DataGridView setup header text using SQL-Server
Introduction
A common method for setting header text property of a DataGridView is done one of two ways when not working with TableAdapter method to populate a DataGridView. The first is to assign the DataSource of the DataGridView to a DataTable or a List then use something like a dictionary where the key is the underlying field name and the value is the header text, iterate the dictionary to assign header text. The second method is to create columns for the DataGridView in the designer, assign header text and a field to the DataPropery.
This article examines an alternate method for providing header text to column in a DataGridView using a single property for a column in a table within a SQL-Server database.
Implementation
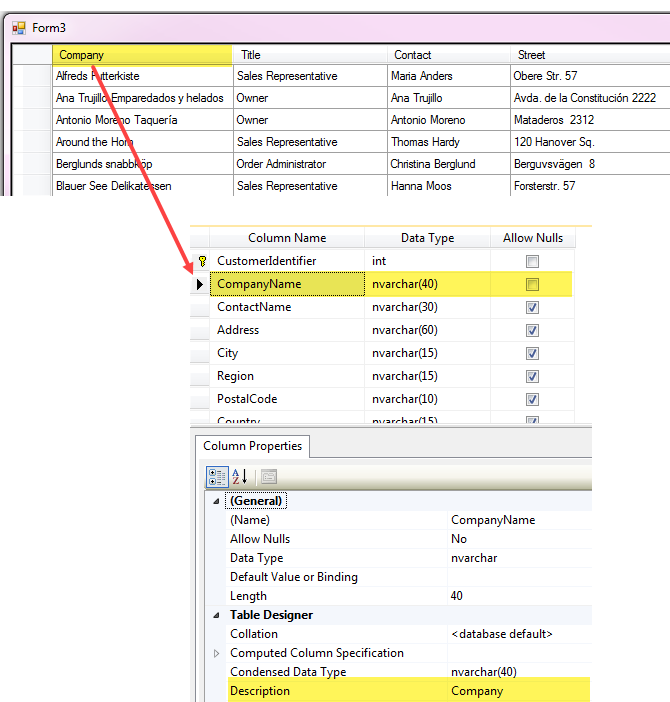
- Open SSMS (SQL-Server Management Studio), select the database, select the table.
- In the Object Explorer right click on the table and select design.
- Select a column.
- Select the property Description and enter a title for what should be seen in a DataGridView. Do not set this property for columns which will not be displayed such as primary or foreign key columns.
- Save your changes.
The next step will be to query the descriptions for the table above. THe proper method to write this query is in SSMS as shown below. In the query below a parameter is used so not to hard code the table name. In our code this translates to a parameter for the SqlClientCommand.
DECLARE @TableName NVARCHAR(50) = 'Customers';
SELECT COLUMN_NAME AS ColumnName ,
ORDINAL_POSITION AS Position ,
prop.value AS [Description]
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES AS tbl
INNER JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS AS col ON col.TABLE_NAME = tbl.TABLE_NAME
INNER JOIN sys.columns AS sc ON sc.object_id = OBJECT_ID(tbl.TABLE_SCHEMA
+ '.'
+ tbl.TABLE_NAME)
AND sc.name = col.COLUMN_NAME
LEFT JOIN sys.extended_properties prop ON prop.major_id = sc.object_id
AND prop.minor_id = sc.column_id
AND prop.name = 'MS_Description'
WHERE tbl.TABLE_NAME = @TableName AND prop.value IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY col.ORDINAL_POSITION
To translate this to VB.NET a return type is needed as per below where Name property is the name of the column, Ordinal is the ordinal position in the physical table, Description if the description set in SQL-Server table/column and Visible is read only property which if there is no description this will be used to hide a column in a DataGridView.
Public Class DataColumn
''' <summary>
''' Name of column
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Name() As String
''' <summary>
''' Ordinal position of column
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Property Ordinal() As Integer
''' <summary>
''' Description of column
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks>
''' May be NULL
''' </remarks>
Public Property Description() As String
''' <summary>
''' Determines if this column should be visible in the user interface.
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public ReadOnly Property Visible() As Boolean
Get
Return Description IsNot Nothing
End Get
End Property
End Class
Using the SQL presented above here is how it's implemented, pass in an existing table name and return a list of DataColumn.
