ASP.NET Core 2.2 Step-by-step: Creating application
Introduction
This article will walk you through the creation of ASP.NET Core application using ASP.NET Core 2.2 from scratch, by utilizing the capabilities of package manager, EF Core, Identity API, Razor Class Library, etc. So, rather than being more theoretical, this article will focus mainly on the implementation part. Wherever required, I’ll throw some light on the conceptual part too.
Prerequisite
Good knowledge of C# and working knowledge of web designing and its concepts.
Machine Configuration
Machine configuration used for this walkthrough is Visual Studio 2017 with .NET Core development tools/SDK. Make sure that you have at least .NET Core 2.2 installed.
Expectation
By the end of this article, the reader would be having a working model of ASP.NET Core website for a Cookie Store.
Good to Start
The background is all set and we are good to go. Let's start by creating our application in a step-by-step fashion.
Creating a new ASP.NET Core 2.2 Application
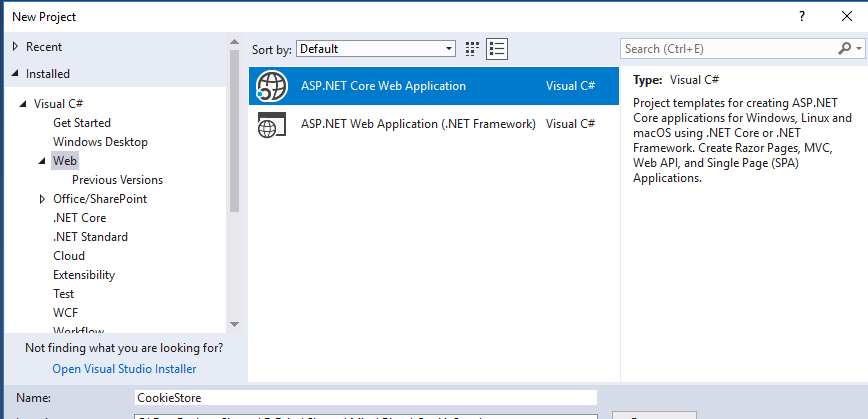
Let’s go to the Visual Studio. Go to File menu, select New and then select Project. On selecting the Web as a category, you will land upon the below dialog:
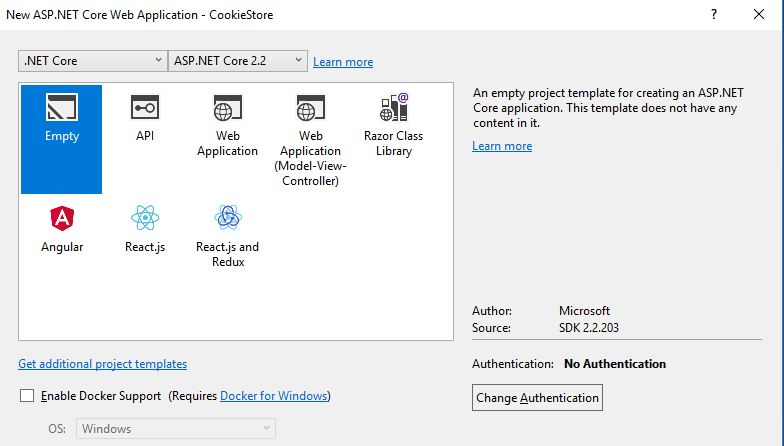
Once you clicked on Ok, you will witness below dialog wherein you can re-verify the selected ASP.NET Core version. Being a learner, it’s good to go with an Empty template as we can take care of each and everything by ourselves rather than relying on auto-generated code. Select Empty and proceed.
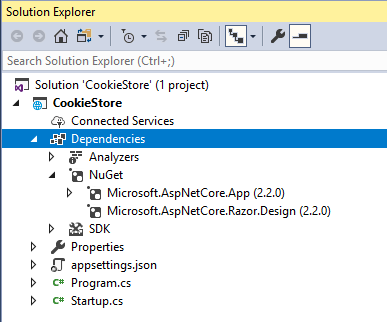
Once the project is successfully created, you can see the dependency node is having required references added as shown below:
Here, let’s remove appsettings.json file as we will be creating our own at later point of time and add a new folder named wwwroot under the project. Once the wwwroot folder is created, you can notice that the folder icon is changed. This is a special folder which stores all the static files (css, image files, java script files, etc.) and is mapped directly to web site URL.
