Iterating directories and files (VB.NET)
Introduction
Working with directories and files is common place in many applications and the .NET Framework has classes for working with directories and files. These classes provided core functionality for all operations although when there is a need to iterate complex folder structures and files methods provided by the .NET Framework uses as is can cause user interfaces to become unresponsive. Learn how to keep user interfaces responsive by following along with non-responsive interfaces, unauthorized access to responsive user interfaces and circumventing unauthorized access to files and folders.
Requires
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2019 or higher
- .NET 5 Framework
- Basic understanding of the VB.NET language
- Delegates
- Events
Note
Make sure to read the direction for downloading the source code as the method is different than conventional cloning a GitHub repository.
Basics
To iterate a folder structure can be done using the following code.
Dim folderName = "TODO"
Dim files() As String = Directory.GetFiles(folderName, "*.vb", SearchOption.AllDirectories)
This works great for a folder structure with a few folders and files while for larger folder structures the above will cause a unresponsive user interface. To keep the user interface responsive using asynchronous Task will keep the user interface responsive.
Dim foundCount = Await Task.Run(
Function()
Dim files() As String = Directory.GetFiles(folderName, "*.vb", SearchOption.AllDirectories)
Return files.Length
End Function)
In both examples no controls on a form get interaction with the code presented. If there is a need to interact with a control e.g. add files to a ListBox simple iterate the array as shown below.
Await Task.Run(
Sub()
Dim files() As String = Directory.GetFiles(folderName, "*.vb", SearchOption.AllDirectories)
For Each file As String In files
ListBox1.Items.Add(file)
Next
End Sub)
Since the task runs in another thread a cross thread violation will be thrown when adding a file to the ListBox. To prevent this call Invoke method on the ListBox.
Await Task.Run(
Sub()
Dim files() As String = Directory.GetFiles(folderName, "*.vb", SearchOption.AllDirectories)
For Each file As String In files
ListBox1.Invoke(
Sub()
ListBox1.Items.Add(file)
End Sub)
Next
End Sub)
Recursion
Although the above examples will work for simple operations there will be cases where as directories and files are iterated other operations may be needed which is where recursive methods will come in handy.
Rather than attempting to jump into writing code without understanding what can happen such as when the user running an application does not have permissions to access directory or a file.
Rather than writing code and expecting no exceptions to be thrown using Visual Studio's debugger to step through code would seem prudent yet for a large directory structure this will be a daunting task which can lead to frustration. Instead a better idea is to start off with no exception handling at first and setup events for watching what is transpiring when using a recursive method.
In this example the task is to iterate a folder with sub folders with the option to cancel the operation as without a cancel option the user must wait or use task manager to end the application.
Full source for the following.
Delegates/events
The following provide subscribers to monitor any exceptions thrown while traversing a folder structure.
Public Delegate Sub OnException(exception As Exception)
Public Shared Event OnExceptionEvent As OnException
These are for when and if permission is denied to read a folder.
Public Delegate Sub OnUnauthorizedAccessException(message As String)
Public Shared Event UnauthorizedAccessExceptionEvent As OnUnauthorizedAccessException
These provide feedback to the calling method
Public Delegate Sub OnTraverseFolder(status As String)
Public Shared Event OnTraverseEvent As OnTraverseFolder
And when a folder is excluded
Public Delegate Sub OnTraverseExcludeFolder(sender As String)
Public Shared Event OnTraverseExcludeFolderEvent As OnTraverseExcludeFolder
Traverse folder basic
- First ensure the folder exists which should be done by the caller but a consideration is that a folder may be removed external from the application.
- Next, to make things interesting exclude some folders (see the following)
- Now using EnumrateDirectories on the current folder within an asynchronous task checking folder attributes for hidden, system and reparse points. If found exclude these folders.
- Check for cancellation, if there is a request to cancel use ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested() where ct is a CancellationToken passed by the calling method.
- In the catch part of try statement a checks are done for user cancelling and unauthorized exceptions then a fall through for general exceptions.
