Entity Framework Core 3 Windows Forms (VB.NET)
Introduction
Learn the basics on how to work with Entity Framework Core 3 using SQL-Server and VB.NET programming language.
Preparation
Since the release of Entity Framework 6 Visual Studio provided developers with an automated process to scaffold a database which has gone away with Entity Framework Core. Unlike C# where a database can be scaffold directly in Visual Studio when the scaffold command executes against a VB.NET project the following will output.
The project language 'VB' isn't supported by the built-in IModelCodeGenerator service. You can try looking for an additional NuGet package, which supports this language; moving your DbContext type to a C# class library referenced by this project; or manually implementing and registering the design-time service for programming language.
There are two ways to scaffold VB.NET, using a third party tool, extension or to write code. In this article code will be written to express tables in a database for use with Entity Framework Core. Rather than write code for an entire database only enough will be done with several tables to understand how to proceed with more tables in a relational database.
All steps are not completely explained but are there to create models yet using the models in the GitHub repository the parts not fully explained can be understood.
Required
- Microsoft SQL-Server service running which Visual Studio handles during setup.
- Microsoft SSMS (SQL-Server Management Studio)
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2017 or higher
- Microsoft Framework 4.7 or higher
Tables
The following tables will be setup for Entity Framework Core, Customers the main table, Countries, Contact and ContactType.
The first step is create the database and tables in SSMS using the data script include in the source code on GitHub listed at the bottom of this article.
Next step, list primary and foreign keys for Customers, Contact and ContactType tables which will be needed when wiring up the DbContext. An easy method is to run the following in a new query window in SSMS.
SELECT
obj.name AS fk_name, sch.name AS schema_name,
tab1.name AS [table], col1.name AS [column],
tab2.name AS referenced_table, col2.name AS referenced_column
FROM
sys.foreign_key_columns AS fkc INNER JOIN
sys.objects AS obj ON obj.object_id = fkc.constraint_object_id INNER JOIN
sys.tables AS tab1 ON tab1.object_id = fkc.parent_object_id INNER JOIN
sys.schemas AS sch ON tab1.schema_id = sch.schema_id INNER JOIN
sys.columns AS col1 ON col1.column_id = fkc.parent_column_id AND col1.object_id =
tab1.object_id INNER JOIN
sys.tables AS tab2 ON tab2.object_id = fkc.referenced_object_id INNER JOIN
sys.columns AS col2 ON col2.column_id = fkc.referenced_column_id AND col2.object_id =
tab2.object_id INNER JOIN
sys.types AS TY ON col1.system_type_id = TY.system_type_id AND col1.user_type_id =
TY.user_type_id AND tab1.name = 'Customers';
SELECT
pk.name AS pk_name,
SCHEMA_NAME(tab.schema_id) AS schema_name,
tab.name AS table_name,
ic.index_column_id AS column_id,
col.name AS column_name
FROM
sys.tables AS tab INNER JOIN
sys.indexes AS pk ON tab.object_id = pk.object_id AND pk.is_primary_key = 1 INNER JOIN
sys.index_columns AS ic ON ic.object_id = pk.object_id AND ic.index_id = pk.index_id INNER JOIN
sys.columns AS col ON pk.object_id = col.object_id AND col.column_id = ic.column_id
WHERE (tab.name = N'Customers')
ORDER BY schema_name, pk_name, column_id;
The following is the output which each value can be copied to code via right clicking on a value and select copy.

NuGet packages
The following packages need to be installed
Visual Studio solution
Entity Framework Core classes will reside in a class project while presentation layer will be a Windows Form project. There are many reasons for separating backend classes from the presentation layer ranging from providing the ability to utilizing the Entity Framework Core classes in other projects to scalability e.g. place a business layer between the backend classes and the presentation layer.
Coding step 1
- Create the class project, in this case named EntityFrameworkCoreNorthWind
- Add both NuGet packages listed above.
- Create a folder named Models which will house classes which represent the tables, Customers, Contact, ContactType and Countries.