Plugging Middleware and Services
Let’s start with the Startup class. This class holds two very important methods named ConfigureServices and Configure. Both these methods are automatically called by ASP.NET Core. Using ConfigureServices, we can add services to dependency injection container using IServiceCollection. So, let’s go and add MVC service as shown below:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
}
Next is ConfigureServices method, which is used to configure the middleware pipeline with the components which will serve our requests. Here is the initial code to plug required middleware:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseStatusCodePages();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvcWithDefaultRoute();
}
Please note that the sequence of adding middleware matters a lot. Now we have done the ground work for setting up the foundation for our application, let’s go ahead and setup other useful components.
Creating Model and Repository Classes
Let’s start by creating a Models folder under solution with a class named Cookie underneath it.
public class Cookie
{
public int Id {get;set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string TinyDescription { get; set; }
public string FullDescription { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
public string ImageUrl { get; set; }
public bool IsCookieOfTheDay { get; set; }
}
Now quickly create an interface with name IRepository under the same folder with two initial methods as shown below:
public interface IRepository
{
IEnumerable GetAllCookies();
Cookie GetCookieById(int id);
}
Next task would be to create some dummy data, which we can use to verify whether our application is working as expected or not. Here is the implementation of IRepository interface:
public class MockRepository : IRepository
{
private List _cookies;
public MockRepository()
{
if (_cookies == null)
{
InitializeRepository();
}
}
private void InitializeRepository()
{
_cookies = new List
{
new Cookie
{ Id=1,Name="Raspberry", Price=110, TinyDescription="Dark chocolate overloaded",
FullDescription ="This is one of the best ever soft and chewy cookie and also been awarded as the best cookie several times.", IsCookieOfTheDay=false,
ImageUrl ="\\Images\\1.png"},
new Cookie{ Id=2, Name="Nuts Overloaded", Price=100, TinyDescription="Truely healthy",
FullDescription ="This cookie is fully loaded with nuts of various types and contains nice amount of peanut butter.", IsCookieOfTheDay=true,
ImageUrl ="\\Images\\2.png"},
new Cookie{Id=3, Name="Chocolate",Price=70,TinyDescription="Amazingly fruity",
FullDescription ="This cookie is best suited for the chocolate lovers. It's less sweet and gives very elegant taste.", IsCookieOfTheDay=false,
ImageUrl ="\\Images\\3.png"},
new Cookie{Id=4, Name="Delicious Oatmeal",Price=50,TinyDescription="Truely healthy",
FullDescription ="This is one of the most moist and flavourful cookie, which can make anyone's mood happy.", IsCookieOfTheDay=false,
ImageUrl ="\\Images\\4.png"},
};
}
public Cookie GetCookie(int id)
{
return _cookies.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Id == id);
}
public IEnumerable GetCookies()
{
return _cookies;
}
}
Let’s go and register this IRepository with dependency injection container inside ConfigureServices method as shown below:
services.AddTransient(); // get me new instance every time
Adding Controller
Let’s create a new folder named Controllers under the project and add an empty controller with the name Home inside it. Just to brief, the controller is responsible for creating a response based on the user’s request with the help of a model by calling a method. Such methods are generally known as action methods in terms of MVC. Below is the code to use IRepository inside the controller to get the data from the model.
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly IRepository _repository;
public HomeController(IRepository repository)
{
_repository = repository;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
Adding View
Till this point, we are already done with the basic Model and Controller. So, the only this pending is View. In ASP.NET Core 2.2, a view can be of two types – Regular/Plain view and Strongly-typed view. But in most of the scenarios, the strongly-typed view is required. Here we would be using Razor.
So, let’s create a new folder named Views under project along with a subfolder named as Home. Right-click on the Home folder and add new item Razor View. On successful addition of View, you will notice that a new file with name Index.cshtml is added under Home folder.
