T-SQL : Data profiling in On-premise SQL Server / Azure SQL database
Introduction
In this post, let us see how we can do data profiling on On-premise SQL Server / Azure SQL database tables using T-SQL script.
Knowledge of the data is really important in all stages of data life cycle from developing a technical solution (building data model or data migration from legacy systems / raw data source) or till taking key business decisions based on the underlying processed data. To get good understanding of data and get familiarized with the data stored in the database, we need to have high level picture of data like how many unique values, count of occurrence of values in a column, count of missing values, length of string stored in a large text column, also few metadata information about the schema holding the data can be helpful sometimes to cope with environment where data changes constantly.
Data profiling provides below high level information about data:
- Number of rows and size of the data in the object, date for the most recent update of the data and the object schema
- Number of null records, distinct values for columns and data type of column
- Minimum, maximum values for numeric columns and check for existence of special characters, leading/trailing spaces for columns of string data type
Data Profiling with different Microsoft tools/products
Data profiling is the primary & key for any data related project and it is easily understandable by the users who manages the data. That's why Microsoft has introduced this feature everywhere now.
1) Azure Data Catalog
Azure Data Catalog is a fully managed cloud service. Data Catalog helps people discover, understand, and use data sources, and it helps organizations get more value from their existing data.
2) Azure Machine learning
In Azure ML studio, after selecting the data source right-click on it to visualize the data and decide on whether any data preparation steps are required.
3) Power BI
Data Profiling allows us to easily find issues with our data within the Power Query Editor
4) SSIS Data Profiling task and viewer
The Data Profiling task provides data profiling functionality inside the process of extracting, transforming, and loading data. Data Profiling task works only with data that is stored in SQL Server. It does not work with third-party or file-based data sources.
5) Using ability to execute external scripts
With the ability to execute external scripts like R & Python from SQL Server, after importing any data source as data frame we can perform data profiling using R & Python packages or modules
Explanation on T-SQL script used in this post for data profiling
Two stored procedures are created to generate data profiling output. Inside the stored procedure, iteration on each table columns are performed using system catalog views to apply the MIN, MAX and other functions on each column to get the data profiling output
