SQL Server Import/Export to Excel using Python script
Introduction
In previous article, we saw how to import/export excel to/from SQL Server by executing R script within T-SQL.
In this post, let us see another similar approach to import excel into SQL Server and export SQL server data to excel by executing Python script within T-SQL.
There are some existing methods to do this using BCP, Bulk Insert, Import & Export wizard from SSMS, SSIS, Azure data factory, Linked server & OPENROWSET query and SQLCMD.
BULK INSERT statement, the BCP tool, or Azure Data Factory can't read Excel files directly
BCP - Workaround has to be done to include the header while exporting
SSIS - Though it supports exporting to excel, with dynamic source & destination, handling mapping between source to target increases the complexity of the package
SQLCMD - Cannot export output in Excel file format
R & Python language extension was introduced in SQL Server 2016 & 2017 as part of machine learning. With support of R in Azure SQL database and Java language extension support in SQL Server 2019, this new approach can be used extensively as it easy, fast and flexible.
Pre-requisites
We have used SQL Server 2019 evaluation edition on Windows 10 64 bit and WideWorldImporters SQL Server sample database for this example.
Below scripts will work starting from SQL Server 2017 and above (as execution of Python language using T-SQL was introduced in SQL Server 2017).
Only pre-requisite step is to install Python services and then from SSMS enable the external scripting feature. Restart the database engine and then verify the installation as mentioned in MSDN.
Provide folder permission to access the excel files during import / export process, right-click on folder -> Properties -> Security -> (Full Control) to "ALL_APPLICATION_PACKAGES".
pandas.DataFrame.to_excel & pandas.read_excel are used to export and import excel which are installed by default
We can check that by running below statement in SSMS:
EXECUTE sp_execute_external_script
@language =N'Python',
@script=N'import pip
for i in pip.get_installed_distributions():
print(i)';
GO
Exporting SQL Server data (list of tables, views) into Excel file
For this approach, we have created a Stored procedure named "usp_ExportExcel" in "WideWorldImporters" database. Executing the Stored procedure based on input parameters exports SQL Server data to excel files
Stored procedure - Has below three input parameters and writes the output to excel file
| Parameter | Description |
| @ExportPath | Path for exporting excel files |
| @SchemaName | List of objects under this schema to be exported. Can have multiple values separated by comma |
| @ObjectlisttoExport | List of tables, views to be exported. Can have multiple values separated by comma |
CREATE OR ALTER PROC usp_ExportExcel (@ExportPath NVARCHAR(MAX),
@SchemaName NVARCHAR(MAX),
@ObjectlisttoExport NVARCHAR(MAX)
