Azure Cosmos DB: A Simple Project Using Cosmos DB And Azure App Service
In my previous article, I talk about Azure Cosmos DB. In this post, I will describe in simple steps how you can deploy a web app with an Azure Cosmos DB on the back end.
Prerequisites
- Azure Cosmos DB account with SQL API
- Azure Web App Service
- Visual Studio 2015 or Higher
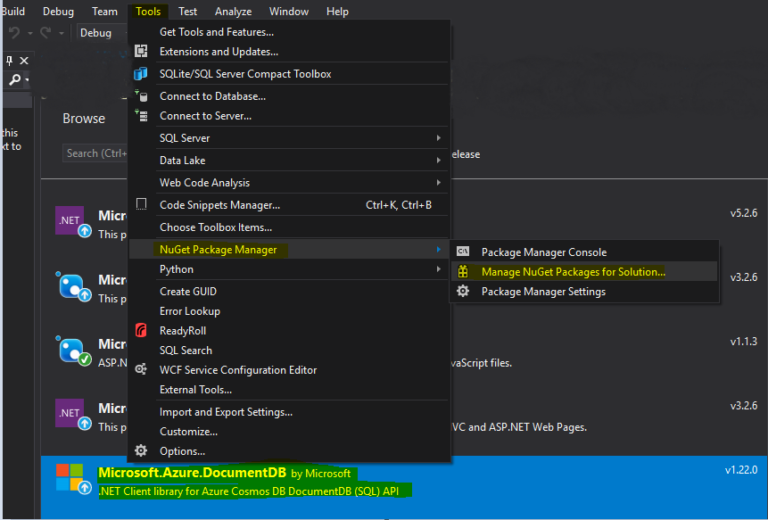
Install Document DB NuGet Package
NuGet is a tool that helps developers to download compiled DLL’s “packages” for their solutions. In the image below, I download the Microsoft.Azure.DocumentDB package which I use it for the demo project.
Web.config Configuration (Connect to Azure Cosmos DB)
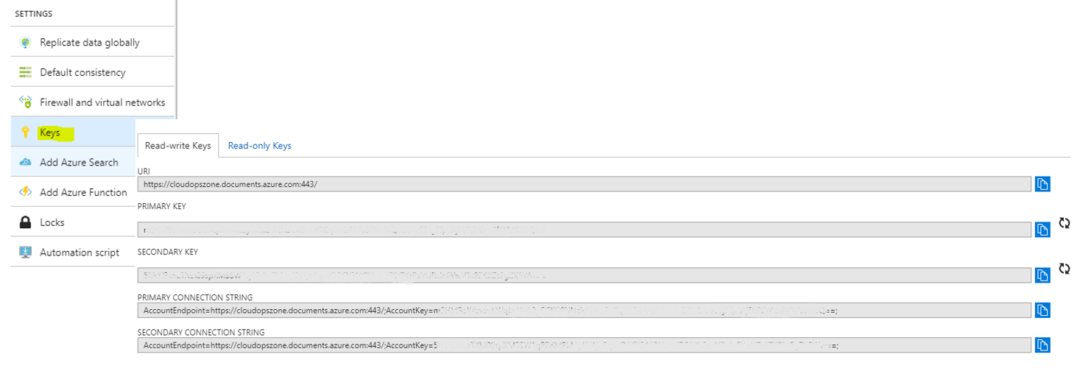
On Solution Explorer, select Web.config and add the following values, endpoint, authKey, database, collection.
<appSettings>
<add key="webpages:Version" value="3.0.0.0" />
<add key="webpages:Enabled" value="false" />
<add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value="true" />
<add key="UnobtrusiveJavaScriptEnabled" value="true" />
<!--Copy the value from the URI field. -->
<add key="endpoint" value="https://cloudopszone.documents.azure.com:443/"/>
<!--Copy the value from PRIMARY OR SECONDARY KEY field. -->
<add key="authKey" value="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"/>
<!--Copy the value from PRIMARY CONNECTION STRING field. -->
<add key="database" value="cloudopszone"/>
<!--Copy the value from PRIMARY CONNECTION STRING field. -->
<add key="collection" value="AdventureWorksData"/>
</appSettings>
Repository Configuration
A repository works intermediary between business access layer and data access layer of the Web application. Below we can see the C# code that I used to create the WebAppCosmosDB.Repository.