- Create a new class files for each of the following: Customers, Contact, ContactType and Countries
- Create a folder named Contexts
- Create an new class file named CustomerContext
- Create a folder named Classes
- Create a new class file named ConfiguationHelper
- Create a folder named Extensions
- Create a new code module file named QueryExtensions
- Create a folder named Projections
- Create a new class file named Customer
- Create a new class file named Customeritem
Coding step 2
Here code is written in the classes Customers, Contacts, Countries and ContactType which represent columns in the database tables and relationships between related tables.
Without the ability to scaffold models as possible with C# it can be a tedious task of hand coding each class. A hidden benefit in having to code most of the code is there is a better understanding of the mechanics of what it takes to configure models while the downside is those are just starting out this may be more than they can handle. For this just starting out try working with Entity Framework 6 Code first from database to get a better understanding of configuration as Visual Studio has templates for Entity Framework 6 although there are a good deal of changes when moving to Entity Framework Core, even from Entity Framework Core first edition to the current edition. The following article Entity Framework dynamic order by (done in Windows forms, Entity Framework 6) may help to get a running start.
To assist use the following SQL in SSMS.
DECLARE @TableName sysname = 'Customers';
DECLARE @Result VARCHAR(MAX) = 'Public Class ' + @TableName;
SELECT @Result = @Result + '
Public Property ' + ColumnName + ' As ' + ColumnType + NullableSign
FROM ( SELECT REPLACE(col.name, ' ', '_') ColumnName ,
column_id ColumnId ,
CASE typ.name
WHEN 'bigint' THEN 'Long'
WHEN 'binary' THEN 'Byte[]'
WHEN 'bit' THEN 'Boolean'
WHEN 'char' THEN 'String'
WHEN 'date' THEN 'DateTime'
WHEN 'datetime' THEN 'DateTime'
WHEN 'datetime2' THEN 'DateTime'
WHEN 'datetimeoffset' THEN 'DateTimeOffset'
WHEN 'decimal' THEN 'Decimal'
WHEN 'float' THEN 'Float'
WHEN 'image' THEN 'Byte()'
WHEN 'int' THEN 'Integer'
WHEN 'money' THEN 'Decimal'
WHEN 'nchar' THEN 'String'
WHEN 'ntext' THEN 'String'
WHEN 'numeric' THEN 'Decimal'
WHEN 'nvarchar' THEN 'String'
WHEN 'real' THEN 'Double'
WHEN 'smalldatetime' THEN 'DateTime'
WHEN 'smallint' THEN 'Short'
WHEN 'smallmoney' THEN 'Decimal'
WHEN 'text' THEN 'String'
WHEN 'time' THEN 'TimeSpan'
WHEN 'timestamp' THEN 'DateTime'
WHEN 'tinyint' THEN 'Byte'
WHEN 'uniqueidentifier' THEN 'Guid'
WHEN 'varbinary' THEN 'Byte()'
WHEN 'varchar' THEN 'String'
ELSE 'UNKNOWN_' + typ.name
END ColumnType ,
CASE WHEN col.is_nullable = 1
AND typ.name IN ( 'bigint', 'bit', 'date',
'datetime', 'datetime2',
'datetimeoffset', 'decimal',
'float', 'int', 'money',
'numeric', 'real',
'smalldatetime', 'smallint',
'smallmoney', 'time',
'tinyint', 'uniqueidentifier' )
THEN '?'
ELSE ''
END NullableSign
FROM sys.columns col
JOIN sys.types typ ON col.system_type_id = typ.system_type_id
AND col.user_type_id = typ.user_type_id
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(@TableName)
) t
ORDER BY ColumnId;
SET @Result = @Result + '
End Class';
PRINT @Result;
Which for the example above produces.
Public Class Customers
Public Property CustomerIdentifier As Integer
Public Property CompanyName As String
Public Property ContactName As String
Public Property ContactId As Integer?
Public Property Address As String
Public Property City As String
Public Property Region As String
Public Property PostalCode As String
Public Property CountryIdentifier As Integer?