1) usp_DataProfiling
2) usp_DataProfiling_Metadata
Data profiling script (two stored procedures) mentioned in this post will generate four result sets :
1) ColumnDataProfiling
2) ColumnUniqueValues
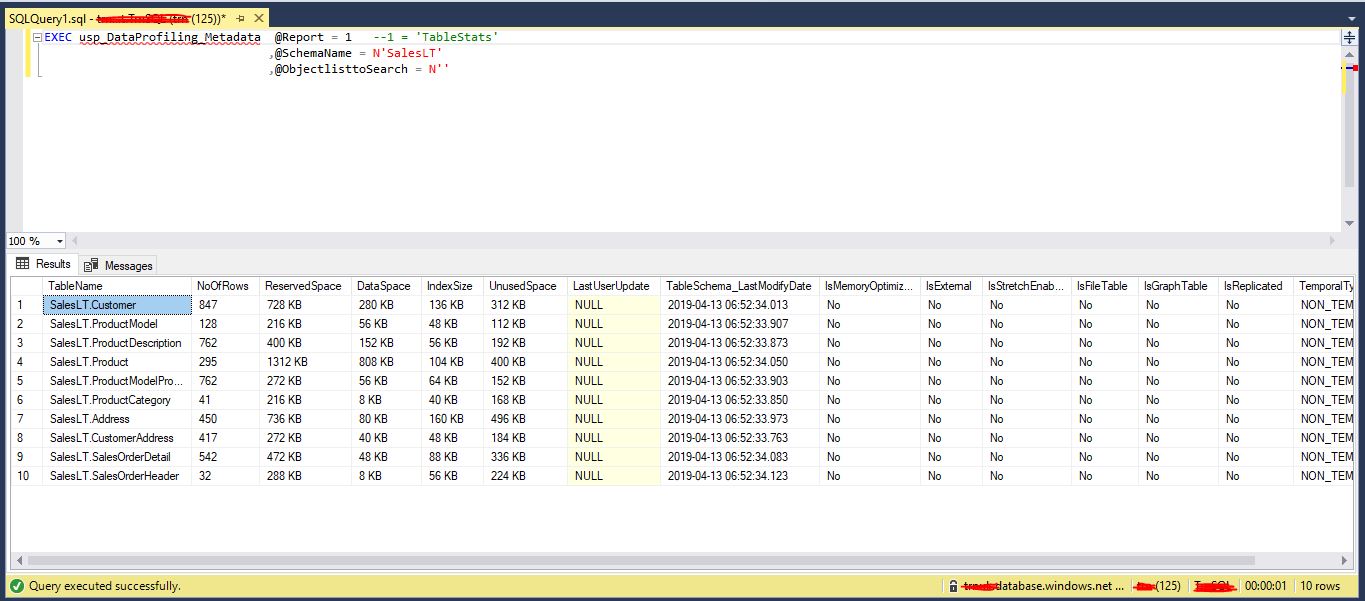
3) TableStats
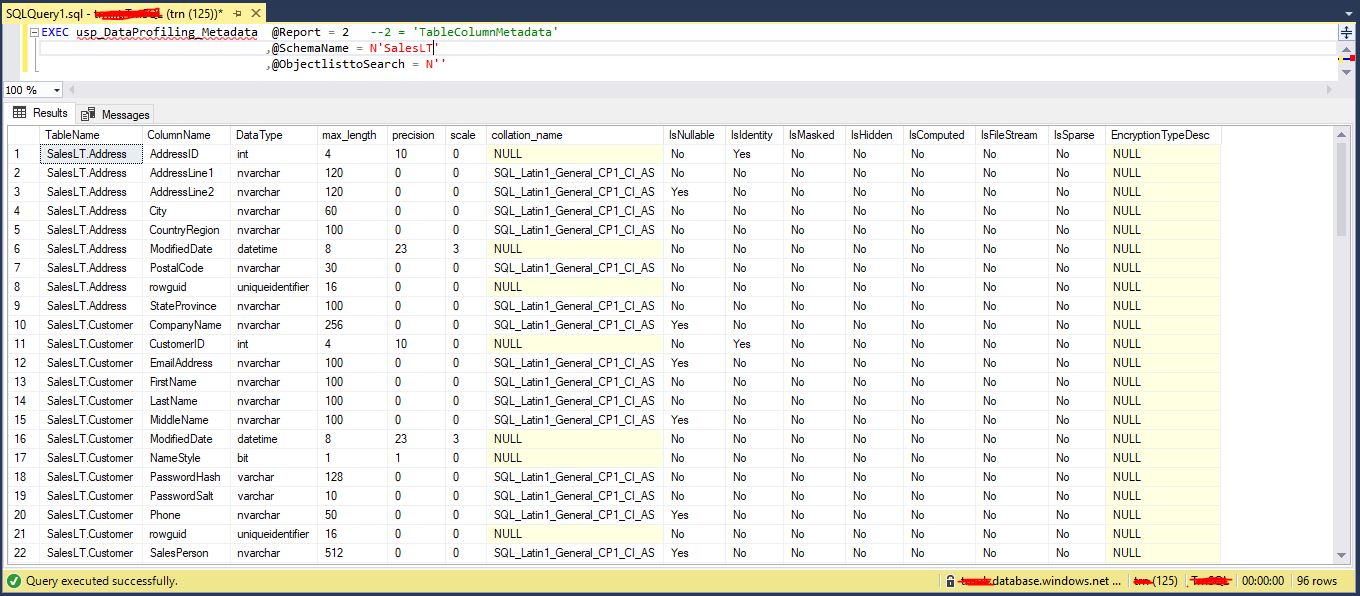
4) TableColumnMetadata
Below are the various input parameters of stored procedure's and it’s usage details:
1) usp_DataProfiling
| Parameter | Description |
| @Report | 1 = ColumnDataProfiling 2 = ColumnUniqueValues |
| @SchemaName | Schema name for which data profiling needs to be done. Multiple values can be passed separated by comma |
| @ObjectlisttoSearch | List of tables separated by comma for which data profiling needs to be done |
| @ExcludeTables | Tables to be excluded from data profiling output. Input format: Schemaname.tablename. Multiple values can be passed separated by comma |
| @ExcludeColumns | Columns to be excluded from data profiling output. Multiple values can be passed separated by comma |
| @ExcludeDataType | Data types to be excluded from data profiling output. Multiple values can be passed separated by comma. These data types are excluded by default 'geography','varbinary','binary','text', 'ntext', 'image', 'hierarchyid', 'xml', 'sql_variant' as they are not really relevant for data profiling |
| @RestrictCharlength |
Resultset shows only one record describing the details of the field, if the field has maximum character length greater than 100 else resultset will show one record per unique value in that field. This default value can be overwritten using this parameter |
| @RestrictNoOfUniqueValues |
Resultset shows only one record describing the details of the field, if that field has more than 50 unique values else resultset will show one record per unique value in that field. This default value can be overwritten using this parameter |
2) usp_DataProfiling_Metadata
| Parameter | Description |
| @Report | 1 = TableStats 2 = TableColumnMetadata |
| @SchemaName | Schema name for which data profiling needs to be done. Multiple values can be passed separated by comma |
| @ObjectlisttoSearch | List of tables separated by comma for which data profiling needs to be done |
Data Profiling using T-SQL script
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE usp_DataProfiling
@Report TINYINT , --1 = 'ColumnDataProfiling', 2 = 'ColumnUniqueValues'
@SchemaName NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'',
@ObjectlisttoSearch NVARCHAR(MAX),
@ExcludeTables NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'',
@ExcludeColumns NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'',
@ExcludeDataType NVARCHAR(100) = N'',
@RestrictCharlength INT,
@RestrictNoOfUniqueValues INT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SET ANSI_WARNINGS OFF;
SET ANSI_NULLS ON;