namespace WebAppCosmosDB
{
public class MvcApplication : System.Web.HttpApplication
{
protected void Application_Start()
{
AreaRegistration.RegisterAllAreas();
FilterConfig.RegisterGlobalFilters(GlobalFilters.Filters);
RouteConfig.RegisterRoutes(RouteTable.Routes);
BundleConfig.RegisterBundles(BundleTable.Bundles);
CosmosDBRepository<Employee>.Initialize();
}
}
}
namespace WebAppCosmosDB.Repository
{
public class CosmosDBRepository<T> where T : class
{
private static readonly string DatabaseId = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["database"];
private static readonly string CollectionId = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["collection"];
private static DocumentClient client;
public static void Initialize()
{
client = new DocumentClient(new Uri(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["endpoint"]), ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["authKey"]);
CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync().Wait();
CreateCollectionIfNotExistsAsync().Wait();
}
private static async Task CreateDatabaseIfNotExistsAsync()
{
try
{
await client.ReadDatabaseAsync(UriFactory.CreateDatabaseUri(DatabaseId));
}
catch (DocumentClientException e)
{
if (e.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
await client.CreateDatabaseAsync(new Database { Id = DatabaseId });
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
}
private static async Task CreateCollectionIfNotExistsAsync()
{
try
{
await client.ReadDocumentCollectionAsync(UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId));
}
catch (DocumentClientException e)
{
if (e.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound)
{
await client.CreateDocumentCollectionAsync(
UriFactory.CreateDatabaseUri(DatabaseId),
new DocumentCollection { Id = CollectionId },
new RequestOptions { OfferThroughput = 1000 });
}
else
{
throw;
}
}
}
public static async Task<IEnumerable<T>> GetItemsAsync(Expression<Func<T, bool>> predicate)
{
IDocumentQuery<T> query = client.CreateDocumentQuery<T>(
UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId))
.Where(predicate)
.AsDocumentQuery();
List<T> results = new List<T>();
while (query.HasMoreResults)
{
results.AddRange(await query.ExecuteNextAsync<T>());
}
return results;
}
public static async Task<IEnumerable<T>> GetItemsAsync()
{
IDocumentQuery<T> query = client.CreateDocumentQuery<T>(
UriFactory.CreateDocumentCollectionUri(DatabaseId, CollectionId))
.AsDocumentQuery();
List<T> results = new List<T>();
while (query.HasMoreResults)
{
results.AddRange(await query.ExecuteNextAsync<T>());
}
return results;
Controllers Configuration
Controllers, responsibility is to control the way that interacts a user with an MVC App, for example, a user sends a request to a Web App and the controller define the response to send back.
Let’s take a quick look at the controller C# code.
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
// GET: Employee
public async Task<ActionResult> Index()
{
var items = await CosmosDBRepository<Employee>.GetItemsAsync();
return View(items);
Models Configuration
Models are used to represent data from a database to the Web interface on an ASP.Net project. For example, on the C# code below we can see the fields that will project on the Web App.
public class Employee
{
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "BusinessEntityID")]
public string BusinessEntityID { get; set; }
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "Title")]
public string Title { get; set; }
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "FirstName")]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "MiddleName")]
public string MiddleName { get; set; }
[JsonProperty(PropertyName = "LastName")]
public string LastName { get; set; }
Views Configuration
Actually, a View is a page that is used from a Web App. This is not a page that point to a path on a hard disk but is mapped to controller actions.
On the C# code below we can see the View for my example.
@model IEnumerable<WebAppCosmosDB.Models.Employee>
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Index";
Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml";
}
<h2>Index</h2>
<table class="table">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.BusinessEntityID)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Title)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.FirstName)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.MiddleName)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.LastName)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model) {
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.BusinessEntityID)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Title)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.MiddleName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.LastName)
</td>
</tr>
Conclusion
Microsoft continues to be next to Development teams and helps them by providing cloud services like Azure Cosmos DB and App Services. In this post, I tried to show how easy is for someone to sit down and write few lines of C# code and be able to integrate them easily into their projects.
You can easily calculate the cost of these services by using Azure Pricing Calculator.