Public Shared Async Function RecursiveFolders(directoryInfo As DirectoryInfo, excludeFileExtensions As String(), ct As CancellationToken) As Task
If Not directoryInfo.Exists Then
RaiseEvent OnTraverseEvent("Nothing to process")
Return
End If
If Not excludeFileExtensions.Any(AddressOf directoryInfo.FullName.Contains) Then
Await Task.Delay(1)
RaiseEvent OnTraverseEvent(directoryInfo.FullName)
Else
RaiseEvent OnTraverseExcludeFolderEvent(directoryInfo.FullName)
End If
Dim folder As DirectoryInfo
Try
Await Task.Run(Async Function()
For Each dir As DirectoryInfo In directoryInfo.EnumerateDirectories()
folder = dir
If (folder.Attributes And FileAttributes.Hidden) = FileAttributes.Hidden OrElse
(folder.Attributes And FileAttributes.System) = FileAttributes.System OrElse
(folder.Attributes And FileAttributes.ReparsePoint) = FileAttributes.ReparsePoint Then
RaiseEvent OnTraverseExcludeFolderEvent($"* {folder.FullName}")
Continue For
End If
If Not Cancelled Then
Await Task.Delay(1)
Await RecursiveFolders(folder, excludeFileExtensions, ct)
Else
Return
End If
If ct.IsCancellationRequested Then
ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested()
End If
Next
End Function)
Catch ex As Exception
'
' Only raise exceptions, not cancellation request
' In OperationsListView class the UnauthorizedAccessException
' and general exceptions are ignored.
'
If TypeOf ex Is OperationCanceledException Then
Cancelled = True
ElseIf TypeOf ex Is UnauthorizedAccessException Then
RaiseEvent UnauthorizedAccessExceptionEvent($"Access denied '{ex.Message.StringBetweenQuotes()}'")
Else
RaiseEvent OnExceptionEvent(ex)
End If
End Try
End Function
Take time to run the above code by downloading the source code then continue to the next code sample.
Traverse/peek at files
In this code sample which uses the same logic as the last code sample will now use less delegate/events and search for text within .txt files.
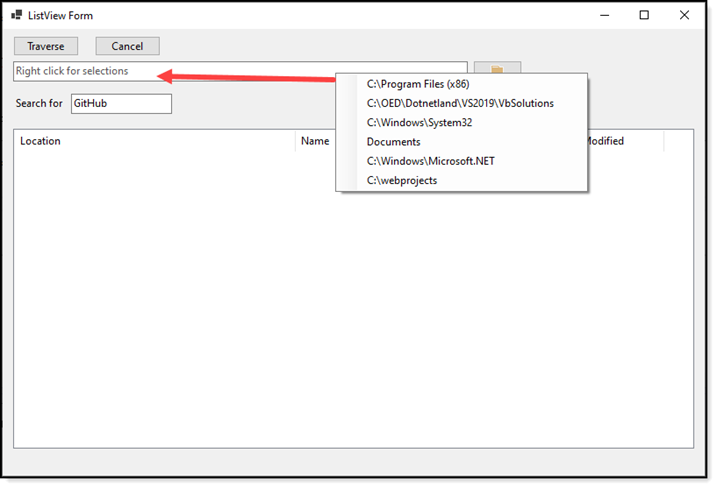
When running this example, right click on the long TextBox and select a folder that exists on the current computer (use the context menu to add, modify or remove others). If there is text in the "search for" TextBox that text will be searched and reported back once the recursive operation has finished.
Class code
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Threading
Public Class OperationsListView
''' <summary>
''' Container for files containing SearchText
''' </summary>
Public Shared FoundFileList As New List(Of FoundFile)
Public Delegate Sub OnTraverseFolder(information As DirectoryItem)
''' <summary>
''' Callback for when a folder is being processed
''' </summary>
Public Shared Event OnTraverseEvent As OnTraverseFolder
''' <summary>
''' For traversing folders, if a cancellation is requested stop processing folders.
''' </summary>
Public Shared Cancelled As Boolean = False
''' <summary>
''' Text to search for in files
''' </summary>
Public Shared SearchText As String
Public Shared Async Function RecursiveFolders(
directoryInfo As DirectoryInfo,
ct As CancellationToken,
Optional fileType As String = "*.txt") As Task
If Not directoryInfo.Exists Then
Return
End If
'
' Let's say you are traversing folders with Git repositories, we don't
' want to include their folders.
'
If Not directoryInfo.FullName.ContainsAny(".git", "\obj") Then
Dim di As New DirectoryItem With {
.Location = Path.GetDirectoryName(directoryInfo.FullName),
.Name = directoryInfo.Name,
.Modified = directoryInfo.CreationTime
}
IterateFiles(di.Location, fileType)
RaiseEvent OnTraverseEvent(di)
End If
Await Task.Delay(1)
Dim folder As DirectoryInfo
Try
Await Task.Run(Async Function()
For Each dir As DirectoryInfo In directoryInfo.EnumerateDirectories()
folder = dir
If Not Cancelled Then
IterateFiles(dir.FullName, fileType)
Await Task.Delay(1)
Await RecursiveFolders(folder, ct)
Else
Return
End If
If ct.IsCancellationRequested Then
ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested()
End If
Next
End Function)
Catch ex As Exception
'
' Operations.RecursiveFolders showed how to recognize
' folders that access has been denied, here these exceptions
' are ignored. A developer can integrate those exceptions here
' if so desired.
