SharePoint: Generate and report AD account metrics in SharePoint Part 4: store AD metrics in SharePoint
Article Series
- Part 1: How to get basic AD Metrics
- Part 2: Getting more complex AD metrics
- Part 3: Getting still more complex AD metrics
- Part 4: How to store AD metrics in SharePoint 2010 < you are here
- Part 5: How to present AD metrics in a SharePoint 2010 dashboard
Introduction
In the previous posting in this series, we explored how to generate more complex AD account metrics using PowerShell. In this posting, we'll explore how to store these metrics in a SharePoint Server 2010 list for convenient access. This will involve the following four steps:
- Creating a new list with appropriate fields.
- Adding the Active Directory remote management tools to the SharePoint host.
- Modifying the PowerShell script developed in previous postings to write results to this list.
- Running the script to verify metrics harvest from Active Directory and their storage in the list.
To prepare for this procedure, the Northwind Traders database was added to a new site collection. All nine of the employees were added to Active Directory and made members of a new group, Northwind. Additionally, the SharePoint Server 2010 service accounts, sp_admin, sp_web and sp_app, were also made members of the Northwind group, along with a test account, sp_test, and the administrators account, brens, for a total of 14 accounts in the Northwind AD group.
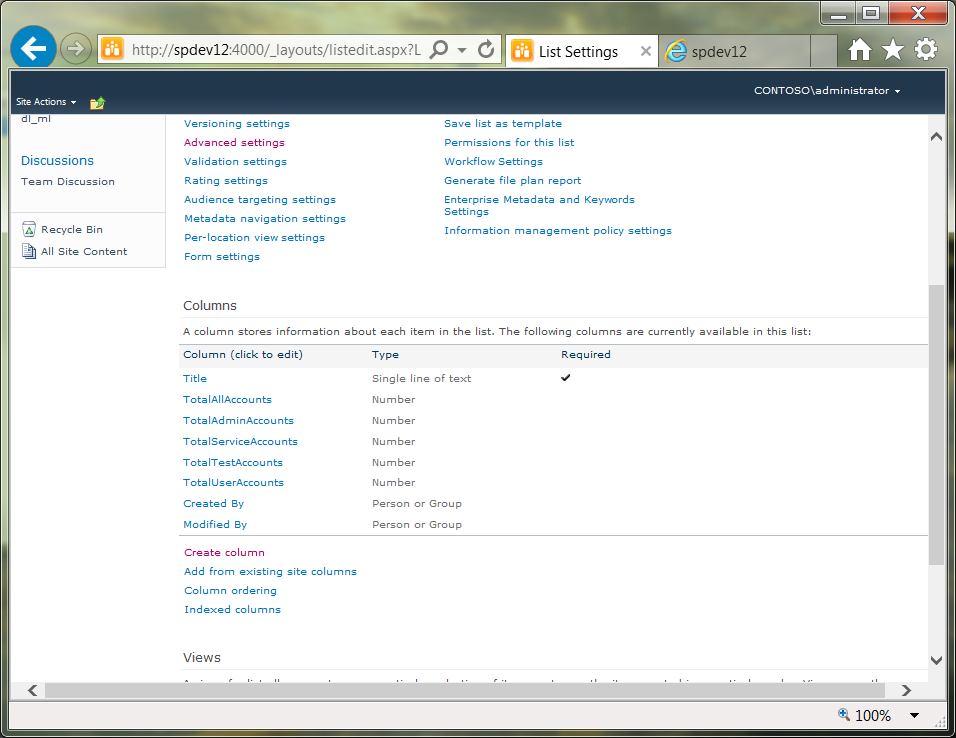
Step 1: Create List
- Create a new custom list in SharePoint Server 2010. Give the list a short name to simplify referencing it in PowerShell.
- Add to this list all of the basic metrics developed previously, including:
- Total accounts
- Total admin accounts
- Total service accounts
- Total test accounts
- Total end-user accounts
- Format these fields as numbers with 0 decimal places:
Step 2: Add Tools
- Open Server Manager.
- Click Add Features.
- Select Remote Server Administration Tools | Role Administration Tools | AD DS and AD DS Tools:

- Install the tools.
Step 3: Modify the Script
Open a PowerShell window on the SharePoint Server.
Add the PowerShell snap-in for SharePoint.