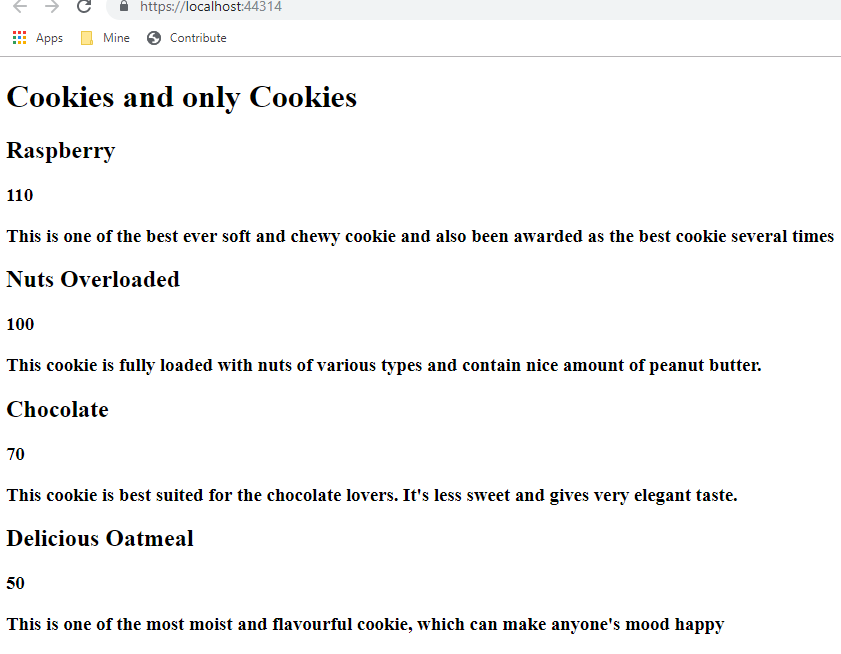
Now it’s time to verify, whether view and controller are tied properly and able to communicate. For this verification purpose, let’s add some title to the page and we will pass the value of this title from controller class using ViewBag. Similarly, we will also show some information about the cookies. Below is the updated method of HomeController:
public IActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.Title = "Cookies and only Cookies";
var cookies = _repository.GetAllCookies().OrderByDescending(x=>x.Price);
return View(cookies);
}
Next is to update the view to read this title value. Here is the code or this:

Now, if you will run the application, you would be able to see below output:
Improvising on including HTML markup
In the above snippet, we have seen that complete HTML markup is written to display a page. Now what if we have lots of views? Are we going to repeat this HTML code for each and every page?
Certainly not. Here comes the templating. We can create a template and refer that template in all the views. Doing this will also reduce the amount of code in individual views. It’s obvious that, if something is to be shared among many components, then it has to be kept in a shared location and that’s where shared folder is introduced as part of the MVC design.
Introducing Layout Template
Add a new folder under Views folder and name it as Shared. Right click on the Shared folder and add a new item Razor Layout. Default name of this newly added item is _Layout.cshtml. and it looks like below:
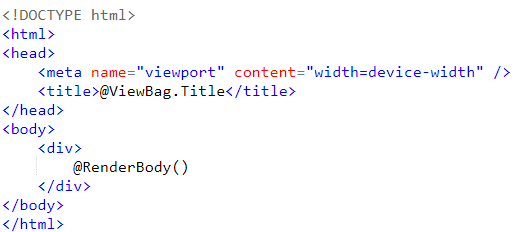
If you will see closely, you may notice that _Layout.cshtml and our view contains most of the common code. So, it’s time to integrate _Layout.cshtml into our view and after integration, our view will contain below code only:
Refining the View even further using _ViewStart
We did a really good job by reducing the line of codes in our view file, but there is still a scope to do more. Again, the layout, which we integrated in our view is going to be duplicated for each and every view. Can we get rid of this duplication also? Of course, Yes.
Let’s add another new item Razor View Start under Views folder with a default name as _ViewStart.cshtml. This file comes with below default code in it as shown below and is invoked automatically:
@{
Layout = "_Layout";
}
Now you can see that this file has already plugged Layout for us, which means line of code in our view is further reduced to just few lines as shown below:

You can re-run your application and verify that it is working as expected.
Introducing ViewModel
You must have noticed that our view is getting data from multiple paths. So, why can’t we get rid of this and create a single entity which would be the source for our view. Let’s try this.
We will add a new folder named ViewModels under project with a new class named HomeViewModel under it. This ViewModel class will be the data source for our Home view. As of now, we will take the bare minimum fields as shown below:
public class HomeViewModel
{
public string Title { get; set; }
public List Cookies { get; set; }
}
Accordingly, we must update our Index method inside HomeController as shown below:
public IActionResult Index()
{
HomeViewModel viewModel = new HomeViewModel
{
Title = "Cookies and only Cookies",
Cookies = _repository.GetAllCookies().OrderByDescending(x => x.Price).ToList()
};
return View(viewModel);
}
Lastly, let’s update the View with reference of HomeViewModel as shown below:

Re-verify the output, it should still be the same.
