VB.NET Fluent Builder Design Pattern
Introduction
The Builder design pattern is a creational design pattern and can be used to create complex objects step by step.
Supposing we have an object with many dependencies and need to acquire each one of these dependencies, certain actions must be issued. In such cases, we can use the Builder pattern in order to:
- Encapsulate, create, and assemble the parts of a complex object in a separate Builder object.
- Delegate the object creation to a Builder object instead of creating the objects directly.
To summarize, by using the Builder design pattern, we were able to create a complex object and its complex parts.
Another thing that is great about builder design pattern is they promote breaking about methods that may have more than three arguments as a best practice for methods for working with business operations is less than three arguments. Still, some objects might have more than 3 attributes or properties and you usually need some way to initialize them via the constructor. Some attribute might not be mandatory, therefore on some occasions, you can get by with a few overloads adding more parameters as needed.
Description
Before looking at writing a builder pattern here are advantages and disadvantages - as mentioned by [Rohid Ayd]:
Advantages of Builder Design Pattern
- The parameters to the constructor are reduced and are provided in highly readable method calls.
- Builder design pattern also helps in minimizing the number of parameters in the constructor and thus there is no need to pass in null for optional parameters to the constructor.
- The object is always instantiated in a complete state
- Immutable objects can be built without much complex logic in the object building process.
Moving through this article, all examples are shown in Windows desktop code but can also be used in web solutions also.
Disadvantages of Builder Design Pattern
- The number of lines of code increases at least to double in builder pattern, but the effort pays off in terms of design flexibility and much more readable code.
- Requires creating a separate ConcreteBuilder for each different type of class item.
Examples
Simple fast food
Easy to understand example, ordering a burger at a fast food place. Imagine you have a choice to add or not have cheese, Pepperoni, Lettuce or Tomato.
A conventional method to create the burger is with a new constructor e.g.
public Burger(size, cheese = True, pepperoni = True, tomato = False, lettuce = True)
This is what's called a telescoping constructor anti-pattern, as stated above a method should when humanly possible not have many arguments as it makes things difficult to understand.
A cleaner solution is to use a builder e.g.
Imports BaseLibrary.BaseClasses
Namespace Builders
Public Class BurgerBuilder
Public ReadOnly Property Size() As Integer
Private mCheese As Boolean
Public Property Cheese() As Boolean
Get
Return mCheese
End Get
Private Set(ByVal value As Boolean)
mCheese = value
End Set
End Property
Private mPepperoni As Boolean
Public Property Pepperoni() As Boolean
Get
Return mPepperoni
End Get
Private Set(ByVal value As Boolean)
mPepperoni = value
End Set
End Property
Private mLettuce As Boolean
Public Property Lettuce() As Boolean
Get
Return mLettuce
End Get
Private Set(ByVal value As Boolean)
mLettuce = value
End Set
End Property
Private mTomato As Boolean
Public Property Tomato() As Boolean
Get
Return mTomato
End Get
Private Set(ByVal value As Boolean)
mTomato = value
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(ByVal size As Integer)
Me.Size = size
End Sub
Public Function AddPepperoni() As BurgerBuilder
Pepperoni = True
Return Me
End Function
Public Function AddLettuce() As BurgerBuilder
Lettuce = True
Return Me
End Function
Public Function AddCheese() As BurgerBuilder
Cheese = True
Return Me
End Function
Public Function AddTomato() As BurgerBuilder
Tomato = True
Return Me
End Function
Public Function Build() As Burger
Return New Burger(Me)
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Then we have the burger class which uses the builder class above.
Namespace BaseClasses
Public Class Burger
Public ReadOnly Property Size() As Integer
Public ReadOnly Property Cheese() As Boolean
Public ReadOnly Property Pepperoni() As Boolean
Public ReadOnly Property Lettuce() As Boolean
Public ReadOnly Property Tomato() As Boolean
Public Sub New(builder As BurgerBuilder)
Size = builder.Size
Cheese = builder.Cheese
Pepperoni = builder.Pepperoni
Lettuce = builder.Lettuce
Tomato = builder.Tomato
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
To construct the burger using the builder class.
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim burger = (New BurgerBuilder(14)).
AddPepperoni().
AddLettuce().
AddTomato().
Build()
End Sub
End Module
This is easier to understand and worth those extra lines of code than using a multi-argument constructor.
Email example
A good example for working with a builder pattern is sending email messages where there are many parts to properly construct an email message and can become very complex and hard to maintain later on plus in today’s world more time than not a tester have eye’s on the code who may not fully understand code that is shown that follows.
