY. The value of “000000000056D340” must be read from right to left. It is the representation of the float value 19800.
We will not go into further details on the following fields but continue to analyze the string until we find the sequence "4C554B45" (highlighted with light purple in the image above). The string “4C554B45” is the value deleted from the NAME column. The string “4C 55 4B 45” is “LUKE.”
We now found all the data we needed. But as you may have understood at this point, data recovery is not an easy process. A dedicated script could be developed. However, we recommend a dedicated software to recover deleted records. This is because the recovery process will be tried and validated over and over again.
Stellar Repair for MS SQL software is very useful in this situation. Even if the database is corrupt, it still allows you to recover deleted records. When using the software, you just need to check the “Include Deleted Records” box while selecting the database file.
Hope this article helped you recover the data from a deleted table in SQL.