Public Property Phone As String
Public Property Fax As String
Public Property ContactTypeIdentifier As Integer?
Public Property ModifiedDate As DateTime?
End Class
Now at the least data annotation and child relations need to be coded into the generated class and optionally implement INotifyPropertyChanged Interface.
For the Customers class there is a property for each column in the customers table along with data annotations which indicate if a property/column is required, maximum length of a column and related tables.
- To express relations between a model to a child model (Customers to ContactType) use InverseProperty as shown below.
- The InverseProperty attribute is used to denote the inverse navigation property of a relationship when the same type takes part in multiple relationships.
- It is used when you need to indicate that navigation property in one class is related to the same foreign key as another navigation property in another class.
- In the child relations, in this case ContactType the InverseProperty is done via <InverseProperty("ContactTypeNavigation")> which means this is easily broken if not careful when changing property names.
- The InverseProperty attribute is used to denote the inverse navigation property of a relationship when the same type takes part in multiple relationships.
- Overriding .ToString serves two purposes, when debugging in this case CompanyName will be displayed when examining customer objects and the second, if a List(Of Customers) were to be displayed in a ComboBox or ListBox .ToString is used for DisplayMember.
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations
Imports System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema
Namespace NorthWindEntityFrameworkCore
Partial Public Class Customers
<Key>
Public Property CustomerIdentifier() As Integer
<Required, StringLength(40)>
Public Property CompanyName() As String
<StringLength(30)>
Public Property ContactName() As String
Public Property ContactId() As Integer?
<StringLength(60)>
Public Property Address() As String
<StringLength(15)>
Public Property City() As String
<StringLength(15)>
Public Property Region() As String
<StringLength(10)>
Public Property PostalCode() As String
Public Property CountryIdentifier() As Integer?
<StringLength(24)>
Public Property Phone() As String
<StringLength(24)>
Public Property Fax() As String
Public Property ContactTypeIdentifier() As Integer?
Public Property ModifiedDate() As Date?
<ForeignKey(NameOf(ContactId)), InverseProperty(NameOf(Contacts.Customers))>
Public Overridable Property Contact() As Contacts
<ForeignKey(NameOf(ContactTypeIdentifier)), InverseProperty(NameOf(ContactType.Customers))>
Public Overridable Property ContactTypeNavigation() As ContactType
<ForeignKey(NameOf(CountryIdentifier)), InverseProperty(NameOf(Countries.Customers))>
Public Overridable Property CountryIdentifierNavigation() As Countries
Public Overrides Function ToString() As String
Return CompanyName
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
This is done for each table in the database. As presented when in a DataGridView or TextBox bound to a BindingList which has change notification there will be no change notification as coded. For change notification implement INotifyPropertyChanged Interface.
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.ComponentModel
Imports System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations
Imports System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema
Imports System.Runtime.CompilerServices
Namespace NorthWindEntityFrameworkCore
''' <summary>
''' INotifyPropertyChanged is optional, if not needed each
''' property can be an auto-property
''' </summary>
Partial Public Class Customers
Implements INotifyPropertyChanged
Private _companyName As String
Private _customerIdentifier As Integer
Private _contactIdentifier As Integer?
Private _countryIdentifierNavigation As Countries
Private _contactTypeNavigation As ContactType
Private _contact1 As Contacts
Private _contactTypeIdentifier As Integer?
Private _phone As String
Private _postalCode As String
Private _city As String
Private _address As String
Private _countryIdentifier As Integer?
<Key>
Public Property CustomerIdentifier() As Integer
Get
Return _customerIdentifier
End Get
Set
_customerIdentifier = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<Required, StringLength(40)>
Public Property CompanyName() As String
Get
Return _companyName
End Get
Set
_companyName = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
Public Property ContactId() As Integer?