Namespace Classes
Module SimpleMailOperations
Public Sub Demo1()
Dim mail As New MailMessage()
mail.From = New MailAddress("jane@comcast.net")
mail.To.Add("bill@comcast.net")
mail.Subject = "This is an email"
Dim plainMessage As AlternateView =
AlternateView.CreateAlternateViewFromString(
"Hello, plain text", Nothing, "text/plain")
Dim htmlMessage As AlternateView =
AlternateView.CreateAlternateViewFromString(
"This is an automated email, please do not respond<br><br>An exception " &
"ocurred in <br><span style=""font-weight: bold; padding-left: 20px;" &
"padding-right:5px"">Application name</span>MyApp<br>" &
"<span style=""font-weight: bold; " &
" padding-left: 5px;padding-right:5px"">Application Version</span>" &
"1.00<br><span style=""font-weight: bold; padding-left: " &
"70px;padding-right:5px"">", Nothing, "text/html")
mail.AlternateViews.Add(plainMessage)
mail.AlternateViews.Add(htmlMessage)
Dim smtp As New SmtpClient("smtp.comcast.net")
smtp.Send(mail)
End Sub
End Module
End Namespace
Considering that the code sample just presented there are various parts that can be improved upon even without a builder pattern which leads into an example of a builder pattern for sending email messages.
Dim mailer As New MailBuilder()
mailer.CreateMail(GmailConfiguration1).
WithRecipient("karen@comcast.net").
WithCarbonCopy("mary@gmail.com").
WithSubject("Test").
AsRichContent().
WithHtmlView("<p>Hello <strong>Bob</strong></p>").
WithPickupFolder().
WithTimeout(2000).
SendMessage()
The MailBuilder class provides spoken work methods easy to read and understand rather than, for some difficult to read the code. Each method in the MailBuilder class returns an instance of itself which is known as chaining.
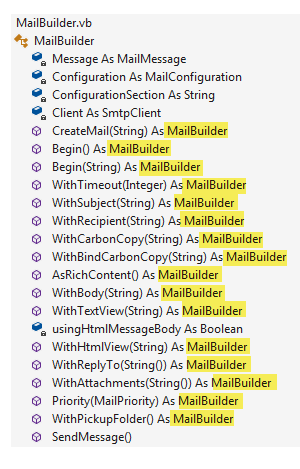
Going back to hiding complexity, the first part of the chain handles configuring the client which is the transport for sending an email message.
Public Function CreateMail(pConfiguration As String) As MailBuilder
Configuration = New MailConfiguration(pConfiguration)
ConfigurationSection = pConfiguration
Client = New SmtpClient(Configuration.Host, Configuration.Port) With {
.Credentials = New NetworkCredential(Configuration.UserName, Configuration.Password),
.EnableSsl = True,
.Timeout = Configuration.TimeOut
}
Message = New MailMessage() With
{
.From = New MailAddress(Configuration.FromAddress),
.IsBodyHtml = False
}
Return Me
End Function
Which in turn creates an instance of MailConfiguration responsible for reading setting from an application's configuration file (see example).
.
Back to the example above, WithRecipient and WithCarbonCopy, both add to MailMessage where both methods below permit multiple entries no different when sending email through an email application such as Microsoft Outlook.
Public Function WithRecipient(pSender As String) As MailBuilder
Message.To.Add(pSender)
Return Me
End Function
Public Function WithCarbonCopy(pSender As String) As MailBuilder
Message.CC.Add(pSender)
Return Me
End Function
Once all desired parts are set the method SendMessage is called which uses values presented to compose and send an email message.
To run test see the following code sample. Note in this code sample email message are sent to a folder below the application folder which is done via a post-build event setup in project properties.
Working with databases
Reading
Another use for the builder pattern is any operation typically performed with database operations. In this section reading, data and updating will be explored using the builder pattern. What is not shown is adding and removal of records yet they can also use the builder pattern from first working with the code examples below.
What the builder pattern will provide, the ability to read all data from joined tables returning all records, an example for filtering by country. Since when there is a chance for editing primary keys are needed but not to be displayed so there are chain methods to indicate to show or hide primary keys. Also is an ORDER BY is needed, which column and ASC DESC order. These can be expanded upon, the entire idea here is to open a developer's mind to possibilities.
To read all customer data, order by the last name in descending order not showing any primary keys and first setting the return data to a BindingSource component which becomes the data source of a DataGridView the following pattern handles this, the same chaining of methods as done with the prior section for sending email messages.
Public Class Form1
Private Sub Form1_Shown(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Shown
Dim initialOrderByFieldName = "LastName"
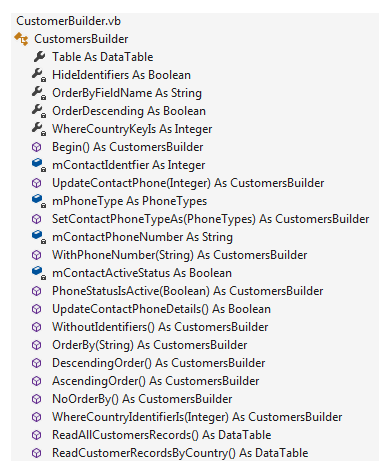
Dim customerReader = New CustomersBuilder
bindingSourceCustomers.DataSource = customerReader.