Improving Look and Feel of the view using Bootstrap
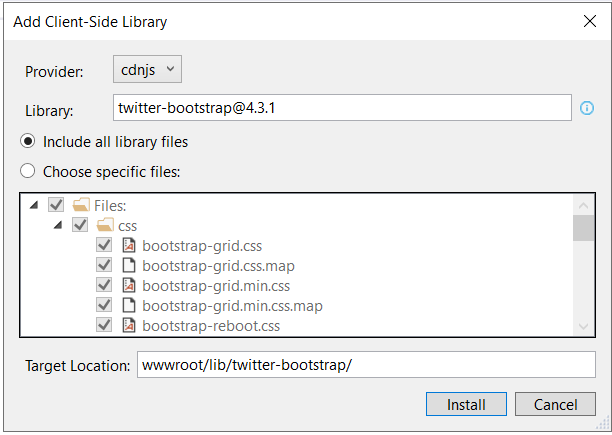
This can be done using a client-side package known as Bootstrap. Depending on the version and updates of Visual Studio, one can choose any of the package manager like Bower, Library Manager (LibMan), etc. Here I’ll go with the Library Manager as my Visual Studio version is 15.8.5. Let’s go and add new item ‘Add Client-Side Library’ at project level and furnish the details as shown below:
Next is to add images to our application. For that, we have to create another folder named Images under wwwroot.
Then we have to add a style sheet to our app and to do that, a new folder named content has to be added under wwwroot and inside that we have to create a css names site.css. Once done, we can add below basic style:
body {
padding-top:50px;
padding-bottom:20px;
background-image: url();
background-repeat: repeat;
}
.body-content{
padding-left: 15px;
padding-right: 15px;
}
Finally, we have to associate css and bootstrap to our _Layout page using <Link> as shown below:

Next is to update view file to accommodate bootstrap. Below is the complete code:
If everything was done well, you will see below web page on running the application:
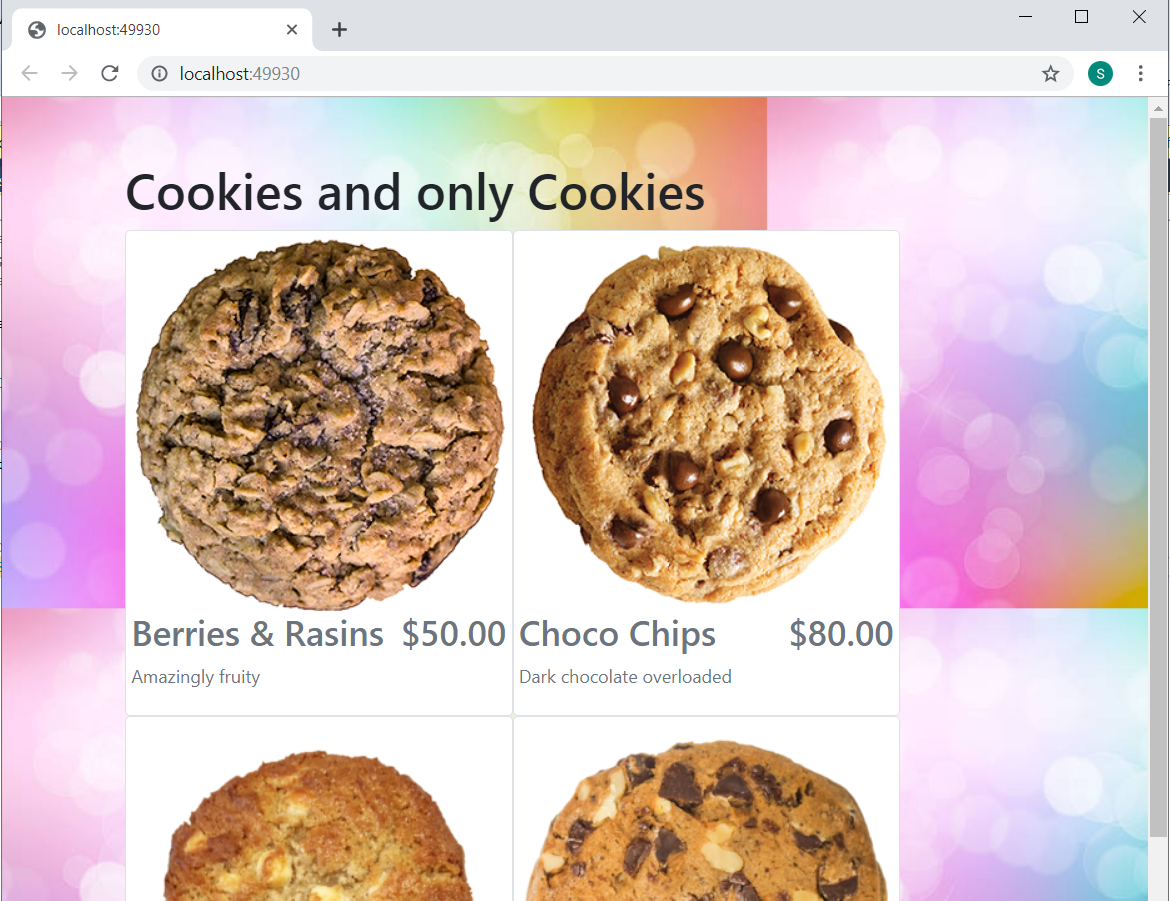
Next is to associate the real database with our application.