)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
BEGIN TRY
IF ISNULL(@ExportPath,'') <> ''
BEGIN
SELECT @ExportPath = CASE WHEN RIGHT(@ExportPath,1) = '\' THEN @ExportPath ELSE CONCAT(@ExportPath,'\') END
DECLARE @ValidPath TABLE (ValidPathCheck BIT)
INSERT @ValidPath
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
@language =N'Python',
@script=N'
import pandas as pd
d = os.path.isdir(ExportFilePath)
OutputDataSet = pd.DataFrame([d],columns=["Filename"])'
,@params = N'@ExportFilePath NVARCHAR(MAX)'
,@ExportFilePath = @ExportPath
IF (SELECT ValidPathCheck FROM @ValidPath) = 1
BEGIN
IF ISNULL(@SchemaName,'') <> '' OR ISNULL(@ObjectlisttoExport,'') <> ''
BEGIN
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS #ExportTablesList, #FinalExportList
CREATE TABLE #ExportTablesList(TableCount INT IDENTITY(1,1),Cols NVARCHAR(MAX),TableName NVARCHAR(200))
--Get the list of objects to be exported
INSERT #ExportTablesList (Cols,TableName)
SELECT CASE WHEN TY.name IN ('date','datetime2','datetimeoffset','time','timestamp','decimal','bit','int','bigint')
THEN CONCAT('TRY_CONVERT(','VARCHAR(MAX),',C.name,') AS ',QUOTENAME(C.NAME))
ELSE C.name END Cols -- To cover poor data type conversions b/n Python & SQL Server
,CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) TableName
FROM Sys.tables T
JOIN sys.columns C
ON T.object_id = C.object_id
JOIN sys.types TY
ON C.[user_type_id] = TY.[user_type_id]
WHERE Schema_name(T.schema_id) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@SchemaName, ','))
-- Ignore the datatypes that are not required to be exported
AND TY.name NOT IN ('geography','varbinary','binary','text', 'ntext', 'image', 'hierarchyid', 'xml', 'sql_variant')
INSERT #ExportTablesList (Cols,TableName)
SELECT CASE WHEN TY.name IN ('date','datetime2','datetimeoffset','time','timestamp','decimal','bit','int','bigint')
THEN CONCAT('TRY_CONVERT(','VARCHAR(MAX),',C.name,') AS ',QUOTENAME(C.NAME))
ELSE C.name END Cols -- To cover poor data type conversions b/n Python & SQL Server
,CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) TableName
FROM Sys.tables T
JOIN sys.columns C
ON T.object_id = C.object_id
JOIN sys.types TY
ON C.[user_type_id] = TY.[user_type_id]
WHERE CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ObjectlisttoExport, ','))
-- Ignore the datatypes that are not required to be exported
AND TY.name NOT IN ('geography','varbinary','binary','text', 'ntext', 'image', 'hierarchyid', 'xml', 'sql_variant')
--Dedup of object list
;WITH dedup
AS
(
SELECT *,ROW_NUMBER()OVER(PARTITION BY TableName,Cols ORDER BY Cols) Rn FROM #ExportTablesList
)
DELETE FROM dedup
WHERE Rn > 1
--Forming columns list as comma separated
SELECT TableName,IDENTITY(INT,1,1) AS TableCount
, STUFF(
(
SELECT ', ' + C.Cols
From #ExportTablesList As C
WHERE C.TableName = T.TableName
FOR XML PATH('')
), 1, 2, '') AS Cols
INTO #FinalExportList