Get
Return _contactIdentifier
End Get
Set
_contactIdentifier = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<StringLength(60)>
Public Property Address() As String
Get
Return _address
End Get
Set
_address = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<StringLength(15)>
Public Property City() As String
Get
Return _city
End Get
Set
_city = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<StringLength(10)>
Public Property PostalCode() As String
Get
Return _postalCode
End Get
Set
_postalCode = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
Public Property CountryIdentifier() As Integer?
Get
Return _countryIdentifier
End Get
Set
_countryIdentifier = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<StringLength(24)>
Public Property Phone() As String
Get
Return _phone
End Get
Set
_phone = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
Public Property ContactTypeIdentifier() As Integer?
Get
Return _contactTypeIdentifier
End Get
Set
_contactTypeIdentifier = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
Public Property ModifiedDate() As Date?
<ForeignKey(NameOf(ContactId)),
InverseProperty(NameOf(Contacts.Customers))>
Public Overridable Property Contact() As Contacts
Get
Return _contact1
End Get
Set
_contact1 = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<ForeignKey(NameOf(ContactTypeIdentifier)),
InverseProperty(NameOf(ContactType.Customers))>
Public Overridable Property ContactTypeNavigation() As ContactType
Get
Return _contactTypeNavigation
End Get
Set
_contactTypeNavigation = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
<ForeignKey(NameOf(CountryIdentifier)),
InverseProperty(NameOf(Countries.Customers))>
Public Overridable Property CountryIdentifierNavigation() As Countries
Get
Return _countryIdentifierNavigation
End Get
Set
_countryIdentifierNavigation = Value
OnPropertyChanged()
End Set
End Property
Public Overrides Function ToString() As String
Return CompanyName
End Function
Public Event PropertyChanged As PropertyChangedEventHandler _
Implements INotifyPropertyChanged.PropertyChanged
Protected Overridable Sub OnPropertyChanged(<CallerMemberName>
Optional memberName As String = Nothing)
RaiseEvent PropertyChanged(Me, New PropertyChangedEventArgs(memberName))
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Once done with Customers class follow the same pattern for Contact, ContactType and Country.
Contacts, use the SQL mentioned earlier to generate the class and properties. Then add in the property to relate back to Customers.
<InverseProperty("Contact")>
Public Overridable Property Customers() As ICollection(Of Customers)
Similarly in ContactTypes add the following property to references back to Customers
<InverseProperty("ContactTypeNavigation")>
Public Overridable Property Customers() As ICollection(Of Customers)
And finally for Countries
<InverseProperty("CountryIdentifierNavigation")>
Public Overridable Property Customers() As ICollection(Of Customers)
As with Customers the above three tables can implement INotifyPropertyChanged interface which is done in the GitHub repository.
DbContext step 3
This is the main class to configure Entity Framework Core
Class signature
Partial Public Class CustomerContext
Inherits DbContext
Next, a private variable to remember the database connection
Private ConnectionString As String
This is followed by the class constructors, the first, parameter-less constructor is what is used in this code sample. This constructor obtains settings from the app.config file and creates a well formed connection string in ConfigurationHelper class
Public Sub New()
Dim configurationHelper = New ConfigurationHelper
ConnectionString = configurationHelper.ConnectionString
End Sub
Public Sub New(options As DbContextOptions(Of CustomerContext))
MyBase.New(options)
End Sub
The following is optional, this code sets up console logging which means for each request for data, updates, deletes and additions will present SQL to Visual Studio's output window.
''' <summary>
''' Configure logging for app
''' https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/miscellaneous/logging?tabs=v3
''' https://github.com/dotnet/EntityFramework.Docs/blob/master/entity-framework/core/miscellaneous/logging.md
''' </summary>
Public Shared ReadOnly ConsoleLoggerFactory As ILoggerFactory = LoggerFactory.
Create(Function(builder) As ILoggerFactory
builder.AddFilter(
Function(category, level)
Return category = DbLoggerCategory.Database.Command.Name AndAlso
level = LogLevel.Information
End Function)
builder.AddConsole()
Return Nothing
End Function)
the following method, OnConfiguring will allow console logging only while working from Visual Studio, outside of Visual Studio there will be no logging.