Import the PowerShell module for Active Directory
Follows is the modified script, simplified and with most comments removed:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.SharePoint.PowerShell $DateTime = Get-Date # Get the Northwind group accounts only $NorthWindAccounts = (Get-ADGroup 'Northwind').DistinguishedName # Extract general metrics $AllAccounts = Get-ADUser -Filter {(memberof -eq $NorthWindAccounts)} -Properties Name, Givenname, Surname, DistinguishedName, Enabled, LastLogonDate, LastLogonTimeStamp, LockedOut, SAMAccountName, CreateTimeStamp, Created, PasswordLastSet, Description [array]$AllAdminAccounts = $AllAccounts | Where-Object {$_.Description -Like '*Admin*'} [array]$AllServiceAccounts = $AllAccounts | Where-Object {$_.Description -Like '*Service*'} [array]$AllTestingAccounts = $AllAccounts | Where-Object {$_.Description -Like '*Testing*'} [array]$AllUserAccounts = $AllAccounts | Where-Object {($_.Description -NotLike '*Admin*') -and ($_.Description -NotLike '*Service*') -and ($_.Description -NotLike '*Testing*')} # Handle null values if (($AllAccounts.count -eq $NULL) -or ($AllAccounts.count -eq 0)){ $AllAccountsValue = 0 } else{ $AllAccountsValue = $AllAccounts.count } if (($AllAdminAccounts.count -eq $NULL) -or ($AllAdminAccounts.count -eq 0)){ $AllAdminAccountsValue = 0 } else{ $AllAdminAccountsValue = $AllAdminAccounts.count } if (($AllServiceAccounts.count -eq $NULL) -or ($AllServiceAccounts.count -eq 0)){ $AllServiceAccountsValue = 0 } else{ $AllServiceAccountsValue = $AllServiceAccounts.count } if (($AllTestingAccounts.count -eq $NULL) -or ($AllTestingAccounts.count -eq 0)){ $AllTestingAccountsValue = 0 } else{ $AllTestingAccountsValue = $AllTestingAccounts.count } if (($AllUserAccounts.count -eq $NULL) -or ($AllUserAccounts.count -eq 0)){ $AllUserAccountsValue = 0 } else{ $AllUserAccountsValue = $AllUserAccounts.count } # Get the site object $SiteURL = "http://spdev12:4000/" $Site = Get-SPWeb $SiteURL # Get the list object from this site $ListName = "dl_ml" $List = $Site.Lists[$ListName] # Prepare a new list row $NewItem = $List.Items.Add() $NewItem["Title"] = $DateTime $NewItem["TotalAllAccounts"] = $AllAccountsValue $NewItem["TotalAdminAccounts"] = $AllAdminAccountsValue $NewItem["TotalServiceAccounts"] = $AllServiceAccountsValue $NewItem["TotalTestAccounts"] = $AllTestingAccountsValue $NewItem["TotalUserAccounts"] = $AllUserAccountsValue # Add the new list row $NewItem.Update() # Dispose the site object $Site.Dispose()
Step 4: Test the Script
- On the SharePoint Server 2010 host, open the PowerShell ISE.
- Paste the script above into a new tab.
- Modify server names, site URLs, list names and column names as necessary.
- Run the script under an account that has at least read privileges to the domain controller.
- Open a browser, and then connect to the site to view the list:

Summary
In this posting, we explored how to generate AD metrics from the server hosting SharePoint Server 2010 Enterprise and then store those metrics in a SharePoint Server 2010 list. All references consulted in writing this posting are listed below. In the next posting in this series, we'll explore how to present these metrics in the Data View and Chart web parts.
References
- Microsoft TechNet: Get-SPWeb
- Nico Marten: Add/Edit list items using PowerShell in SharePoint 2010
- Microsoft TechNet: Windows PowerShell for SharePoint Foundation 2010 reference
- MSDN: SharePoint 2010 with Windows PowerShell Remoting Step by Step
- PowerShell and ActiveDirectory module - Find Users that are not members of particular groups
- MSDN: SharePoint 2010 and PowerShell 3.0 (not compatible)
- TechNet: Active Directory Administration with Windows PowerShell
- Windows Server Forums: Connect to different domain controller
- ITPro: There is more than one way to access SharePoint 2010 PowerShell cmdlets
Notes
- Microsoft.SharePoint.PowerShell: From what I've found thus far, there doesn't appear to be a way to install the this snap-in on other machines to facilitate remote scripting. The only options found were: remote desktop or remote PowerShell session.
- Import-Module ActiveDirectory: this isn't normally needed for the machine hosting SharePoint Server 2010. However, it is needed in order to interact with domain controllers and extract account metrics from them.
- If you see this error after running the above PowerShell script, check the case of the fieldnames that you are using against what they are in the SharePoint list.