Getting real data using EF Core
EF core is an ORM which supports cross-platform capabilities like ASP.NET Core. It’s worth mentioning that as of now, EF Core only supports Code-First approach. Below are the steps which need to be taken care to fully integrate the EF with our application:
- Create Entity Classes
- Create Database Context
- Setup Connection string
- Changes to Application Configuration
Let’s create a new class named DatabaseContext under Models folder and place the below code in it:
public class DatabaseContext:DbContext
{
public DatabaseContext(DbContextOptions options):base(options)
{
}
public DbSet Cookies { get; set; }
}
DataContext plays a vital role of connecting our application to actual database. Till now, we were using mocked values using MockRepository class. So, it’s time to create an actual class named Repository under Models folder having below code:
public class DatabaseContext:DbContext
{
public DatabaseContext(DbContextOptions options):base(options)
{
}
public DbSet Cookies { get; set; }
}
Next is to set up the connection string. Hope most of you are aware that ASP.NET Core no more uses Web.Config file, rather it uses appsettings.json. So, add a new item ‘App Settings File’ named appsettings.json and update the connection string in it. My code looks something like this:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;Database=CookiesDataStore;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
As a final step, we have to register EF core with our application and that can be done by updating ConfigureServices() in Startup class as shown below:
public class Startup
{
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; set; }
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
services.AddTransient();
services.AddMvc();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseStatusCodePages();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvcWithDefaultRoute();
}
}
It’s time to build the code and verify that there are no more compilation errors.
Creating a Database
In order to view something on web page, we need a data in our database. Here we will use Package Manager console with below command:
PM> add-migration CookiesDatabaseMigration
PM> update-database
To add some initial data to database, we will create a new class called DbInitializer under Models folder with below code:
public static class DbInitializer
{
public static void Seed(DatabaseContext dbContext)
{
if (!dbContext.Cookies.Any())
{
dbContext.AddRange(
new Cookie
{
Name = "Choco Chips",
Price = 80,
TinyDescription = "Dark chocolate overloaded",
FullDescription = "This is one of the most moist and flavourful cookie, which can make anyone's mood happy.",
IsCookieOfTheDay = false,
ImageUrl = "\\Images\\Chocochip.png"
},
new Cookie
{
Name = "Nuts & Peanuts",
Price = 75,
TinyDescription = "Truely healthy",
FullDescription = "This cookie is fully loaded with nuts of various types and contain nice amount of peanut butter.",
IsCookieOfTheDay = true,
ImageUrl = "\\Images\\ChocolateChipWalnut.png"
},
new Cookie
{
Name = "Berries & Rasins",
Price = 50,
TinyDescription = "Amazingly fruity",
FullDescription = "This is one of the best ever soft and chewy cookie and also been awarded as the best cookie several times.",
IsCookieOfTheDay = false,
ImageUrl = "\\Images\\Nuts.png"
},
new Cookie
{
Name = "Coconut",
Price = 100,
TinyDescription = "Truely healthy",
FullDescription = "This cookie is best suited for the nut lovers. It's less sweet and gives very elegant taste.",
IsCookieOfTheDay = false,
ImageUrl = "\\Images\\Coconut.png"
}
);
}
dbContext.SaveChanges();
}
}
Next is to call this DbInitializer from Program class and here is the updated code for the same:
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
var host = CreateWebHostBuilder(args).Build();
using (var scope = host.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
try
{
var context = services.GetRequiredService();
DbInitializer.Seed(context);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// TODO
}
}
host.Run();
}
Now quickly run the application and you will see the same output as before.