Begin().
OrderBy("LastName").
DescendingOrder.
WithoutIdentifiers().
ReadAllCustomersRecords()
DataGridView1.DataSource = bindingSourceCustomers
Suppose customers want to control sorting and order of a sort, present them with controls such as ComboBox and CheckBox controls with a button to perform the sort.
Sample builder pattern, in this case done in sections rather than in a continuous chain.
Private Sub readCustomersButton_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs)
bindingSourceCustomers.DataSource = Nothing
Dim customerReader = New CustomersBuilder
customerReader.Begin()
customerReader.OrderBy(columnNamesComboBox.Text)
If decendingOrderCheckBox.Checked Then
customerReader.DescendingOrder()
Else
customerReader.AscendingOrder()
End If
bindingSourceCustomers.DataSource = customerReader.ReadAllCustomersRecords()
DataGridView1.DataSource = bindingSourceCustomers
DataGridView1.ExpandAllColumns
DataGridView1.NormalizeColumnHeaders()
End Sub
Another possibility is to only show records meeting a condition, in this case by country using a ComboBox to select from.
Private Sub readCustomersByCountryButton_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles readCustomersByCountryButton.Click
bindingSourceCustomers.DataSource = Nothing
Dim customerReader = New CustomersBuilder
bindingSourceCustomers.DataSource = customerReader.
Begin().
NoOrderBy.
WhereCountryIdentifierIs(CType(countriesComboBox.SelectedItem, Country).Identifier).
ReadCustomerRecordsByCountry()
DataGridView1.DataSource = bindingSourceCustomers
DataGridView1.ExpandAllColumns
DataGridView1.NormalizeColumnHeaders()
End Sub
Updating
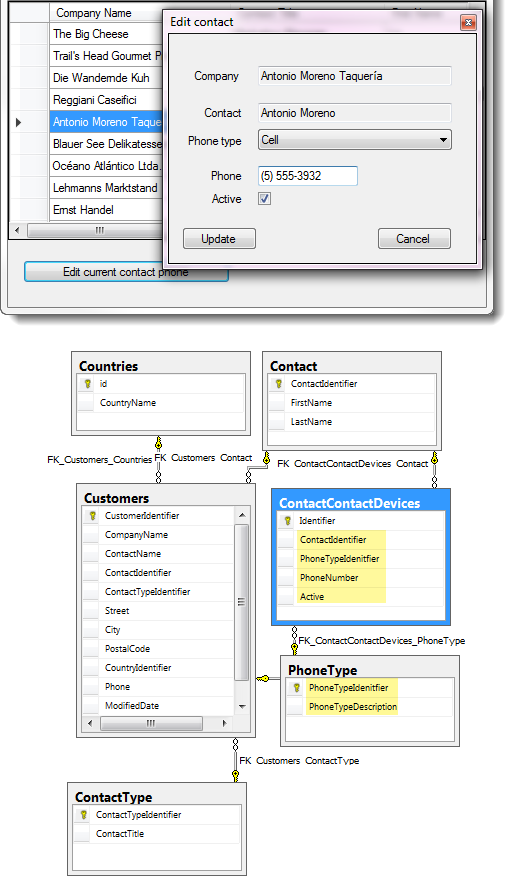
Using the same builder class other operations can be performed. In the following section, the builder class will be used to update a contact phone information where there are several tables which are required to first percent data then to edit data. The importance of knowing back end data structure is that this adds to the complexity and by using a builder fluent pattern although there is a little more code then without chaining via the builder pattern later down the road the code is easier to read and maintain.
First, the CustomersBuilder is created followed by specifying which contact to update, the phone type (Office, Cell, Home), the status and finally to perform the update operation.
Dim customerReader = New CustomersBuilder
Dim result = customerReader.
Begin().
UpdateContactPhone(contact.Id).
SetContactPhoneTypeAs(contact.PhoneType).
WithPhoneNumber(contact.PhoneNumber).
PhoneStatusIsActive(contact.Active).
UpdateContactPhoneDetails()
If Not result Then
MessageBox.Show($"Failed to update contact for {companyName}")
End If
Once UpdateContactPhoneDetails is called the code path moves to a data class which takes one argument of type Contact. The method to update is shown below, a method which can also be called without using the CustomersBuilder class.