Public Function ColumnDetails(pTableName As String) As List(Of DataColumn)
mHasException = False
Dim columnData = New List(Of DataColumn)
Dim selectStatement =
"SELECT COLUMN_NAME AS ColumnName, ORDINAL_POSITION AS Postion,prop.value AS [Description] " &
"FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES AS tbl " &
"INNER JOIN INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS AS col ON col.TABLE_NAME = tbl.TABLE_NAME " &
"INNER JOIN sys.columns AS sc ON sc.object_id = OBJECT_ID(tbl.TABLE_SCHEMA + '.' + tbl.TABLE_NAME) AND sc.name = col.COLUMN_NAME " &
"LEFT JOIN sys.extended_properties prop ON prop.major_id = sc.object_id AND prop.minor_id = sc.column_id AND prop.name = 'MS_Description' " &
"WHERE tbl.TABLE_NAME = @TableName " &
"ORDER BY col.ORDINAL_POSITION"
Try
Using cn As New SqlConnection With {.ConnectionString = ConnectionString}
Using cmd As New SqlCommand With {.Connection = cn}
cmd.CommandText = selectStatement
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@TableName", pTableName)
cn.Open()
Dim reader = cmd.ExecuteReader()
While reader.Read()
columnData.Add(New DataColumn() With {.Name = reader.GetString(0), .Ordinal = reader.GetInt32(1), .Description = reader.GetStringSafe("Description")})
End While
End Using
End Using
Catch ex As Exception
mHasException = True
mLastException = ex
End Try
Return columnData
End Function
Once the above method is called a call to return data as shown below where in this case it's a customer table.
Public Function GetCustomers() As DataTable
mHasException = False
Dim dtCustomers = New DataTable
Dim selectStatement = "SELECT CustomerIdentifier, CompanyName, ContactName ,Address," &
"City,Region,PostalCode,Country,Phone,Fax,ContactTypeIdentifier,ModifiedDate " &
"FROM dbo.Customers"
Try
Using cn As New SqlConnection With {.ConnectionString = ConnectionString}
Using cmd As New SqlCommand With {.Connection = cn}
cmd.CommandText = selectStatement
cn.Open()
dtCustomers.Load(cmd.ExecuteReader())
End Using
End Using
Catch ex As Exception
mHasException = True
mLastException = ex
End Try
Return dtCustomers
End Function
Pulling this together, a DataGridView is placed on a form at design time, no properties are set. In form shown event load the DataTable, in this case from GetCustomers then iterate the column descriptions to set column header text and for columns in the List(Of DataColumn) which the Visible property is false hide those columns in the DataGridView. The code in the sole button permits accessing the primary key in tangent with the company name so it can be validated e.g. with SSMS open visually inspect the record.
Public Class Form1
Private ReadOnly _bsCustomers As New BindingSource
Private ReadOnly _operations As DataOperations = New DataOperations
''' <summary>
''' - Populate a DataGridView with a single table.
''' - Set header text using information returned from parsing each columns description property
''' * Note in this code there is zero check for if the column exists in the DataGridView while
''' in form3 a check is done to see if the column exists in the underlying DataTable.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub Form1_Shown(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Shown
' get customer data into DataTable
_bsCustomers.DataSource = _operations.GetCustomers()
DataGridView1.DataSource = _bsCustomers
' get column details for customers table
Dim results = _operations.ColumnDetails("Customers")
If _operations.IsSuccessFul Then
' set column header text and hide column with no description
For Each dataColumn As DataColumn In results
If dataColumn.Visible Then
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).HeaderText = dataColumn.Description
Else
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).Visible = False
End If
Next
DataGridView1.ExpandColumns
Else
MessageBox.Show(_operations.LastExceptionMessage)
End If
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Show ability to get hidden and visible field values
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub cmdCurrentRow_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles cmdCurrentRow.Click
'
' Cast Current property to a DataRow which provides access to properties of current row
' in the DataGridView.
'
If _bsCustomers.Current IsNot Nothing Then
Dim row = CType(_bsCustomers.Current, DataRowView).Row
MessageBox.Show($"Primary key: {row.Field(Of Integer)("CustomerIdentifier")} Company: {row.Field(Of String)("CompanyName")}")
End If
End Sub
End Class
If you decided to place a DataGridView on a form, in the DataGridView designer add columns and set the DataProperty and do nothing else with a slight modification to the latter code the header text can be set.