SELECT @RestrictCharlength = IIF(@RestrictCharlength IS NULL OR @RestrictCharlength = '',100,@RestrictCharlength)
SELECT @RestrictNoOfUniqueValues = IIF(@RestrictNoOfUniqueValues IS NULL OR @RestrictNoOfUniqueValues = '',50,@RestrictNoOfUniqueValues)
DECLARE @TableColList TABLE (Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),Tbl NVARCHAR(128),colname NVARCHAR(200),ColType NVARCHAR(150))
IF ISNULL(@SchemaName,'') <> '' OR ISNULL(@ObjectlisttoSearch,'') <> ''
BEGIN
INSERT @TableColList
SELECT DISTINCT CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) TableName
,C.name
,CASE WHEN TY.is_user_defined = 1 THEN (SELECT name FROM sys.types
WHERE system_type_id = user_type_id
AND system_type_id = TY.system_type_id)
ELSE TY.name
END
FROM Sys.tables T
JOIN sys.columns C
ON T.object_id = C.object_id
JOIN sys.types TY
ON C.[user_type_id] = TY.[user_type_id]
-- Ignore the datatypes that are not required
WHERE TY.name NOT IN ('geography','varbinary','binary','text', 'ntext', 'image', 'hierarchyid', 'xml', 'sql_variant')
AND (Schema_name(T.schema_id) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@SchemaName, ','))
OR CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ObjectlisttoSearch, ',')))
AND (TY.name NOT IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ExcludeDataType, ','))
AND TY.name = TY.name)
AND (C.name NOT IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ExcludeColumns, ','))
AND C.name = C.name)
AND (CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) NOT IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ExcludeTables, ','))
AND CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) = CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name))
END ELSE
BEGIN
INSERT @TableColList
SELECT DISTINCT CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) TableName
,C.name
,CASE WHEN TY.is_user_defined = 1 THEN (SELECT name FROM sys.types
WHERE system_type_id = user_type_id
AND system_type_id = TY.system_type_id)
ELSE TY.name
END
FROM Sys.tables T
JOIN sys.columns C
ON T.object_id = C.object_id
JOIN sys.types TY
ON C.[user_type_id] = TY.[user_type_id]
-- Ignore the datatypes that are not required
WHERE TY.name NOT IN ('geography','varbinary','binary','text', 'ntext', 'image', 'hierarchyid', 'xml', 'sql_variant')
AND (TY.name NOT IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ExcludeDataType, ','))
AND TY.name = TY.name)
AND (C.name NOT IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ExcludeColumns, ','))
AND C.name = C.name)
AND (CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) NOT IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ExcludeTables, ','))
AND CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) = CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name))
END
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS #Final