''' <summary>
''' Connection string is obtained from app.config
''' Logging is only enabled with the Visual Studio debugger
''' </summary>
''' <param name="optionsBuilder"></param>
Protected Overrides Sub OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder As DbContextOptionsBuilder)
#If DEBUG Then
If Not optionsBuilder.IsConfigured Then
optionsBuilder.
UseSqlServer(ConnectionString).
UseLoggerFactory(ConsoleLoggerFactory).
EnableSensitiveDataLogging()
End If
#Else
If Not optionsBuilder.IsConfigured Then
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(ConnectionString)
End If
#End If
End Sub
Configuring relations, constraints, default values and more is done in OnModelCreating method.
Protected Overrides Sub OnModelCreating(modelBuilder As ModelBuilder)
modelBuilder.Entity(Of Customers)(
Sub(entity)
entity.HasKey(Function(customer) customer.CustomerIdentifier).
HasName("PK_Customers_1")
entity.Property(Function(customer) customer.ModifiedDate).
HasDefaultValueSql("(getdate())")
entity.HasOne(Function(customer) customer.Contact).
WithMany(Function(contacts) contacts.Customers).
HasForeignKey(Function(customer) customer.ContactId).
HasConstraintName("FK_Customers_Contacts")
entity.HasOne(Function(customer) customer.ContactTypeNavigation).
WithMany(Function(contactType) contactType.Customers).
HasForeignKey(Function(customer) customer.ContactTypeIdentifier).
HasConstraintName("FK_Customers_ContactType")
entity.HasOne(Function(customer) customer.CountryIdentifierNavigation).
WithMany(Function(countries) countries.Customers).
HasForeignKey(Function(customer) customer.CountryIdentifier).
HasConstraintName("FK_Customers_Countries")
End Sub)
OnModelCreatingPartial(modelBuilder)
End Sub
Walk through configuring the above.
Working with the Customer entity. The following describes the primary key for the Customer table, to get the key name PK_Customers1 run the following script. Keep the script results open as they will be needed below.
entity.HasKey(Function(customer) customer.CustomerIdentifier).
HasName("PK_Customers_1")
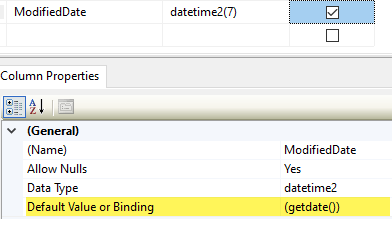
ModifiedDate column of Customers has a default value of GetDate so we need to tell EF Core about this.
entity.Property(Function(customer) customer.ModifiedDate).
HasDefaultValueSql("(getdate())")
Next, tell EF Core about relations using the script to get the foreign key names.
entity.HasOne(Function(customer) customer.Contact).
WithMany(Function(contacts) contacts.Customers).
HasForeignKey(Function(customer) customer.ContactId).
HasConstraintName("FK_Customers_Contacts")
entity.HasOne(Function(customer) customer.ContactTypeNavigation).
WithMany(Function(contactType) contactType.Customers).
HasForeignKey(Function(customer) customer.ContactTypeIdentifier).
HasConstraintName("FK_Customers_ContactType")
entity.HasOne(Function(customer) customer.CountryIdentifierNavigation).
WithMany(Function(countries) countries.Customers).
HasForeignKey(Function(customer) customer.CountryIdentifier).
HasConstraintName("FK_Customers_Countries")
EntityTypeConfigurationtion methods
- HasKey method is used to denote the property that uniquely identifies an entity (the EntityKey), and which is mapped to the Primary Key field in a database
- HasForeignKey method is used to specify which property is the foreign key in a relationship.
- HasConstraintName method enables you to specify the name of the foreign key constraint for a relationship.
- WithMany method is used to configure the many side of a one-to-many relationship.
Database Connection
Rather than hard code the database connection string, the following class reads the connection string from the app.config file. This is common practice for changing from development, test and production database environments.
