ASP.NET MVC 5: Code First Migration With Entity Framework And MySQL
Introduction
We know how to use Code First Migration in SQL Server. But in most cases, a customer will think we can use it for the open source database. So that’s the reason we pick the “MySQL” database, and we can follow the same steps we follow in the “SQL” database. In this article, we are going to explain Code First Migration in ASP.NET MVC 5 with Entity FrameWork and MySQL.
Prerequisites
- MySQL Installer
- MySQL Workbench
- Visual Studio ( We are using Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition ).
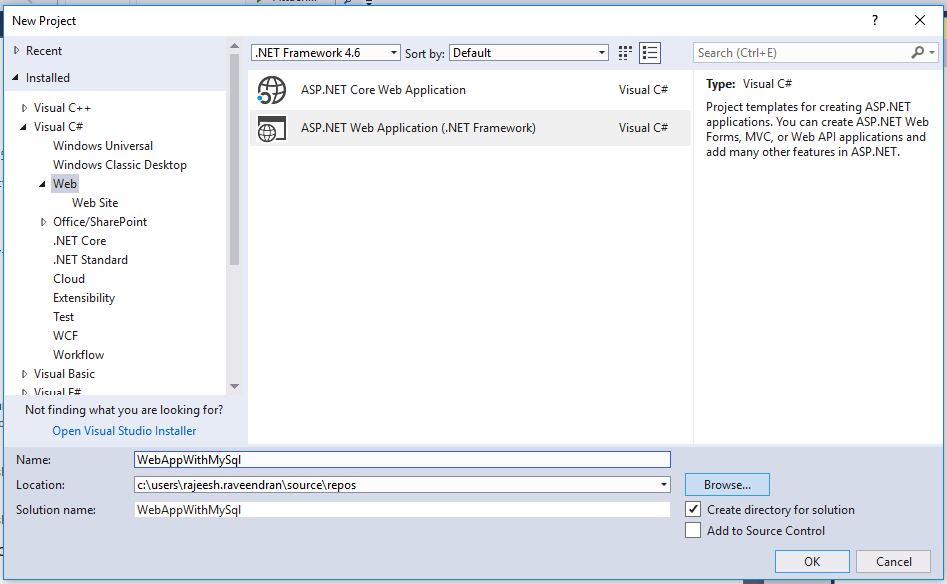
Create a Web Application using MVC 5
Click File -> New -> Project -> Visual C# -> Web -> ASP.Net Web Application ( .NET Framework ).
Click on “OK” then click on “MVC”.
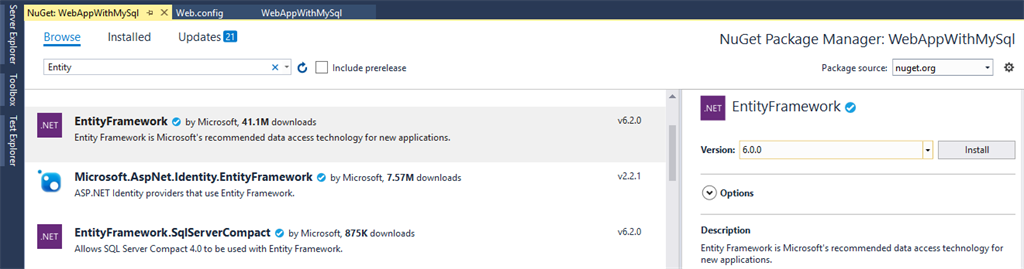
Install Entity Framework & MySQL Entity
Go to Visual Studio “Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Manage Nuget Packages for Solution” or right-click your web application and click “Manage NuGet Packages”.
EntityFramework
Search EntityFramework in the “Browse” Section.
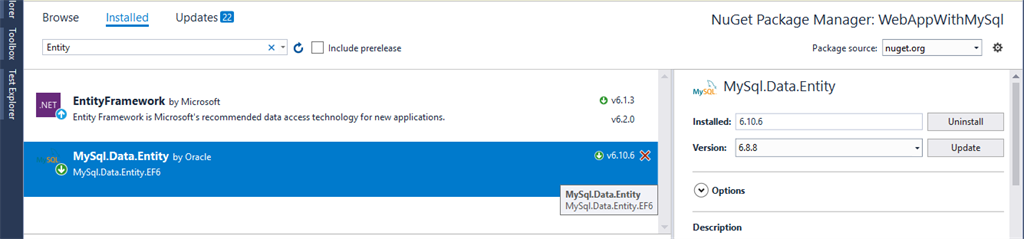
MySql.Data.Entity
Search MySql.Data.Entity in the “Browse” Section.