From #ExportTablesList As T
GROUP BY TableName
DECLARE @I INT = 1
,@TableName NVARCHAR(200)
,@SQL NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
,@PythonScript NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
,@ExportFilePath NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
--Loop through the object list to export as excel
WHILE @I <= (SELECT COUNT(TableName) FROM #FinalExportList)
BEGIN
-- Just for testing purpose top 10 records are selected
SELECT @SQL = CONCAT('SELECT TOP 10 ',Cols,' FROM ',TableName,';')
,@TableName = TableName
FROM #FinalExportList WHERE TableCount = @I
SET @PythonScript = N'
FullFilePath = ExcelFilePath+TableName+".xlsx"
InputDataSet.to_excel(FullFilePath,sheet_name=TableName.split(".")[-1],index=False)'
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
@language = N'Python'
,@script = @PythonScript
,@input_data_1 = @SQL
,@params = N'@ExcelFilePath NVARCHAR(MAX), @TableName NVARCHAR(200)'
,@ExcelFilePath = @ExportPath -- file path where Excel files are placed
,@TableName = @TableName
SET @I = @I + 1
END
END ELSE PRINT 'Schema name of objects or list of objects (separated by comma) to be exported need to be mentioned'
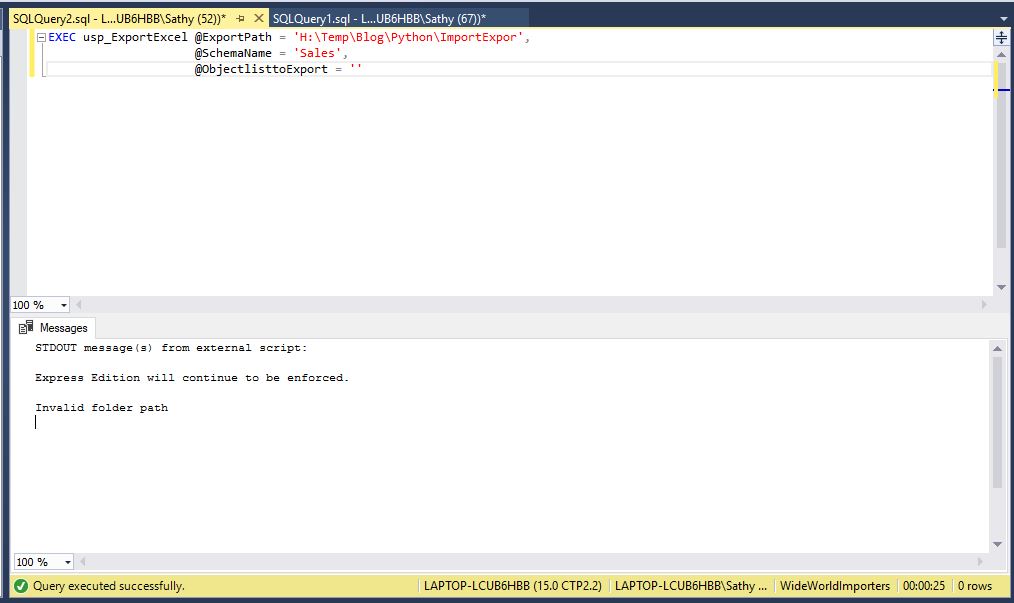
END ELSE PRINT 'Invalid folder path'
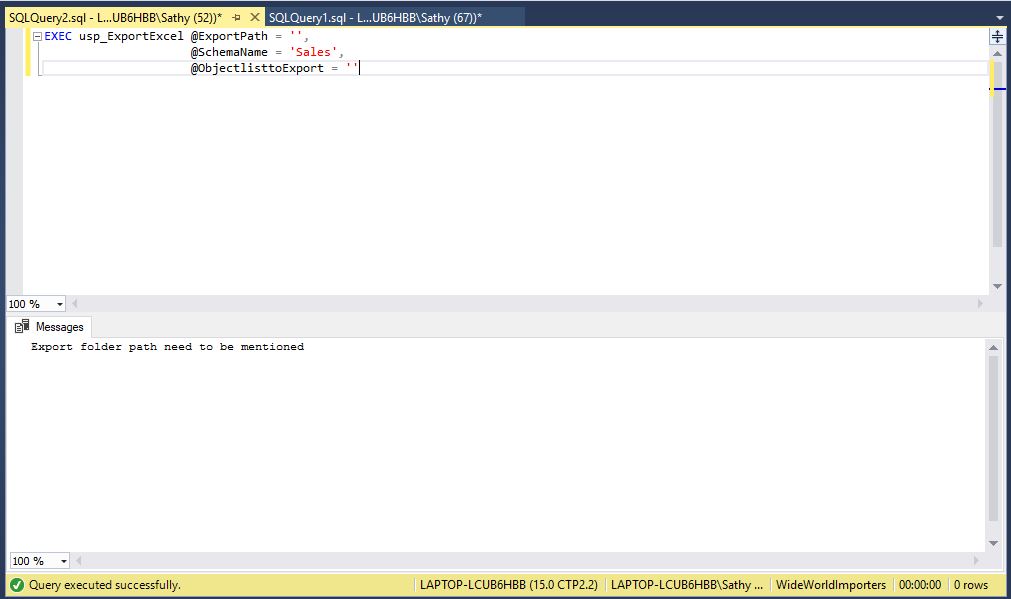
END ELSE PRINT 'Export folder path need to be mentioned'
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT 'Issue while executing this SP, please check whether there is permission to execute the script / to access the folder and input params are valid'
END CATCH
END
Sample execution code blocks:
EXAMPLE 1:
--Export path is mandatory
EXEC usp_ExportExcel @ExportPath = '',
@SchemaName = 'Sales',
@ObjectlisttoExport = ''
EXAMPLE 2:
--SP can check if the folder path is valid
EXEC usp_ExportExcel @ExportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExpor',
@SchemaName = 'Sales',
@ObjectlisttoExport = ''
EXAMPLE 3:
--Either Schema name or list of objects needs to be passed
EXEC usp_ExportExcel @ExportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
@SchemaName = '',
@ObjectlisttoExport = ''
EXAMPLE 4:
--Example for exporting list of objects separated by comma
EXEC usp_ExportExcel @ExportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
@SchemaName = '',
@ObjectlisttoExport = 'Application.People,Sales.Orders,Purchasing.Suppliers,Warehouse.Colors'
EXAMPLE 5:
--Example for exporting list of objects separated by comma and tables under Application schema
EXEC usp_ExportExcel @ExportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
@SchemaName = 'Application',
@ObjectlisttoExport = 'Application.People,Sales.Orders,Purchasing.Suppliers,Warehouse.Colors'
EXAMPLE 6:
--Example for exporting all tables under Application,Sales,Purchasing & Warehouse schema
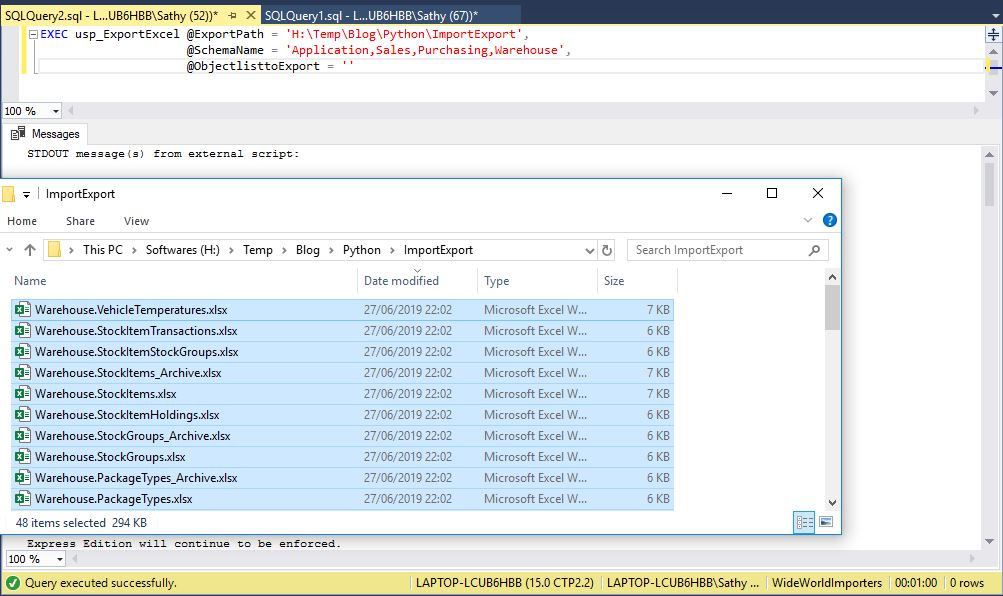
EXEC usp_ExportExcel @ExportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