Public Function UpdatePhone(contact As Contact, Optional showCommand As Boolean = False) As Boolean
Dim updateStatement As String =
"UPDATE dbo.ContactContactDevices " &
"SET " &
"PhoneTypeIdenitfier = @PhoneTypeIdenitfier, " &
"PhoneNumber = @PhoneNumber ," &
"Active = @Active " &
"WHERE ContactIdentifier = @ContactIdentifier"
Using cn As New SqlConnection With {.ConnectionString = ConnectionString}
Using cmd As New SqlCommand With {.Connection = cn, .CommandText = updateStatement}
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@PhoneTypeIdenitfier", contact.PhoneTypeIdenitfier)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@PhoneNumber", contact.PhoneNumber)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Active", contact.Active)
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@ContactIdentifier", contact.Id)
If showCommand Then
Console.WriteLine(cmd.ActualCommandText())
End If
Try
cn.Open()
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery()
Catch ex As Exception
mHasException = True
mLastException = ex
End Try
End Using
End Using
Return IsSuccessFul
End Function
By using a builder pattern coupled with a data class everything is segmented, allows a developer to use or forgo the builder class. If the update method existed prior to the builder class this means the developer did a good job of writing the update method, one argument and using a base class for exception handling.
Misc/Reports
Another use for a builder is for creating reports that for printing or simply displaying in the user interface. To keep it simple the report will be on products.
The product class
Namespace ProductBuilderClasses
Public Class Product
Public Property Name() As String
Public Property Price() As Double
End Class
End Namespace
The first step is to define a class for the report. This is the object, we are going to build with the Builder design pattern.
Namespace ProductBuilderClasses
Public Class ProductStockReport
Public Property HeaderPart() As String
Public Property BodyPart() As String
Public Property FooterPart() As String
Public Overrides Function ToString() As String
Return New StringBuilder().
AppendLine(HeaderPart).
AppendLine(BodyPart).
AppendLine(FooterPart).
ToString()
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Now we need a builder interface to organize the building process:
Namespace Interfaces
Public Interface IProductStockReportBuilder
Function BuildHeader() As IProductStockReportBuilder
Function BuildBody() As IProductStockReportBuilder
Function BuildFooter() As IProductStockReportBuilder
Function GetReport() As ProductStockReport
End Interface
End Namespace
Here is the concrete builder class which is going to implement this interface, needs to create all the parts for our stock report object and return that object as well. So, let’s implement our concrete builder class:
Namespace ProductBuilderClasses
Public Class ProductStockReportBuilder
Implements IProductStockReportBuilder
Private productStockReport As ProductStockReport
Private products As IEnumerable(Of Product)
Public Sub New(products As IEnumerable(Of Product))
Me.products = products
productStockReport = New ProductStockReport()
End Sub
Private Function BuildHeader() As IProductStockReportBuilder _
Implements IProductStockReportBuilder.BuildHeader
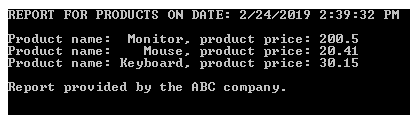
productStockReport.
HeaderPart = $"REPORT FOR PRODUCTS ON DATE: {Date.Now}{Environment.NewLine}"
Return Me
End Function
Private Function BuildBody() As IProductStockReportBuilder _
Implements IProductStockReportBuilder.BuildBody
productStockReport.BodyPart = String.Join(
Environment.NewLine,
products.Select(Function(p) $"Product name: {p.Name,8}, product price: {p.Price}"))
Return Me
End Function
Private Function BuildFooter() As IProductStockReportBuilder _
Implements IProductStockReportBuilder.BuildFooter
productStockReport.FooterPart = vbLf & "Report provided by the ABC company."
Return Me
End Function
Public Function GetReport() As ProductStockReport _
Implements IProductStockReportBuilder.GetReport
Dim productStockReport = Me.productStockReport
Clear()
Return productStockReport
End Function
Private Sub Clear()
productStockReport = New ProductStockReport()
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Now it's time to build the object.
Namespace ProductBuilderClasses
Public Class ProductBuilderDemo
Public Sub New()
Dim products = New List(Of Product) From
{
New Product With {.Name = "Monitor", .Price = 200.5},
New Product With {.Name = "Mouse", .Price = 20.41},
New Product With {.Name = "Keyboard", .Price = 30.15}
}
Dim builder = New ProductStockReportBuilder(products)
Dim director = New ProductStockReportDirector(builder)
director.BuildStockReport()
Dim report = builder.GetReport()
'
' Display to the console
'
Console.WriteLine(report)
End Sub
End Class
End Namespace
Test, in this case, is done in a console application.
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim demo As New ProductBuilderDemo
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module
Summary
In this article/code sample the Builder pattern has been shown with real-world examples on how the Builder pattern might be applied coupled with advantages and disadvantages of the pattern. Having options such as this pattern can make code easier to read and maintain.
See also
SQL-Server- C# Find duplicate record with the identity
Builder Pattern C#
Builder Pattern
Builder Pattern
Source code
Although there is an attached Visual Studio 2017 solution there is also the same code on a GitHub repository which over time may get updated while not always in this code sample.