For each column in the DataGridView prefix the column name with col (or your choice of a prefix) followed by the field name. For example, for the field CustomerIdentifier the DataGridView column name would be colCustomerIdentifier. In the For-Each add the prefix as shown below, the rest of the code remains as is from the code block above.
For Each dataColumn As DataColumn In results
If dataColumn.Visible Then
DataGridView1.Columns($"col{dataColumn.Name}").HeaderText = dataColumn.Description
Else
DataGridView1.Columns($"col{dataColumn.Name}").Visible = False
End If
Next
Caveats
In the above examples all columns were used and matched againsts the List(Of DataColumn), most likely this is not always the case, suppose one or two fields are left out and the above logic is used, what will happen? A runtime exception will be thrown as there is no assertion to determine if a column in the DataGridView exists.
To circumvent this a check is needed to assert a column in the List(Of DataColumn) exists in the DataGridView. In the following example an assertion is performed to determine if a column exists in the DataGridView from in the List(Of DataColumn).
For Each dataColumn As DataColumn In customerResults
If DataGridView1.Columns.Contains(dataColumn.Name) Then
If dataColumn.Visible Then
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).HeaderText = dataColumn.Description
Else
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).Visible = False
End If
End If
Next
The next thing to consider is joining one or more tables to the primary table. In this case there are two tables, Customers and ContactType.
Public Function GetCustomersAndContactTypes() As DataTable
mHasException = False
Dim dtCustomers = New DataTable
Dim selectStatement = "SELECT C.CustomerIdentifier , C.CompanyName , CT.ContactTitle , C.ContactName , C.[Address] , " &
"C.City , C.Region , C.PostalCode , C.Country , C.ContactTypeIdentifier , C.ModifiedDate " &
"FROM Customers AS C " &
"INNER JOIN ContactType AS CT ON C.ContactTypeIdentifier = CT.ContactTypeIdentifier; "
Try
Using cn As New SqlConnection With {.ConnectionString = ConnectionString}
Using cmd As New SqlCommand With {.Connection = cn}
cmd.CommandText = selectStatement
cn.Open()
dtCustomers.Load(cmd.ExecuteReader())
End Using
End Using
Catch ex As Exception
mHasException = True
mLastException = ex
End Try
Return dtCustomers
End Function
The solution is to get column details for both tables and iterate them as done with a single table as shown below.
' get customer data into DataTable
_bsCustomers.DataSource = _operations.GetCustomersAndContactTypes()
DataGridView1.DataSource = _bsCustomers
' get column details for customers table
Dim customerResults = _operations.ColumnDetails("Customers")
Dim contactResults = _operations.ColumnDetails("ContactType")
If _operations.IsSuccessFul Then
' set column header text and hide column with no description
For Each dataColumn As DataColumn In customerResults
If DataGridView1.Columns.Contains(dataColumn.Name) Then
If dataColumn.Visible Then
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).HeaderText = dataColumn.Description
Else
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).Visible = False
End If
End If
Next
For Each dataColumn As DataColumn In contactResults
If DataGridView1.Columns.Contains(dataColumn.Name) Then
If dataColumn.Visible Then
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).HeaderText = dataColumn.Description
Else
DataGridView1.Columns(dataColumn.Name).Visible = False
End If
End If
Next
DataGridView1.ExpandColumns
Else
MessageBox.Show(_operations.LastExceptionMessage)
End If
Summary
What has been presented, a property of a column in a SQL-Server database table that if not used for other purposes allows header text to be set from the database. The downside is this is that the property is being used for something it was not intended for. Doing so means if you decide to document columns to create reports you can’t do so. This means the methods presented will not work for everyone yet if you never intend to document columns this is an alternate to setting header text and be consistent on all applications that use these tables setup via the Description property.
Running the code samples
There is one class project for data operations and a Windows Form project. The Windows form project has three forms where Form3 is set as default. Form3 has all the proper assertions while Form1 and Form2 do not. Form2 difference from Form1 in that Form1 has no predefined columns in the DataGridView while Form2 does have predefined columns in the DataGridView,
Requires
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 or higher.
- Microsoft SQL-Server, at minimum the Express edition
- SSMS (SQL-Server Management Studio).
- Before running the code samples, execute the SQL script in the class project script.sql to create the database, table and populate the tables.
Source code
https://github.com/karenpayneoregon/DataGridViewColumnHeaderFromSqlServer