@SchemaName = 'Application,Sales,Purchasing,Warehouse',
@ObjectlisttoExport = ''
Importing Excel file into SQL Server
For this approach, we have created a Stored procedure named "usp_ImportExcel" in "WideWorldImporters" database. Executing the Stored procedure based on input parameters imports excel files to SQL Server table
Stored procedure - Has below six input parameters
| Parameter | Description |
| @ImportPath | Path where excel files are placed for importing into SQL Server |
| @DBConnectionString | Target SQL Server database connection string where files are imported. Can be Database=DB name; Trusted_Connection=True or Database=DB name;Uid= user name;Pwd=Password |
| @ImportAll | If set to 1 then all files in the mentioned path are imported. If set to 0 then only mentioned files are imported |
| @CombineTarget | Flag to decide single target table for each source file (files with same structure) or separate target table for each source file |
| @ExcelFileName | If @ImportAll = 0 then excel file name needs to be passed to this parameter |
| @ExcelSheetName | If @ImportAll = 0 then corresponding sheet name of the excel file needs to be passed to this parameter |
From SSMS -> Object Explorer -> WideWorldImporters (database) ->Tables (right-click) -> Filter -> Filter Settings -> set Schema contains dbo. So that we can clearly see the tables being created on the fly while importing the files.
CREATE OR ALTER PROC usp_ImportExcel (@ImportPath NVARCHAR(MAX),
@DBConnectionString NVARCHAR(MAX),
@ImportAll BIT,
@CombineTarget BIT,
@ExcelFileName NVARCHAR(200),
@ExcelSheetName NVARCHAR(50)
)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
BEGIN TRY
IF ISNULL(@ImportPath,'') <> '' AND ISNULL(@DBConnectionString,'') <> ''
BEGIN
SELECT @ImportPath = CASE WHEN RIGHT(@ImportPath,1) = '\' THEN @ImportPath ELSE CONCAT(@ImportPath,'\') END
DECLARE @Serv NVARCHAR(200) = CONCAT(CHAR(39),CHAR(39),@@SERVERNAME,CHAR(39),CHAR(39))
DECLARE @ValidPath TABLE (ValidPathCheck BIT)
INSERT @ValidPath
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
@language =N'Python',
@script=N'
import pandas as pd
d = os.path.isdir(ImportFilePath)
OutputDataSet = pd.DataFrame([d],columns=["Filename"])'
,@params = N'@ImportFilePath NVARCHAR(MAX)'
,@ImportFilePath = @ImportPath
IF (SELECT ValidPathCheck FROM @ValidPath) = 1
BEGIN
IF (@ImportAll = 0 AND (ISNULL(@ExcelFileName,'') <> '' AND ISNULL(@ExcelSheetName,'') <> ''))
OR (@ImportAll = 1 AND (ISNULL(@ExcelFileName,'') = '' AND ISNULL(@ExcelSheetName,'') = ''))
BEGIN
DECLARE @PythonScript NVARCHAR(MAX) =CONCAT('
import pandas as pd
import os
import glob
from revoscalepy import RxSqlServerData, rx_data_step
sqlConnString = "Driver=SQL Server;Server=Serv; ',@DBConnectionString,'"
Filefolderepath = ImportFilePath+"*.xlsx"
if ImportAll ==1 and CombineTarget==0:
for FullFilePath in glob.glob(Filefolderepath):
Filename = os.path.basename(FullFilePath).replace(".xlsx","")