Adding Navigation
As part of navigation, we will create a details page which will hold the details of selected cookie. To get the details of a selected cookie, a new method has to be added in HomeController class as shown below:
public IActionResult Details(int id)
{
var cookie = _repository.GetCookie(id);
return View(cookie);
}
And of course, we have to add the view for this method with the name Details.cshtml under HomeController:
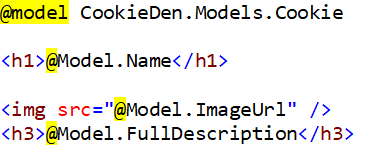
Now, we want to navigate to Details view from Index view. So, we will use tag helpers as shown below:
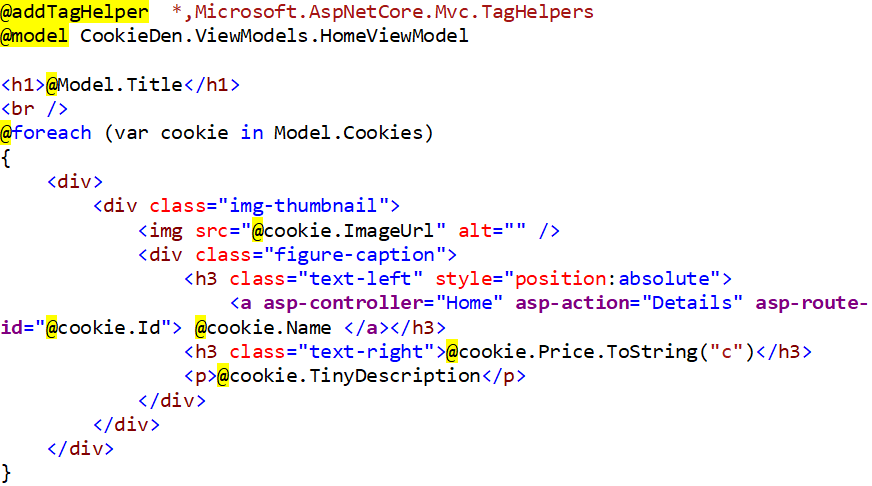
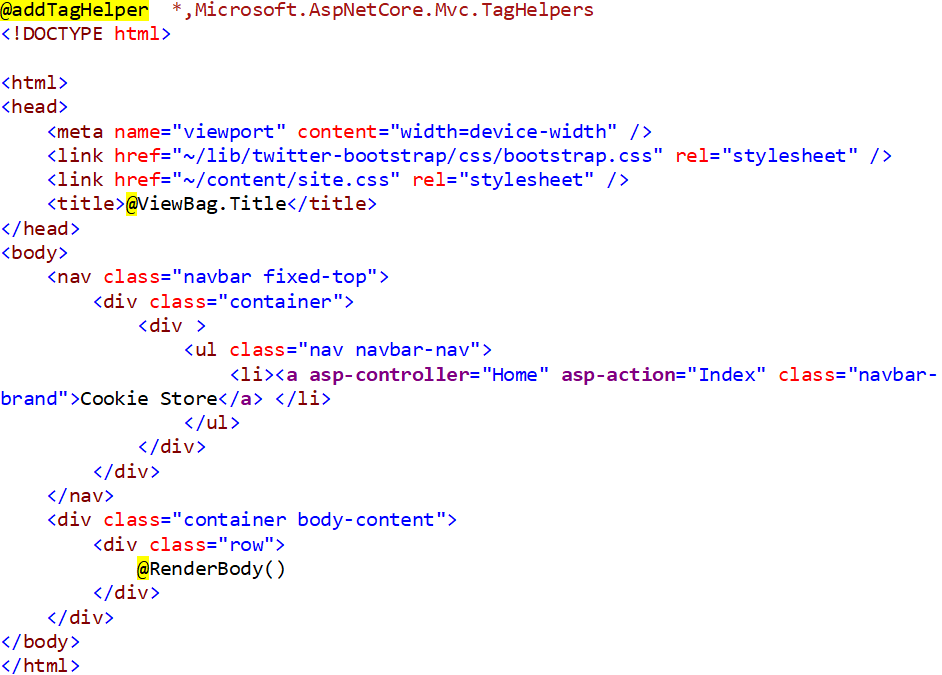
One last thing is to add navigation on our front page and that can be done using nav element. Below is the updated code of*_Layout.cshtml*:
Now quickly run the application and you will be able to see the links on top of the page as:
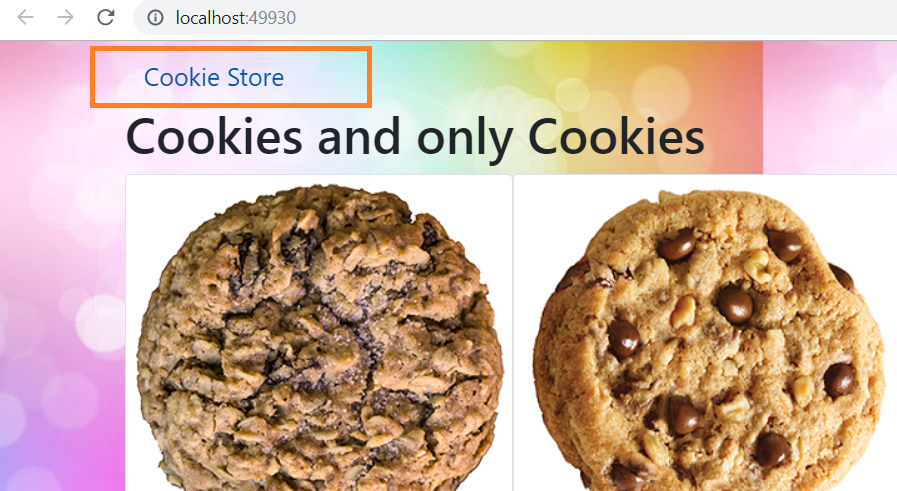 https://www.codeproject.com/KB/Articles/5061469/Working/Image10.png
https://www.codeproject.com/KB/Articles/5061469/Working/Image10.png
Adding Form to Request Comments
Now, let’s add a for m by which user can give feedback or comments for our lovely cookies. In order to do that, we have to add a new model entity named Feedback as shown below:
public class Feedback
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Content { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
}
Next is to update database with this new entity and that can be done by running add-migration command as:
PM> Add-Migration Feedback
Let’s quickly add the interface and a method in that to save feedback and code for that is as shown below:
public class FeedbackRepository: IFeedbackRepository
{
private readonly DatabaseContext _dbContext;
public FeedbackRepository(DatabaseContext context)
{
_dbContext = context;
}
public void AddFeedback(Feedback feedback)
{
_dbContext.Feedbacks.Add(feedback);
_dbContext.SaveChanges();
}
}