CREATE TABLE #Final (Id BIGINT IDENTITY(1,1),TableName NVARCHAR(128),ColumnName NVARCHAR(200),ColumnType NVARCHAR(150),ColumnUniqueValues NVARCHAR(MAX),UniqueValueOccurance BIGINT,MissingDataRowCount BIGINT,MinValue NVARCHAR(MAX),MaxValue NVARCHAR(MAX),SpecialCharacters BIGINT,LeadingTrailingSpaces BIGINT,MinFieldValueLen BIGINT,MaxFieldValueLen BIGINT,Comment NVARCHAR(MAX))
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS #temp
CREATE TABLE #temp (Id BIGINT IDENTITY(1,1),TableName NVARCHAR(128),ColumnName NVARCHAR(200),Cnt BIGINT,MaxLen BIGINT,MinLen BIGINT,MissingDataCount BIGINT,MinValue NVARCHAR(MAX),MaxValue NVARCHAR(MAX),SpecialCharacters BIGINT,LeadingTrailingSpaces BIGINT)
DECLARE @I INT = 1
,@SQL NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
,@tblname NVARCHAR(128)
,@Colname NVARCHAR(200)
,@ColType NVARCHAR(150)
,@Cnt BIGINT
,@MaxLen BIGINT
,@MinLen BIGINT
,@MissingData BIGINT
,@MaxVal NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
,@MinVal NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
,@MinMAxSQL NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
,@SpecialCharacters BIGINT
,@LeadingTrailingSpaces BIGINT
WHILE @I <= (SELECT MAX(Id) FROM @TableColList)
BEGIN
SELECT @Colname = QUOTENAME(colname),@tblname = Tbl,@ColType = ColType FROM @TableColList
WHERE Id = @I
SELECT @MinMAxSQL = CASE WHEN @ColType IN ('date','datetime','datetime2','datetimeoffset','time','timestamp')
THEN CONCAT(' FORMAT (MIN(',@Colname,'), ''yyyy-MM-dd,hh:mm:ss'') MinValue,FORMAT (MAX(',@Colname,'), ''yyyy-MM-dd,hh:mm:ss'') MAXValue')
WHEN @ColType = 'bit'
THEN '0 AS MinValue,1 AS MaxValue'
ELSE CONCAT('CASE WHEN EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM ',@tblname,' WHERE ISNUMERIC(',@Colname,') = 0)','THEN NULL ELSE MIN(',@Colname,') END MinValue
,CASE WHEN EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM ',@tblname,' WHERE ISNUMERIC(',@Colname,') = 0)','THEN NULL ELSE MAX(',@Colname,') END MAXValue')
END
EXEC (';WITH CTE AS (
SELECT COUNT_BIG(DISTINCT '+@Colname+') Cnt
,MAX(LEN('+@Colname+')) MaxLen
,MIN(LEN('+@Colname+')) MinLen
,SUM(CASE WHEN '+@Colname+' IS NULL OR CAST('+@Colname+' AS VARCHAR(MAX)) = '''' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) MissingData
,'+@MinMAxSQL+'
,CASE WHEN '''+@ColType+''' IN (''nvarchar'',''varchar'',''nchar'',''char'')
THEN SUM(CASE WHEN '+@Colname+' LIKE ''%[^a-zA-Z0-9 ]%'' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END)
ELSE NULL END SpecialCharacters
,CASE WHEN '''+@ColType+''' IN (''nvarchar'',''varchar'',''nchar'',''char'')
THEN SUM(CASE WHEN ISNULL(DATALENGTH('+@Colname+'),'''') = ISNULL(DATALENGTH(RTRIM(LTRIM('+@Colname+'))),'''') THEN 0 ELSE 1 END)
ELSE NULL END LeadingTrailingSpaces
FROM '+@tblname+' )
INSERT #temp(TableName,ColumnName,Cnt,MaxLen,MinLen,MissingDataCount,MinValue,MaxValue,SpecialCharacters,LeadingTrailingSpaces)