'
If TypeOf ex Is OperationCanceledException Then
Cancelled = True
End If
End Try
End Function
Public Shared Sub IterateFiles(folderName As String, fileType As String)
If String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(SearchText) Then
Exit Sub
End If
Dim files = Directory.GetFiles(folderName, fileType)
If files.Length > 0 Then
For Each fileName As String In files
Dim current = fileName
Dim result = File.
ReadLines(fileName).
Select(Function(text, index) New With {
Key text,
Key .LineNumber = index + 1
}).
Where(Function(anonymous) anonymous.text.Contains(SearchText)).
ToList()
If result.Count > 0 Then
For Each foundFileItem In From anonymous In result Select item = New FoundFile() With {
.Text = anonymous.text,
.LineNumber = anonymous.LineNumber,
.FileName = current} Where Not FoundFileList.Contains(item)
FoundFileList.Add(foundFileItem)
Next
End If
Next
End If
End Sub
End Class
Form code
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Threading
Imports System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles
Imports FileHelpers
Imports RecurseFolders.Classes
Imports RecurseFolders.LanguageExtensions
Public Class ListViewForm
''' <summary>
''' Provides an opportunity to cancel traversal of folders
''' </summary>
Private _cts As New CancellationTokenSource()
Private Async Sub TraverseButton_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles TraverseButton.Click
If FoldersListView.Items.Count > 0 Then
FoldersListView.Items.Clear()
End If
Await Task.Delay(1)
If String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(FolderTextBox.Text) Then
MessageBox.Show("Please select a folder")
Exit Sub
End If
If Not Directory.Exists(FolderTextBox.Text) Then
MessageBox.Show($"{FolderTextBox.Text} folder does not exist")
Exit Sub
End If
If _cts.IsCancellationRequested = True Then
_cts.Dispose()
_cts = New CancellationTokenSource()
End If
OperationsListView.SearchText = SearchTokenTextBox.Text
ProcessingLabel.Visible = True
ProcessedTitleLabel.Visible = True
OperationsListView.Cancelled = False
Await OperationsListView.RecursiveFolders(New DirectoryInfo(FolderTextBox.Text), _cts.Token)
FoldersListView.AutoResizeColumns(ColumnHeaderAutoResizeStyle.HeaderSize)
ProcessingLabel.Visible = False
ProcessedTitleLabel.Visible = False
FocusListView()
If String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(OperationsListView.SearchText) Then
Exit Sub
End If
If OperationsListView.FoundFileList.Count = 0 Then
MessageBox.Show("Nothing to show")
Else
Dim resultForm = New FoundFileResultsForm
resultForm.FoundFileList = OperationsListView.FoundFileList
Try
resultForm.ShowDialog()
Finally
resultForm.Dispose()
End Try
End If
End Sub
Private Sub FocusListView()
FoldersListView.FocusedItem = FoldersListView.Items(0)
FoldersListView.Items(0).Selected = True
ActiveControl = FoldersListView
End Sub
Private Sub CancelButton_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles CancelButton.Click
CancelOperation()
End Sub
Private Sub CancelOperation()
_cts.Cancel()
ProcessingLabel.Visible = False
ProcessedTitleLabel.Visible = False
End Sub
Private Sub ListViewForm_Shown(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Shown
ProcessingLabel.Visible = False
ProcessedTitleLabel.Visible = False
OperationsListView.Cancelled = False
AddHandler OperationsListView.OnTraverseEvent, AddressOf OnTraverseEvent
FoldersListView.SetDoubleBuffered()
FolderSelectionContextMenuStrip.Items.Cast(Of ToolStripItem)().ToList().ForEach(Sub(item) AddHandler item.Click, AddressOf ContextMenuStrip1_Click)
SetCueText(FolderTextBox, "Right click for selections")
End Sub
Private Async Sub OnTraverseEvent(information As DirectoryItem)
Await Task.Delay(100)
FoldersListView.InvokeIfRequired(Sub(listView)
listView.Items.Add(New ListViewItem(information.ItemArray))
End Sub)
ProcessingLabel.InvokeIfRequired(Sub(label)
label.Text = $"{FoldersListView.Items.Count}"
End Sub)
End Sub
Private Sub ContextMenuStrip1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs)
Dim selection = CType(sender, ToolStripMenuItem).Text
If selection = "Documents" Then
FolderTextBox.Text = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.MyDocuments)
Else
FolderTextBox.Text = selection
End If
End Sub
Protected Overrides Function ProcessCmdKey(ByRef msg As Message, keyData As Keys) As Boolean
If keyData <> Keys.Escape Then
Return MyBase.ProcessCmdKey(msg, keyData)
End If
CancelOperation()
Return True
End Function
''' <summary>
''' No folders, stop context menu from opening
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub OpenFolderContextMenuStrip_Opening(sender As Object, e As ComponentModel.CancelEventArgs) _
Handles OpenFolderContextMenuStrip.Opening
If FoldersListView.Items.Count = 0 Then
e.Cancel = True
Else
'
' Get selected
'
End If
End Sub
End Class
Notes on above code
- Cross thread exceptions prevention is done with the following language extension which uses assertion in the event there is a failure with invoke.