xl = pd.ExcelFile(FullFilePath)
for sheetname in xl.sheet_names:
Output = pd.read_excel(FullFilePath, sheetname=sheetname, na_filter=False).astype(str)
if not Output.empty:
sqlDS = RxSqlServerData(connection_string = sqlConnString,table = "".join(fl for fl in Filename if fl.isalnum())+"_"+"".join(sh for sh in sheetname if sh.isalnum()))
rx_data_step(input_data = Output, output_file = sqlDS,overwrite = True)
if ImportAll ==1 and CombineTarget==1:
df2=pd.DataFrame()
for FullFilePath in glob.glob(Filefolderepath):
Filename = os.path.basename(FullFilePath).replace(".xlsx","")
xl = pd.ExcelFile(FullFilePath)
for sheetname in xl.sheet_names:
Output = pd.read_excel(FullFilePath, sheetname=sheetname).columns.astype(str)
Output = ",".join(list(Output))
df1 = pd.DataFrame([[Filename,sheetname,FullFilePath,Output]],columns=["Filename","sheetname","FullFilePath","Headers"])
df2=df2.append(df1,ignore_index=True)
sqlDS = RxSqlServerData(connection_string = sqlConnString,table = "Tbl_PyImpExp1")
rx_data_step(input_data = df2, output_file = sqlDS,overwrite = True)
if ImportAll ==0:
Filename =ImportFilePath+ExcelFileName+".xlsx"
exists = os.path.isfile(Filename)
if exists and ExcelSheetName in pd.ExcelFile(Filename).sheet_names:
Output = pd.read_excel(Filename, sheetname=ExcelSheetName, na_filter=False).astype(str)
if not Output.empty:
sqlDS = RxSqlServerData(connection_string = sqlConnString,table = "".join(fl for fl in ExcelFileName if fl.isalnum())+"_"+"".join(sh for sh in ExcelSheetName if sh.isalnum()))
rx_data_step(input_data = Output, output_file = sqlDS,overwrite = True)
else:
print("Invalid Excel file or sheet name")')
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
@language = N'Python'
,@script = @PythonScript
,@params = N'@ImportFilePath NVARCHAR(MAX),@ImportAll BIT,@CombineTarget BIT,@ExcelFileName NVARCHAR(200),@ExcelSheetName NVARCHAR(50),@Serv NVARCHAR(200)'
,@ImportFilePath = @ImportPath
,@ImportAll = @ImportAll
,@CombineTarget = @CombineTarget
,@ExcelFileName = @ExcelFileName
,@ExcelSheetName = @ExcelSheetName
,@Serv = @Serv
IF @ImportAll =1 AND @CombineTarget =1
BEGIN
IF OBJECT_ID('Tbl_PyImpExp1') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Tbl_PyImpExp2
;WITH FileList
As(
SELECT [Filename]
,[sheetname]
,[Headers]
,[FullFilePath]
,ROW_NUMBER()OVER(ORDER BY (SELECT 1)) Rn
,ROW_NUMBER()OVER(PARTITION BY [Headers] ORDER BY [Headers]) Grp
,DENSE_RANK()OVER(ORDER BY [Headers]) Grp1
FROM [dbo].[Tbl_PyImpExp1]
)
SELECT *,FIRST_VALUE([Filename]) OVER (PARTITION BY Grp1 ORDER BY Grp ASC) AS TableName
INTO Tbl_PyImpExp2
FROM FileList
END
IF EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM Tbl_PyImpExp2)
BEGIN
DECLARE @I INT = 1
,@SQL NVARCHAR(MAX) =N''
SET @PythonScript = CONCAT('
import pandas as pd
from revoscalepy import RxSqlServerData, rx_data_step
sqlConnString = "Driver=SQL Server;Server=Serv; ',@DBConnectionString,'"