Imports System.Configuration
Namespace Classes
''' <summary>
''' Get database server and default catalog from app.config
''' </summary>
Public Class ConfigurationHelper
Private Shared Function GetAppSetting(config As Configuration, key As String) As String
Dim element As KeyValueConfigurationElement = config.AppSettings.Settings(key)
If element IsNot Nothing Then
Dim value As String = element.Value
If Not String.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value) Then
Return value
End If
End If
Return ""
End Function
Public ReadOnly Property ConnectionString() As String
Get
Dim config As Configuration = Nothing
Dim exeConfigPath As String = Me.GetType().Assembly.Location
Try
config = ConfigurationManager.OpenExeConfiguration(exeConfigPath)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
If config IsNot Nothing Then
Return $"Data Source={GetAppSetting(config, "DatabaseServer")};" &
$"Initial Catalog={GetAppSetting(config, "DefaultCatalog")};" &
"Integrated Security=True"
Else
Return ""
End If
End Get
End Property
End Class
End Namespace
app.config
<appSettings>
<add key="DatabaseServer" value = ".\SQLEXPRESS" />
<add key="DefaultCatalog" value = "NorthWindAzureForInserts" />
<add key="UsingLogging" value = "true" />
</appSettings>
Loading data - Includes
Entity Framework Core uses eager for loading data.
Eager loading is the process whereby a query for one type of entity also loads related entities as part of the query, so that we don't need to execute a separate query for related entities. Eager loading is achieved using the Include() method.
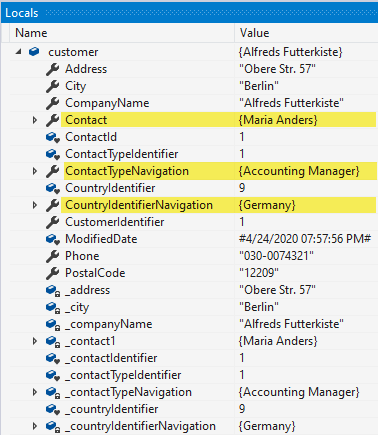
This means the following statement to return the first customer will not have navigation properties populated.
Public Shared Sub Simple()
Using context As New CustomerContext
Dim customer = context.Customers.FirstOrDefault()
End Using
End Sub
To get navigation properties use .Include and .ThenInclude (which is not used here).
Public Shared Sub Simple()
Using context As New CustomerContext
Dim customer = context.Customers.Include(Function(cust) cust.Contact).
Include(Function(cust) cust.ContactTypeNavigation).
Include(Function(cust) cust.CountryIdentifierNavigation).
FirstOrDefault()
End Using
End Sub
If in a application a read operation is only performed once the above code is fine while when there are several reads consider using the following language extension methods.
The first returns all customers along with their navigation properties while the second returns a single customer. Both extensions are included in the GitHub repository source. Note that both are asynchronous methods where an asynchronous method such as these could be a millisecond slower then it's synchronous counter part using asynchronous means the user interface remains responsive.
Simple example
Public Shared Async Sub Simple(Optional identifier As Integer = 1)
Using context As New CustomerContext
Dim customer = Await context.Customers.IncludeContactCountry(identifier)
End Using
End Sub
Imports System.Runtime.CompilerServices
Imports EntityFrameworkCoreNorthWind.NorthWindEntityFrameworkCore
Imports Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore
Namespace Extensions
Public Module QueryExtensions
<Extension>
Public Function IncludeContactCountry(
query As IQueryable(Of Customers)) As IQueryable(Of Customers)
Return query.
Include(Function(customer) customer.Contact).
Include(Function(customer) customer.ContactTypeNavigation).
Include(Function(customer) customer.CountryIdentifierNavigation)
End Function
<Extension>
Public Function IncludeContactCountry(
query As IQueryable(Of Customers), identifier As Integer) As Task(Of Customers)
Return query.
Include(Function(customer) customer.Contact).
Include(Function(customer) customer.ContactTypeNavigation).
Include(Function(customer) customer.CountryIdentifierNavigation).