SELECT '''+@tblname+''','''+@Colname+''',Cnt,ISNULL(MaxLen,0) MaxLen,ISNULL(MinLen,0) MinLen,ISNULL(MissingData,0) MissingData,MinValue,MAXValue
,ISNULL(SpecialCharacters,0) SpecialCharacters,ISNULL(LeadingTrailingSpaces,0) LeadingTrailingSpaces FROM CTE')
SELECT @Cnt = Cnt,@MaxLen = MaxLen,@MinLen = MinLen,@MissingData = MissingDataCount,@MinVal=MinValue,@MaxVal=MAXValue
,@SpecialCharacters = SpecialCharacters ,@LeadingTrailingSpaces = LeadingTrailingSpaces
FROM #temp
WHERE Id = @I AND TableName = @tblname AND ColumnName = @Colname
IF ISNULL(@MaxLen,'') < @RestrictCharlength AND ISNULL(@Cnt,'') < @RestrictNoOfUniqueValues
BEGIN
SET @SQL = CONCAT('SELECT ''',@tblname,''',''',@Colname,''',''',@ColType,''',',@Colname,',COUNT_BIG(',@Colname,'),',@MissingData,',''',@MinVal,''',''',@MaxVal,''',',@SpecialCharacters,',',@LeadingTrailingSpaces,',',@MinLen,',',@MaxLen,',','''','This field has Unique values = ',@Cnt,'''',' FROM ',@tblname,' GROUP BY ',@Colname)
INSERT #Final (TableName,ColumnName,ColumnType,ColumnUniqueValues,UniqueValueOccurance,MissingDataRowCount,MinValue,MaxValue,SpecialCharacters,LeadingTrailingSpaces,MinFieldValueLen,MaxFieldValueLen,Comment)
EXEC(@SQL)
END
ELSE
BEGIN
INSERT #Final (TableName,ColumnName,ColumnType,MissingDataRowCount,MinValue,MaxValue,SpecialCharacters,LeadingTrailingSpaces,MinFieldValueLen,MaxFieldValueLen,Comment)
SELECT @tblname,@Colname,@ColType,@MissingData,@MinVal,@MaxVal,@SpecialCharacters,@LeadingTrailingSpaces,@MinLen,@MaxLen,CONCAT('This field has Unique values = ',@Cnt)
END
SET @I = @I + 1
END
IF @Report = 1
BEGIN
SELECT DISTINCT TableName,ColumnName,ColumnType,MissingDataRowCount,MinValue,MaxValue,SpecialCharacters
,LeadingTrailingSpaces,MinFieldValueLen,MaxFieldValueLen,Comment
FROM #Final
ORDER BY TableName,ColumnName
END
IF @Report = 2
BEGIN
SELECT TableName,ColumnName,ColumnUniqueValues,UniqueValueOccurance,Comment
FROM #Final
ORDER BY TableName,ColumnName
END
END
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE usp_DataProfiling_Metadata
@Report TINYINT , --1 = 'TableStats', 2 = 'TableColumnMetadata'
@SchemaName NVARCHAR(MAX) = N'',
@ObjectlisttoSearch NVARCHAR(MAX) = N''
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS #TblList
CREATE TABLE #TblList(Id INT IDENTITY(1,1),TableName NVARCHAR(200) )
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS #Tblstats
CREATE TABLE #Tblstats (TableName NVARCHAR(200),NoOfRows NVARCHAR(100),ReservedSpace NVARCHAR(100)
,DataSpace NVARCHAR(100),IndexSize NVARCHAR(100),UnusedSpace NVARCHAR(100)
,LastUserUpdate DATETIME)
IF ISNULL(@SchemaName,'') <> '' OR ISNULL(@ObjectlisttoSearch,'') <> ''
BEGIN
INSERT #TblList (TableName)
SELECT CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(SCHEMA_ID),'.',name) TableName
FROM Sys.tables
WHERE (Schema_name(schema_id) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@SchemaName, ','))