if ImportAll ==1 and CombineTarget==1:
FinalImport=pd.DataFrame()
for index, row in InputDataSet.iterrows():
Tbl = "".join(T for T in row["TableName"] if T.isalnum())
Import = pd.read_excel(row["FullFilePath"], sheetname=row["sheetname"], na_filter=False).astype(str)
Import["ImportKey"] = row["TableName"]+"_"+row["sheetname"]
FinalImport=FinalImport.append(Import,ignore_index=True)
if not FinalImport.empty:
sqlDS = RxSqlServerData(connection_string = sqlConnString,table = Tbl)
rx_data_step(input_data = FinalImport, output_file = sqlDS,overwrite = True)')
WHILE @I <= (SELECT MAX(Grp1) FROM Tbl_PyImpExp2)
BEGIN
SET @SQL = CONCAT('SELECT FullFilePath,sheetname,TableName FROM Tbl_PyImpExp2 WHERE Grp1 = ',@I)
EXEC sp_execute_external_script
@language = N'Python'
,@script = @PythonScript
,@input_data_1 = @SQL
,@params = N'@ImportAll BIT,@CombineTarget BIT,@Serv NVARCHAR(200)'
,@Serv = @Serv
,@ImportAll = @ImportAll
,@CombineTarget = @CombineTarget
SET @I = @I + 1
END
END
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS Tbl_PyImpExp1,Tbl_PyImpExp2
END
END ELSE PRINT 'Invalid parameters: If ImportAll = 0 then pass Excel file & Sheet Name as input. If ImportAll = 1 then pass Excel file & Sheet Name blank'
END ELSE PRINT 'Invalid folder path'
END ELSE PRINT 'Import folder path or database connection string need to be mentioned'
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
PRINT 'Issue while executing this SP, please check whether there is permission to execute the script / to access the folder and input params are valid'
END CATCH
END
Sample execution code blocks:
EXAMPLE 1:
--Path where files to be imported is mandatory
EXEC usp_ImportExcel @ImportPath = '',
@DBConnectionString = '',
@ImportAll = 0,
@CombineTarget = 0,
@ExcelFileName = '',
@ExcelSheetName = ''
EXAMPLE 2:
--SP can check if path provided is valid
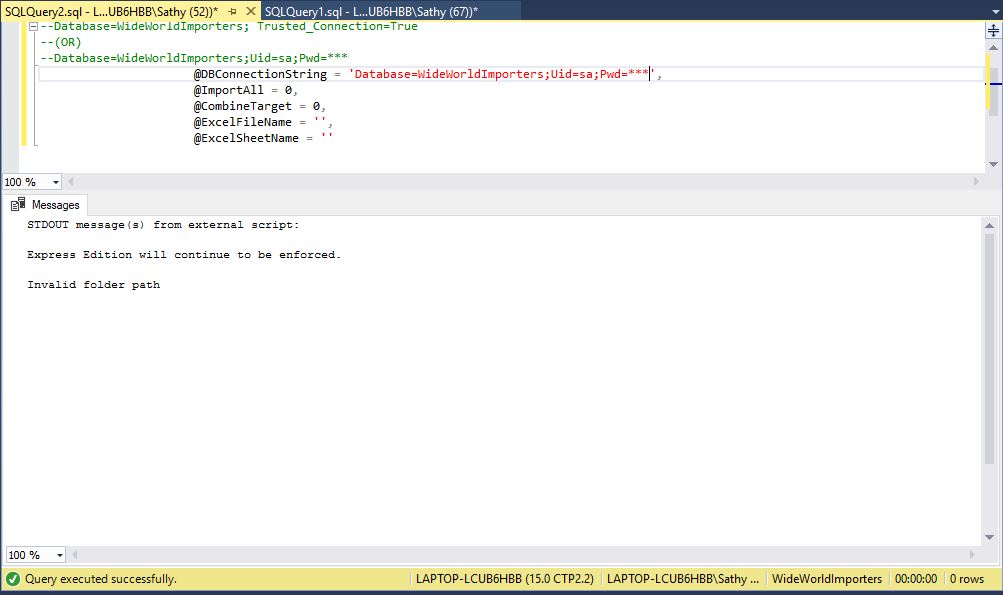
EXEC usp_ImportExcel @ImportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExpor',
--Database=WideWorldImporters; Trusted_Connection=True
--(OR)
--Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***
@DBConnectionString = 'Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***',
@ImportAll = 0,
@CombineTarget = 0,
@ExcelFileName = '',
@ExcelSheetName = ''
EXAMPLE 3:
--Example to import a Excel file Warehouse.VehicleTemperatures with sheet name VehicleTemperatures
EXEC usp_ImportExcel @ImportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
--Database=WideWorldImporters; Trusted_Connection=True
--(OR)
--Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***
@DBConnectionString = 'Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***',
@ImportAll = 0,
@CombineTarget = 0,
@ExcelFileName = 'Warehouse.VehicleTemperatures',
@ExcelSheetName = 'VehicleTemperatures'
EXAMPLE 4:
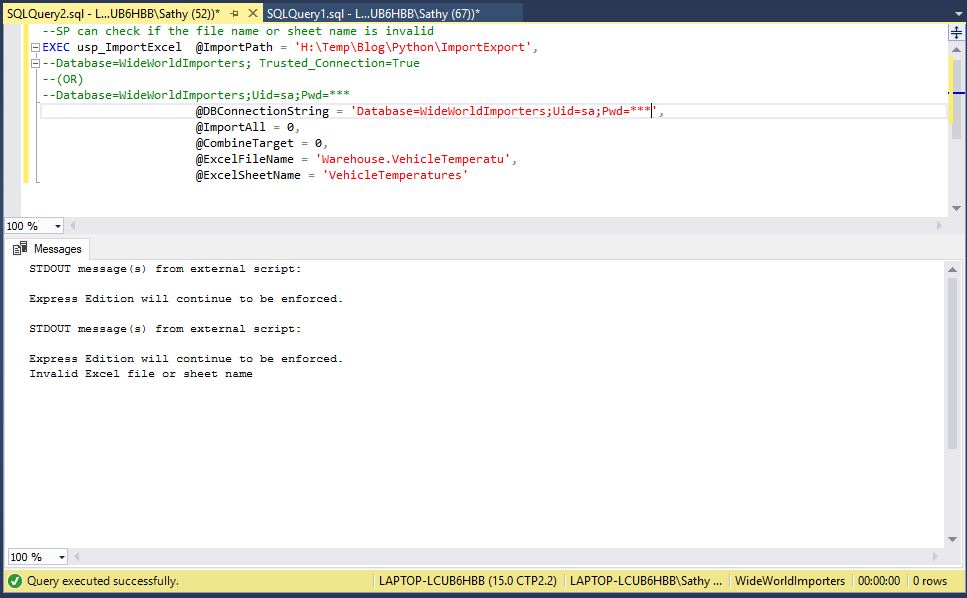
--SP can check if the file name or sheet name is invalid