Next is to register this new interface with dependency injection container under ConfigureServices method:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
…
services.AddTransient();
services.AddMvc();
}
Now it s time to do UI changes for feedback functionality. Below is the code for FeedbackController and its view:
public class FeedbackController : Controller
{
private readonly IFeedbackRepository _feedbackRepository;
public FeedbackController(IFeedbackRepository feedbackRepository)
{
_feedbackRepository = feedbackRepository;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Index(Feedback feedback)
{
_feedbackRepository.AddFeedback(feedback);
return View();
}
}
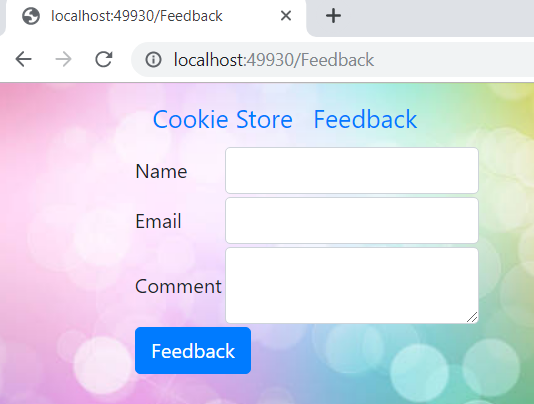
Next is to add the Feedback link on our application front page and that can be done by updating Layout page as shown below:
On click of Feedback, navigation will occur on below page:
Securing application Configuring Identity
As part of this section, we will explore the ASP.NET Core identity API and to accommodate this, we have to update bit of our existing code. Let’s start with DatabaseContext class. Now, instead of inheriting with DbContext, we will interit DatabaseContext class with IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser> and at the same time we have to update our middleware pipeline by adding app.UseAuthentication().
Next, we have to update our database with user info. So, we have to run add and update migration as shown below:
PM> add-migration AuthenticationAdded
PM> update-database
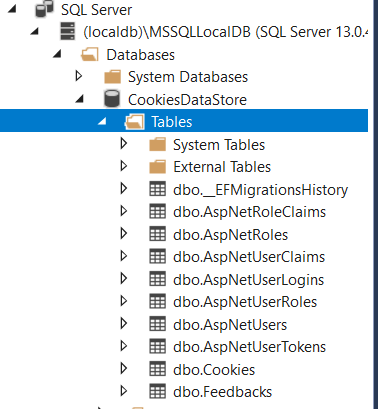
On successful execution, you will see that below tables are created in database:
Adding Authentication Support
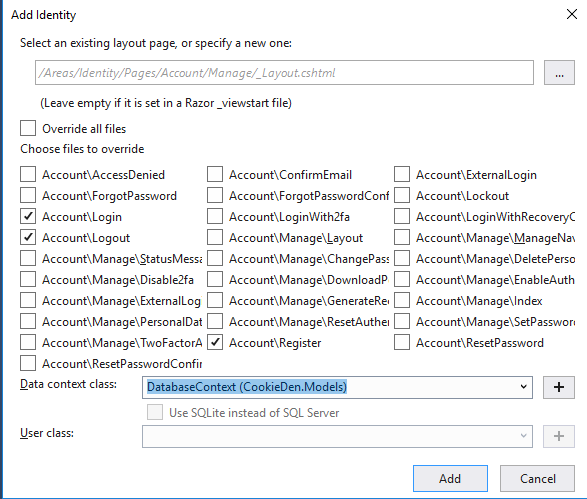
To add authentication capabilities to our application, we will use out of box functionality provided by the Razor Class Library which comes with ASP.NET Core. To do this, right click on the project and select Add and then New Scaffolded Item…, select Identity.