FirstOrDefaultAsync(Function(customer) customer.CustomerIdentifier = identifier)
End Function
End Module
End Namespace
Making changes while using these methods when attached to a DbContext and hooking up to a BindingList with implementing INotifyPropertyChanged any changes will be saved via SaveChanges. If data is not going to change a projection can be used.
Projections
A projection is just a way of mapping one set of properties to another. In relation to Entity Framework specifically, it’s a way of translating a full entity (database table) into a VB.NET class with a subset of those properties. The values can also be altered/joined/removed on the way through as well. Anything you can do in a SELECT statement in SQL is possible. (from Expression and Projection Magic for Entity Framework Core)
The following class is a projection which returns a subset of properties of Customers class and are read only.
Imports System.Linq.Expressions
Imports EntityFrameworkCoreNorthWind.NorthWindEntityFrameworkCore
Namespace Projections
Public Class CustomerItem
Public Property CustomerIdentifier() As Integer
Public Property CompanyName() As String
Public Property ContactName() As String
Public Property ContactId() As Integer?
Public Property CountryIdentifier() As Integer?
Public Property CountryName() As String
Public Property ContactTypeIdentifier() As Integer?
Public Overrides Function ToString() As String
Return $"{CompanyName} - {ContactName}"
End Function
Public Shared ReadOnly Property Projection() As Expression(Of Func(Of Customers, CustomerItem))
Get
Return Function(customers) New CustomerItem() With {
.CustomerIdentifier = customers.CustomerIdentifier,
.CompanyName = customers.CompanyName,
.ContactId = customers.ContactId,
.ContactName = $"{customers.Contact.FirstName} {customers.Contact.LastName}",
.CountryIdentifier = customers.CountryIdentifier,
.CountryName = customers.CountryIdentifierNavigation.Name,
.ContactTypeIdentifier = customers.CountryIdentifier
}
End Get
End Property
End Class
End Namespace
To implement, returning all Customers.
Method within a class.
Public Shared Async Function ReadCustomersProjected() As Task(Of List(Of CustomerItem))
Return Await Task.Run(
Async Function()
Using context As New CustomerContext
Return Await context.Customers.IncludeContactCountry.Select(CustomerItem.Projection).ToListAsync()
End Using
End Function)
End Function
In a form load data into a ComboBox.
Private Async Sub ListCustomerItemsButton_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) _
Handles ListCustomerItemsButton.Click
Dim customerItem As List(Of CustomerItem) =
Await Operations.ReadCustomersProjected()
CustomerItemComboBox.DataSource = customerItem
End Sub
In the sample project which is very simple several read methods are demonstrated by populating ComboBox and TextBox controls. Demonstrations were intentionally done simple for easy of learning. In a following up to this article code samples will be presented using the same class project and windows form project to work with a DataGridView to present data with text and combo box DataGridView columns with immediate updates similar to how Microsoft Access performs updates. The code for this will be adapted from several article using Entity Framework, see the GitHub repository which list the TechNet articles. Another follow up will be on sorting Entity Framework Core data in a DataGridView, see the following article for how this is done in Entity Framework which will work with Entity Framework Core.
External resources
Various sources to assist learning how to work with Entity Framework Core. Note that most show code in C#
Microsoft documentation:
- Installing Entity Framework Core
- Creating and configuring a model
- Database providers
- In-memory database provider testing
- GitHub/efcore
Other
- Entity Framework Tutorials (in C#)
- Code Project Getting Started with Entity Framework Core: Database-First Development (C#)
Summary
In this article, first steps to implement Entity Framework Core into a Windows Form solution have been presented. There will be several following up articles teaching how to implement Entity Framework Core with Windows forms controls and customizing the DbContext.
See also
VB.NET Entity Framework: Wiki portal
Source code
Clone, open in Visual Studio or download, unzip and open in Visual Studio.
https://github.com/karenpayneoregon/ef-core-projections
Once opened in Visual Studio copy the database script included in the Visual Studio solution, run in SSMS followed by performing a NuGet restore packages.