EXEC usp_ImportExcel @ImportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
--Database=WideWorldImporters; Trusted_Connection=True
--(OR)
--Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***
@DBConnectionString = 'Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***',
@ImportAll = 0,
@CombineTarget = 0,
@ExcelFileName = 'Warehouse.VehicleTemperature',
@ExcelSheetName = 'VehicleTemperatures'
EXAMPLE 5:
--Example to import all the excel files in a folder to separate tables with naming convention filename_sheetname
EXEC usp_ImportExcel @ImportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
--Database=WideWorldImporters; Trusted_Connection=True
--(OR)
--Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***
@DBConnectionString = 'Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***',
@ImportAll = 1,
@CombineTarget = 0,
@ExcelFileName = '',
@ExcelSheetName = ''
EXAMPLE 6:
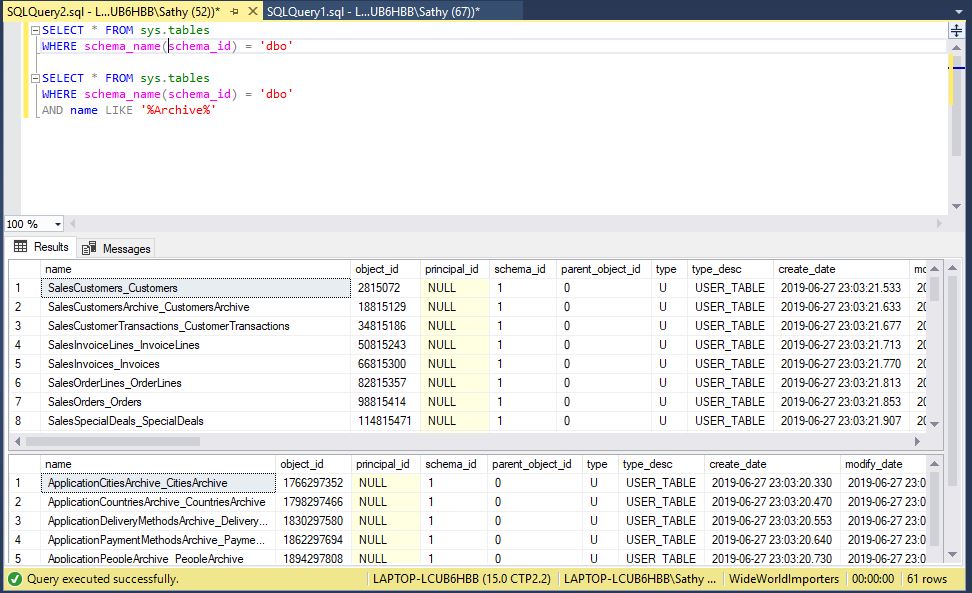
If we execute below queries, we can see 46 tables in total (including 15 archive tables) been created from above examples.
Please note _archive tables has same schema as the base tables.
SELECT * FROM sys.tables
WHERE schema_name(schema_id) = 'dbo'
SELECT * FROM sys.tables
WHERE schema_name(schema_id) = 'dbo'
AND name LIKE '%Archive%'
Now let us drop all the tables created from above examples
USE WideWorldImporters;
DROP TABLE ApplicationCities_Cities
DROP TABLE ApplicationCitiesArchive_CitiesArchive
DROP TABLE ApplicationCountries_Countries
DROP TABLE ApplicationCountriesArchive_CountriesArchive
DROP TABLE ApplicationDeliveryMethods_DeliveryMethods
DROP TABLE ApplicationDeliveryMethodsArchive_DeliveryMethodsArchive
DROP TABLE ApplicationPaymentMethods_PaymentMethods
DROP TABLE ApplicationPaymentMethodsArchive_PaymentMethodsArchive
DROP TABLE ApplicationPeople_People
DROP TABLE ApplicationPeopleArchive_PeopleArchive
DROP TABLE ApplicationStateProvinces_StateProvinces
DROP TABLE ApplicationStateProvincesArchive_StateProvincesArchive
DROP TABLE ApplicationSystemParameters_SystemParameters
DROP TABLE ApplicationTransactionTypes_TransactionTypes
DROP TABLE ApplicationTransactionTypesArchive_TransactionTypesArchive
DROP TABLE PurchasingPurchaseOrderLines_PurchaseOrderLines
DROP TABLE PurchasingPurchaseOrders_PurchaseOrders
DROP TABLE PurchasingSupplierCategories_SupplierCategories
DROP TABLE PurchasingSupplierCategoriesArchive_SupplierCategoriesArchive
DROP TABLE PurchasingSuppliers_Suppliers
DROP TABLE PurchasingSuppliersArchive_SuppliersArchive
DROP TABLE PurchasingSupplierTransactions_SupplierTransactions
DROP TABLE SalesBuyingGroups_BuyingGroups
DROP TABLE SalesCustomerCategories_CustomerCategories
DROP TABLE SalesCustomerCategoriesArchive_CustomerCategoriesArchive
DROP TABLE SalesCustomers_Customers
DROP TABLE SalesCustomersArchive_CustomersArchive
DROP TABLE SalesCustomerTransactions_CustomerTransactions
DROP TABLE SalesInvoiceLines_InvoiceLines