Once we installed EntityFramework and MySql Entity in our application it will generate a SQL and MySQL Provider inside the EntityFramework Section in Web.Config.
<entityFramework>
<defaultConnectionFactory type="System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.SqlConnectionFactory, EntityFramework" />
<providers>
<provider invariantName="System.Data.SqlClient" type="System.Data.Entity.SqlServer.SqlProviderServices, EntityFramework.SqlServer" />
<provider invariantName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" type="MySql.Data.MySqlClient.MySqlProviderServices, MySql.Data.Entity.EF6, Version=6.8.8.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=c5687fc88969c44d"></provider></providers>
</entityFramework>
Model Class
We just created a sample model class for demo purposes.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web;
namespace WebAppWithMySql.Models
{
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
}
}
Creation of DBContext
Create a dbcontext class in our application. The following dbcontext will point out our connection string in WebConfig.
using MySql.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity;
using WebAppWithMySql.Models;
namespace WebAppWithMySql
{
[DbConfigurationType(typeof(MySqlEFConfiguration))]
public class WebAppContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Student> Products
{
get;
set;
}
public WebAppContext()
//Reference the name of your connection string ( WebAppCon )
: base("WebAppCon") { }
}
}
Connection String
We added the same connection string name that we added in the dbcontext class. The following connection string represents “MySql” Db.
<connectionStrings>
<add name="WebAppCon" providerName="MySql.Data.MySqlClient" connectionString="server=localhost;userid=root;password=;database=WebAppMySql;persistsecurityinfo=True" />
</connectionStrings>
Migration Steps
Go to Visual Studio "Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Package Manager Console". Then execute the following command.
- Enable-Migrations – ( We need to enable the migration, only then can we do the EF Code First Migration ).
- Add-Migration IntialDb (migration name) – ( Add a migration name and run the command ).
- Update-Database -Verbose — if it is successful then we can see this message (Running Seed method).
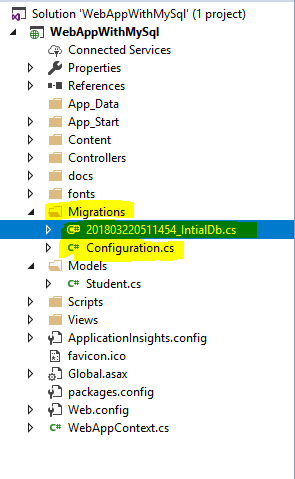
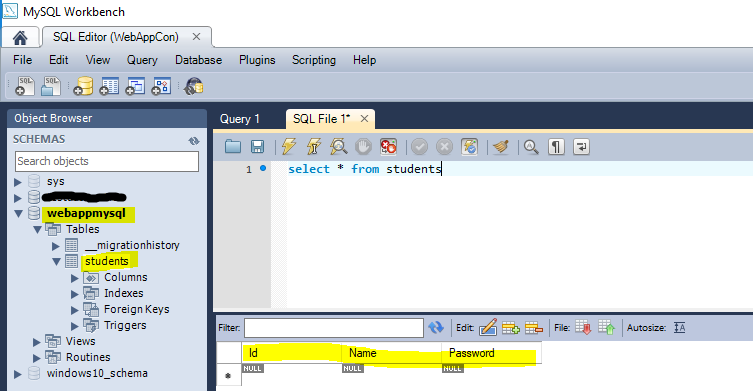
Once Migration is done, we can see that the respective files are auto-generated under the “Migrations” folder.
Output
Reference
Summary
In this article, we explained Code First Migration in ASP.NET MVC 5 with Entity Framework and MySQL. Hope this article is useful for all Azure beginners.
See Also
It's recommended to read more articles related to ASP.NET Core & Azure App Service.
- ASP.NET CORE 1.0: Getting Started
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Project Layout
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Middleware And Static files (Part 1)
- Middleware And Staticfiles In ASP.NET Core 1.0 - Part Two
- ASP.NET Core 1.0 Configuration: Aurelia Single Page Applications
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Create An Aurelia Single Page Application
- Create Rest API Or Web API With ASP.NET Core 1.0
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Adding A Configuration Source File
- Code First Migration - ASP.NET Core MVC With EntityFrameWork Core
- Building ASP.NET Core MVC Application Using EF Core and ASP.NET Core 1.0
- Send Email Using ASP.NET CORE 1.1 With MailKit In Visual Studio 2017
- ASP.NET Core And MVC Core: Session State
- Startup Page In ASP.NET Core
- Sending SMS Using ASP.NET Core With Twilio SMS API
- Create And Deploy An ASP.NET Core Web App In Azure
- Chat Bot with Azure Bot Service
- Channel Configuration - Azure Bot Service To Slack Application