OR CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(SCHEMA_ID),'.',name) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ObjectlisttoSearch, ',')))
END ELSE
BEGIN
INSERT #TblList (TableName)
SELECT CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(SCHEMA_ID),'.',name) TableName
FROM Sys.tables
END
DECLARE @Tblstats TABLE(TableName NVARCHAR(200),NoOfRows NVARCHAR(100),ReservedSpace NVARCHAR(100)
,DataSpace NVARCHAR(100),IndexSize NVARCHAR(100),UnusedSpace NVARCHAR(100)
)
DECLARE @I INT = 1
,@tblname NVARCHAR(128) = N''
,@last_user_update DATETIME
WHILE @I <= (SELECT COUNT(1) FROM #TblList)
BEGIN
SELECT @tblname=TableName FROM #TblList WHERE Id = @I
INSERT @Tblstats
EXEC sp_spaceused @tblname;
SELECT TOP 1 @last_user_update=last_user_update
FROM sys.dm_db_index_usage_stats
WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID(@tblname)
ORDER BY last_user_update DESC
INSERT #Tblstats(TableName,NoOfRows,ReservedSpace,DataSpace,IndexSize,UnusedSpace,LastUserUpdate)
SELECT @tblname,NoOfRows,ReservedSpace,DataSpace,IndexSize,UnusedSpace,@last_user_update
FROM @Tblstats
DELETE FROM @Tblstats
SET @I = @I + 1
END
IF @Report = 1
BEGIN
;WITH Systbl
AS
(
SELECT DISTINCT CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(SCHEMA_ID),'.',name) TableName
,modify_date TableSchema_LastModifyDate
,CASE WHEN is_replicated = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsReplicated
,CASE WHEN is_filetable = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsFileTable
,CASE WHEN is_memory_optimized = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsMemoryOptimized
,temporal_type_desc TemporalTypeDesc
,CASE WHEN is_remote_data_archive_enabled = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsStretchEnabled
,CASE WHEN is_external = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsExternal
,CASE WHEN is_node = 1 OR is_edge = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END IsGraphTable
FROM sys.tables ST
JOIN #TblList T
ON CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(SCHEMA_ID),'.',name) COLLATE DATABASE_DEFAULT = T.TableName COLLATE DATABASE_DEFAULT
)
SELECT B.*,A.TableSchema_LastModifyDate
,A.IsMemoryOptimized
,A.IsExternal
,A.IsStretchEnabled
,A.IsFileTable
,A.IsGraphTable
,A.IsReplicated
,A.TemporalTypeDesc
FROM Systbl A
JOIN #Tblstats B
ON A.TableName COLLATE DATABASE_DEFAULT = B.TableName COLLATE DATABASE_DEFAULT
END
IF @Report = 2
BEGIN
SELECT DISTINCT CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) TableName
,C.name ColumnName
,CASE WHEN TY.is_user_defined = 1 THEN (SELECT name FROM sys.types
WHERE system_type_id = user_type_id
AND system_type_id = TY.system_type_id)
ELSE TY.name
END AS DataType
,C.max_length
,C.precision
,C.scale
,C.collation_name
,CASE WHEN C.is_nullable = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsNullable
,CASE WHEN C.is_identity = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsIdentity
,CASE WHEN C.is_masked = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsMasked
,CASE WHEN C.is_hidden = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsHidden
,CASE WHEN C.is_computed = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsComputed
,CASE WHEN C.is_filestream = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsFileStream
,CASE WHEN C.is_sparse = 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END AS IsSparse
,C.encryption_type_desc EncryptionTypeDesc
FROM Sys.tables T
JOIN sys.columns C
ON T.object_id = C.object_id
JOIN sys.types TY
ON C.[user_type_id] = TY.[user_type_id]
WHERE (Schema_name(T.schema_id) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@SchemaName, ','))
OR CONCAT(SCHEMA_NAME(T.SCHEMA_ID),'.',T.name) IN (SELECT value FROM STRING_SPLIT(@ObjectlisttoSearch, ',')))
END
END
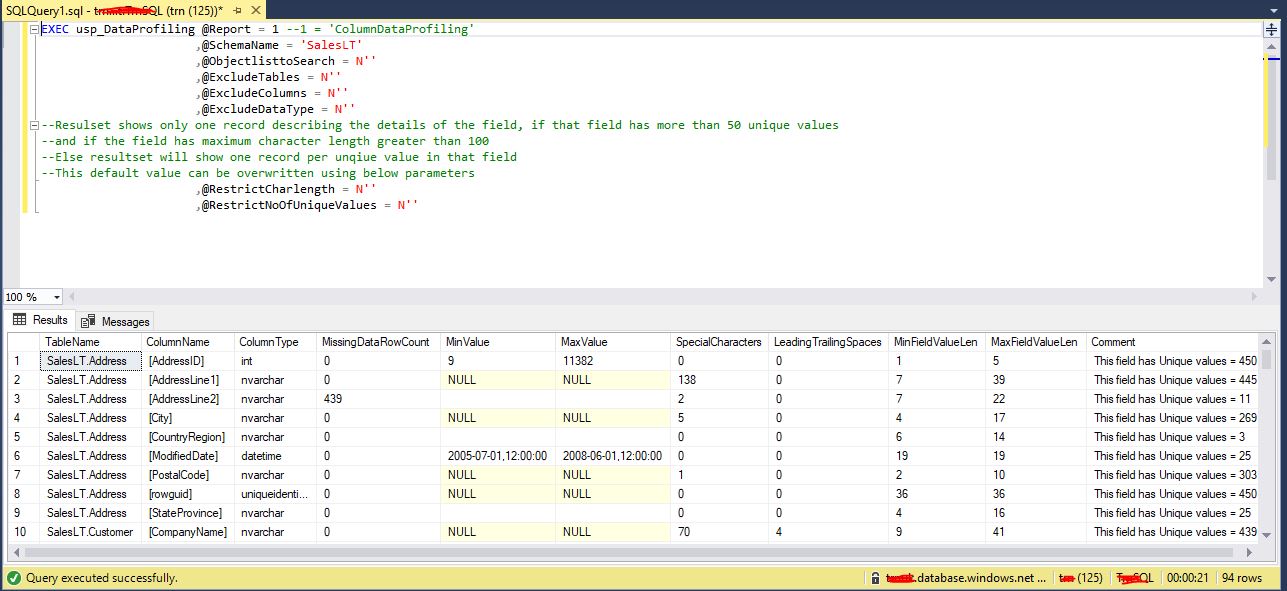
Below screenshots shows the sample execution of data profiling stored procedures in Azure SQL database :
ColumnDataProfiling report for SalesLT schema in AdventureWorksLT database
ColumnUniqueValues report for SalesLT schema in AdventureWorksLT database
TableStats report for SalesLT schema in AdventureWorksLT database
TableColumnMetadata report for SalesLT schema in AdventureWorksLT database
KYD (Know your data) SSRS report using above T-SQL script output as dataset
KYD SSRS reports are created using above data profiling stored procedure's output as dataset. Below four reports are interlinked using table name and created as drill-through reports: ColumnDataProfiling -> ColumnUniqueValues -> TableStats -> TableColumnMetadata
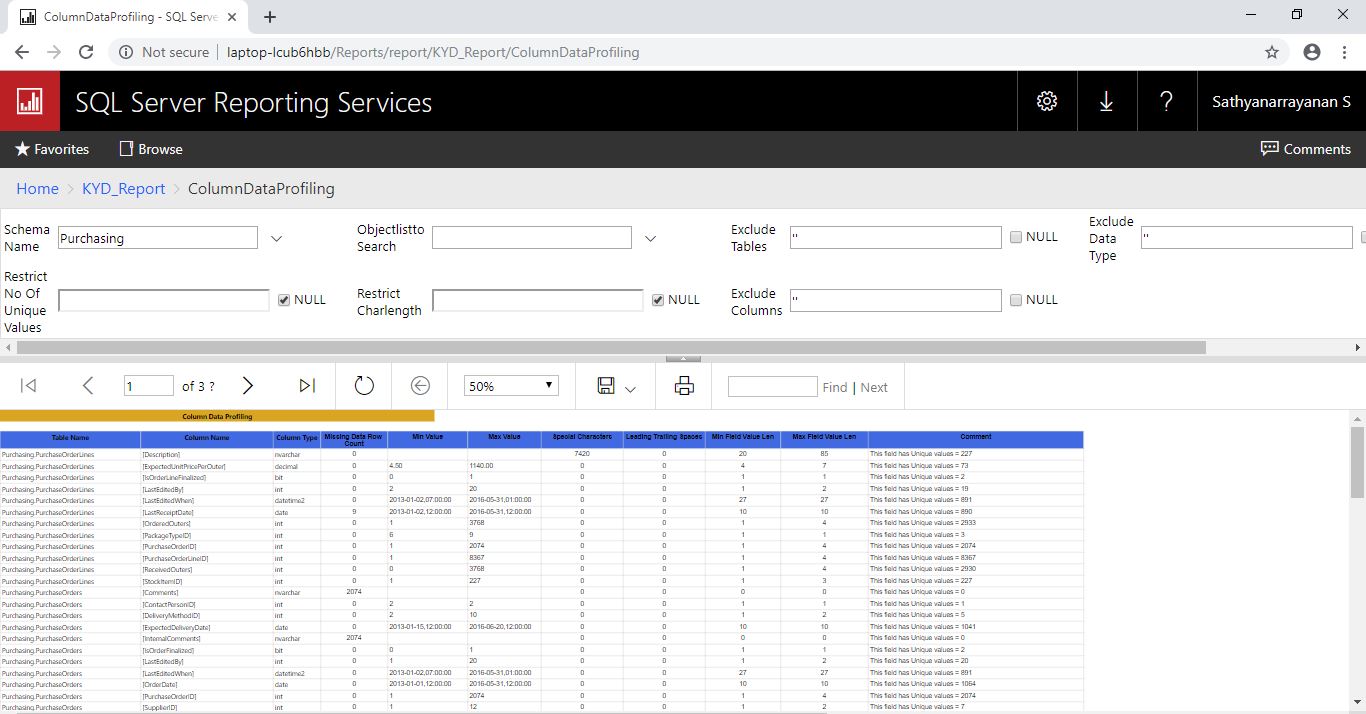
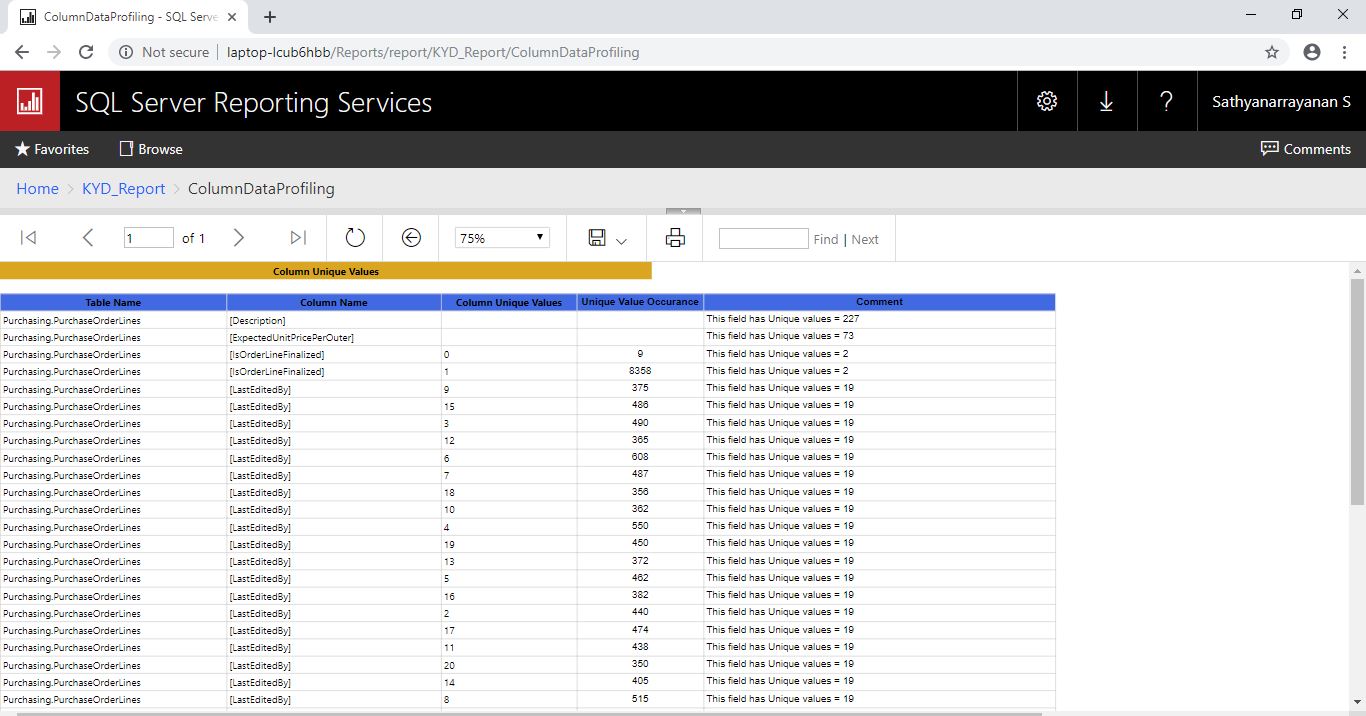
Below screenshot shows the ColumnDataProfiling report output for "Purchasing" schema from WideWorldImporters database
Below screenshot shows the ColumnUniqueValues report output after clicking on Purchasing.PurchaseOrderLines table name in previous report
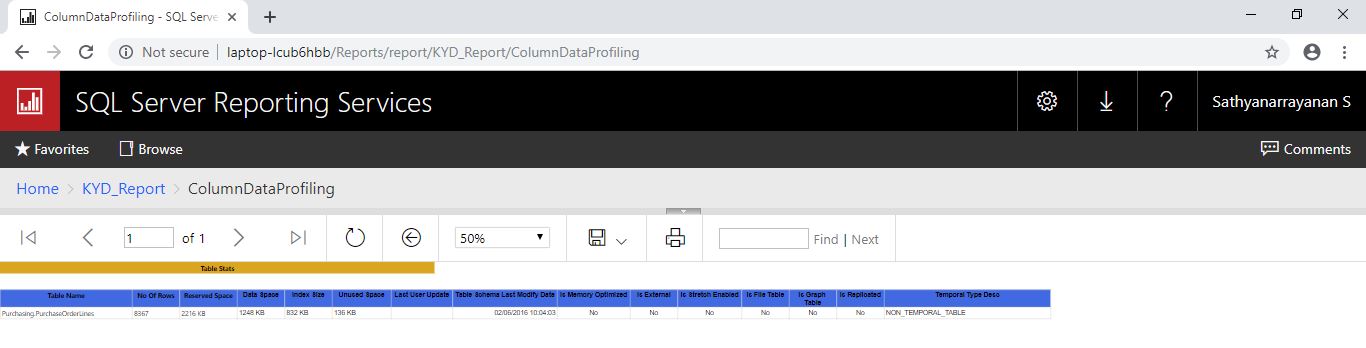
Below screenshot shows the TableStats report output after clicking on Purchasing.PurchaseOrderLines table name in previous report
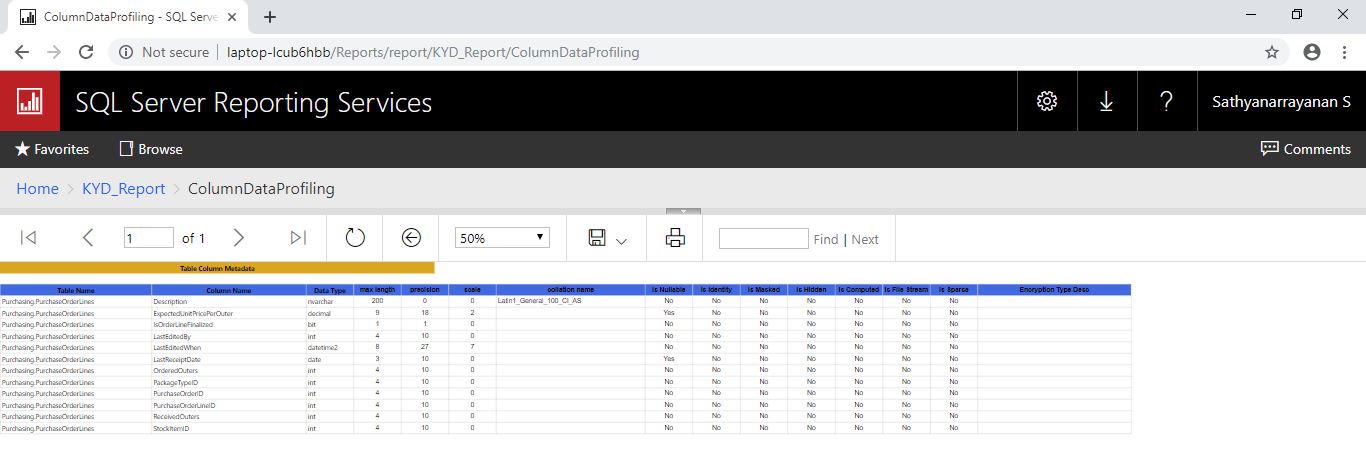
Below screenshot shows the TableColumnMetadata report output after clicking on Purchasing.PurchaseOrderLines table name in previous report
Version details of above solution
Above mentioned t-sql scripts and ssrs reports are developed and tested under below environments:
1) Azure SQL Database (paas) - Compatibility level - SQL Server 2017(140) with sample database AdventureWorksLT
2) On-premise SQL Server 2019 with sample database WideWorldImporters
3) SSRS reports built using Microsoft SQL Server Data Tools (Build number - 14.0.61705.170) for Visual studio 2015 and hosted to SQL Server reporting services 2017
Below are some of the key functions and system objects used to build the above solution:
IIF - Returns one of two values, depending on whether the Boolean expression evaluates to true or false in SQL Server (starting with 2012 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
COUNT_BIG - COUNT_BIG operates like the COUNT function. COUNT_BIG always returns a bigint data type value (starting with 2008 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
CONCAT - This function returns a string resulting from the concatenation, or joining, of two or more string values in an end-to-end manner (starting with 2012 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
STRING_SPLIT - A table-valued function that splits a string into rows of substrings, based on a specified separator character (starting with 2016 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
QUOTENAME - Returns a Unicode string with the delimiters added to make the input string a valid SQL Server delimited identifier (starting with 2008 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
FORMAT - FORMAT function for locale-aware formatting of date/time and number values as strings (starting with 2012 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
ISNUMERIC - Determines whether an expression is a valid numeric type (starting with 2008 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
CREATE OR ALTER - CREATE [OR ALTER]. This statement combines CREATE and ALTER statements and creates object if it does not exist, or alter it if it is already there (starting with 2016 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
DROP IF EXISTS - New syntax for conditional DROP statements (starting with 2016 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
sp_spaceused - Displays the number of rows, disk space reserved, and disk space used by a table, indexed view, or Service Broker queue in the current database, or displays the disk space reserved and used by the whole database
(starting with 2012 & supported in Azure SQL Database).
In addition to these, some of the columns used to fetch metadata information from sys.tables & columns system catalog views are version specific.
We can upgrade or downgrade the above solution to SQL Server versions atleast 2008 or greater than that by tweaking the above functions using alternative approach / script to perform the same operation
Summary
For any user (data scientist, analyst or developer), data profiling helps to identify the issues with data at an early stage and rectify the low quality data where possible / necessary. More we know about our data, lesser the risk of failure. We can also download stored procedures, sample execution script and ssrs report mentioned in this post from TechNet gallery repository.
See Also
- /en-us/azure/data-catalog/data-catalog-get-started
- https://social.technet.microsoft.com/wiki/contents/articles/52793.t-sql-search-for-string-or-phrase-in-sql-server-database.aspx