Post above action, we will get below dialog which mentions about all the views are readily available for us to use. Here I will be choosing three views with required data context as shown below:
public class IdentityHostingStartup : IHostingStartup
{
public void Configure(IWebHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.ConfigureServices((context, services) => {
services.AddDefaultIdentity(IdentityUser)
.AddEntityFrameworkStores(DatabaseContext);
});
}
}
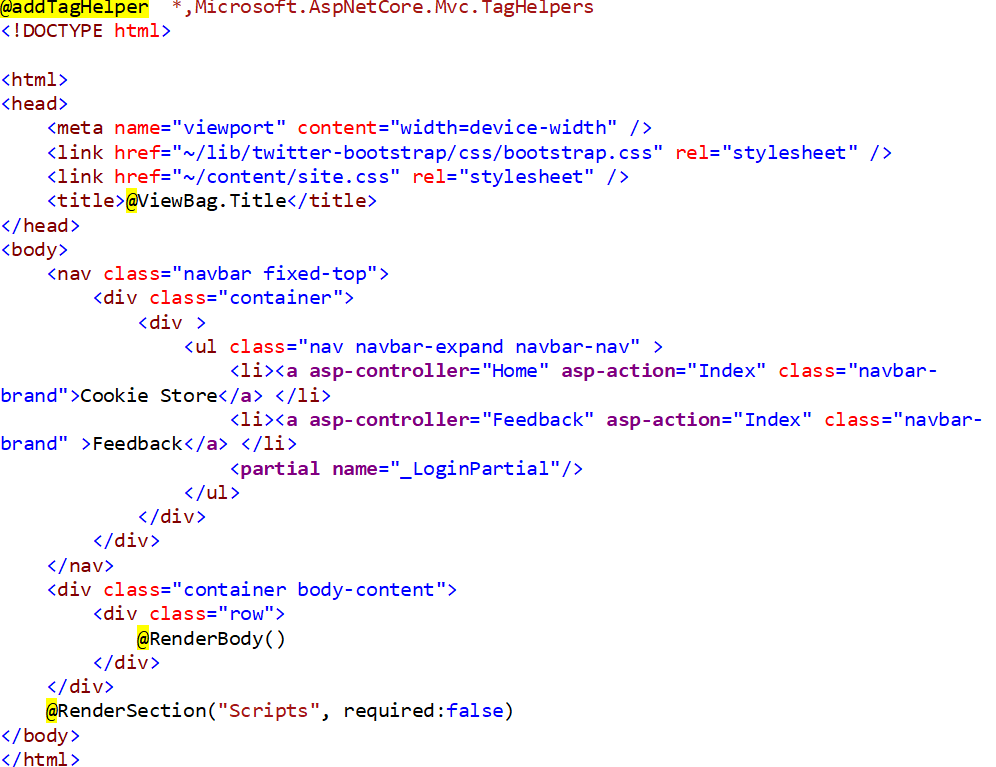
By above code, we are using our database context to save identity information. Finally, we have to provide link on our navigation bar, so just plug the login stuff to _Layout page by going with <Partial> as shown below:
Now run the application and you will see two additional links added to navigation bar. Of course, you can go ahead and play with Register and Login functionality now. Isn’t it cool.
Adding authorization Support
Till here, we have provided login functionality but what about restricting any user from using some functionality of website, for example, only the logged in users should be allowed to provide feedback. Here comes in the concept of Authorization. Let’s quickly do it by decorating our Feedback controller with Authorize attribute as shown below:
[Authorize]
public class FeedbackController : Controller
{
……
}
We are done and it’s time to run the application and verify all the things.
Hope you enjoyed creating your own ASP.NET Core application with all the basic concepts covered.
References
Course by Gill Cleeren and MSDN docs