DROP TABLE SalesInvoices_Invoices
DROP TABLE SalesOrderLines_OrderLines
DROP TABLE SalesOrders_Orders
DROP TABLE SalesSpecialDeals_SpecialDeals
DROP TABLE WarehouseColdRoomTemperatures_ColdRoomTemperatures
DROP TABLE WarehouseColdRoomTemperaturesArchive_ColdRoomTemperaturesArchive
DROP TABLE WarehouseColors_Colors
DROP TABLE WarehouseColorsArchive_ColorsArchive
DROP TABLE WarehousePackageTypes_PackageTypes
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockGroups_StockGroups
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockGroupsArchive_StockGroupsArchive
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockItemHoldings_StockItemHoldings
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockItems_StockItems
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockItemStockGroups_StockItemStockGroups
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockItemsArchive_StockItemsArchive
DROP TABLE WarehouseStockItemTransactions_StockItemTransactions
DROP TABLE WarehouseVehicleTemperatures_VehicleTemperatures
Now let's try example 6 which consolidates the target when source files have same structure:
--Example to import all the excel files in a folder to same target tables when the files has same structure by setting @CombineTarget = 1
EXEC usp_ImportExcel @ImportPath = 'H:\Temp\Blog\Python\ImportExport',
--Database=WideWorldImporters; Trusted_Connection=True
--(OR)
--Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***
@DBConnectionString = 'Database=WideWorldImporters;Uid=sa;Pwd=***',
@ImportAll = 1,
@CombineTarget = 1,
@ExcelFileName = '',
@ExcelSheetName = ''
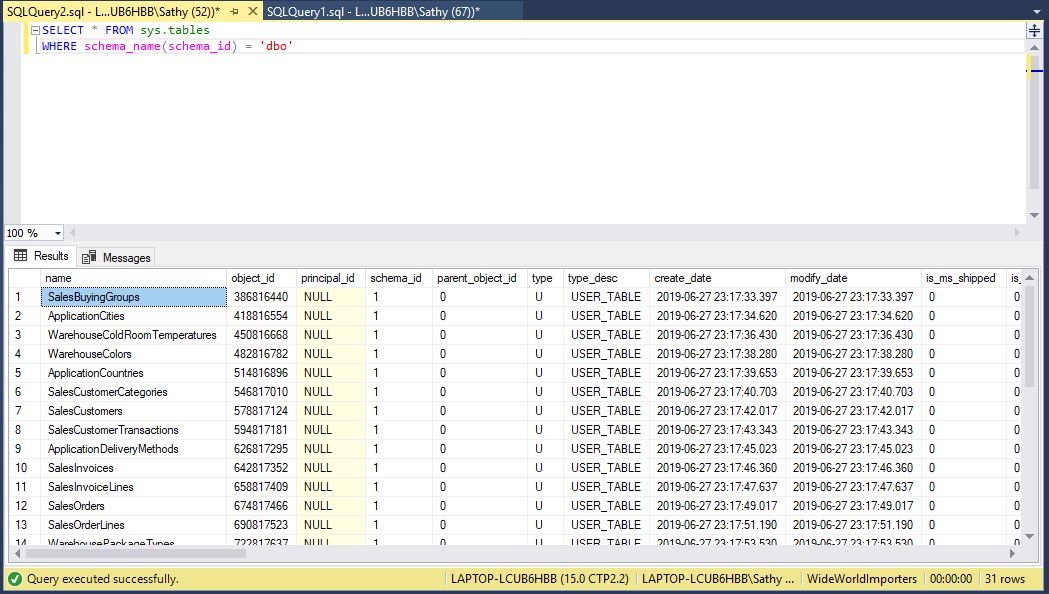
Now let us see how many tables created this time:
Previously we saw 46 tables been created, this time it is 31 tables this is because 15 archive tables which has same schema as the base table are imported into same target
SELECT * FROM sys.tables
WHERE schema_name(schema_id) = 'dbo'
Stored procedures mentioned in this post for importing / exporting are also published in TechNet Gallery and scripts can be downloaded from here. Other steps with examples are explained in this post. We need to be careful with indentations in python script as formatting them without understanding the code can result in error.
Summary
This post is just to give an overview of this new approach of importing / exporting to excel files in SQL Server using Python script. With respect to moving data (Import / Export) between SQL Server & Excel, there are various scenarios based on each requirement. We have covered some of them but tweaking the solutions mentioned above can cover any scenario.
See Also
https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/52528.sql-server-importexport-to-excel-using-r-script.aspx
https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/52624.sql-server-export-sql-file-output-to-excel-file-with-r-script.aspx