- When dealing with large folders e.g. C:\Windows\System32 or perhaps a folder with many folders with documents and or images this can cause the ListView to flicker so the following language extension prevents flickering.
- Overriding ProcessCmdKey shows how to provide easy shortcuts for in this case cancelling the operation.
- If the following code was not in place running the iterate folder code would never run without this code. This is because if a cancellation was done the current take of the CancellationTokenSource is in a cancel state and must be recreated.
Removing a folder structure
The following code will remove an entire folder structure if the user has permissions, it's wise to a) implement the same assertion as with the last two code samples and also for the Delete method to use extreme caution as if there are no permission issues the specified folder and underlying folders are removed..
Public Shared Sub RecursiveDelete(directoryInformation As DirectoryInfo)
If Not directoryInformation.Exists Then
RaiseEvent OnDeleteEvent("Nothing to process")
Return
End If
Dim attr = File.GetAttributes(directoryInformation.FullName)
If attr.HasFlag(FileAttributes.Directory) Then
If ProcessDirectory.Contains(directoryInformation.Name) Then
RaiseEvent OnDeleteEvent($"Folder: {directoryInformation.FullName}")
End If
End If
For Each dir As DirectoryInfo In directoryInformation.EnumerateDirectories()
Try
RecursiveDelete(dir)
Catch ex As Exception
RaiseEvent OnExceptionEvent(ex)
End Try
Next
If ProcessDirectory.Contains(directoryInformation.Name) Then
directoryInformation.Delete(True)
End If
End Sub
Recursion control usage
Recusion is not just for disk operations, another useage is to find all controls on a form while conventional methods don't inheritently find controls on child controls like panels and group boxes.
The following language extension does this.,
<Extension>
Public Iterator Function Descendants(Of T As Class)(control As Control) As IEnumerable(Of T)
For Each child As Control In control.Controls
Dim thisControl As T = TryCast(child, T)
If thisControl IsNot Nothing Then
Yield CType(thisControl, T)
End If
If child.HasChildren Then
For Each descendant As T In child.Descendants(Of T)()
Yield descendant
Next
End If
Next
End Function
Then either use it or write wrappers e.g.
<Extension>
Public Function ButtonList(pControl As Control) As List(Of Button)
Return pControl.Descendants(Of Button)().ToList()
End Function
Dim ButtonList = ButtonList to get all buttons on the form and any child controls, Dim ButtonList = Panel1.ButtonList for only buttons on a specific panel.
Math is another way to use recursion e.g. (from Microsoft docs)
Function Factorial(n As Integer) As Integer
If n <= 1 Then
Return 1
End If
Return Factorial(n - 1) * n
End Function
Summary
Code has been presented to provide a base framework to work asynchronously with directory and file operations to iterate folder structures. Only consider these methods when conventional methods as presented in the basic section cause the user interface to become unresponsive.
Source code
Clone the following GitHub repository (which contains more projects then needed) or create a batch file and insert the following and run. Note the Git is needed.
mkdir code
cd code
git init
git remote add -f origin https://github.com/karenpayneoregon/vb-vs2019-samples
git sparse-checkout init --cone
git sparse-checkout add FileHelpers
git sparse-checkout add RecurseFolders
git pull origin master
:clean-up
del .gitattributes
del .gitignore
del .yml
del .editorconfig
del *.md
del *.sln
See also
Basic asynchronous operations (VB.NET)
.NET: What does async & await generate?